APES Unit 4 Vocabulary
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
acid deposition
any form of precipitation with acidic components (e.g. sulfuric acid, nitric acid, etc)
aka acid rain
adiabatic heating/cooling
responses to changes in PRESSURE, which are a factor in global air circulation patterns
heating: as air descends, the higher pressure causes its volume to decrease (contract), leading to an increase in temperature
cooling: as air rises, the lower pressure causes its volume to increase (expand), which in turn cools the air
albedo
the measure of reflectivity of a surface, indicating how much sunlight is reflected back into space
e.g. ice sheets (which are white & highly reflective) reflect solar energy, but as the ice melts and reveals the dark ocean/ground, solar radiation is being absorbed
asthenosphere
the outer part of the mantle, composed of semi-molten rock
100-412km below Earth’s surface
pressure & temp are so high that rocks melt, making them semi-molten
axial tilt
Earth's tilt on its axis relative to its orbital plane around the Sun, affecting seasons
e.g. when Earth’s axis tilts toward the Sun, it is summer for that hemisphere
base saturation
(chemical property of soil)
proportion of bases to acids, expressed as percentage
bases: essential for nutrition (Ca, K, Mg, Na)
acids: detrimental (Al, H)
cation exchange capacity (CEC)
(chemical property of soil)
the ability of soil or other substances to hold and exchange positively charged ions (calcium, magnesium, and potassium)
crucial factor in determining soil fertility and nutrient availability for plants
high CEC means a soil can hold onto more nutrients (clay & organic matter have a high CEC)
chemical weathering
change in chemical composition of mineral compounds (e.g. carbonation, hydrolysis, oxidation, hydration)
releases essential nutrients from rocks
important part of phosphorus cycle
climate
patterns of temperature, precipitation, wind, and other atmospheric conditions in a region
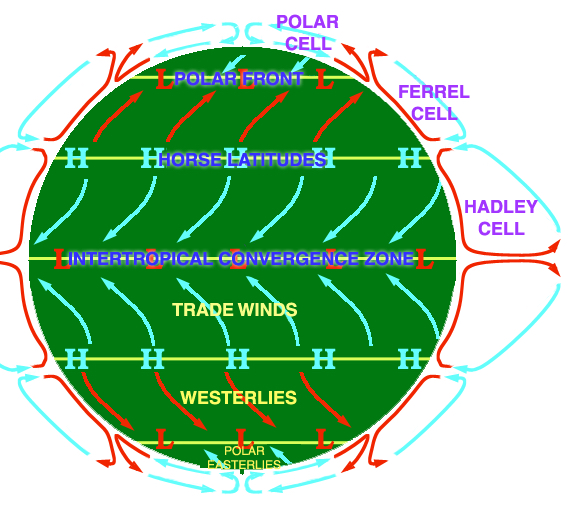
convection cells: Hadley, Ferrell, Polar
global patterns of air movement, initiated by the unequal heating of Earth
Hadley: occur between 0° and 30° latitudes (directly north and directly south of the equator). at the equator, these cells start with warm, rising air. then, as the air moves away from the equator, the air falls as cooler air.
Ferrell: occurs between 30° and 60° latitudes. around 30° latitude, the cold, dry air of a Hadley cell falls, pushing warm air up.
Polar: occur at latitudes greater than 60°. it starts around the 60° latitude line where warm air from the ferrell cell is pushed up. at higher latitudes, the air cools and falls as dry air on the poles.
convergent boundary
tectonic plate boundary where two plates move towards each other, resulting in collision or subduction
leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity
core/mantle/crust
layers of the Earth
Core: innermost (made of iron & nickel)
Mantle: middle (semi-solid rock)
Crust: outermost layer (solid rock)
Coriolis effect
the deflection of moving objects (wind, water, etc.) caused by Earth's rotation
in the Northern Hemisphere, objects veer to the right; in the Southern Hemisphere, to the left
divergent boundary
tectonic plate boundary where plates move away from each other
leads to the formation of new crust through seafloor spreading or rift valleys
earthquake
natural disaster caused by the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, resulting in shaking and trembling of the ground
measured by the Richter scale
ENSO: El Nino Southern Oscillation (El Nino, La Nina)
climate patterns influencing global weather
El Niño causes the Pacific jet stream to move south and spread further east
La Niña causes the jet stream to move northward and to weaken over the eastern Pacific
epicenter
the point on the Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
where the seismic waves reach first and are most intense
erosion
process of wearing away or displacement of rocks and soil by wind, water, or other natural agents
leads to changes in landscapes and landforms
exosphere
the outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere, where gases transition into space
satellites orbit in this region
floodplain
land beside rivers, ponds, lakes, and oceans that gets flooded regularly
creates fertile soil for agriculture and pose risks to settlements
gyre
large systems of circulating ocean currents (kind of like slow-moving whirlpools)
affects temp, salinity, & nutrient distribution globally
5 most important gyres: the North Atlantic Gyre, the South Atlantic Gyre, the North Pacific Gyre, the South Pacific Gyre, and the Indian Ocean Gyre
hot spot
places where molten material from the mantle reach the lithosphere
igneous
rocks formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava
can be intrusive (formed underground) or extrusive (formed on the surface)
insolation
the thermal radiation received from the Sun per unit surface area of the Earth
areas where the Equator come into closer contact with the Sun, meaning they receive higher insolation
belt near the Equator where trade winds converge / area of Earth that receives the most intense sunlight (Equator) and where the ascending branches of the two Hadley cells converge
causes uplift, cloud formation, and heavy rainfall
plays a crucial role in global climate patterns
latent heat release
release of energy as heat when water vapor condenses into precipitation
lithosphere
the rigid, brittle outer layer of Earth (100km thick), consisting of the crust and upper mantle
magma
molten or semi-molten material found beneath the Earth's surface
moves in convection cells (hot, less dense material rises, cooler more dense material falls)
can erupt as lava and form igneous rocks upon cooling
mesosphere
layer of Earth's atmosphere above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere
as you go up in this layer, temperature decreases
metamorphic
rocks formed from pre-existing rocks that undergo intense heat and pressure, causing them to recrystallize without melting
e.g. marble, quartzite, soapstone, etc
parent material
the unconsolidated material from which soil develops, including rocks, minerals, and organic matter
influences soil properties and composition
permeability
measure of how easily substances can flow through a medium (how water moves through the soil)
from most to least permeability: sand > silt > clay
physical weathering
mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals
abiotic causes: water, wind, temp variations
biotic causes: plant roots, burrowing animals
porosity
% of space in the soil sample
e.g. clay has many small pore spaces to hold water (porosity), but water cannot permeate
rain shadow effect
effect that describes when one side of a mountain receives more precipitation than the other side
on the windward side, warm, moist air rises up the mountain, cools, and falls as precipitation
however, the leeward side doesn’t receive much precipitation because the air doesn't have much moisture left
richter scale
measures earthquake magnitude
logarithmic scale (each whole number increase represents 10 times greater amplitude and 31.6 times more energy released)
rock cycle
the process by which one rock type changes into another (between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks)
saltwater intrusion
movement of saline water into freshwater aquifers
saltwater infiltrates freshwater aquifers and contaminates drinking water
saturation point
maximum amount of water vapor that can be in the air at a given temperature
once you reach that point, it rains!
seafloor spreading
process that takes place at divergent boundaries on the ocean floor
two tectonic plates move apart from each other, magma goes up through the space between the plates, & the cool ocean water cools it down and more rock forms
sedimentary rocks
formed as sediment (eroded rocks and the remains of plants and animals) builds up and is compressed
processes: weathering, compaction and cementation
e.g. sandstone, shale, and limestone
seismic activity
vibrations & movements in the Earth's crust caused by the release of energy from tectonic plates
soil degradation
the physical, chemical and biological decline in soil quality
anthropogenic causes: compaction of soil from livestock & machinery causes drying, water logging, & increased resistance for root development
soil horizons
distinct layers of soil that form as a result of various processes
O Horizon (Humus): surface litter, like leaves and other decaying matter
A Horizon (Topsoil): mixture of organic materials with minerals
E Horizon (Eluviated): zone of leaching, nutrients from upper horizons moves to lower horizons
B-Horizon (Subsoil): zone of accumulation where minerals such as iron and other nutrients accumulate
C Horizon (Parent Material): the material that is broken down to create the soil
Bedrock: solid rock that lies beneath the parent material and soil
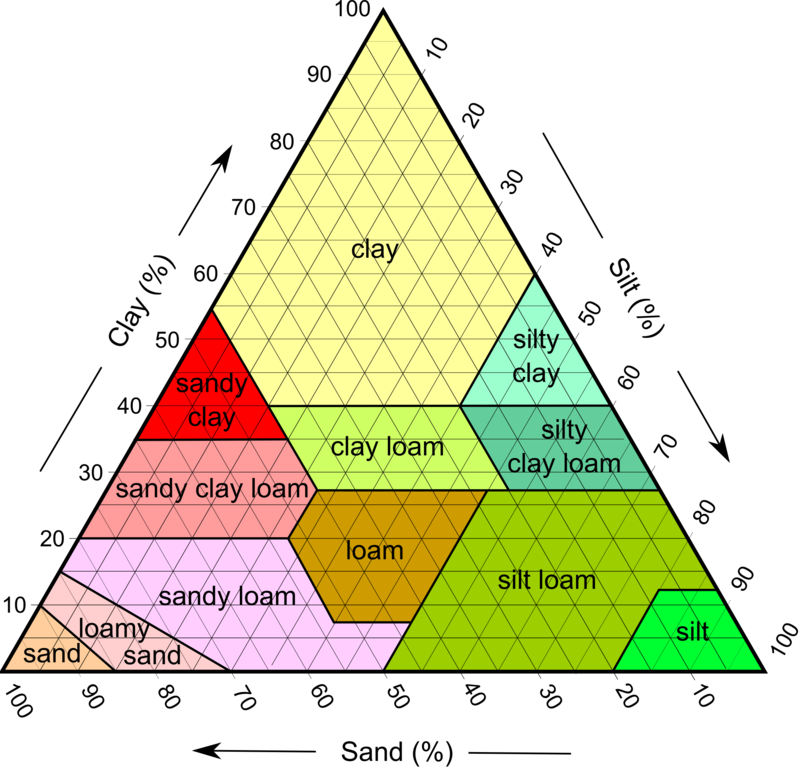
soil texture triangle
identify soil using the percentage of clay, silt, and sand
clay lines go straight across, silt lines go down diagonally, and sand lines go up diagonally
stratosphere
layer of Earth's atmosphere above the troposphere (10-50 km above the Earth's surface)
contains the ozone layer
subduction
when the MORE dense plate is pushed underneath the LESS dense plate, forming volcanoes and a trench
happens at a convergent boundary
thermohaline circulation
the pattern by which the density of water increases as it becomes colder and saltier; thus it sinks at high latitudes and is replaced by warmer water from the tropics flowing north
key mechanism that impacts the Earth’s climate
climate change (warming near Greenland) is affecting this pattern
thermosphere
50 to 100km in altitude & the temperature increases as you increase in altitude because it receives a lot of UV radiation and energy from the sun
traps protons, electrons, and other ions given off by the sun
transform boundary
type of plate boundary where plates slide past each other horizontally
pressure builds up and when that pressure is released suddenly, an earthquake occurs
troposphere
starts at ground level and goes up 10km
shallowest layer of the atmosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases, & all weather occurs in this atmospheric layer
upwelling
cold water from the deep ocean rises toward the surface of the ocean
caused by strong winds & rotation of the Earth, which moves warmer surface waters offshore allowing the cold, nutrient rich water to rush up (nutrient rich water is primarily found at the bottom of the ocean)
water holding capacity
measure of the ability of air to hold water
i.e warmer air has a higher water vapor capacity, while colder air has a lower water vapor capacity
weather
short-term changes in temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloud cover, wind direction, and other conditions in the troposphere at a given place and time