Vocal Pedagogy - Written Exam 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
A ___________ can be considered any object through which the sound wave can be filtered, subsequently enhancing and modifying the final sound product (amplifying the sound).
Resonator
Are the chest and sub-glottal airways good resonators for your voice?
No
What controls the opening and closing of the nasal port to enhance resonance?
Velum or soft palate
Are the nasal and sinus cavities good resonators?
No
What are the most important resonators?
Oropharynx (back of the throat) and oral cavity (mouth)
The coupling of all primary resonating cavities into a single, highly complex, and variable resonating system is often referred to as the _____________
Vocal tract
The ________ is enlarged when the larynx is lowered in a relaxed, non-depressed manner.
Pharynx
Are the vocal cords thick or thin in the chest voice? ---in head voice?
Thin-head voice
Thick-chest voice
What is the Italian term for “bright and dark” to describe a balanced tone quality.
Chiaroscuro
Define “muscular antagonism”
Antagonistic muscles act opposite to the agonist muscles to bring about a muscle action
Why is understanding how epigastrium works important according to your reading as a singing teacher? image & image 2
In singing, the epigastrium is the area where the abdominal muscles and diaphragm meet, considered a crucial point for "breath support" - essentially providing a consistent flow of air when singing by engaging both muscle groups simultaneously, while the diaphragm itself is the primary muscle responsible for deep inhalation and controlled exhalation needed to produce a sustained vocal sound.
How should the tongue lie in a singer’s mouth when the singing sings “ah” vowel?
Tip of the tongue should be touching the bottom teeth, and the sides of the tongue should be lying gently resting on top of the bottom molars. The middle of the tongue should be relaxed and flat.
Intrinsic bilateral muscles adjust the vocal folds and cartilages in what four ways?
Adduct (close)-Lateral CA
Abduct (open)-Posterior CA
Lengthen (thin)-for high notes-CT
Shorten (thick)-for low notes-TA
Extrinsic muscles stabilize the ____
larynx
What bone is the root of the tongue attached to? Why is the bone attached to the tongue important information to know as a singer and a singer teacher?
The root of the tongue is attached to the hyoid bone. The hyoid bone, which is part of the larynx (voice box), plays a crucial role in vocal technique because it can influence the movement of the larynx, causing it to move up and down. For singers and singing teachers, understanding the connection between the tongue and the larynx is essential. By learning how tongue position affects vowel and consonant articulation in the mouth, they can better control laryngeal positioning for optimal sound production.
The tree types of normal phonations are...
Hard (glottal)
Soft (breathy)
Balanced (optimal) creating chiaroscuro
Three types of vocal onsets are...
Hard, soft, balanced (chiaroscuro)
What is the space between the vocal folds called?
Glottis
What do hypo function and hyper function mean?
Hypo-low energy (soft onset)
Hyper-high energy (hard onset)
State why self awareness is important in singing using these two videos: video 1, video 2
Understanding yourself as both a learner and a teacher in your current state is crucial. It involves acknowledging and accepting who you are, learning about yourself, and focusing on controlling what you can, while letting go of the need to control what you cannot. It's equally important not to blame others or external circumstances.
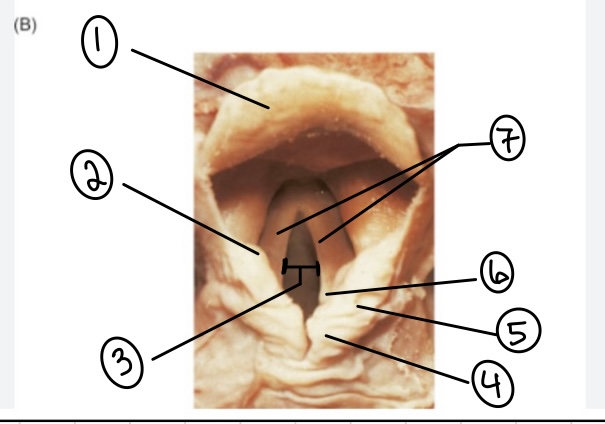
What is the term for spot #1?
Epiglottis
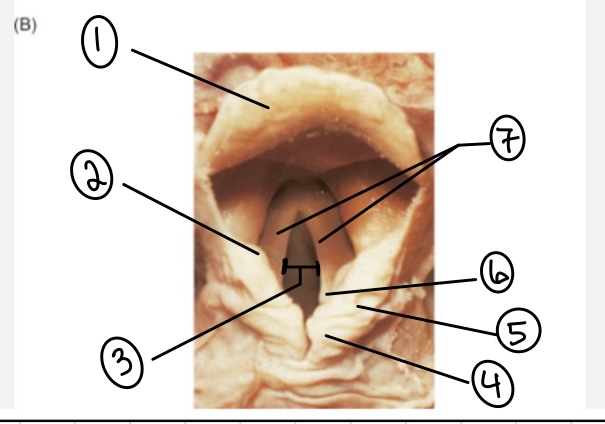
What is the term for spot #2?
Vestibular fold (false vocal cord)
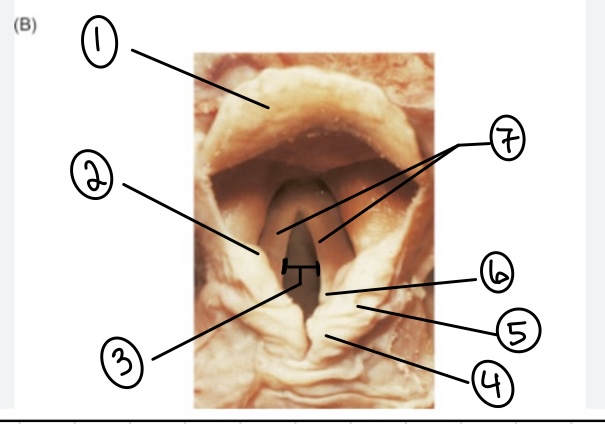
What is the term for spot #3?
Rima glottidis
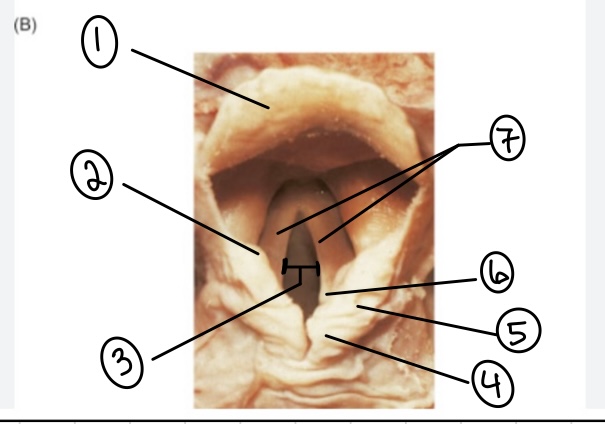
What is the term for spot #4?
Corniculate cartilage
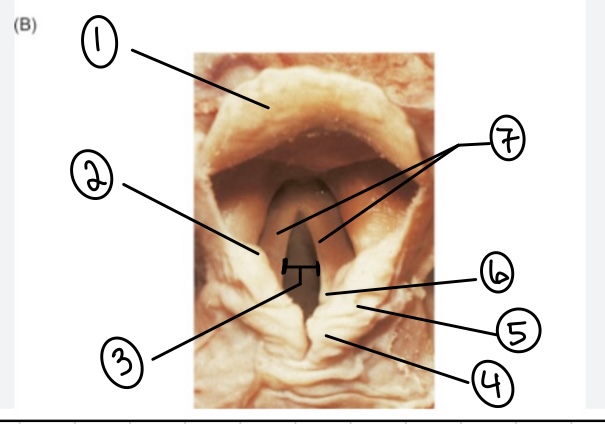
What is the term for spot #5?
Cuneiform cartilage
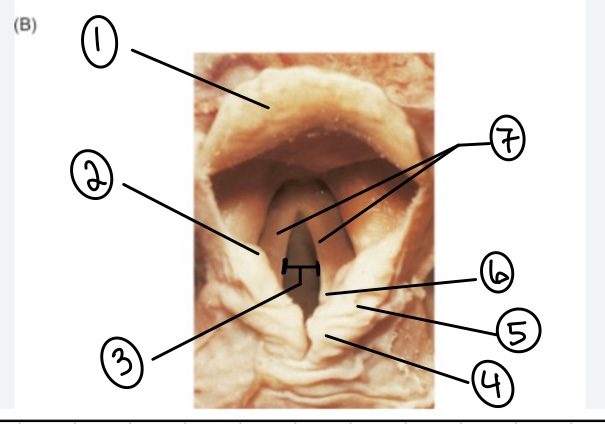
What is the term for spot #6?
Arytenoid cartilage
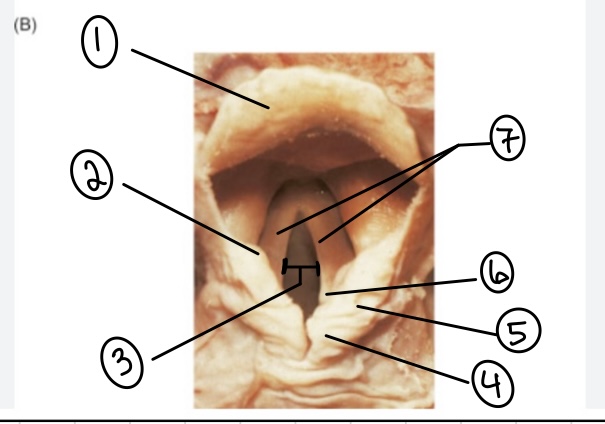
What is the term for spot #7?
Vocal folds (true vocal cords)
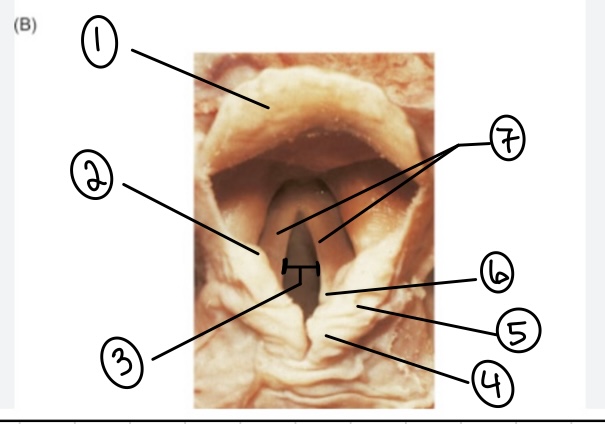
What is the term for the area above the epiglottis?
Base of tongue
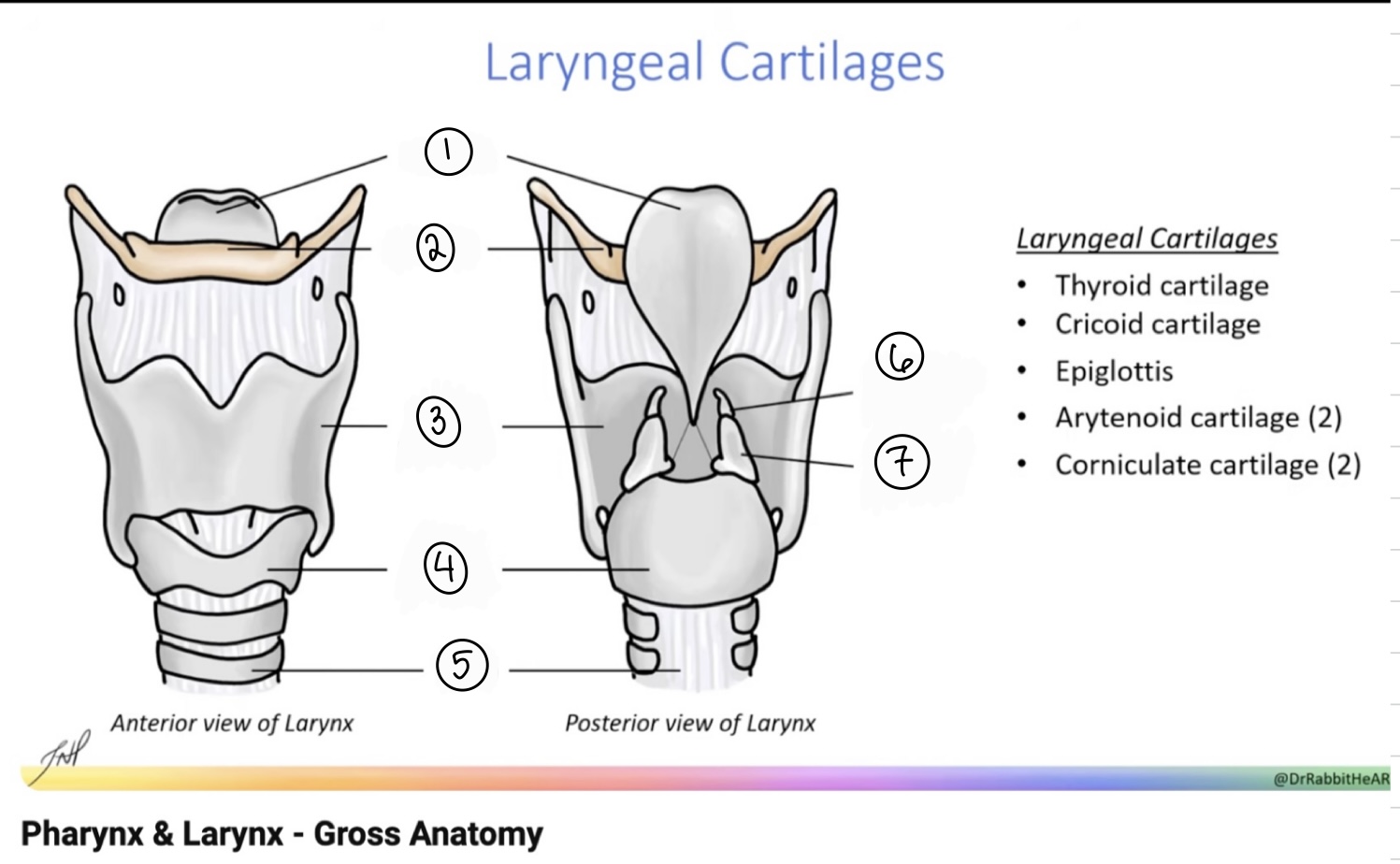
What is the term for spot #1?
Epiglottis
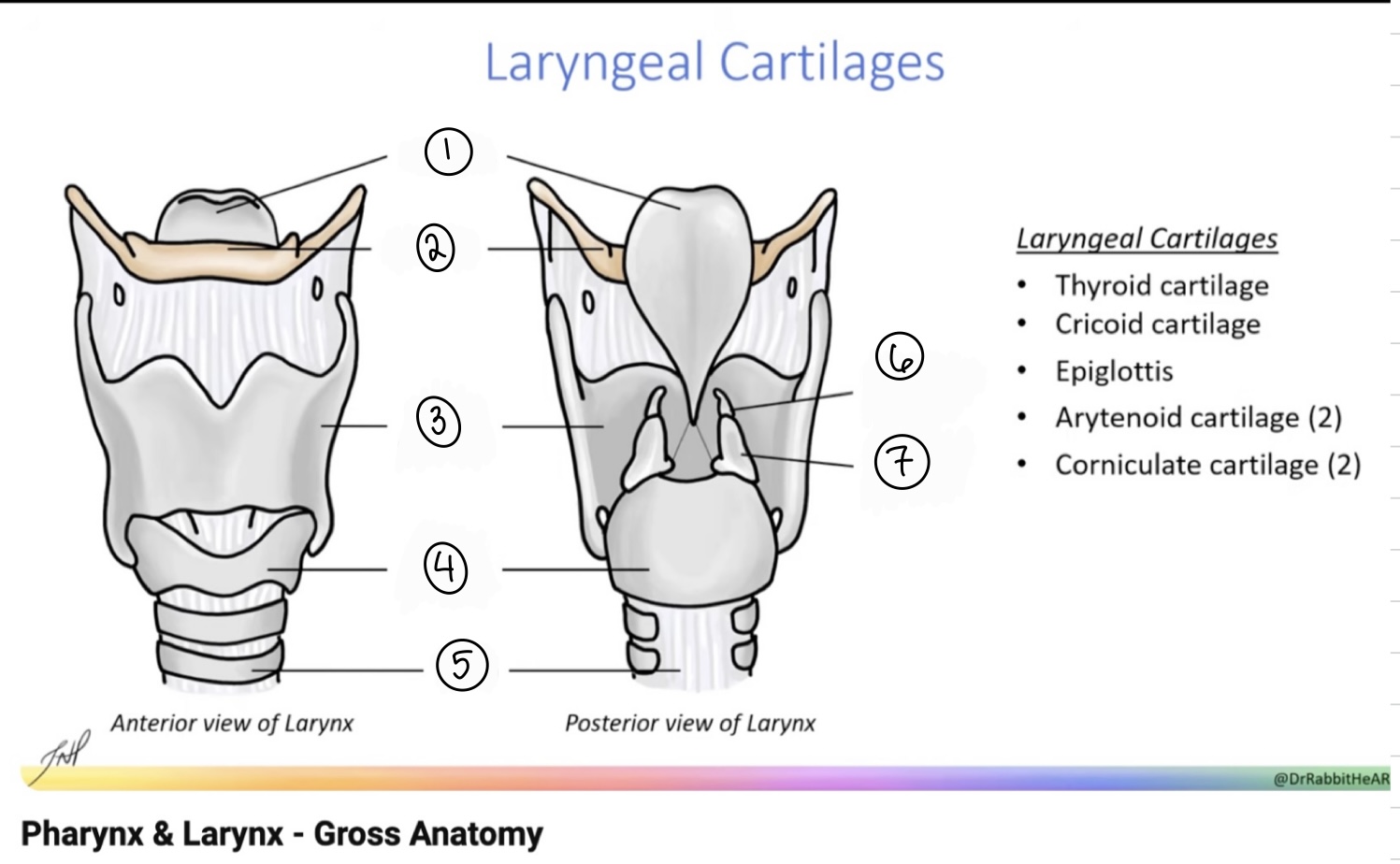
What is the term for spot #2?
Hyoid bone
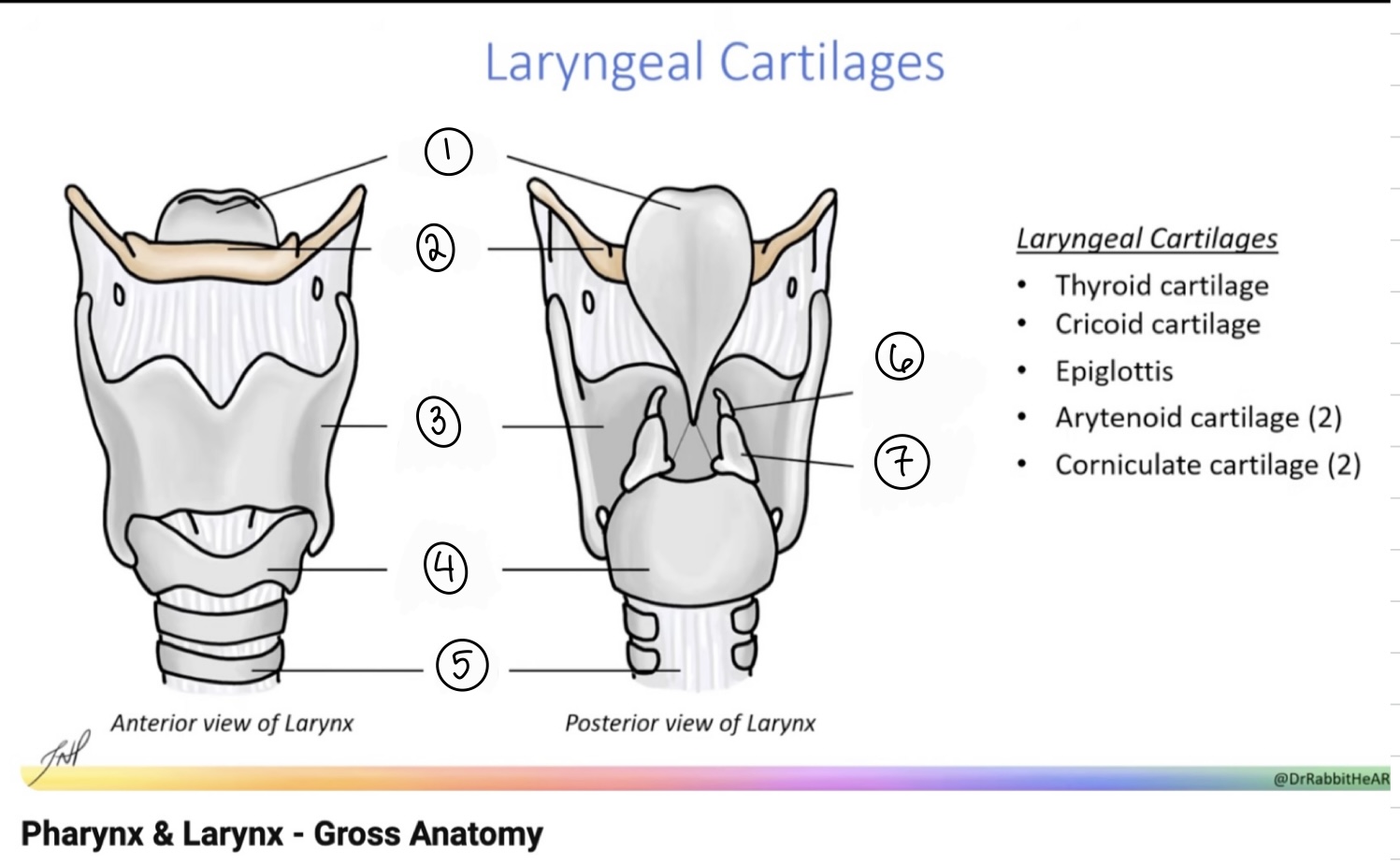
What is the term for spot #3?
Thyroid cartilage
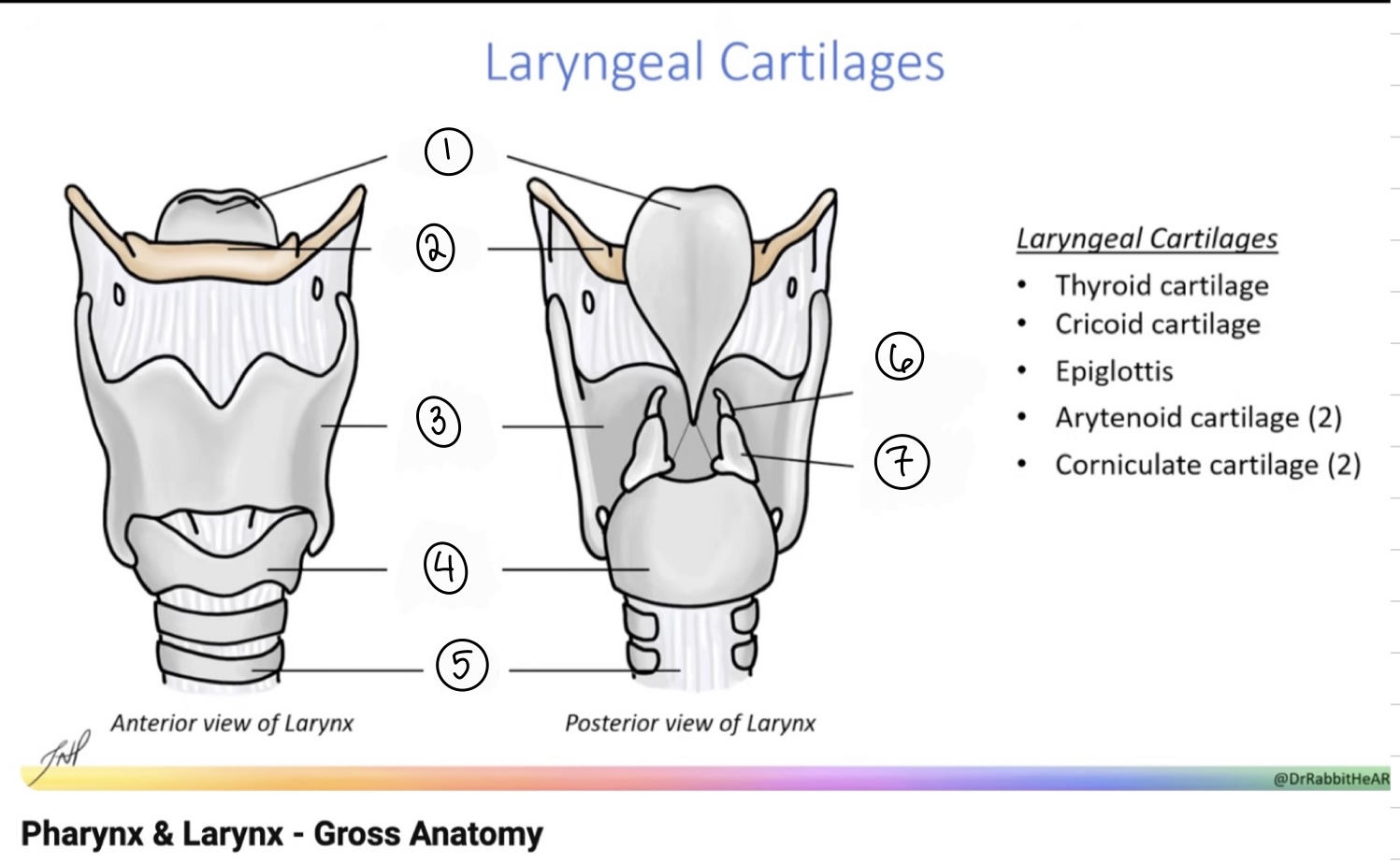
What is the term for spot #4?
Cricoid cartilage
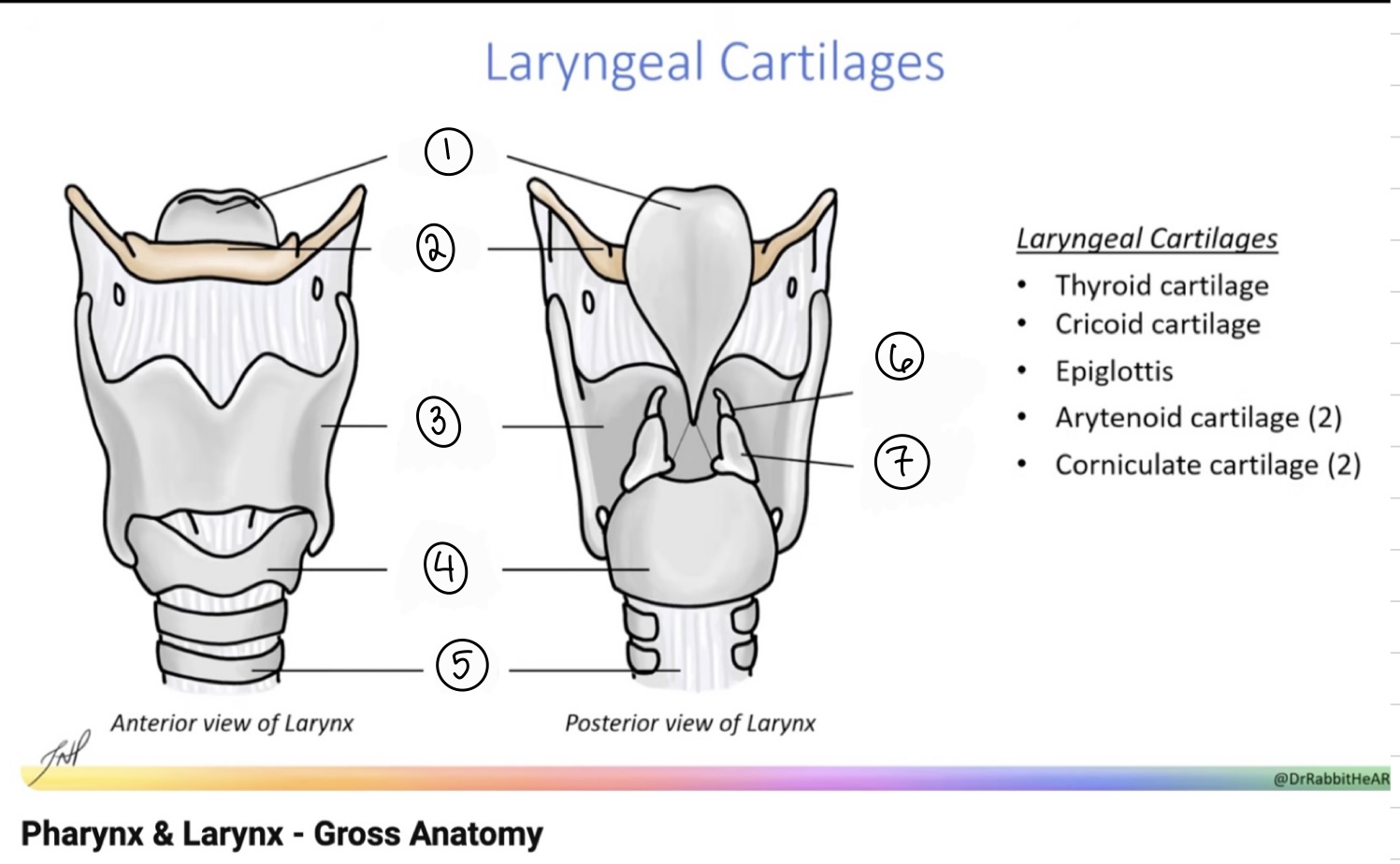
What is the term for spot #5?
Trachea
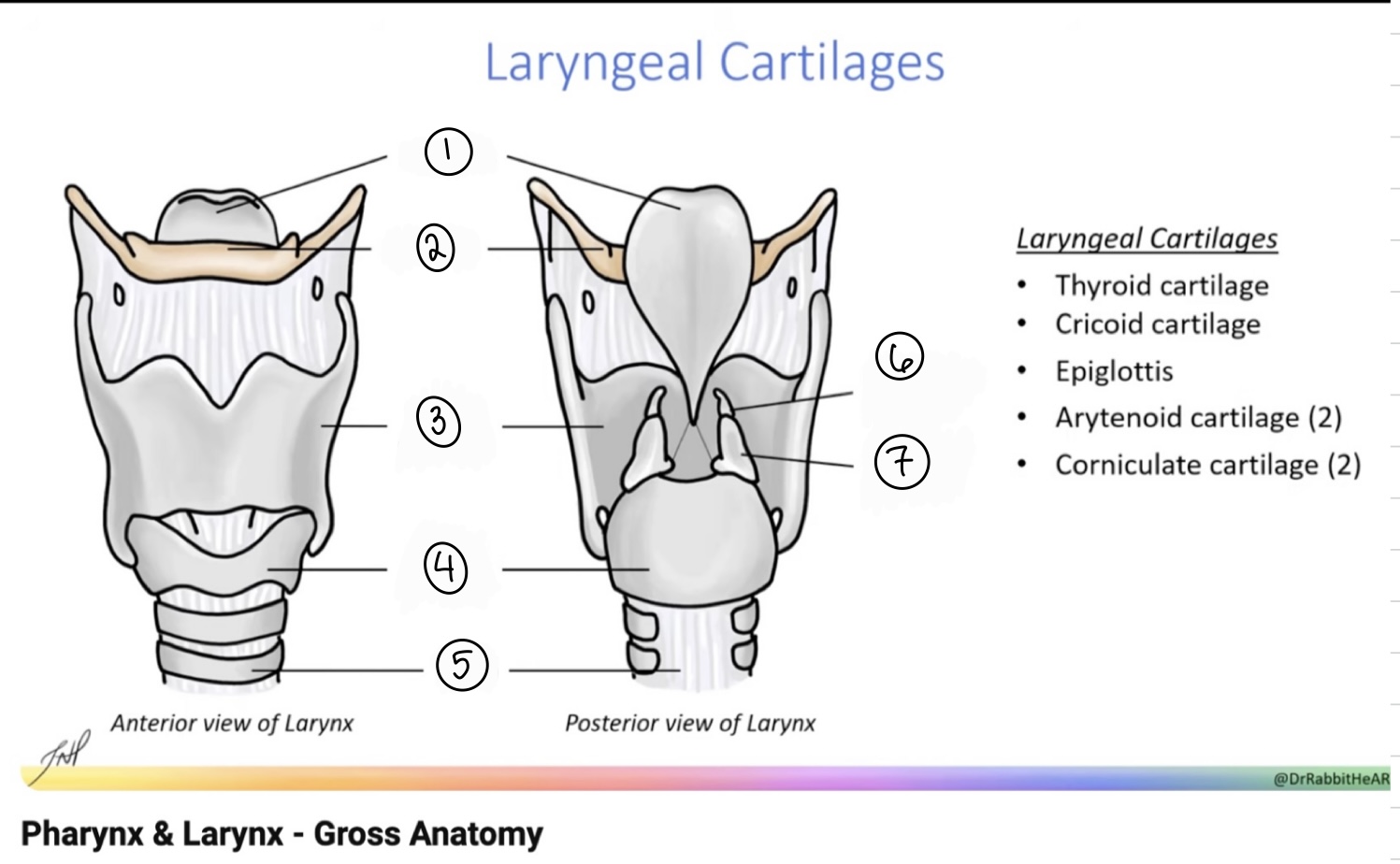
What is the term for spot #6?
Corniculate cartilage
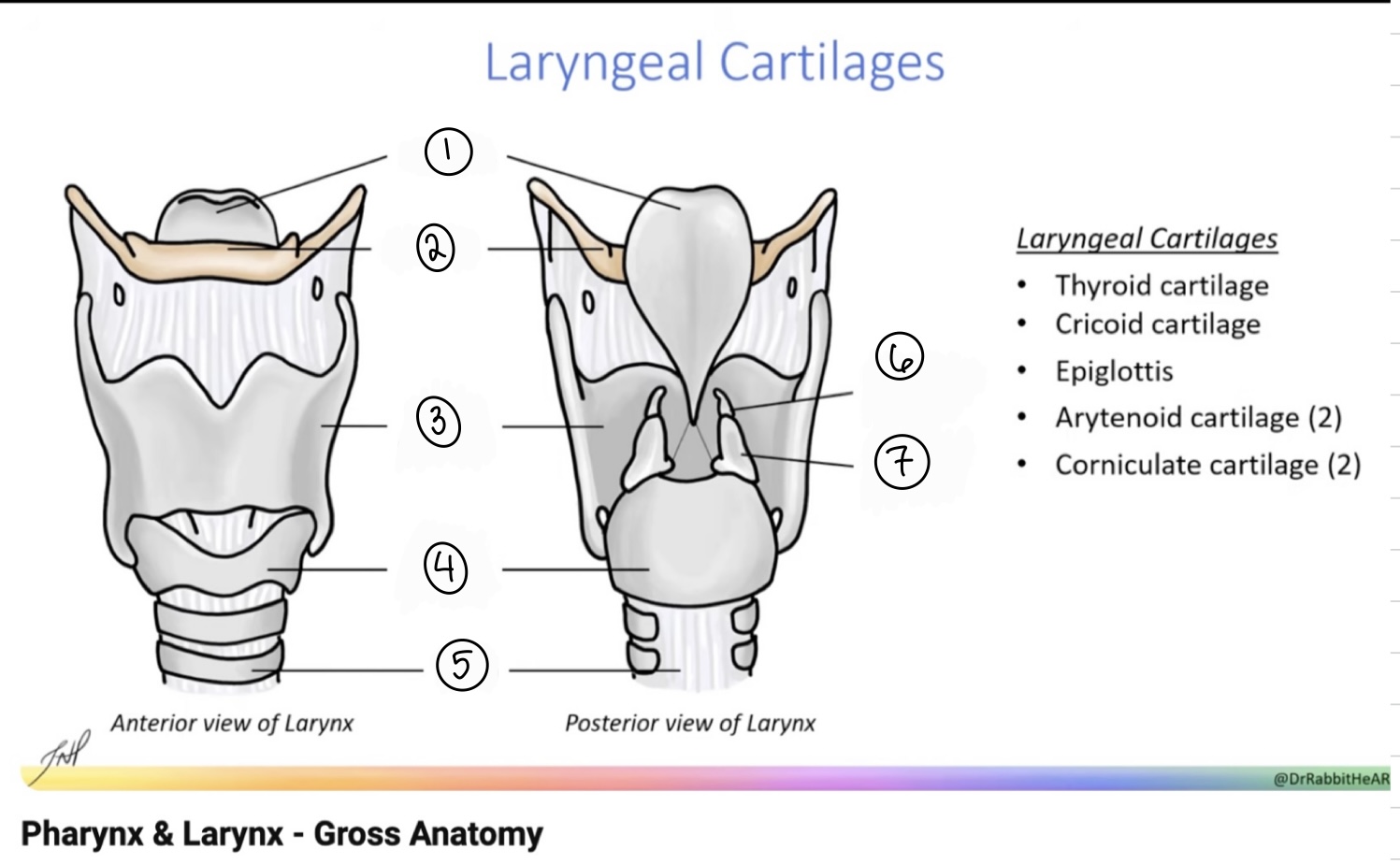
What is the term for spot #7?
Arytenoid cartilage