Module 2: Medical Screening
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Intro:
Many Visceral problems will mimic _____ dysfunctions
Many MSK problems will take on the characteristics of _____ pathology.
MSK
Visceral
PT’s Role in Disease Prevention: Direct Access > Prevention
In Primary Prevention, a PT should aim at stopping the disease process that leads to development of disease, illness and other pathological heath conditions through what 3 factors?
Education
Risk Factor Reduction
General Health Promotion
PT’s Role in Disease Prevention: Direct Access > Early Detection
In Secondary Prevention:
Early detection of diseases, illnesses, and other pathological health conditions through what?
This does not ____ the condition but may decrease ____ and/or ____ of the disease
This can improve outcome, including improved what?
Regular Screening
Prevent the condition but may Duration and/or Severity
QOL
PT’s Role in Disease Prevention: Direct Access » Improve QOL
In Tertiary Prevention:
Providing ways to limit ___ __ ___ while improving _____ in pts w chronic and/or irreversible disease
Degree of Disability while improving in Function
Intro:
The focus of this class and PT as a profession is NOT what?
Is it within our scope of practice, nor we trained properly to make diagnosis?
NOT the diagnosis of pathology
NAUR
Intro:
What approach is taken because it allows us to make decision based on possible system breakdowns?
Based on these decisions, it affords us the opportunity to decide what?
Systems Approach
Whether the pt is appropriate for PT OR whether physician referral is required
Systems Based Approach:
Bosissonnault suggests that the main difference between PT screening and medical screenings lies where?
He suggests that:
Physicians approach a problem from a ____ level
PT approaches the disease process on a ____ approach
Lies in their approach to assessing and categorizing findings
Suggests
Physician: Disease Level (Ex: Mitral Valve Prolapse)
PT: Systems Approach (Ex Cardiovascular System Dysfunction)
Neuromusculoskeletal Symptoms:
To understand what is NOT a MSK issue, you must first understand what?
Neuromusculoskeletal Issue
MSK Problems:
What are 4 aspects of MSK Pathology?
Reacts to movement and changes in position
Are often related of a specific MOI
Symptoms change in intensity and duration based on mechanical factors
Rest should relieve symptoms
NON-MSK Problems:
What are 4 aspects of NON-MSK Pathology?
DO NOT react to movement and changes in position
Are NOT related to specific MOI
Symptoms DO NOT change in intensity and duration based on mechanical factors
Rest DOES NOT relieve symptoms
What are the 5 main topics to ask during Subjective Assessment?
Location of Pain
Description of Pain
Behavior of Symptoms
Hx of Symptoms
Family Hx
Special Considerations
Location of Symptoms:
Does area of symptoms in and of itself aid us in determining whether symptoms are of MSK or visceral origin?
There is great ___ in visceral and MSK pain referral patterns.
Symptom locations aid us in:
Determining….
Guiding….
Naur
Overlaps
Symptom Location
Determining regions to focus examination
Guides in determining further directions our testing must take in order to make accurate dx
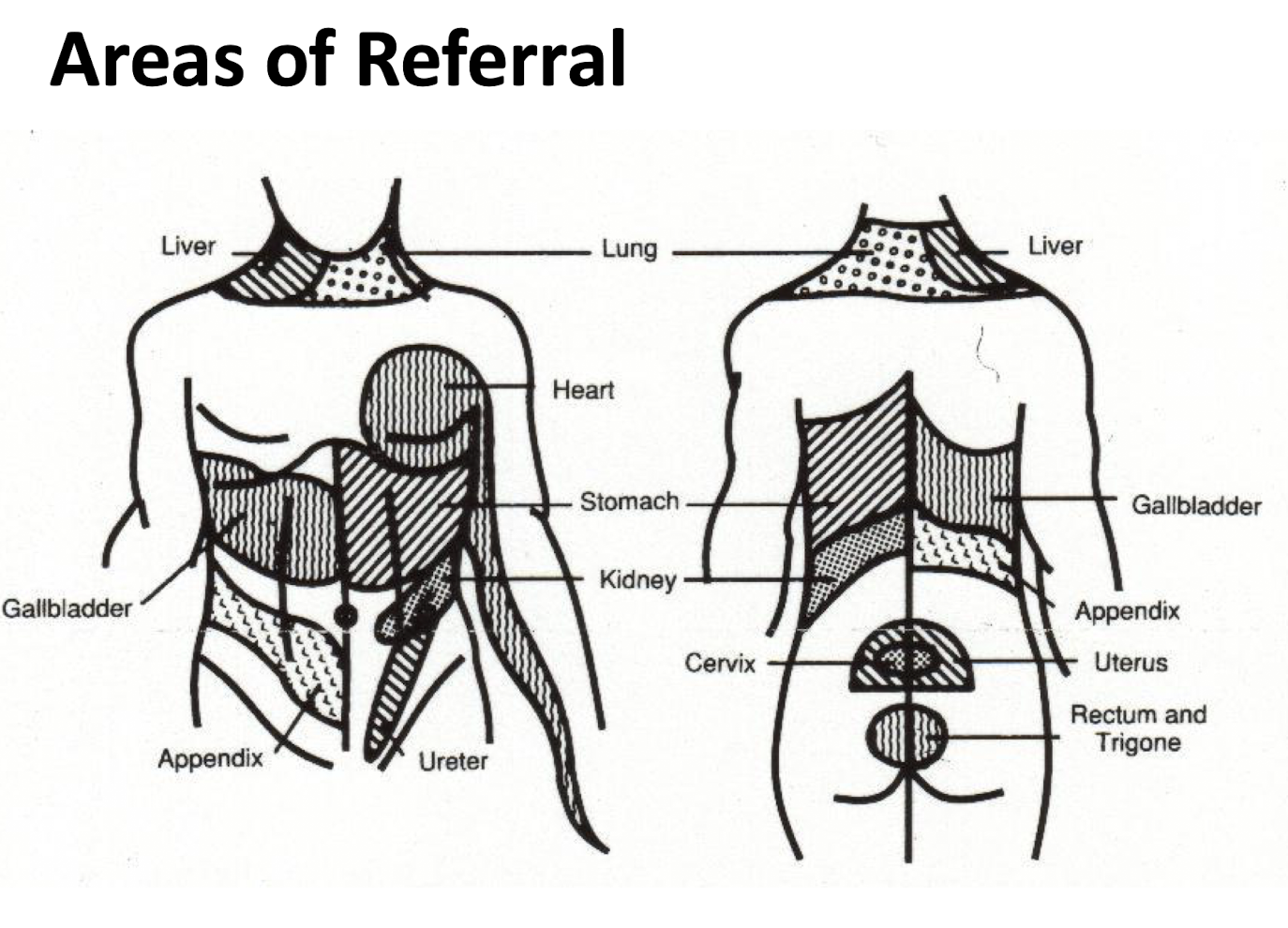
Organ Pain Locations:
Organ refer pain…
____ to the side they are located
Within the ____ they are located
Ipsilateral
Quadrant
What are the 9 Quadrants of the Body?
Q1-Q9
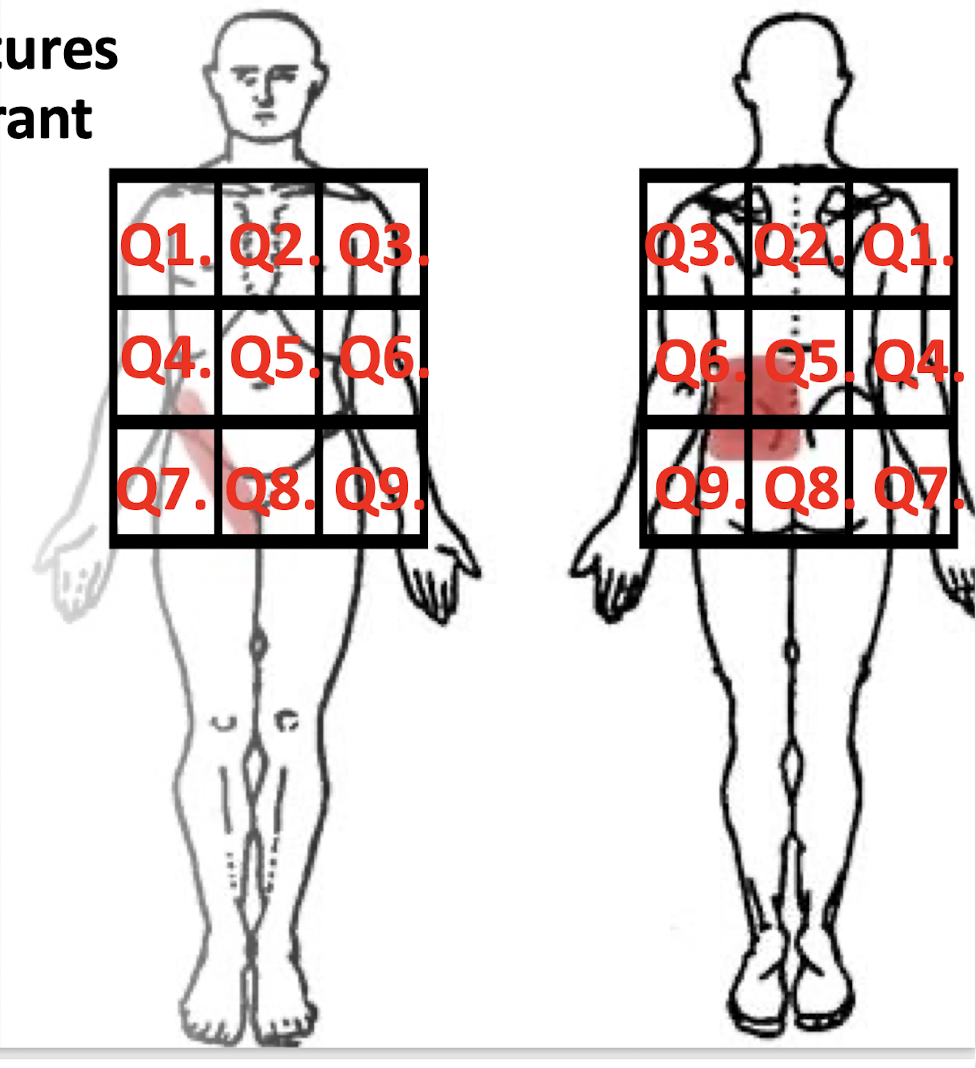
Where are the Areas of Referral for each organ?
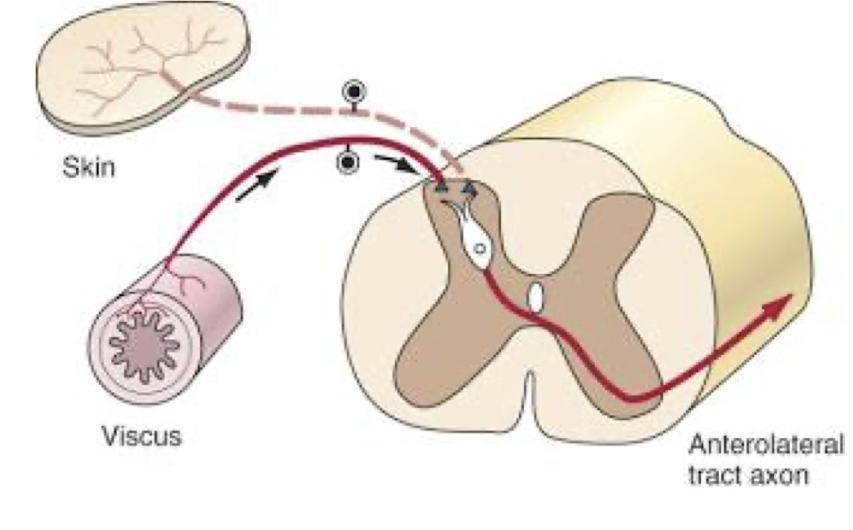
Referred Pain and Convergence:
Various systemic and visceral disorders may be the origin of what?
The proposed neurological mechanism of these phenomena what?
Origin of symptoms referred to other areas of the body
Convergence of visceral and somatic afferent nerve fibers
Description of Symptoms:
T/F: Descriptor may vary from person to person and should NOT be utilized soley in the determination of possible visceral involvement
True
Description of Symptoms:
Visceral Pain has been described as what?
Sharp
Severe
Poorly Localized and Vague
Description of Symptoms:
If a pt describes this type of pain, what structure or system could be affected?
Cramping and Colicky Pain (Craping Last Several Min)
Throbbing, Pressure, Tightness, Heaviness, Restless Leg
Weakness, Poor Balance, Numbness
Deep and Poorly Localized Constant Pain
Cramping and Colicky Pain (Craping Last Several Min)
Visceral Smooth Muscle
GI, Ureter, Gallbladder
Throbbing, Pressure, Tightness, Heaviness, Restless Leg
Cardiovascular System
Weakness, Poor Balance, Numbness
Nervous System
Deep and Poorly Localized Constant Pain
Cancer or Stones
Behavior of Symptoms: Aggs and Eases for Visceral Conditions
Easing Factors: (2)
Agg Factors: (2)
Easing Factors: (2)
Rest should NOT relieve symptoms
Positions should NOT ease symptoms
Agg Factors: (2)
Position should NOT aggravate symptoms
Nocturnal Pain
Behavior of Symptoms:
What type of pain pattern is common for pts w Visceral conditions?
It is common complaint of pts w visceral or non MSK involvement that their pain is what 2 things?
Complaints of what are also indicators of visceral involvement?
What 3 activities are commonly required to return to sleep?
24 hr pattern
Constant and Non Varying Pain
Increases in Pain at Night
Activities:
Walking
Pacing
Sitting Up
Personal Hx of Symptoms:
Visceral disease processes usually CANNOT be attributed to what 2 occurrences?
They are ___ in nature.
Traumatic Injury OR Certain Repetitive Strains or Activities
Insidious
Fam Hx:
It is wise to question pts regarding what when considering visceral structures as source of pain?
T/F: Often, parents or siblings will have pathology that may help in the diagnosis of the pt’s problem
What 6 conditions have Genetic Predispositions?
Fam Hx of Disease and Visceral Pathology
True
6 Conditions
Autoimmune
Cardiovascular
Pulmonary
Endocrine
GI
Cancer
Red Flags:
Red Flags are clinical indicators of what?
Thus requiring further what?
Possible serious underlying pathology
Urgent medial intervention
Red Flag Category 1: Immediate Medical Attention
What are the 6 main S/S?
STOP AND REFER OUT
LOC (loss of consciousness)
AMS (altered mental status)
Shock
Severe non mechanical pain
Progressive neurological deficits (the faster the more dangerous they are)
Angina and heart related symptoms
Red Flag Category 2: Requires Questioning and Precautionary Exam/Tx
What are the 9 main S/S?
PROCEED W CAUTION
Trauma
Clonus
Gait Deficits
Hx of Cancer
Long Term Corticosteroid Use
Non-Healing Sores or Wounds
Recent Unexplained Weight Loss
Unremitting and Unchanging Pain
Nocturnal Pain
Red Flag Category 3: Requires Further Physical Testing and Differentiation
What are 7 main S/S?
PROCEED NORMALLY
Chronic or Persistent Pain
Reoccuring Pain
Abnormal Reflexes
Bilateral or Unilateral Radiculopathy or Parethesias
Unexplained Referred Pain
Unexplained Significant Weakness
No MOI
Yellow Flags:
Yellow Flags can relate to the pt’s what? (7)
It is often a reference to what?
Pt’s
Attitudes
Emotion
Beliefs
Behaviors
Family
Judgement
Workplace
Fear Avoidance Behavior
Blue Flags:
Blue Flags can be considered in terms of what?
Employees often has fears and misconceptions about what of their own previous experiences?
Employee and Workplace
Misconceptions about work and health