ch.8 stats
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Confidence interval (+,+)
first proportion greater
confidence interval (-,-)
second proportion greater
Confidence interval (-,+)
no convincing evidence of a difference (0 means no difference)
confidence interval
Point estimate ± margin of error
confidence level INCREASE
Margin of error INCREASE (wider interval)
confidence level DECREASE
Margin of error DECREASE (narrower interval)
n INCREASE
margin of error DECREASE
margin of error
only account for sampling variability
if p hat not given when fining sample size
ALWAYS .05
when find sample size
always round up
when do we use comined p hat
two sample z test for p1-p2
when do we NOT use 10% rule
whe it is a two sample z test p1-p2
when do we do interval or test
when given confidence, when given alpha
z interval
then two sample p hat1- p hat2 at begining and in the standard error
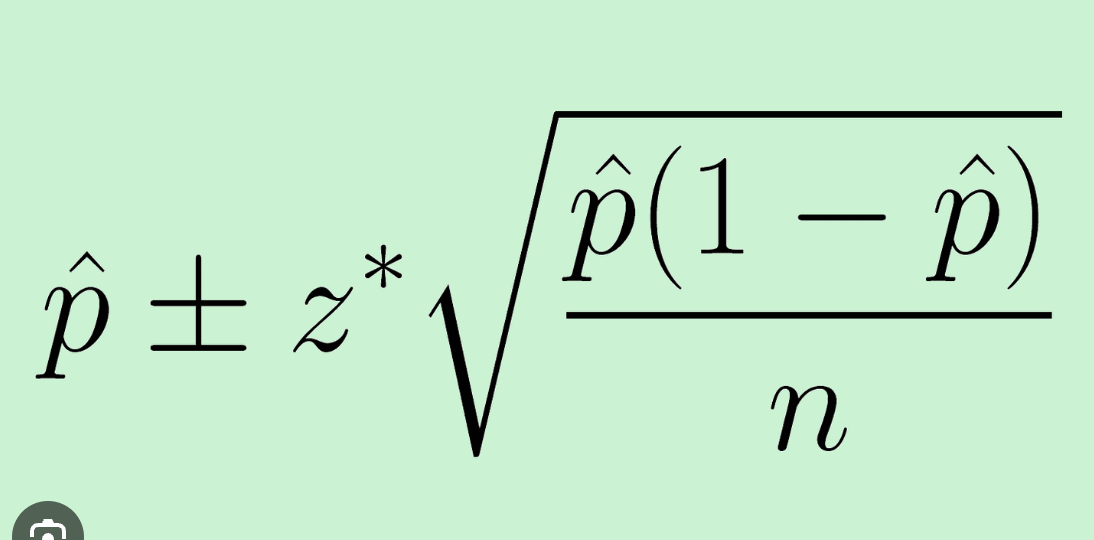
one sample test statistic
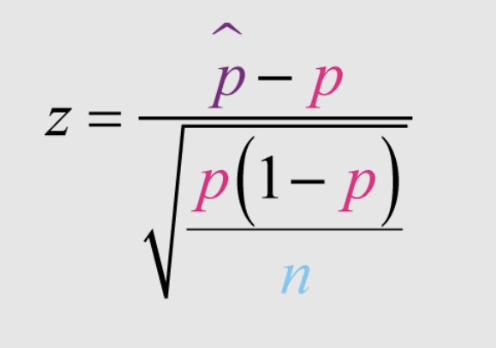
when do we double p value
when Ha is not equal
when is the Ha not equal
when no clear direction is defined
Type I
reject the null when null is true
type II
fail to reject null when should of rejected
to increase power
increase sample size
increase alpha
increase distance to Ha
power is…
The probability that a statistical test correctly rejects the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true
p-value greater then alpha
fail to reject null, do not have convincing evidenxe for Ha
p-vale is less than alpha
reject the null, do have convincing evidence for Ha
power
1-p(typeII error)
p-value
The probability of getting a sample result as extreme or more extreme than what you observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true. (always assume null true)