Medchem
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
What is the precursor of Sulfinamide
Protonsil
What is the active metabolite of Protonsil
Sulfinalimide
Which of the following is a precursor of Sulfinilamide
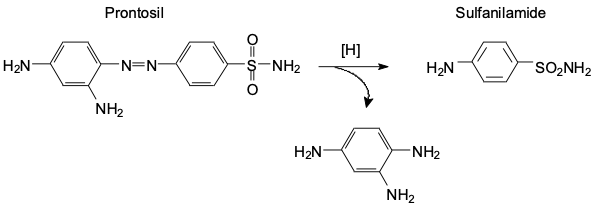
What does the R group have to be to become sulfanilamide
H
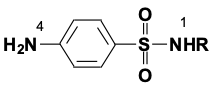
What must the N4 amino group have to be sulfinilamide
Free/unsubstitued and on the para position
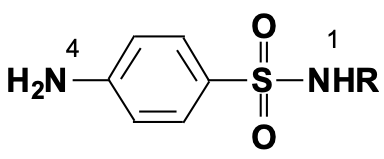
Can you change the aromatic ring
No
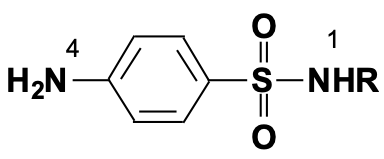
Where is substitution allowed here
N1
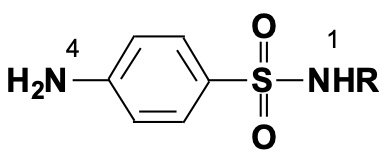
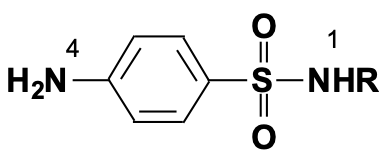
What would enhance the activity of this structure
Electron withdrawing group at N1
Which state of ionization is better for penetration
Unionized to penetrate cell membrane
What do sulfonamides inhibit
Dihydropeteroate diphosphate to inhibit folate enzyme synthesis
What type of inhibitor is Sulfonamide
Competitive Inhibitor
Which sulfa drugs are short/medium acting
Sulfisoxazole
Sulfamethoxazole
Sulfadiazine
Sulfacetamide
What are long acting sulfa drugs
Sulfamerazine
What are Ultra Long Acting sulfa Drugs
Sulfalene
What sulfa drugs are used for burn therapy
Mafenide
Silver Sulfadiazine
What is Trimethoprim
Selective folate reductase inhibitor
What is Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole
Combo drug that has synergestic activity
How do sulfa drugs get metabolized
Glucorinidation and metabolized by acetylation
What is sulfa drugs excreted as
N4 acetate and glucornides
What is the goal of acetylation
Conjugation pathway to attach water soluble moiety
What are some serious adverse effects of sulfa drugs
Liberates billirubin which in newborns cant be glucornidated so cant metabolize and leads to gray baby syndrome
What does Fosfomycin inhibit
PEP transferase
What does Cycloserine inhibit
Akanine racemase to convert L-ALa into D-ala and combine to make D-ala D-ala
What does Vancomycin inhibit
Formation of pentapeptide
What does Bacitracin inhibit
phospholipid carrier
What do B lactams inhibit
D-ala transpeptidase
What causes Penicillins to be acidic
COOH
What are the advantages of COOH on Penicillin
To make water soluble parent abx and Pass 1st pass effect
What are the prototype penicillins
Penicllin G and and Penicillin V
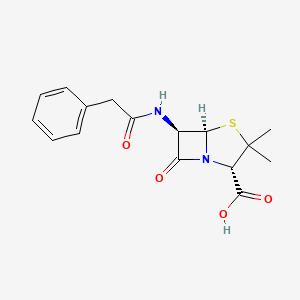
What Penicillin class is this
Pen G =Prototype
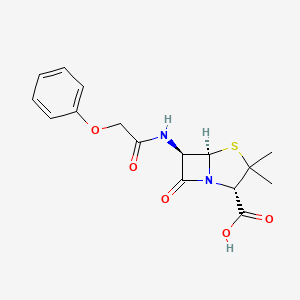
What Penicillin is this
Pen V = prototype
Which penicillins are structurally bulky and known as penicillinase resistant penicillins
Nafcillin
Oxacillin
Cloxacillin/dicloxacillin
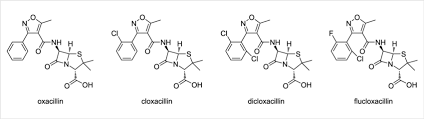
Which penicillins are these and what class
penicillinase resistant penicillins
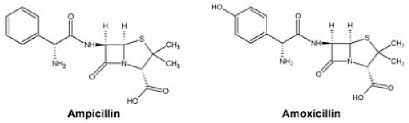
Which class of pencillins is. this
Aminopenicillins
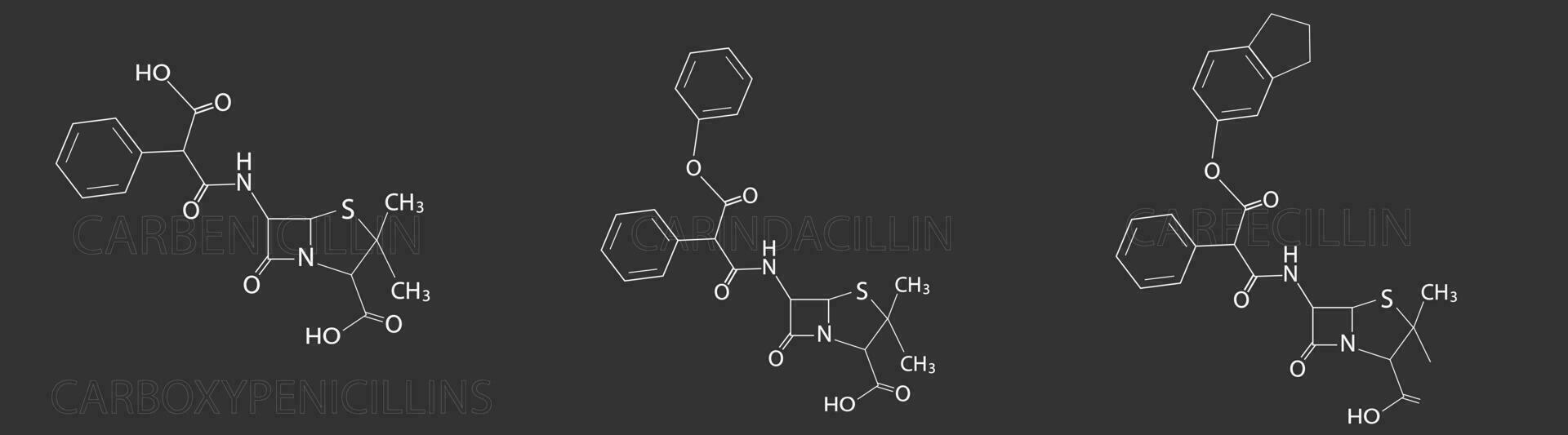
Which class of penicillins is this
Carboxypenicillins
What class of penicillins is this
Acyl Ureidopencillins
What is the advantage of aminopencillins
Orally stable and used for kids
What is the difference between penicillins and cephalosporins
Cephalosporins have a modified bicyclic structure with an extra carbon that allows for further substitution
When do you find an R3 group on a cephalosporin
For orally adminstered cephalosporins
What is the role of R3 esters in cephalosporins
Provide extra protection around carboxylic acid
What functional groups are found in later generations of cephalosporins
amino thiazole and oxime group
What functional group is not found in parenterally adminstered cephalosporins
R3
Compare the stability of R2 in earlier generations vs later generations
Not as stabe R2
Which functional group causes bleeding and kidney damage
MTT
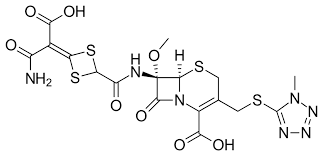
What is an AE of this structure
Bleeding and Kidney damage because of MTT
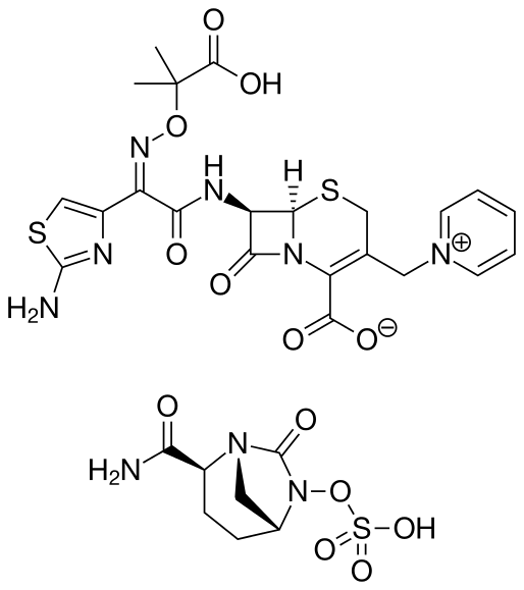
What is this
Cetazidime which is combined with Avobactam and metronidazole for complicated intraabdominal infectionn
What is the first 4th gen cephalosporin
Cefpirome
Which drug is a semi synthetic broad spectrum prodrug cephalosporin
Ceftaroline Fosamil
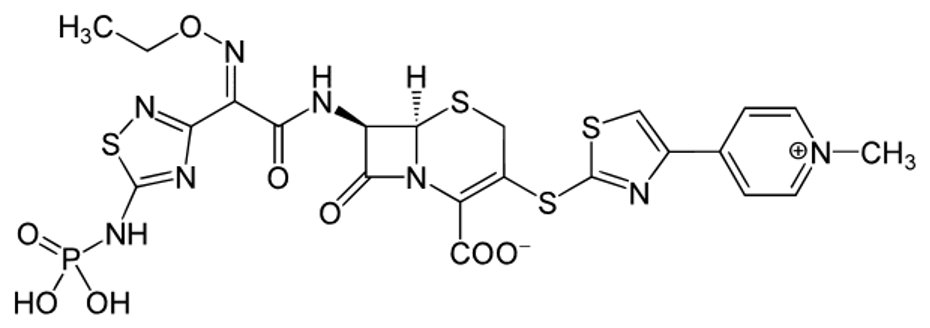
How do you know a cephalosporin is oral
Primary aliphatic amine
Which drug is a fifth generation prodrug
Ceftabiprole
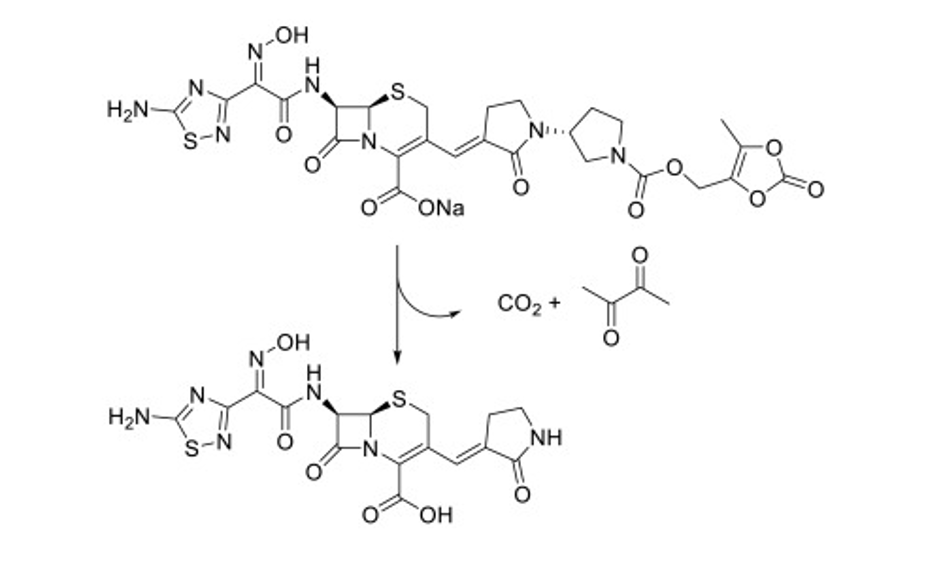
What do beta lactamase inhibitors lack
Antibacterial activity and affinity for D-ala transpeptidase
Which combinition of B lactam is becomes single chemicals in vivo
Sultamicillin into ampicillin and sulbactam
Which beta lactamse inhibitors are non beta lactam containing
Vaborbactam
Avibactam
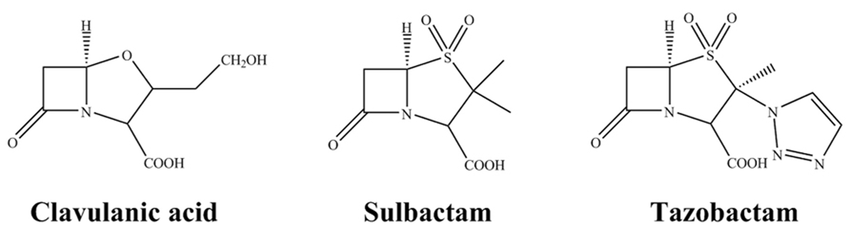
What are these
Beta lactamase inhibitors
What is the problem with carbapenems
Chemical and Metabolic instability where DHP 1 enzyme inactivates it
How did imipenem solve the carbapenem problem
The NH2 group made it bulkier so that sulfur couldnt liberate that portion
What is Cilastin
DHP1 inhibitor that was given with Imipenem
What structural aspect of meropenem created DHP-1 resistance
the methyl group on the thiazole
What type of bonding does Carbapenems have
Covalent bonding
What is Vabomere
Vaborbactam + Meropenem whcih protects meropenem from degradation by beta lactamases
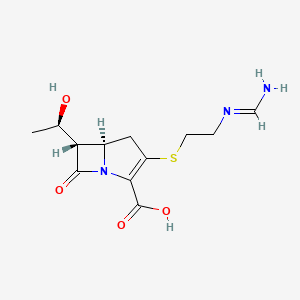
What is this
Imipenem
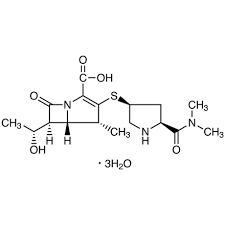
What is this
Meropenem
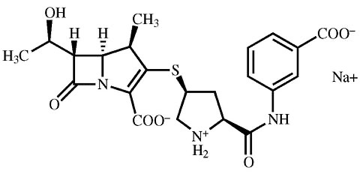
What is this and whats the advantage
Ertapenem and longer half life
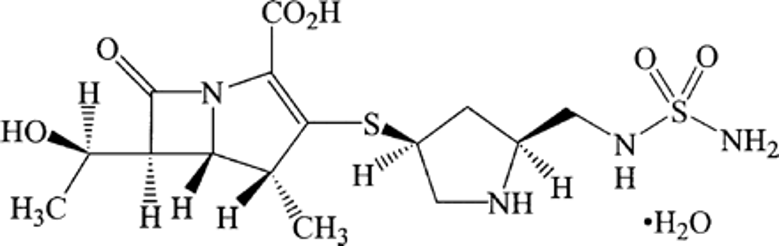
What is this structure
Doripenem
What does Aztreonam have enhanced activity against
Pseudomonas
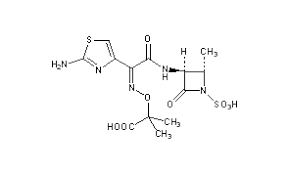
What is this
Aztreonam =monobactam
What is the prototype for Quinolones
Nalidixic Acid
What is the MOA of Quinolones
Bactericidal
Inhibits DNA gyrase, Topoisomerase IV
What position is the F in flouroquinolones
6 carbon
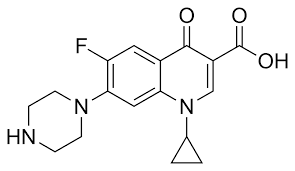
What is this
Flouroquinolone
What is important about R7 of flouroquinolones
Controls GABA binding NSAID interaction
What does R1 of flouroquinolones control
Phototoxicty
What part of Flouroquinolones is the metal binding and chelating site
The dicarbonyl functional group
What part of flouroquinolones controles the gyrase and antibacterial potency
The F
What part of flouroquinolones is essential for gyrase binding and bacterial membrane transport
the dicarbonyl group
What functional groups do Macrolides contain
Desosamine which are amino sugars
Ester
Cladinose= methyl substituted amino sugar
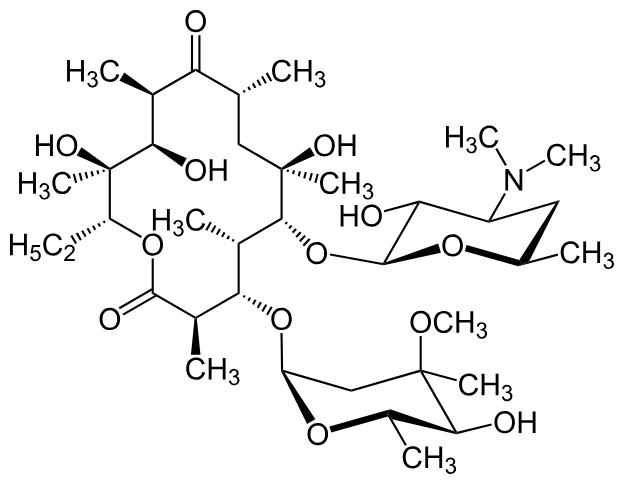
What is this
Erythromycin
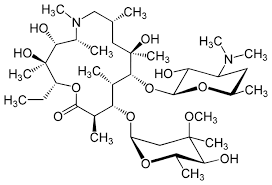
what is this
Azithromycin
Which macrolide doesnt contain a cladinose but instead has a imidazolyl and pyridyl ring through a butyl chain
Ketolide
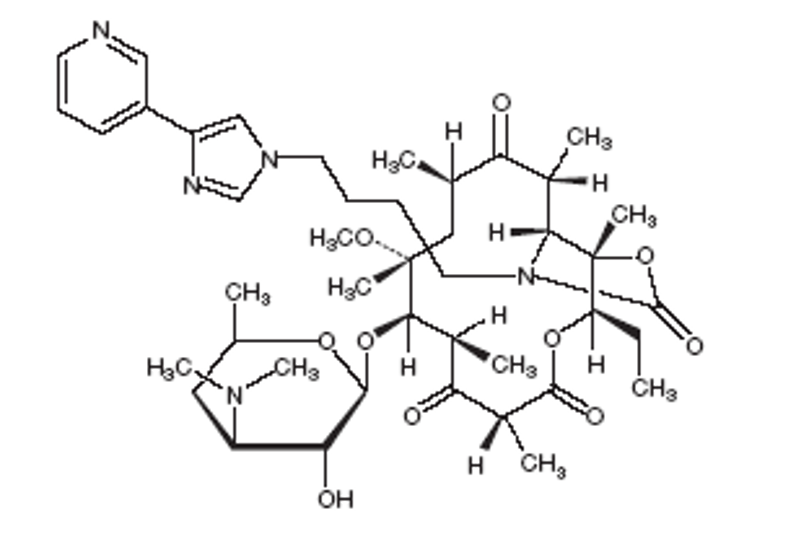
What is this
ketolide
What is Fidaxomicin
A narrow spectrum macrocyclic antibiotic used for C diff
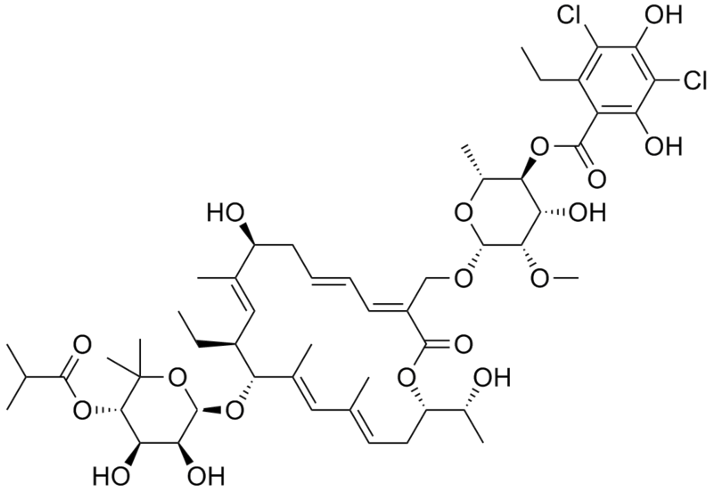
What is this
Fidaxomicin
Which Human MAb is used to treat c dif
Bezlotoxumab
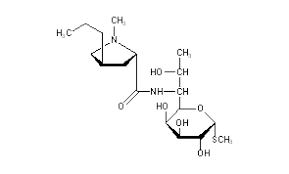
What is this
Lincomycin
What does the structure of Aminoglycosides contain
Highly substiuted 1,3 diamino cyclohexane ring with glycosidic connections with aliphatic amines
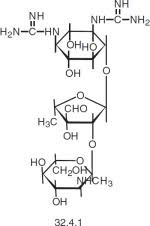
What is this
Streptomycin
Which tetracycline is a glycylcycline and carries a glycylamido moiety
Tigecycline
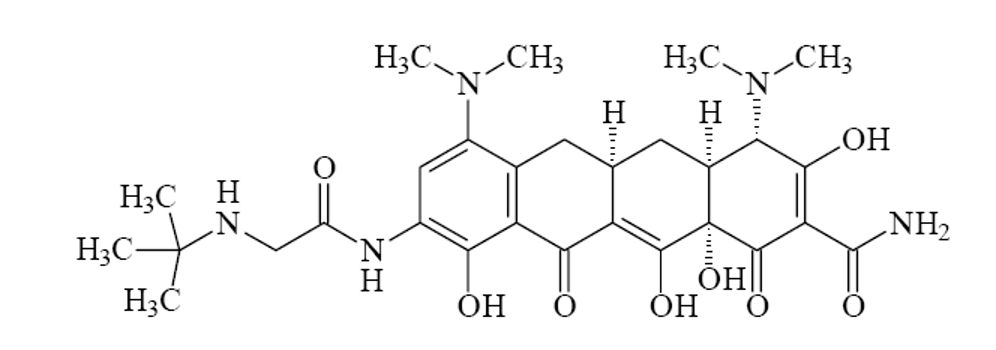
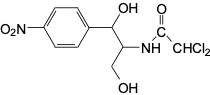
Which drug causes grey baby syndrome
Chloramphenicol
Explain the structure of Eravacycline
Fully synthetic flourocycline with C7 F and pyrrolidinoacetamido
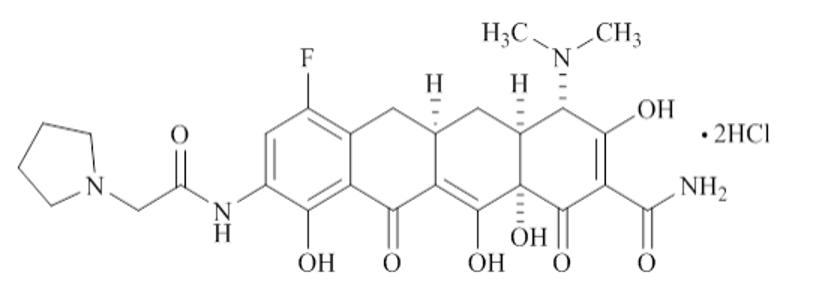
What is this
Eravacycline
What drugs are used for Protozoal Infections
Metronidazole
Benzindazole
What are ways to overcome tetracycline resistance
Eravacycline and Tigecycline
What class of drugs is Metronidazole
Nitro Imidazole class
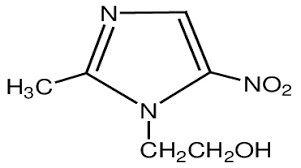
What is this
Metronidazole
What is the use of nitrofurantoin
Orally adminstered and used to treat uncomplicated lower UTI
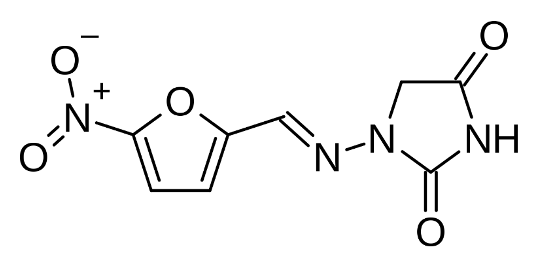
What is this structure
Nitrofurantoin
What is Fosfomycin derived from
Phosphonic acid
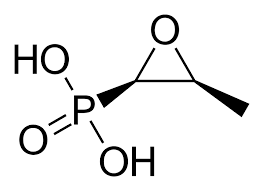
What is this
fosfomycin
Can you use phosphate as a drug on its own
No because its too water soluble
What is the basic pharmacophore for Oxazolidneones
Oxazole a 5 membered heterocycle