intro to introduction to geotechnical engineering
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
down to midway through ch 5 slides; should also review old exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
physical/descriptive/non-design/index properties
color
density
size
stiffness
aka compactibility, workability
compressibility
aka deformation properties
atterberg limits
aka consistency limits, defines plasticity. plasticity can affect strength, hydraulic conductivity, etc. (important characteristics)
granular/cohesionless soils
silt, sand, gravel
#4 sieve
4.75 mm, sand divider
#200 sieve
0.075 mm, silt & clay divider. this is where naming convention changes as well
plasticity index
I_p = w_l - w_p
Plasticity Index = Liquid Limit – Plastic Limit
liquidity index
I_l = (w - w_p)/I_p
activity
A = %Clay / %PI
Measure of how much the clay will swell; differentiates types of clay minerology
double layer thickness

K
hydraulic conductivity/water permeability
dielectric constant
stoke’s law
for hydrometer analysis

bank soil
soil before it is excavated from the ground
gamma_d_f
average dry unit weight of fill
gamma_d_c
average dry unit weight of cut (i.e., the bank soil)
S
degree of saturation
Vwater/Vvoids
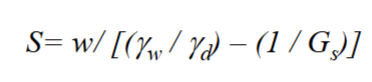
n
porosity
e/(1+e) = Vv/V
e
void ratio
Vv/Vs
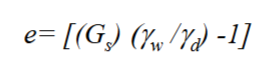
Se =
wG
other useful relations
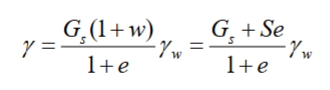
other useful relations - for S=100%
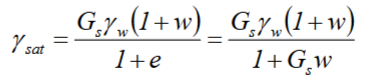
G
specific gravity
density of material/density of water
w
water content
Ww/Ws * 100%
bulk density
mass of soil divided by its volume; does not default.
dry: M_s / V
moist: M/V
unit weight
a type of specific weight (which are always represented by gamma)
total W of soil / total V of soil (also = rho*g)
defaults to moist
lb/ft³
kN/m³
dry unit weight
weight of solids / total volume = total unit weight/(1+w)
solids unit weight
weight of solids / volume of solids
mass
lbm or kg
weight
lbf or N
unit weight of water
9.81 kN/m³ = 62.4 pcf = Ww/Vw
relative density
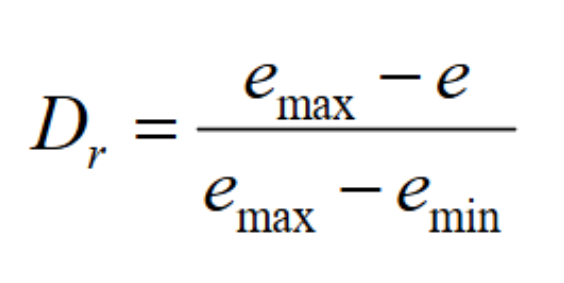
relative compaction
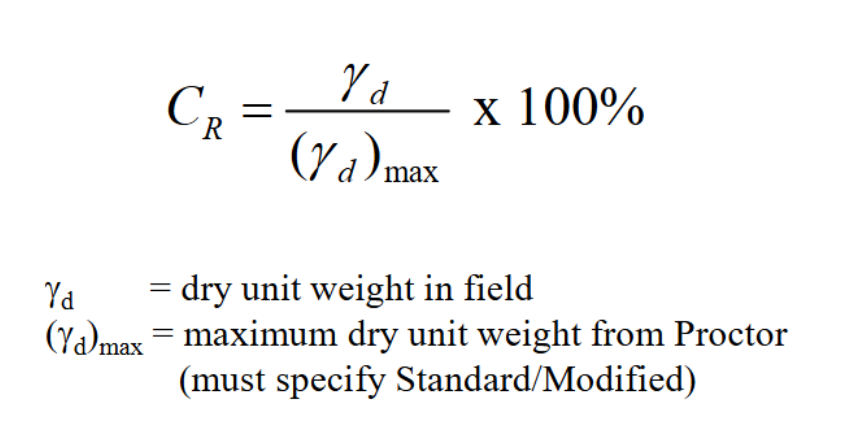
“below groundwater level”
always means it’s saturated 100%
“completely dry”
0% saturated
#40 sieve
0.425 mm
ZAV
zero air voids curve
density of water
1 g/cm³