FS 2- FORENSIC PHOTOGRAPHY
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Magnification in Photography
1. Photomicrography
2. Microphotography
3. Photomacrography
4. Telephotography
Photomicrography
Taking a magnified photograph of small object through attaching a camera to the ocular of a compound microscope so as to show a minute details of the physical evidence.
Microphotography
It is a production by optical reduction, of vey small photographs from much larger subjects. It is just the opposite of photomicrography.
Photomacrography
Used synonymously with macrophotography. It is the taking of a magnified or enlarged photograph on small objects without the use of microscope, by attaching an extended macro lens or tube lens to the camera. It is the art of taking extreme close-up photographs of small subjects such as insects, flowers, or other small objects.
Telephotography
Is the process of taking photograph of a far object with the aid of a long focus and Telephoto lens.
Parallax error
The image you see through the viewfinder is different from the image the lens will capture.
Focusing Control
Setting of proper distance in order to form a sharp image.
Diaphragm Control
Usually serves as the aperture stop, and controls the aperture.
Shutter Speed
The amount of time the shutter inside the camera is open to expose your photo.
Types of Shutters
1. Focal-Plane Shutters
2. Leaf Shutters
3. Diaphragm Shutters
4. Central Shutters
Focal-Plane Shutters
Usually implemented as pair of cloth, metal, or plastic curtains which shield the film from light.
Leaf Shutters
Is a type of camera shutter consisting of a mechanism with one or more pivoting metal leaves which normally does not allow light through the lens onto the film, but which when triggered opens the shutter by moving the leaves to uncover the lens for the required time to make an exposure, then shuts.
Diaphragm Shutters
Is a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades which briefly uncover the camera aperture to make the exposure.
Central Shutters
Is a camera shutter normally located within the lens assembly where a relatively small opening allows light to cover the entire image. The term is also used for shutters behind, but near to, the lens.
Inherent Lens Defects or Abberations
1. Spherical Aberration
2. Coma
3. Curvature of Field
4. Distortion
5. Chromatic Abberation
6. Astigmatism
Spherical Abberation
When light passing through the near central part of a converging lens is bended more sharply than those rays falling in the edge, thus the rays coming from the edges are focused on a plane nearer the lens tan those coming from the central part.
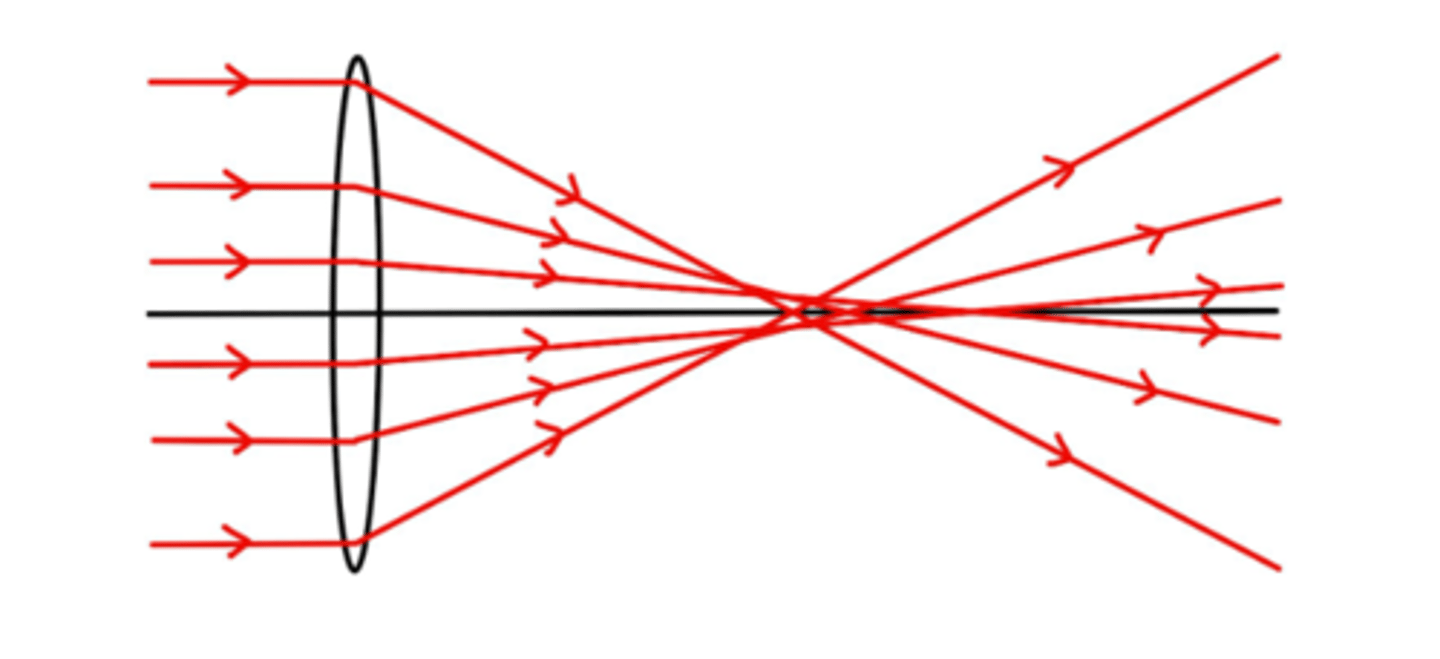
Coma
This is another form of spherical abberation but is concerned with the light rays entering the lens obliquely. The defect is noticeable only on the outer edges and not on the central part of the lens. If a lens has coma, circular objects reproduced at the corners of the negative are comet-like form.
Curvature of Field
This is a kind of defect where the image formed by a lens come to a sharper focus in curved surface than a flat surface.

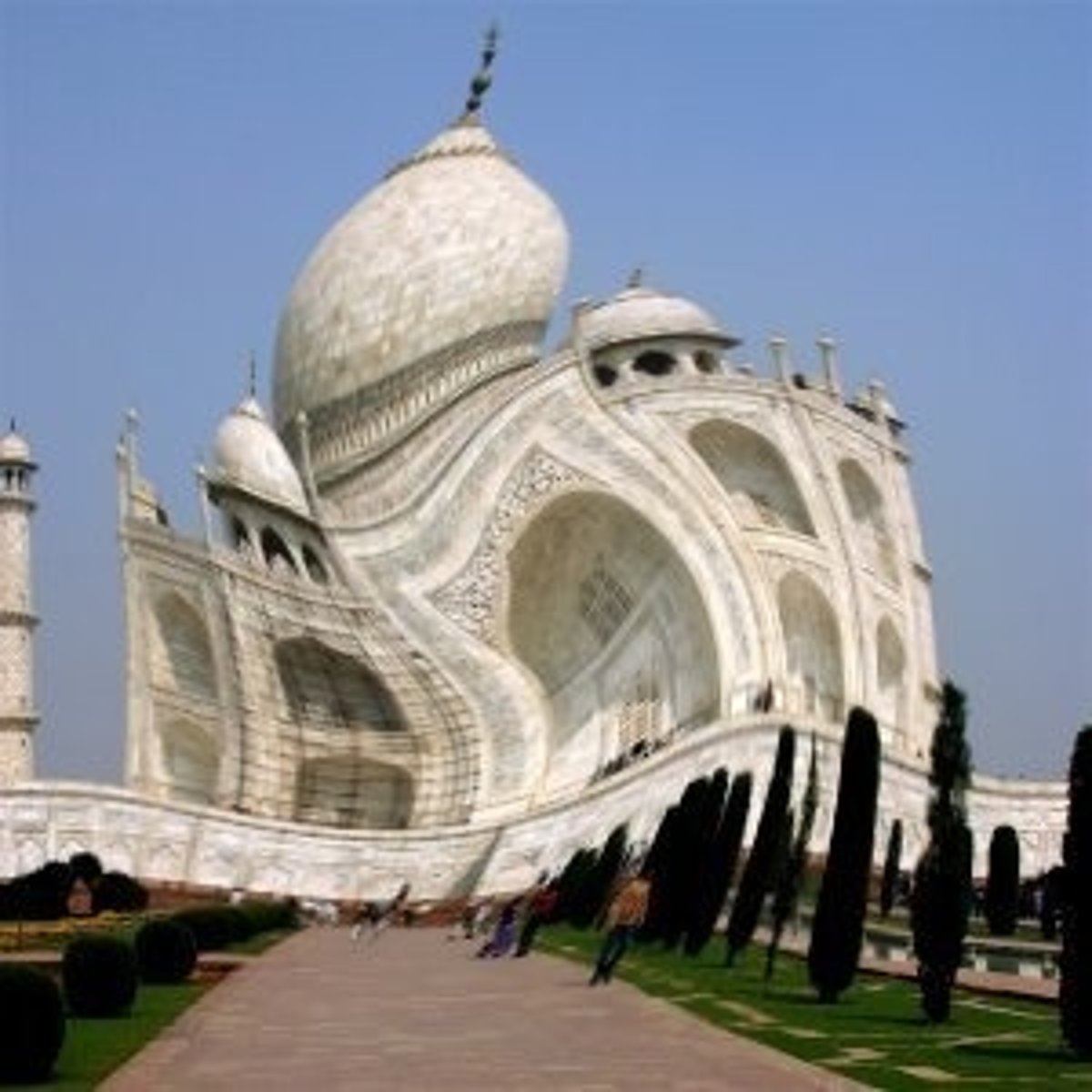
Distortion
Incapable of rendering straight lines correctly; either horizontal or vertical lines in an object.

Chromatic Abberation
This defect is the inability of the lens to bring photographic rays of different wavelengths to the same focus.
Astigmastism
This defect is present when the size of image produced by photographic rays of one wavelength is different from the size produced by another.
Types of Lenses (as to degree of correction to lens abberation)
1. Achromatic Lens
2. Rapid-Rectilinear lens
3. Anastigmatic Lens
4. Apochromatic Lens
Achromatic Lens
Corrected for chromatic abberation.
Rapid-Rectilinear lens
Corrected for distortion.
Anastigmatic Lens
Corrected for astigmatism.
Apochromatic Lens
Also corrected for astigmatism but with higher degree of correction to color.
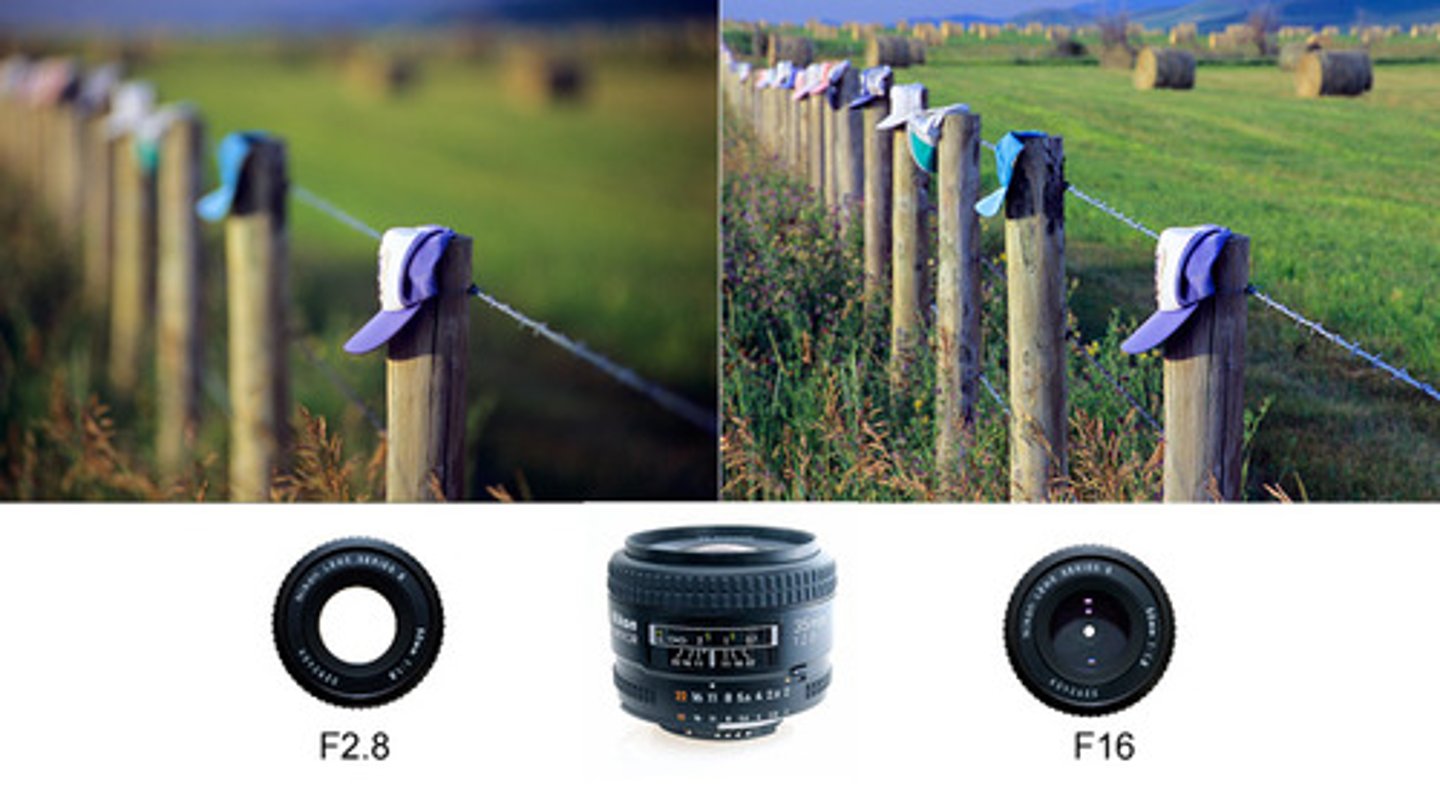
Depth of Field
Is the distance between the closest and farthest objects in a photo that appears acceptably sharp.

Positive or Converging Lens
This lens is always thicker at the center and thinner at the sides.
Negative or Diverging Lens
This lens is always thinner at the center and thicker at the sides.
Bending of Light
1. Reflection
2. Refraction
3. Diffraction
Reflection
It bounces off in all directions due to the microscopic irregularities of the interface. Objects that caused reflection are opaque object.
Kinds of Objects
1. Transparent Objects
2. Translucent Objects
3. Opaque Objects
Diffraction
It is described as the apparent bending of waves around small obstacles and the spreading out of waves past small openings. It is also described as the bending of light when it hits a sharp edge of an opaque object.
Refraction
It is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed.
Transparent Objects
Allows sufficient visible light to pass through them that the object on the other side may be clearly seen.
Translucent Objects
Allows light to pass, however diffuse it sufficiently that objects on the other side may not be clearly distinguished.
Opaque Objects
So greatly diffuse the light that recognizing the object on the other side is very difficult if not impossible.
Sources of Light
Natural and Artificial.
Natural Light Source (Sunlight)
1. Bright Sunlight
2. Hazy Sunlight
3. Dull Sunlight
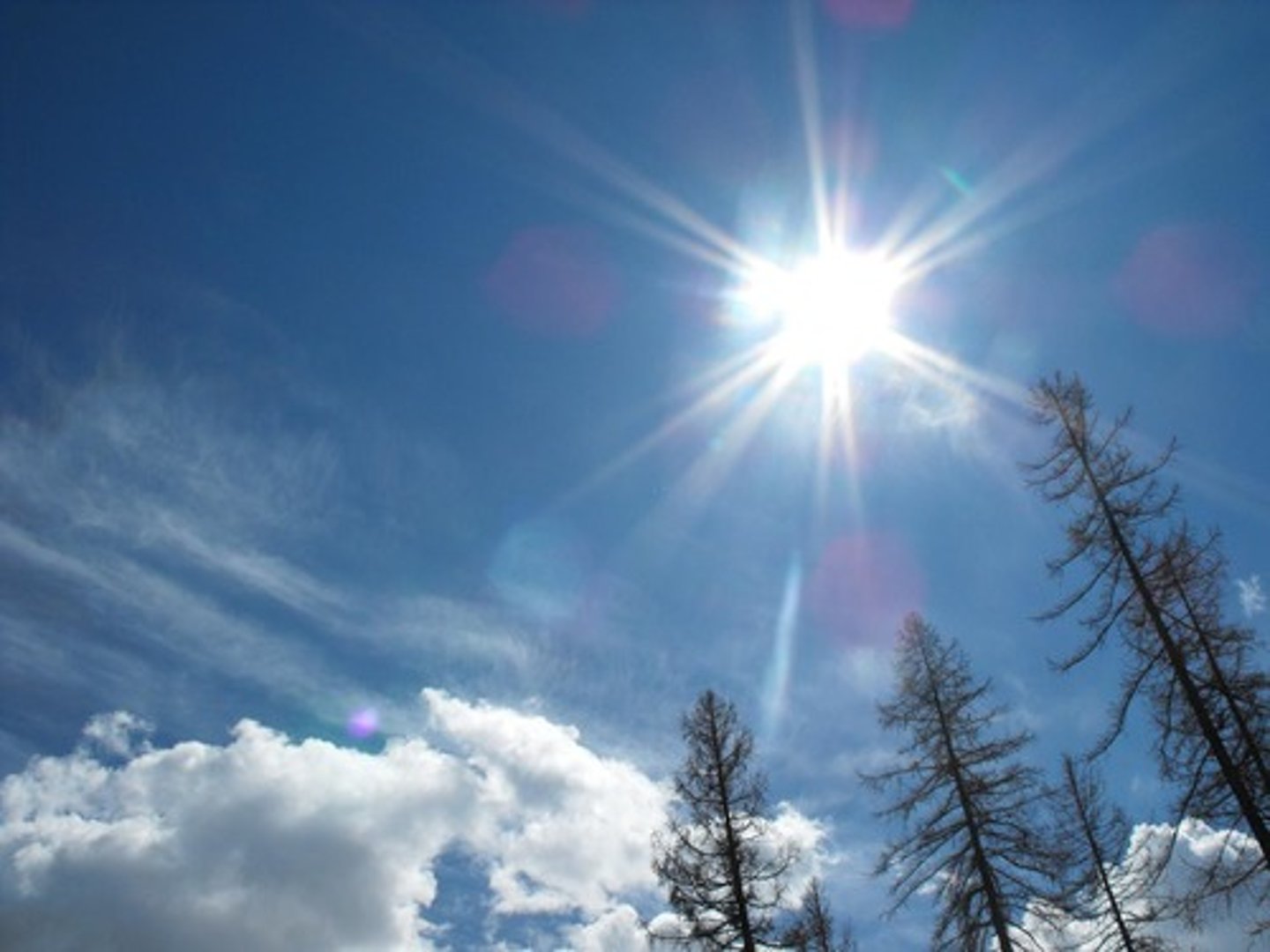
Bright Sunlight
A lighting condition where objects in open space cast a deep and uniform or distinct shadow.

Hazy Sunlight
Objects in open space cast a transparent shadow.
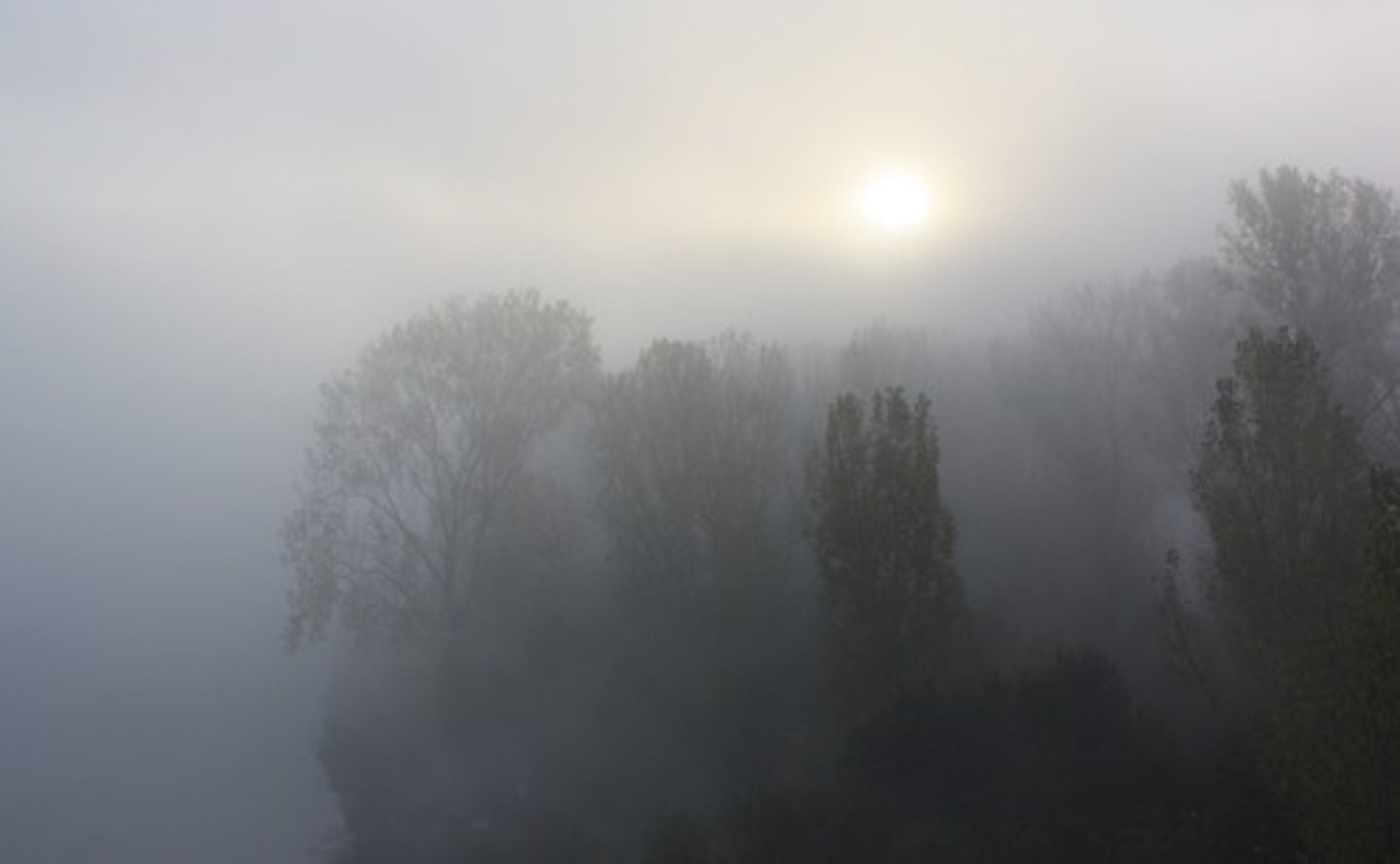

Dull Sunlight
Objects in open space cast no shadow.