Chapter 5: How Cells Work
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
metabolic pathway
multistep sequence of chemical reactions
photosynethesis
process that creates energy in the form of glucose from its environment
cellular respiration
process that creates usable energy in the form of ATP from glucose
metabolism
all the chemical reactions involved in the capture, storage, and use of energy by living organisms
anabolism
energy-requiring synthesis reactions
catabolism
energy-releasing breakdown reactions
energy carriers
molecules that store energy and deliver it for cellular activities (like ATP, NADPH, FADH2)
light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions (calvin cycle)
photosynthesis stages
light, water, NADP+, ADP
light reaction inputs
oxygen, ATP, NADPH
light reaction outputs
light reaction
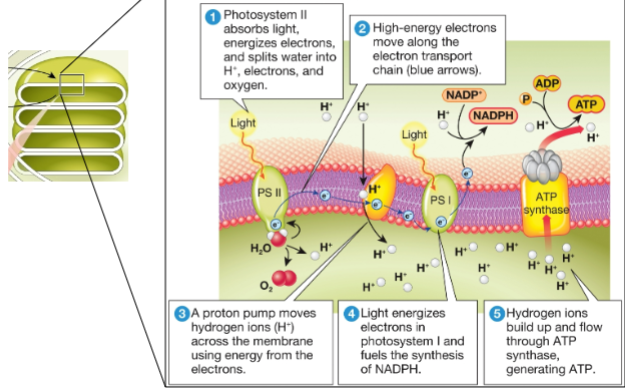
CO2, ATP, NADPH
calvin cycle inputs
Glucose, ADP, NADP+
calvin cycle outputs
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosporylation
cellular respiration stages
glucose, NAD+, ADP
glycolysis inputs
Pyruvate, NADH, ATP
glycolysis outputs
cytoplasm
glycolysis location
pyruvate, NAD+, FAD, ADP
Krebs inputs
CO2, NADH, FADH2, ATP
Krebs outputs
matrix
Krebs cycle location
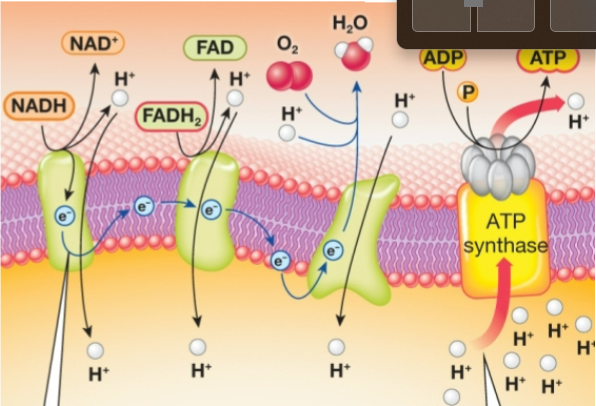
O2, NADH, FADH2, ADP
oxidative phosphorylation inputs
H2O, NAD+, FAD, ATP, heat
oxidative phosphorylation outputs
inner membrane
oxidative phosphorylation location
oxidative phosphorylation
fermentation
converts the products of glycolysis into alcohol or lactic acid to regenerate the NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue int he absence of oxygen
rubisco
enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle