Introduction to Cosmology and Stellar Evolution
1/296
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
297 Terms
What is cosmology?
The study of the visible universe from its origin to its development into modern time and how the universe could end.
What principle was put forward by cosmologists in 1920?
The cosmological principle, which states that the physical laws that apply to one part of the universe apply everywhere.
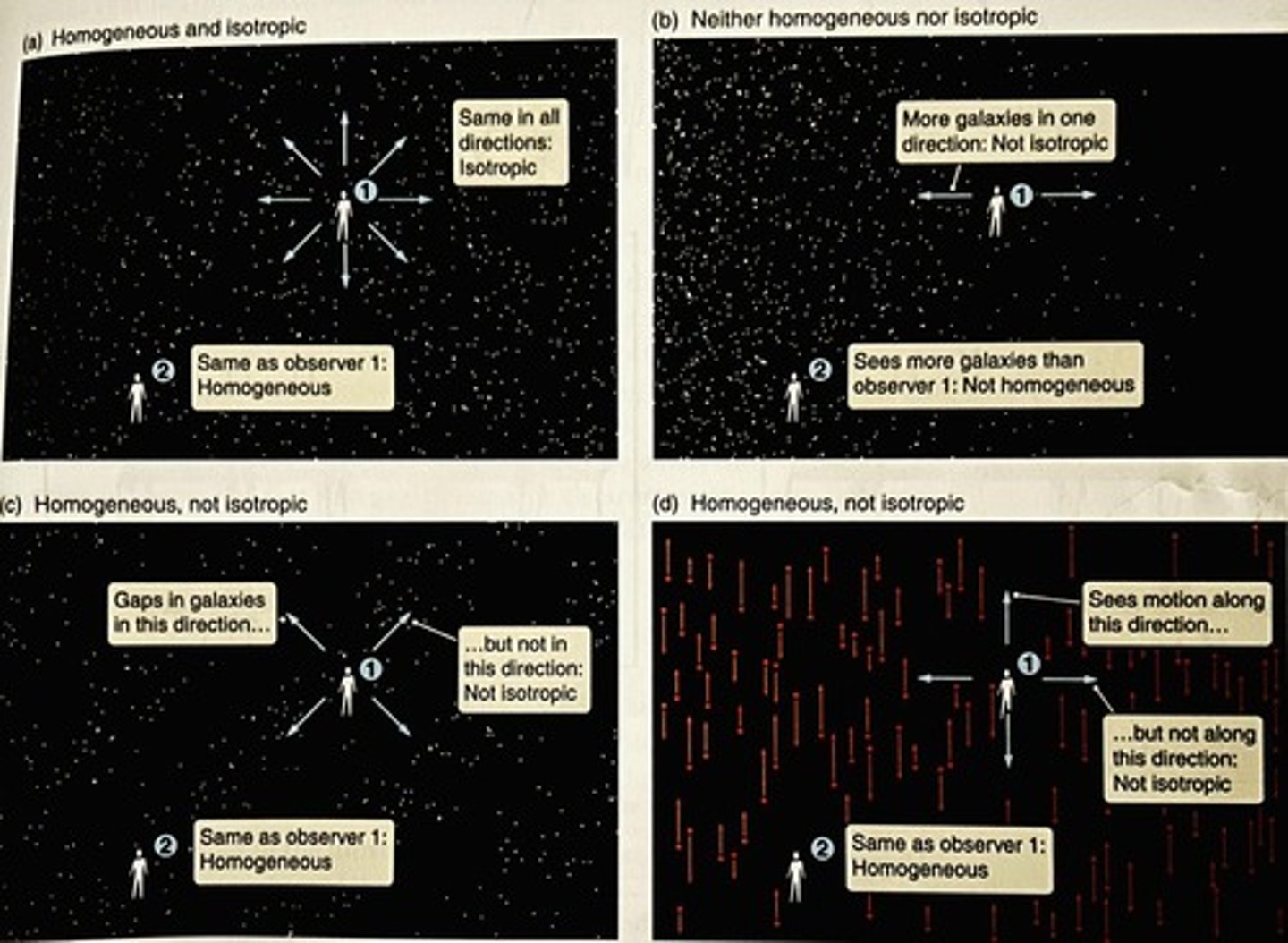
What assumptions does the cosmological principle make?
It assumes that gravity acts the same way on distant galaxies as it does in our galaxy and that observations from any galaxy should be similar.
What does a homogeneous universe imply?
It implies that the universe has the same composition and properties in all parts.
What does isotropic mean in the context of the universe?
Isotropic means that the universe appears the same in all directions.
What significant discovery did Edwin Hubble make in the 1920s?
He found that every galaxy appeared to be moving away from us, indicating an expanding universe.
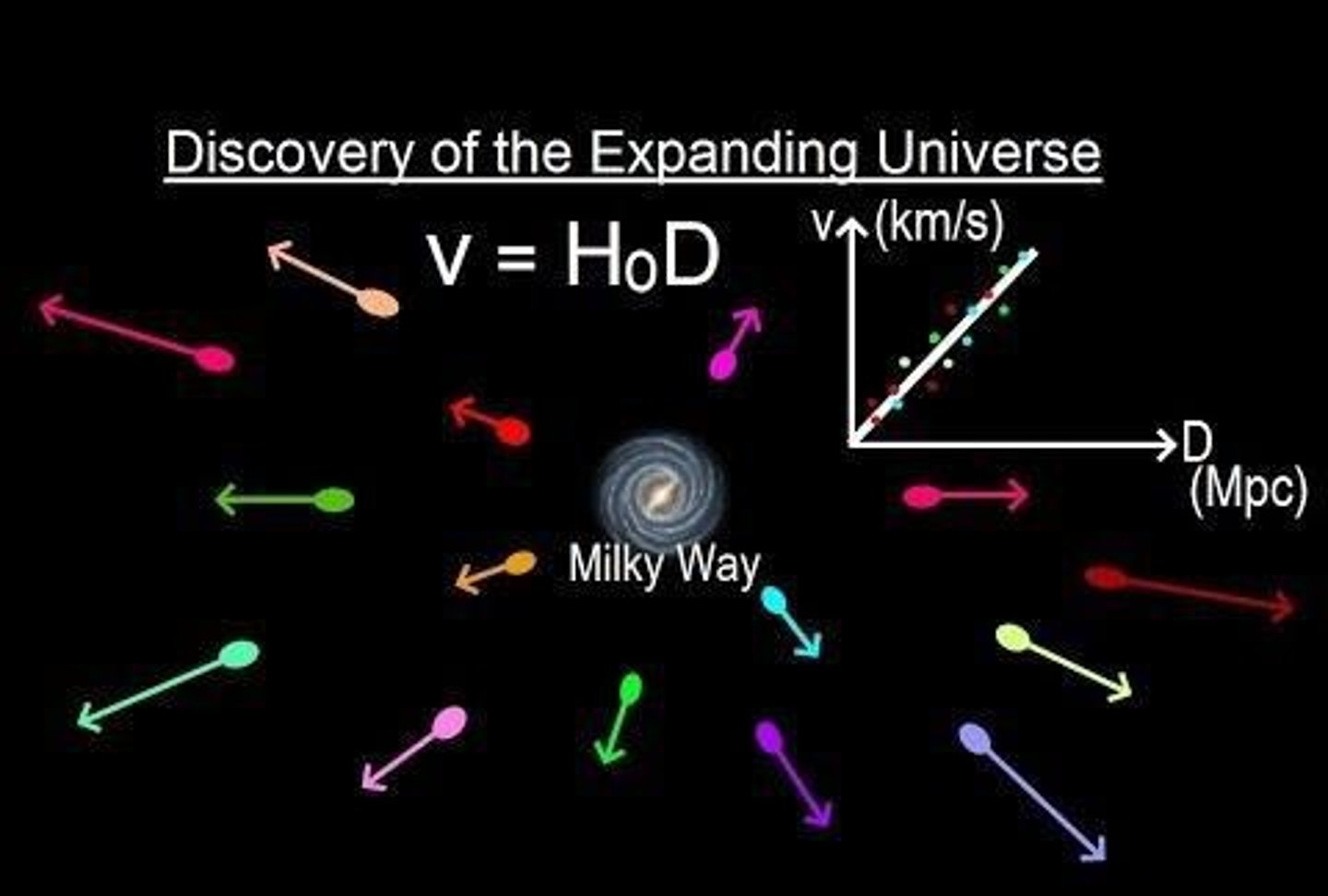
What is Hubble's Law?
The relationship between recession velocity and distance from Earth, expressed as V = Ho D, where Ho is Hubble's Constant.
What is the value of Hubble's Constant (Ho)?
70 km/(s Mpc).
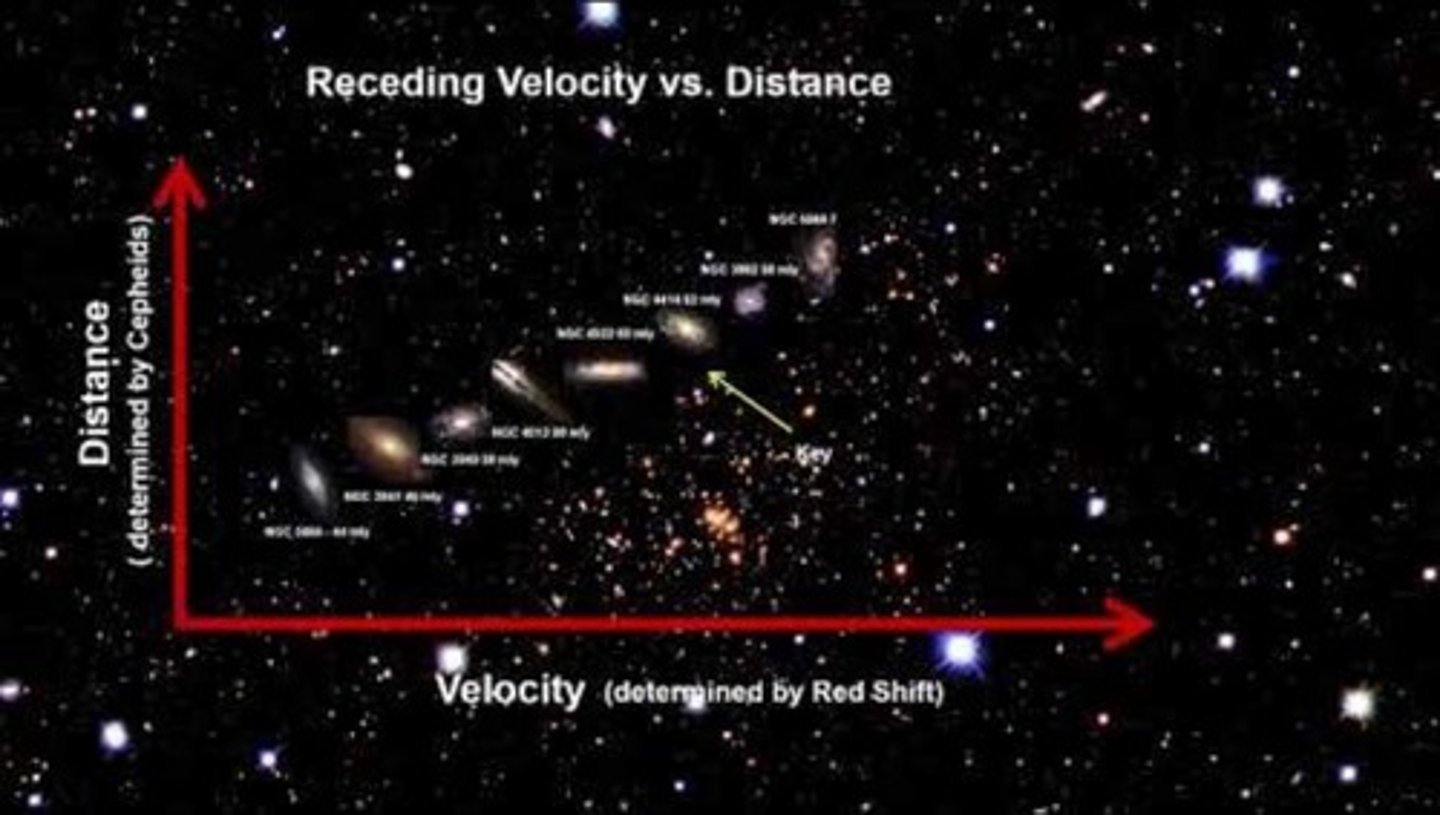
What does the redshift of galaxies indicate?
It indicates that galaxies are moving away from us, with those farther away having a higher velocity.
What does Hubble's Law allow astronomers to determine?
It allows them to determine the distance of galaxies by looking at their redshift.
How does Hubble's Law relate to time?
The distance of a galaxy from Earth is proportional to the look back time via the speed of light.
What is the speed of light?
The speed of light in space is approximately 3x10^8 m/s.
How long does it take light to travel from the Sun to Earth?
It takes light approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the surface of the Sun to Earth.
What is a lightyear?
A lightyear is the distance that light travels in one year.
What is the implication of an expanding universe?
It implies that all galaxies are moving away from each other.
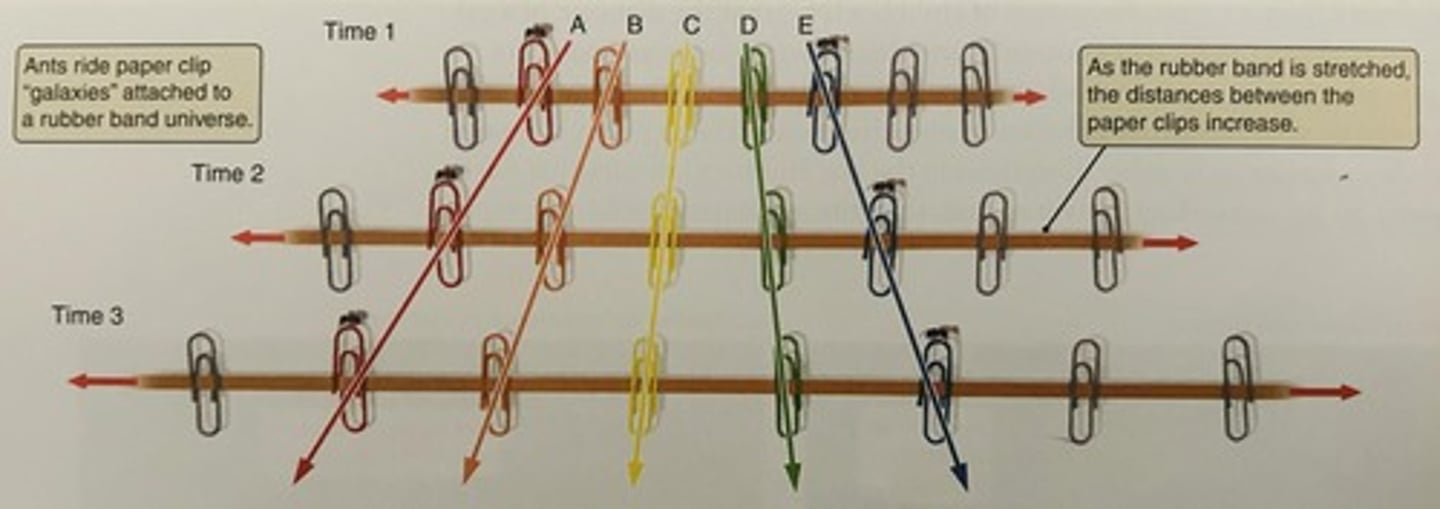
What is the exception to Hubble's Law?
The exception is galaxies that are close together, where gravitational pull can be stronger than the expansion of space.
What does the term 'Doppler shift' refer to in cosmology?
It refers to the change in frequency or wavelength of light from galaxies moving away from us, resulting in a redshift.
What does the combination of a homogeneous and isotropic universe imply?
It implies that the universe is uniform in composition and properties, and looks the same in all directions.
What phenomenon does Hubble's discovery initiate a discussion about?
The phenomenon of how everything in the universe is always moving away from each other.
What does it mean for space to expand?
It means that space itself is increasing in size, dragging galaxies and stars with it.
What is the relationship between distance and redshift according to Hubble's Law?
The larger the distance to a galaxy, the higher the redshift or recession velocity.
Why can't we know the exact moment of events in space?
Because it takes time for light emitted from objects to reach Earth, meaning we see them as they were in the past.
What is the significance of measuring distances in lightyears in astronomy?
It helps astronomers understand how far away celestial objects are based on the time it takes light to travel from them to Earth.
What is a lightyear in meters?
1 lightyear = 9.46 x 10^15 meters.
What does the distance of a galaxy measured in lightyears imply about the light we see?
If a galaxy is 5 lightyears away, the light we see traveled 4.73 x 10^16 meters and took 5 years to reach us.
What does Hubble's law relate to in cosmology?
Hubble's law relates redshift and look back time, indicating that objects farther away are viewed as they were in the early universe.
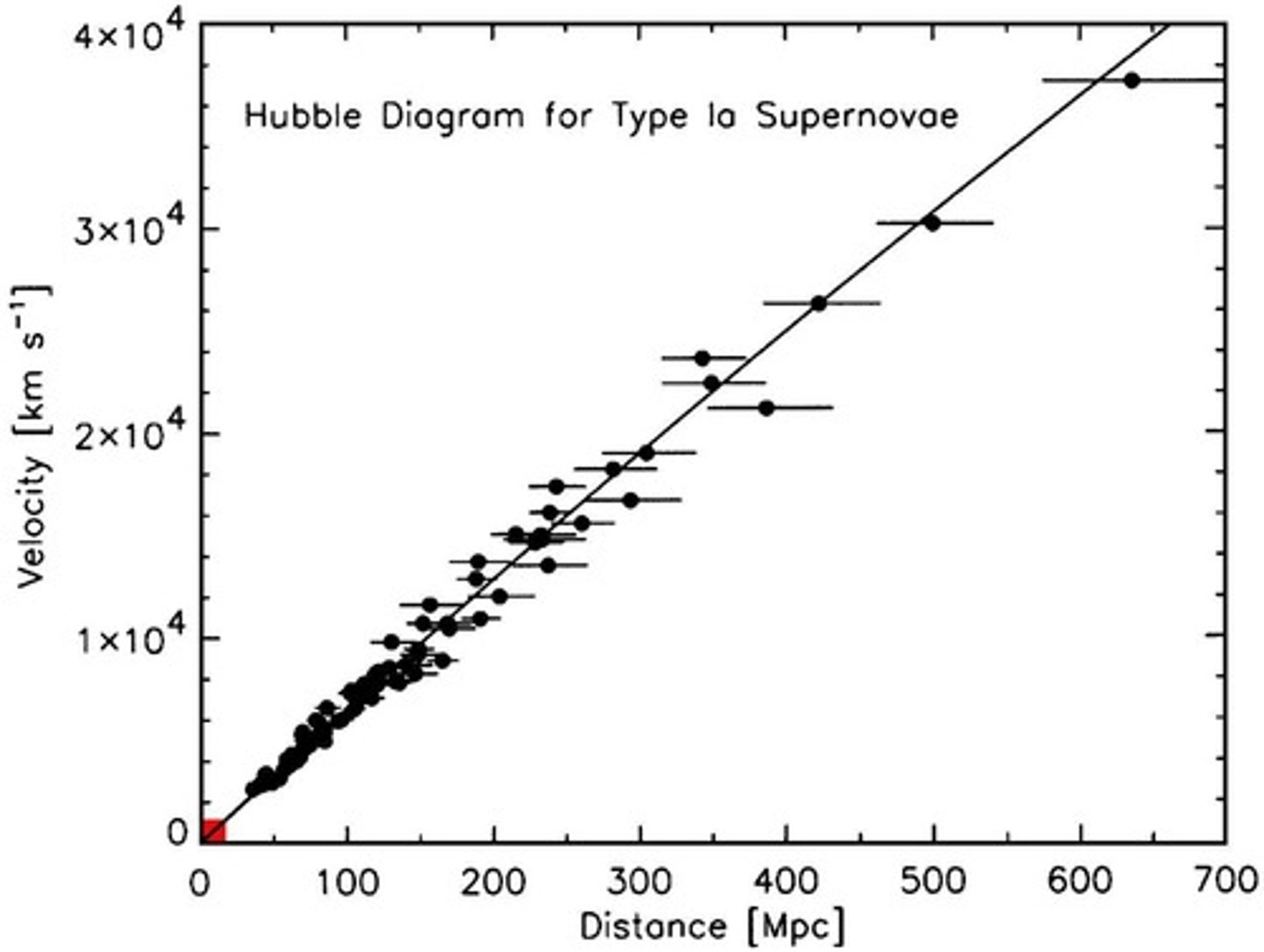
What is the significance of observing distant galaxies?
We see how galaxies looked in the past, which allows us to explore the universe's development over time.
How can Hubble's constant be used in cosmology?
Using Hubble's constant, we can estimate the age of the universe, calculated as 1/H0 = 13.8 billion years.
What does running Hubble's Law in reverse suggest about the early universe?
It suggests that the early universe may have started as a hot, dense core or point containing the entire makeup of the universe.
What is the Big Bang Theory?
The Big Bang Theory states that the universe began as a point of hot, dense material, leading to an explosion that created energy, mass, space, and time.
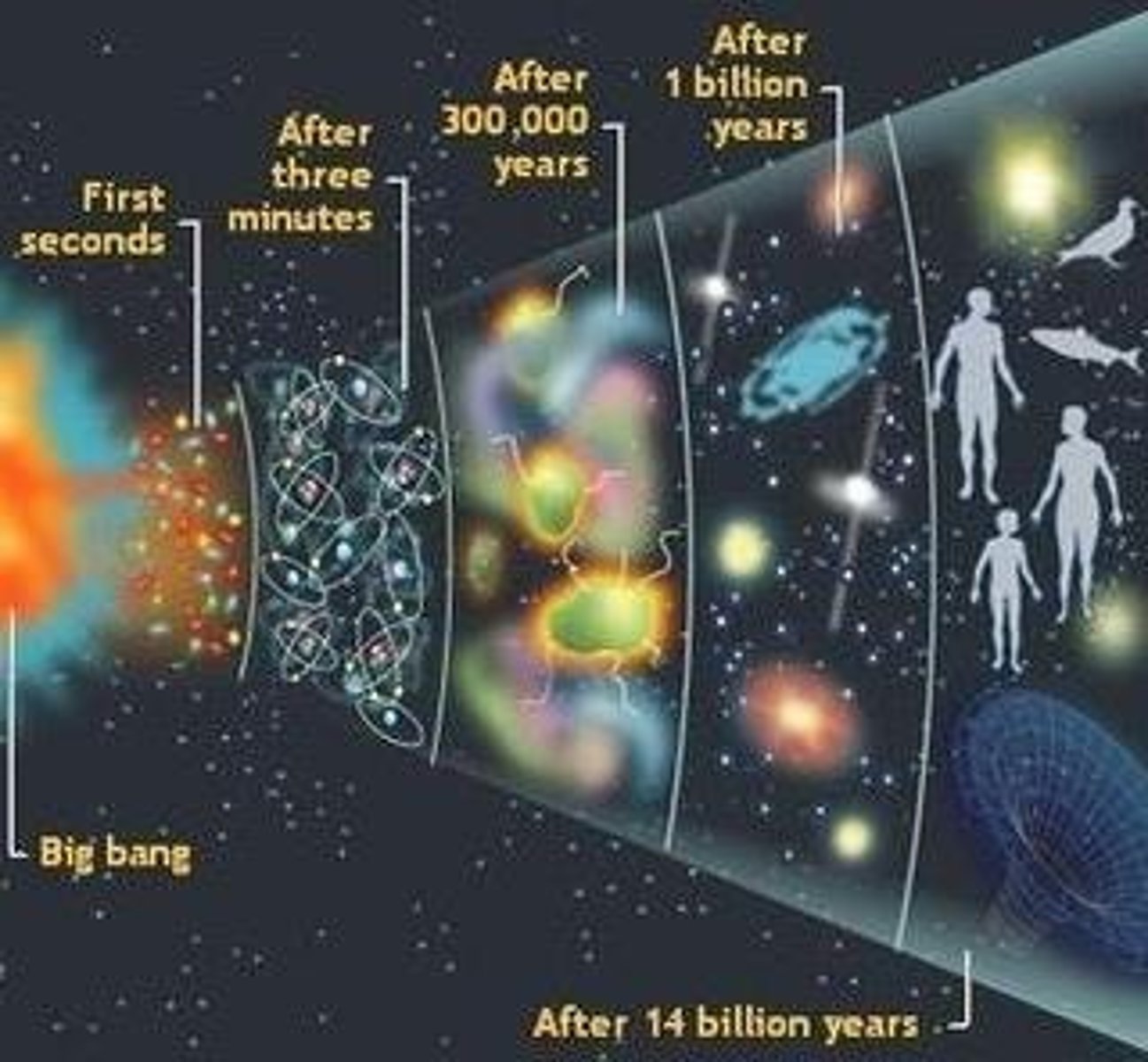
What is a singularity in the context of the Big Bang?
A singularity refers to the hot dense point present before the Big Bang.
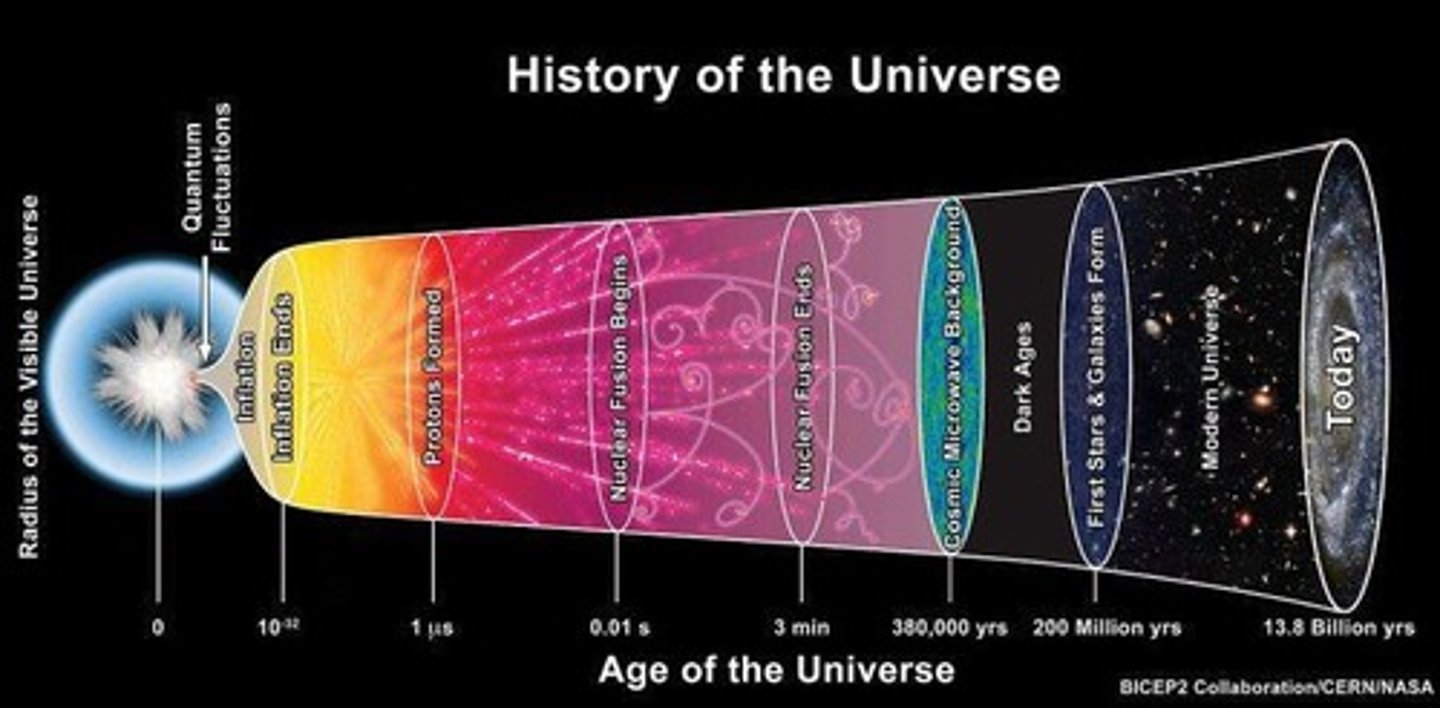
What are the two main sections of the universe's development?
The two sections are the Radiation Era and the Matter Era.
What characterizes the Radiation Era?
The Radiation Era is the first portion of the universe's development, containing only radiation or energy, lasting from the explosion to about 380,000 years.
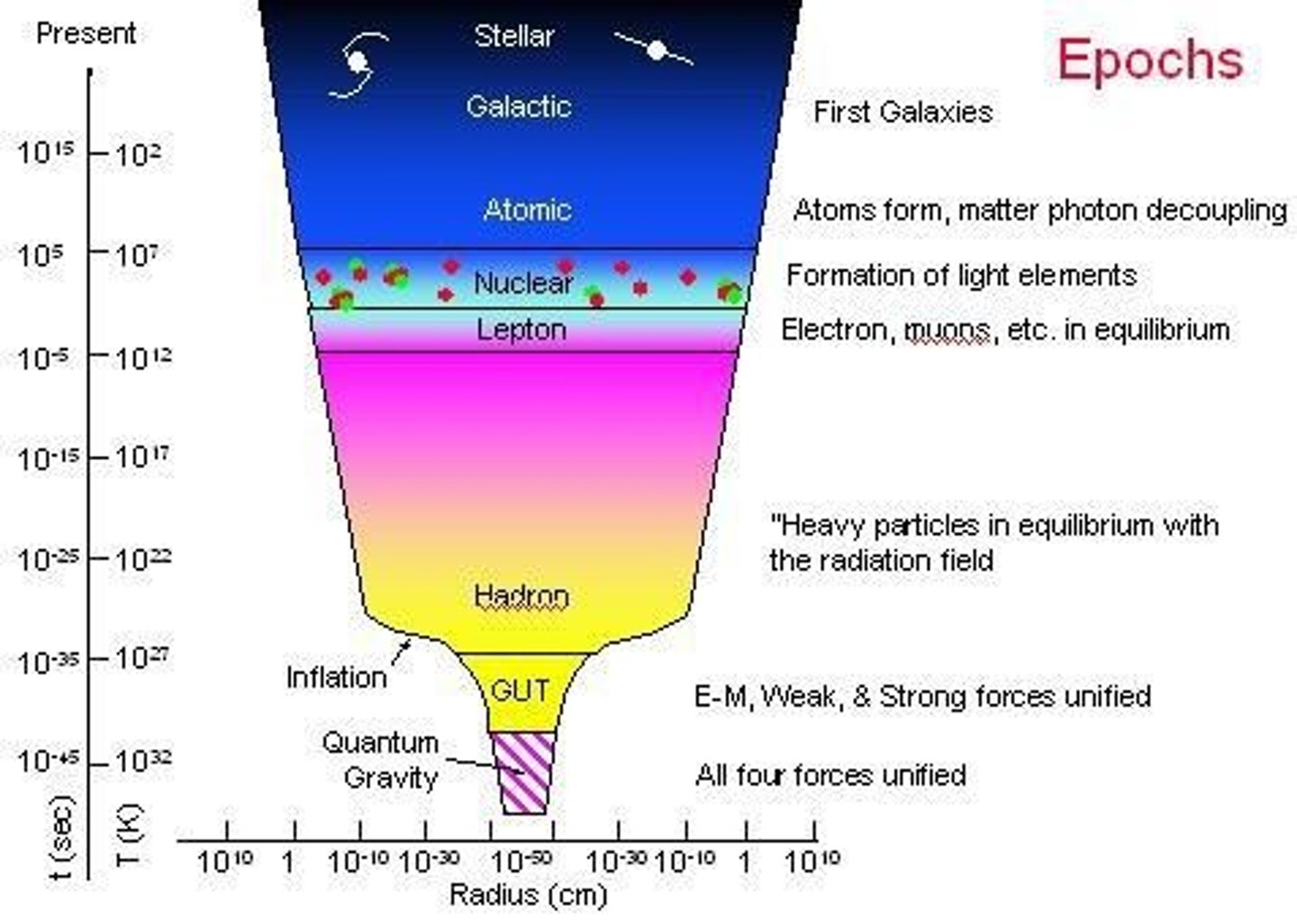
What are epochs in the context of the universe?
Epochs mark important new phases of the universe's development from the hot dense singularity to the formation of stars and galaxies.
Name some epochs under the Radiation Era.
Planck Epoch, Grand Unified Epoch, Inflationary Epoch, Electroweak Epoch, Quark Epoch, Hadron Epoch, Lepton Epoch, Nuclear Epoch.
What is the Planck Epoch?
The Planck Epoch is the immediate stage after the Big Bang where all initial makings of the universe are located, with a size about 1 billionth the size of a particle.
What is the Super Force?
The Super Force is the only force that existed during the Planck Epoch, characterized by attractions or repulsions due to physical properties.
What happens during the Grand Unified Epoch and Electroweak Epoch?
Forces begin to separate from the Super Force, creating the fundamental forces we know today.
What are the four fundamental forces that emerged after the Super Force?
Gravity, Weak Force, Electromagnetic Force, and Strong Nuclear Force.
What is the Inflationary Epoch?
The Inflationary Epoch occurs approximately 10^-36 seconds after the Big Bang, marked by a sudden increase in size and expansion of the universe.
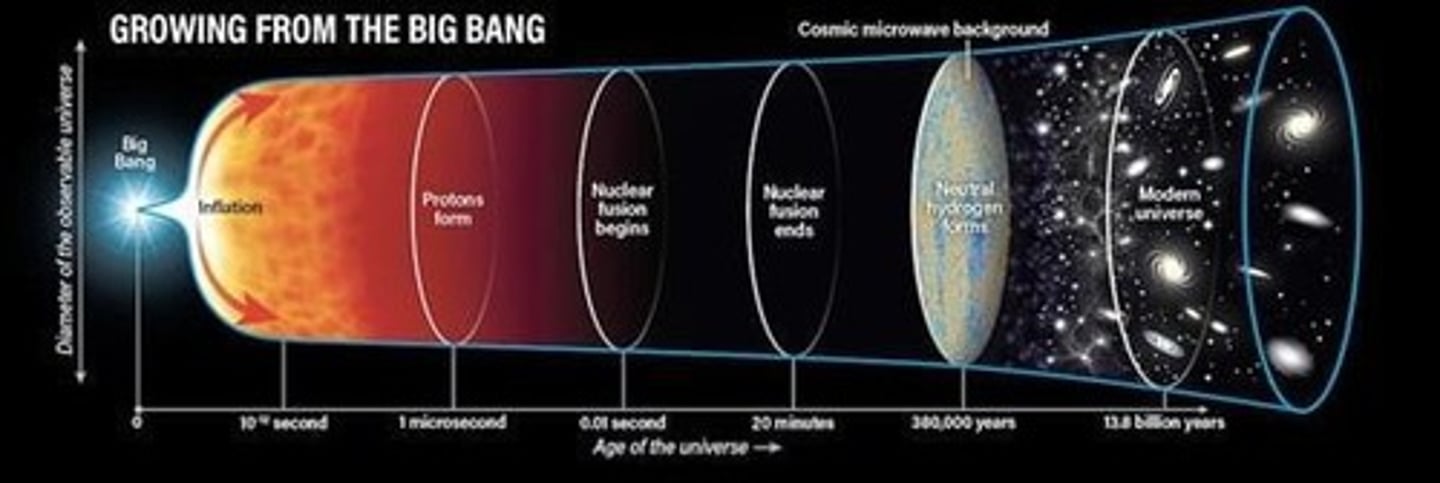
How did the size of the universe change during the Inflationary Epoch?
The universe expanded from the size of a particle to the size of a small baseball.
What is the significance of the Theory of Everything?
The Theory of Everything aims to unify all fundamental forces and particles in a single framework, particularly relevant during the Planck Epoch.
What does the term 'look back time' refer to?
Look back time refers to the time it takes for light from distant objects to reach us, allowing us to see them as they were in the past.
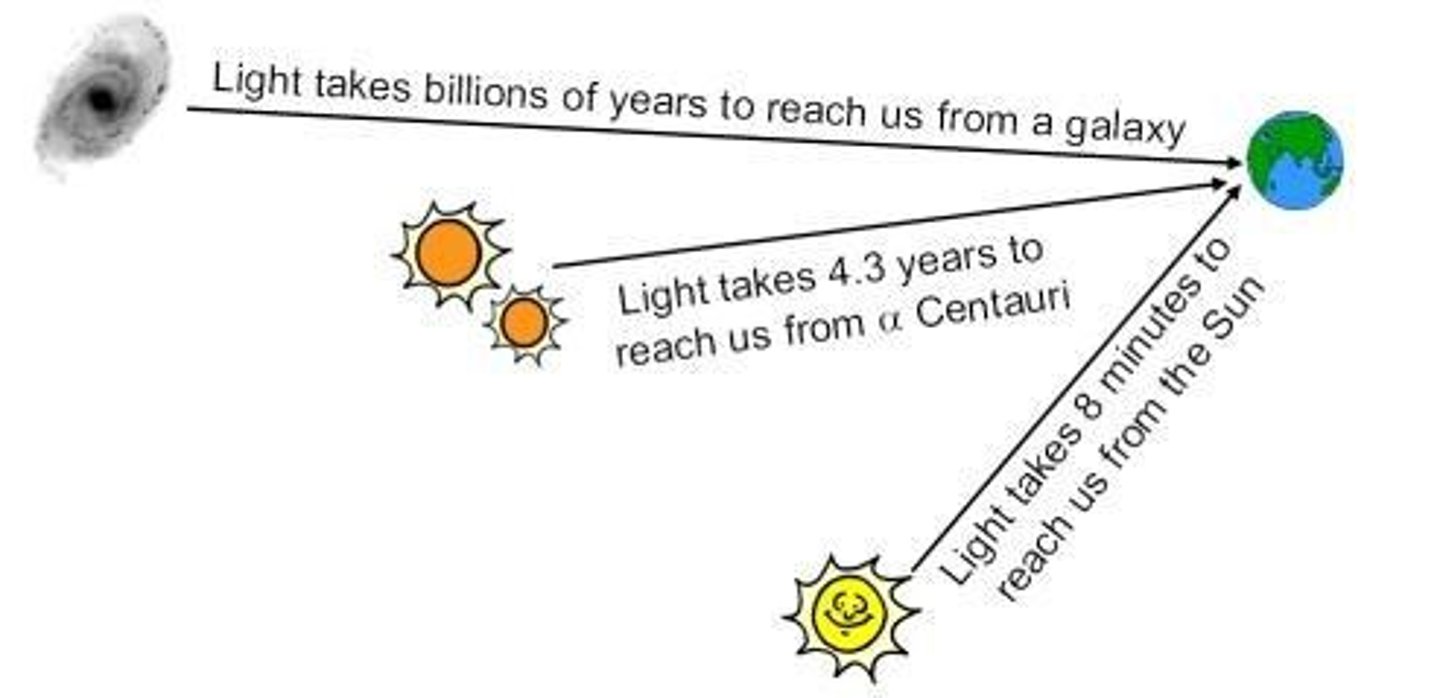
Why is it important to understand the early universe?
Understanding the early universe helps us map out the universe's development and how galaxies have changed over time.
What is the relationship between the universe's expansion and its age?
Hubble's Law shows how the universe expands, and by inverting it, we can estimate how long it has been expanding, leading to the estimated age of 13.8 billion years.
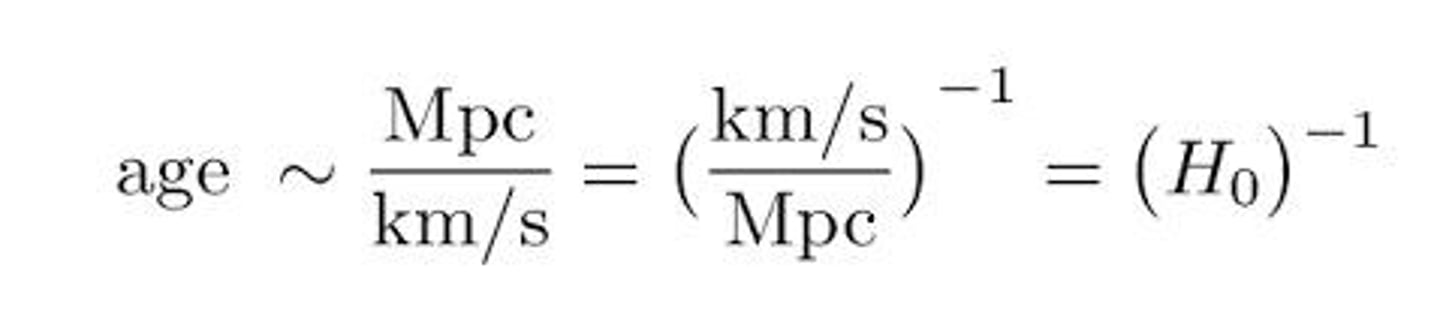
What is the consequence of observing light from distant galaxies?
We may see light emitted millions of years ago, but not the light generated today, meaning we might observe galaxies that no longer exist.
What happens to the temperatures of the universe as it expands?
The temperatures drop, allowing material to create particles.
What is the Quark Epoch?
The stage when quarks, the subatomic particles that make up protons and neutrons, are created.
What occurs during the Lepton Epoch?
Electrons and other lepton particles (neutrinos, muons, tau) are created.
What is the ****** Epoch?
The stage when quarks combine to create protons, neutrons, and other particles.
What significant event occurs during the Nuclear Epoch?
Protons and neutrons combine to form the universe's first element, Helium.
What is the Matter Era characterized by?
The beginning of the formation of Helium from protons and electrons.
What are the three epochs of the Matter Era?
Atomic, Galactic, and Stellar epochs.
What is the Atomic Epoch marked by?
The creation of Neutral Hydrogen.
When did the Atomic Epoch occur?
About 30,000 to 50,000 years after the big bang.
What significant change occurs during the recombination process?
Light can scatter throughout the universe, marking the end of the opaque universe.
What is the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)?
The first form of radiation visible in the universe, emitted after recombination.
What did the universe look like before the recombination?
The universe was opaque and very bright, not dark.
How did the CMB limit our view of the universe?
It restricts us from seeing beyond the surface light of the universe.
What was the initial state of the radiation emitted from the CMB?
It was likely a visible light color before being redshifted.
What is the significance of the discovery of the CMB?
It was essential in proving the Big Bang Theory valid.
What occurred after the CMB radiation was emitted?
A period of darkness known as the Dark Ages, where no stars or galaxies formed.
What happens during the Stellar Epoch?
Gas cools and is pulled together by gravity, leading to star formation.
What effect does the energy from nuclear fusion in stars have on neutral hydrogen?
It ionizes the neutral hydrogen, causing electrons to flip their magnetic poles.
What is the Galactic Epoch?
The period when gas begins to form galaxies or large clusters of gas.
What does the CMB show about the distribution of matter in the universe?
It shows spots where matter is grouped together, indicating future galaxies.
What is the significance of the redshift observed in the CMB?
As the universe expanded, the light was redshifted from visible to infrared to microwave.
What was the state of hydrogen and helium during the Dark Ages?
They were still too hot to form stars.
What is the relationship between the Cosmic Microwave Background and the Big Bang Theory?
The CMB supports the Big Bang Theory by providing evidence of the early universe's conditions.
What is Reionization?
Reionization is the process during which the universe underwent a significant change, emitting radiation (21-cm radiation) as the poles flipped back.
What is 21-cm radiation?
21-cm radiation is a radio wave with a wavelength of 21 cm, marking the second time radiation was emitted in the universe.
What does mapping the universe in 21-cm radiation provide?
It provides the next timestamp in the universe's development, allowing us to see the second point when radiation was emitted.
What is the Hydrogen Epoch of Reionization Array (HERA)?
HERA is a telescope being developed at UC Berkeley to measure 21 cm reionization radiation.
What is the Space-Time Continuum Theory?
The Space-Time Continuum Theory describes the universe as a four-dimensional fabric where large bodies of matter interact, modeling space and time together.
How does the Space-Time Continuum relate to gravity?
It explains gravity as the bending of the space-time fabric by mass, rather than a force pulling objects together.
What recent discovery supports the Space-Time Continuum Theory?
The discovery of gravitational waves supports the theory as a good model for explaining gravitational effects.
What does the Accelerating Universe imply?
It implies that the universe is not only expanding but also accelerating in its expansion over time.
What is believed to cause the acceleration of the universe?
Dark energy is believed to cause the acceleration by applying negative pressure that counters gravity.
What percentage of the universe is made up of dark energy?
Dark energy is believed to make up about 68% of the universe that is not normal or dark matter.
What are the three potential fates of the universe?
The three potential fates are the Big Crunch, Big Rip, and Big Freeze.
What is the Big Crunch?
The Big Crunch is a scenario where the universe stops expanding and gravity pulls everything back into a singularity.
What is the Big Rip?
The Big Rip occurs when the universe expands so rapidly that gravity can no longer hold matter together, leading to the disintegration of systems.
What is the Big Freeze?
The Big Freeze is the theory that the universe will eventually become very cold and dark as star formation ceases and remnants cool down.
What temperature does the universe currently exist at?
The universe currently exists at approximately 2.7 Kelvin.
What is the ultimate temperature the universe may reach?
The universe may eventually reach 0 Kelvin, the coldest possible temperature.
What is the significance of the Big Bang in cosmology?
The Big Bang marks the beginning of the universe, but its exact origin and nature remain uncertain.
What does the term 'dark energy' refer to?
Dark energy refers to the unknown energy that is believed to drive the acceleration of the universe's expansion.
How does the Space-Time Continuum model help in understanding the universe?
It helps explain and model the effects of gravity and the interactions of large objects in the universe.
What is the mathematical representation of the Space-Time Continuum?
The Space-Time Continuum is often represented mathematically as a four-dimensional fabric.
What happens to the universe as it continues to expand?
As the universe expands, it cools down, leading to potential scenarios like the Big Freeze.
What are the implications of the universe's accelerating expansion?
The implications include potential outcomes like the Big Rip, where gravitational forces weaken and matter disperses.
What are the challenges in measuring dark energy?
Dark energy is termed 'dark' because it has not been measured directly, only inferred from its effects on the universe.
What is the concept of the Multiverse?
The Multiverse suggests there are multiple universes, some parallel and others independent of us.
What is a Parent Universe?
A Parent Universe is a large universe that contains many baby universes, of which we are considered a baby universe.
What is the likelihood of life existing elsewhere in the universe?
The likelihood is high due to the vast number of stars and planets, suggesting we may not be special.
What types of life is NASA looking for in the universe?
NASA is looking for intelligent life, animals, unintelligent life, and bacteria.
How did life likely begin on Earth?
Life on Earth probably began from extremophiles, organisms that could survive in the initially harsh environment.
What is NASA's current focus in the search for extraterrestrial life?
NASA is focusing on moons with subsurface oceans to search for bacterial life.
What is the Europa Clipper mission?
The Europa Clipper is a satellite designed to orbit Europa and study its composition and subsurface ocean.
What are the 'we are here' messages sent by NASA?
NASA has sent messages intended for intelligent life to find and deduce our location.