Plant morphology - PLSC 214 Exam 1
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Mycorrhizae
Fungus that grows in association with the roots of a plant in a symbiotic relationship
Angiosperms
Covered seeds, flowering plants
Gymnosperms
Naked seeds, conifers/cone-bearers
Cotyledon
First leaf or pair of leaves developed by the embryo from a seed
Monocot
Flowering plant embryo developing a single cotyledon
Dicot
Flowering plant embryo developing two cotyledons
Leaf
Includes blade, venation, bud, and petiole
Blade
Portion of leaf distinct from the petiole
Midrib
Main vein running through the center of leaf
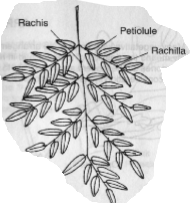
Petiole
Stalk of a leaf
Stipule
Leaf-like appendages that occur at the base of the petioles in some leaves
Bud
An undeveloped flower, leafy shoot, or stem
Apex
Tip of the leaf
Sinus
Cleft or recess between two lobes
Lobe
Rounded segments of the leaf with adjacent sinuses
Margin
Outer edge of the leaf
Base
Lowest point of the leaf where it connects to the petiole
Simple Leaf
Bud exists at the base of a single leaflet
Compound Leaf
Located at the base of a leaf containing multiple leaflets
Rachis
Main axis of structure for compound leaves
Palmately Compound
Leaflets coming form one point at the end of the Petiole

Odd Pinnate
Leaflets paired along either side of the central rachis with a terminal non-paired leaflet

Even Pinnate
Leaflets paired along either side of the central rachis with a non terminal leaflet
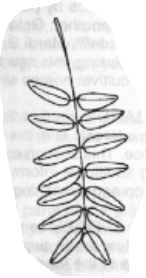
Bipinnate
Pinnate leaflet structure existing on another pinnate structure
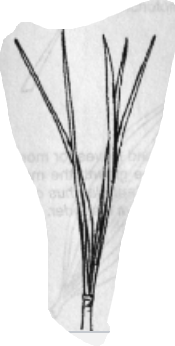
Needle-like Leaves
Leaves that are long and narrow, often evergreen, may be flattened or rounded
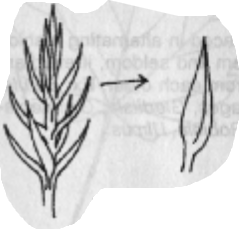
Awl-like Leaves
Narrow, flat, stiff, shark-pointed leaves, usually less than ½”
Scale-like Leaves
Small Leaves that are often compressed to the branches
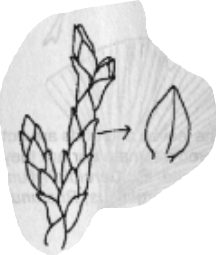
Nodes
Points of attachment for leaves, roots, and flowers
Internodes
Regions in between nodes
Opposite Leaf Arrangement
Leaves and buds exist across from each other on the stem
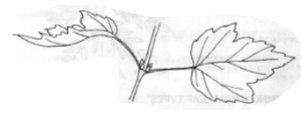
Alternate Leaf Arrangement
Leaves and buds are arranged in alternating patterns on the stem

Whorled Leaf Arrangement
Three or more leaves and buds arranged a the same point on the stem

Subopposite Leaf Arrangement
Leaves and buds are arranged in patterns that are not truly opposite or alternate

Obovate
Leaf Shape:
Oblanceolate
Leaf Shape:
Obcordate
Leaf Shape:
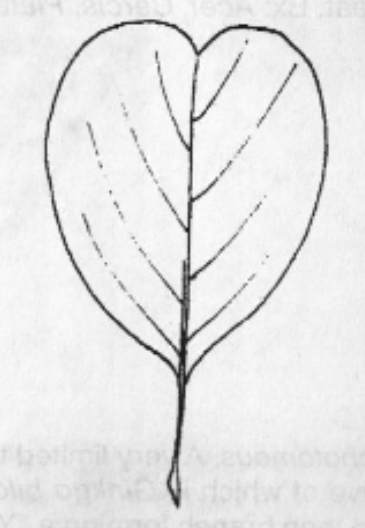
Oblong
Leaf Shape:
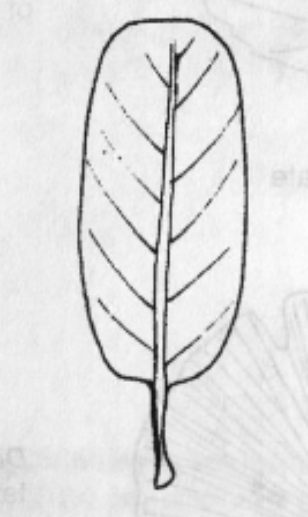
Linear
Leaf Shape:
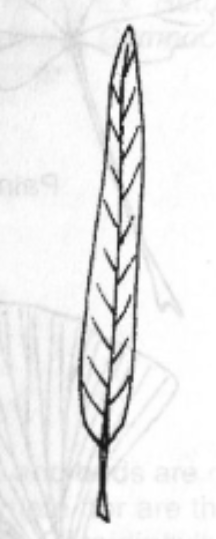
Ovate
Leaf Shape:
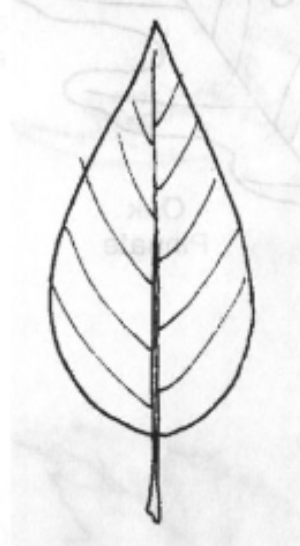
Lanceolate
Leaf Shape:
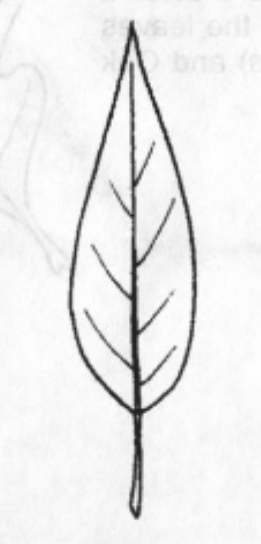
Cordate
Leaf Shape:
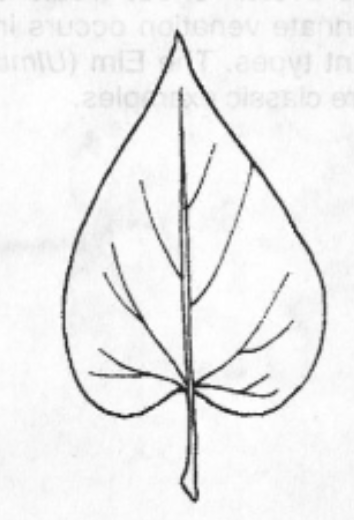
Elliptical
Leaf Shape:
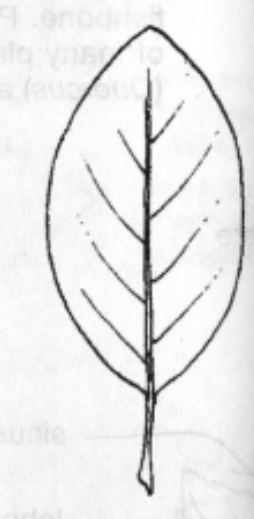
Hastate
Leaf Shape:
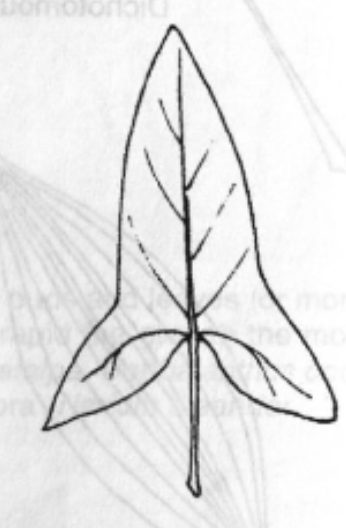
Reniform
Leaf Shape:
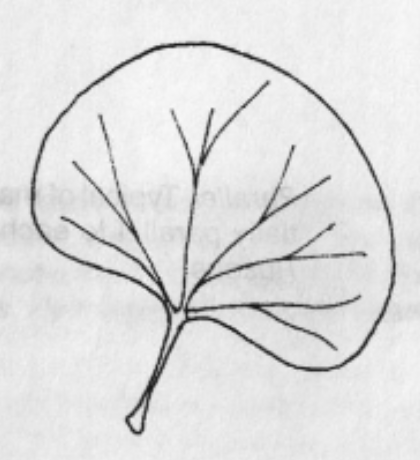
Cuneate
Leaf Shape:
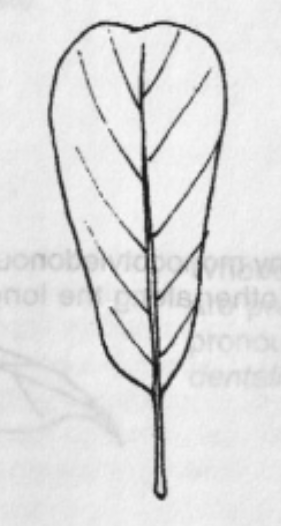
Peltate
Leaf Shape:
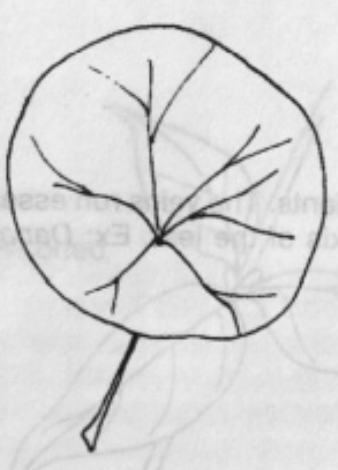
Entire
Leaf Margins:

Serrate
Leaf Margins:
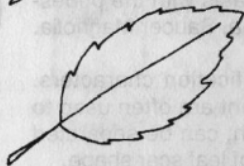
Serrulate
Leaf Margins:

Doubly-Serrate
Leaf Margins:

Dentate
Leaf Margins:
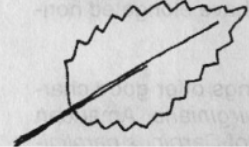
Crenate
Leaf Margins:
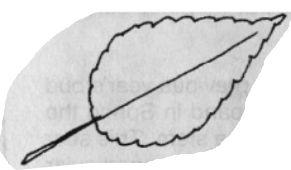
Incised
Leaf Margins:

Sinuate
Leaf Margins:

Undulate
Leaf Margins:

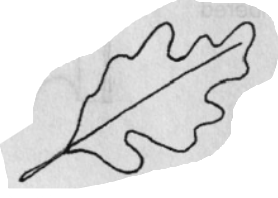
Lobed
Leaf Margins:
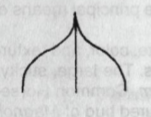
Acuminate
Leaf Apex:
Acute
Leaf Apex:
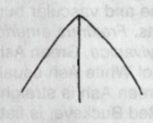
Truncate
Leaf Apex:

Emarginate
Leaf Apex:
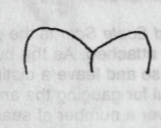
Mucronate
Leaf Apex:

Cuspidate
Leaf Apex:

Cuneate
Leaf Base:
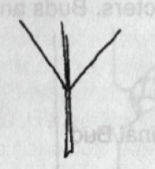
Acute
Leaf Base:
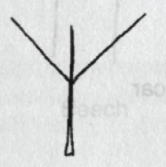
Rounded
Leaf Base:

Cordate
Leaf Base:

Oblique
Leaf Base:

Sagittate
Leaf Base:

Hastate
Leaf Base:
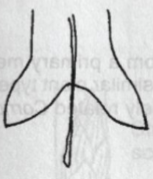
Truncate
Leaf Base:

Auriculate
Leaf Base:
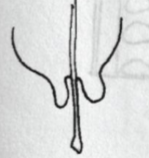
Parallel Venation
Veins run parallel lines to margin
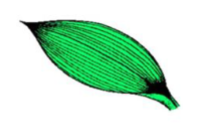
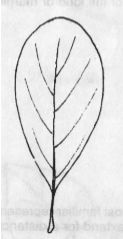
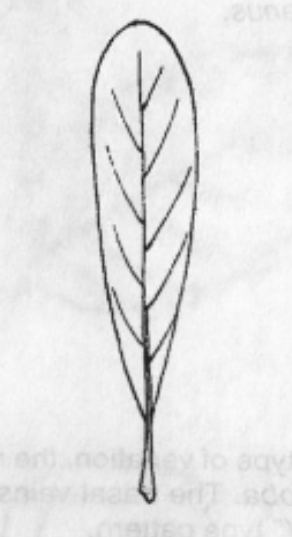
Pinnate Venation
Veins extend from a midrib toward the edge

Palmate Venation
Veins radiate from a central point in a fan shape away from the petiole

Glabrous
Having smooth, hairless leaf surface
Glutinous
Sticky leaf surface
Scabrose
Rough sandpaper-like leaf surface
Glaucous
Whitish or blueish waxy covering leaf surface
Pubescent
Hairy leaf surface
Uniform Pith
Solid core filled with pith parenchyma (pith cells)
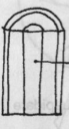
Chambered Pith
Solid Core of pith cells absence, only contains distinct partitions (think bamboo)
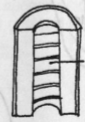
Hollow Pith
Disintegrated pith with a large central cavity
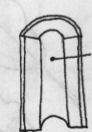
Evacuated/Spongey Pith
Pith cells are perforated with holes
Narrowly Conical
Bud morphology:
Ovoid
Bud morphology:

Conical
Bud Morphology:

One-scaled
Bud morphology:
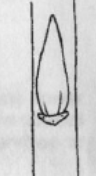
Superposed
Bud morphology:
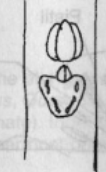
Accessory
Bud morphology:

Taproot
Sends a main root deep into the soil in search for water/nutrients
Fibrous Root
Roots grow down and out in search of nutrients and water
Rhizomes
Modified stem that grows laterally under the surface, sending out new roots and shoots at nodes
Stolons
Horizontal stem growing laterally along the group, sending out new roots and shoots at nodes
Tubers
Swollen, fleshy root that stores nutrients
Bulbs
Compressed stems growing underground that stores nutrients and surrounds a flower bud
Smooth Bark
Bark with little to no texture, common among younger trees
Papery Bark
Bark with horizontal peeling in large sheets or thin strips
Knobby
Bark that looks warty or bumpy
Furrowed
Fissured bark, similar to plow lines, deeper with age, sometimes in diamond pattern
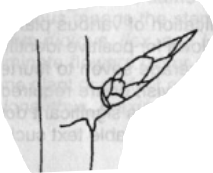
Pistil
Female reproductive organ of a flower, consists of ovary, style, and stigma