n165 quiz 1
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
gyrus
a ridge of cerebral cortex
The Cafe Illusion
An example of the concept of a constructive brain where our visual system detects overall features of an image. Information of small parts of the visual scene is received and the brain interprets this slanting on a broader scale. The illusion demonstrates the effect of some simple image processing.
hippocampus
the most ancient part of the cerebral cortex and has at most three layers.
What allows us to distinguish between different neocortical architentonic fields?
relative variations in thickness or cell type
What is the surface covering of the brain?
Cortical sheet
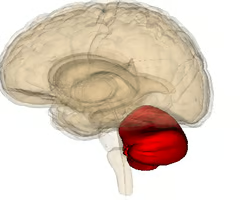
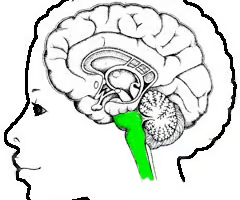
What structure is that? (Hint: involved in error-correction, balance and motor control
cerebellum the small, highly ridged portion of the brain that sits inferior to the cerebral cortex and posterior to the brain stem
Sulcus
a valley of cerebral cortex
Cortical Sheet
the outer surface covering of cerebral cortex, composed of gray matter (neuron cell bodies)
Cerebral Cortex
the large, folded part of the brain that sits above the cerebellum and brainstem, made up of gray and white matter
What do differences in frontal lobe sizes, olfactory bulb size, and amount of brain folding across species tell us?
may correspond to differences in behavior
anterior
towards the front
Posterior
towards the back
superior
towards the top
inferior
towards the bottom
What view is this?
lateral
What view would this be?
medial
dorsal (for brain)
towards the top
What view of the brain would this be?
ventral (for brain)
rostral (for brain)
towards the front
caudal (for brain)
towards the back
sagittal (mid-sagittal)
a vertical slice of the brain cut down the center from the anterior to the posterior giving a view from left or right
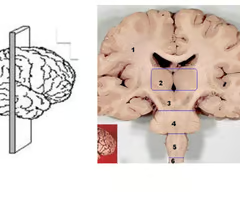
coronal (frontal)
plane gives superior to inferior giving a view from the front or back of the brain
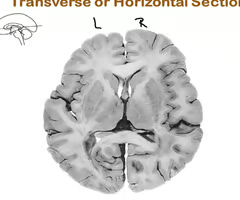
axial (transverse, horizontal)
plane forms a view from the top or bottom of the brain
Central Nervous System
this system is composed of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous system
composed of peripheral nerves that connect the CNS to the limbs, trunk, and internal organs
Autonomous nervous system
a subdivision of the PNS that controls visceral functions that includes para and sympathetic nervous systems. divided into sensory and motor subsystems
Parasympathetic ANS
this division of the ANS maintains rest
Sympathetic ANS
this division of the ANS prepares for action
cranial nerves
a set of 12 specialized nerves that act as the PNS (motor control and sensory info) to the head and neck
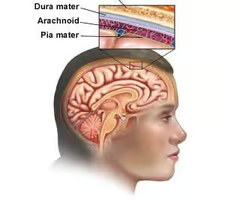
meninges
the three protective layers of tissue between the brain and the spinal cord that protects CNS the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
CNS
This system is within the meninges
PNS
This system is outside the meninges, we see regeneration here
dura mater
the durable, leathery outer protective layer of the meninges
The two divisions of the dura mater
periosteal and meningeal dura mater
Arachnoid mater
the spider web-like middle protective layer of the meninges that is filled with CSF
Pia mater
the thin, shiny, inner protective layer of the meninges that "shrink wraps" the brain
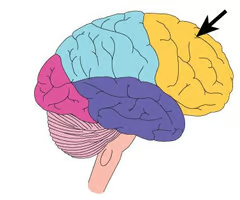
Frontal lobe
the anterior portion of the cerebral cortex, involved in emotion, cognition, and executive control
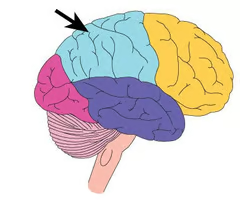
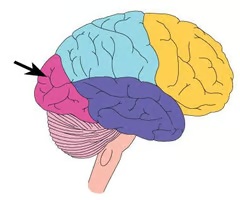
Parietal lobe
the superior posterior portion of the cerebral cortex superior to the occipital and temporal lobes, posterior to the frontal lobe
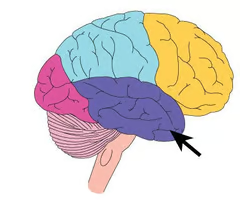
Temporal lobe
the inferior portion of the cerebral cortex, anterior to the occipital lobe and inferior to the others
Occipital lobe
the posterior portion of the cerebral cortex, primarily involved in vision processing
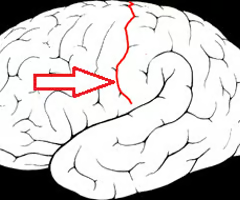
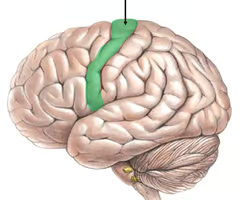
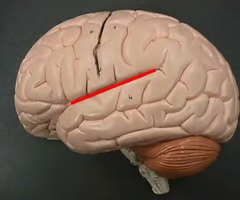
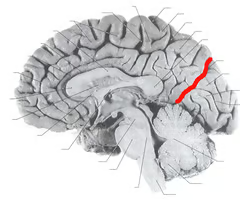
Central Sulcus
the sulcus dividing the frontal and parietal lobes, surrounded on each side by motor and sensory cortex
lateral fissure
the gap that divides the temporal from the frontal and parietal lobes
Parieto-occipital sulcus
the sulcus that divides the parietal and occipital lobes
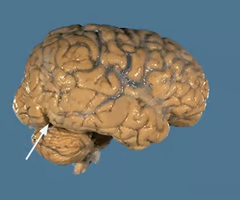
Pre-occipital notch
the notch that serves as the bottom point of the imaginary dividing line between the temporal and occipital lobes
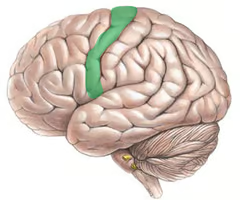
what cortex is highlighted here?
motor cortex
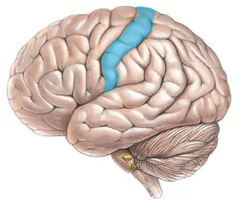
what cortex is highlighted here?
somatosensory cortex
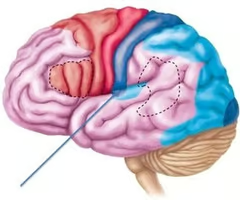
what cortex is highlighted here?
auditory cortex
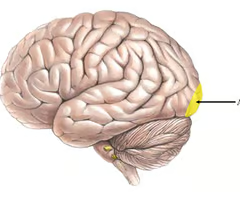
what cortex is highlighted here?
visual cortex
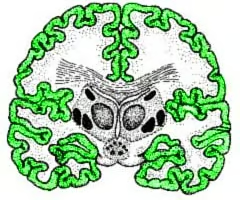
gray matter
outer 'bark' of the cerebral cortex composed of neuronal cell bodies; this is where computations happen; much of the cortex consists of six layers
White matter
inner region of cerebral cortex composed of the axons of the neurons with cell bodies in the gray matter
cell bodies of gray matter
there are 6 layers across most of the thorax where each layer is different with distinct neuron types, thickness, function and it varies throughout the cortex in a regular way
sparse coding
what we see in the brain where incoming inputs or info decrease the number of neurons firing
neuron
the basic cell in the brain that processes and transmits information in the form of electrical and chemical signals
dendrite
the branched portion of a neuron which receives inputs from synapses with other cells and sends small depolarizations towards the cell body
cell body
the "main" portion of a cell that contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles necessary for the cell to survive; contains the summation of inputs
axon hillock
the base of the axon, where it meets the cell body of the neuron; action potentials are initiated here
axon
the long cell structure that carries depolarizations away from the cell body of a neuron to the synapse
axon terminal
the very end of a branch of a neuron's axon, specialized to release neurotransmitters from vesicles into the synapse in response to an action potential for communication
glial cell
surround neurons in CNS and PNS and provide myelination as well as other support for them; most abundant cell types in CNS. types differ between CNS and PNS
myelin sheath
a layer of protective tissue wrapped around axons of neurons to hasten the transmission of action potentials
neuronal communication
includes electrical conduction along the axon and chemical transmission via neurotransmitter release at the synapse
classification of neuronal cell types
cells that undergo histochemical staining techniques and that are classified based on their size, shape, and function; main cell found in white matter
action potential
an all-or-none phenomenon, it is a wave of electricity that travels down the axon of a neuron transmitting information via spike rate
intracellular fluid
the fluid inside the cell membrane
extracellular fluid
the fluid outside the membrane
electrical potential
the difference in voltage between the intra- and extracellular fluid; this difference is created by the passive and active movement of charged ions across the cell membrane i.e. K+, Na+, Ca2+; potential is carried by these ions.
Information is transmitted between neurons by _, not strength.
rate
At rest, the potential hovers around _.
-70 mV
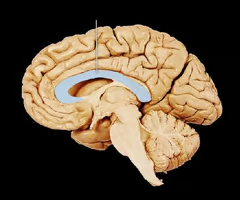
corpus callosum
the main connection of white matter that is integral for communication between the two cerebral hemispheres
Cerebral Spinal fluid
the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord that cushions the nervous system; fluid is similar to blood plasma; occupies subarachnoid space.
ventricle
CSF filled cavities in the brain in which CSF flows through, there are four total structures of these
choroid plexus
the specialized cells lining the ventricles responsible for the creation of CSF
Lumbar Puncture
an invasive method to withdraw CSF for testing from a low part of the spinal column just below the spinal cord
Arachnoid Granulations
the bubblelike portions of the arachnoid mater into the draining venous sinus system that are responsible for the removal of CSF from around the brain into the blood system. these act as one way valves where normally the pressure of the CSF is higher than the venous system
Hydrocephalus
[water on the brain] disorder of CSF causing problems with CSF flow or reuptake; leads to head enlargement, developmental or acquired; primarily treated with a shunt to siphon CSF away from the brain into the abdomen. This can be congenital or acquired
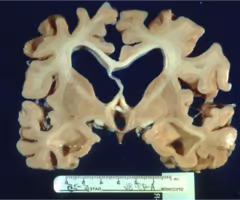
hydrocephalus ex vacuo
large spaces develop inside cortex due to loss of cortical tissue - 'cortical atrophy' seen in dementia; NOT really hydrocephalus, atrophy is incited.
non-communicating hydocephalus
caused by something obstructing the normal flow of CSF leading to an increase in pressure. blockages can be from things like a tumor/mass or clot of blood/infection. whole pressure system does not communicate therefore CSF production continues where the flow past the block is normal
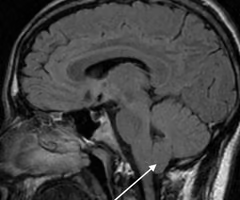
Chiari malformation
this is an anatomical/congenital condition in which the brain tissue extends into spinal cord and occurs when there is an abnormality pressing on the brain and forcing it downward; CSF is blocked; discontinuous hydrocephaly.
Communicating hydrocephalus
hydrocephalus caused by a problem with the normal uptake/reabsorption of CSF through the arachnoid granulations; whole CSF system would have increased in pressure
shunt (ventriculoperitoneal shunt)
in brain disorders, a shunt is a tube placed under the skin (decreasing risk of infection) drainage to abdominal cavity allows for fluid to be safely reabsorbed by the body, as seen in hydrocephalus and strokes
circle of willis
a circle of arteries that supply blood to the brain. this arrangement of blood vessels allows for the collateral blood flow to the brain
Arteries of Circle of Willis
internal carotid artery, middle cerebral artery, and basliar artery.
carotid artery
a blood vessel that supplies the head and neck with oxygenated blood on each side. supplies blood to the lateral and frontal part of the brain. artery divides the neck into the internal circle of willis and external neck artery
Vertebral artery
a blood vessel that runs up the back of the neck, one on each side, that join at the base of the skull to form the basilar artery. these vessels supply the posterior part of the brain and goes through many twists and turns. can cause turbulent blood flow and thus increase risk of thrombus development.
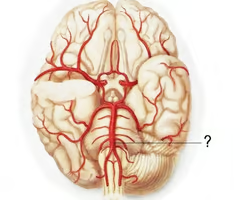
basilar artery
the artery that supplies the pons, cerebellum, posterior cerebrum, and inner ear. this vessel is formed by the merging of the vertebral arteries
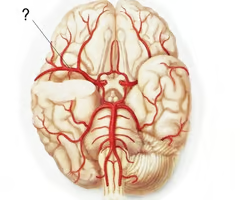
middle cerebral artery
the artery that supply oxygen to most medial portions of frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes; strokes here can affect leg use and cause large amounts of brain swelling as part of the inflammatory response
stroke
rapid loss of brain tissue and function as a result of disruption/lack of the blood supply to the brain
transient ischemic attack (TIA)
'mini stroke' same wide-range of possible symptoms as a stroke, but symptoms are only temporary, lack of O2 in the brain
ischemia
lack of oxygen arising from restriction in blood supply
ischemic stroke
a stroke resulting from restriction of blood flow and lack of oxygen into a region of brain tissue
thrombus
a clot or atherosclerotic plaque that forms in place within a blood vessel obstructing blood flow. this can close off blood flow at the place it forms or may break apart to form an embolus
embolus
a moving clot that then lodges in a small vessel
carotid stenosis
abnormal narrowing of the carotid artery often caused by atherosclerotic plaque formation; common site of obstruction
Primary symptom from this specific stroke would be leg weakness for example, so what artery did this stroke manifest?
Anterior cerebral artery (ACA) stroke
Anterior cerebral artery
is one of a pair of arteries on the brain that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes.
Hemorrhage
bleeding, the loss of blood from the circulatory system
Hemorrhagic stroke
a stroke resulting from blood bleeding into the brain, damaging tissue
aneurysm
a localized blood filled bulge of a blood vessel, this event can occur at weak spots of the circle of willis, the branching points.
subarachnoid hemorrhage
bleeding that occurs between the arachnoid and the pial meningeal layers. the subarachnoid space is the space where the CSF flows around the brain and spinal cord, the space that is also filled with spider-web-like protrusions of the arachnoid mater
intracerebral hemorrhage
bleeding that occurs within the brain tissue itself; this would be below the pia mater