EVSC module 7 Biosphere Integrity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
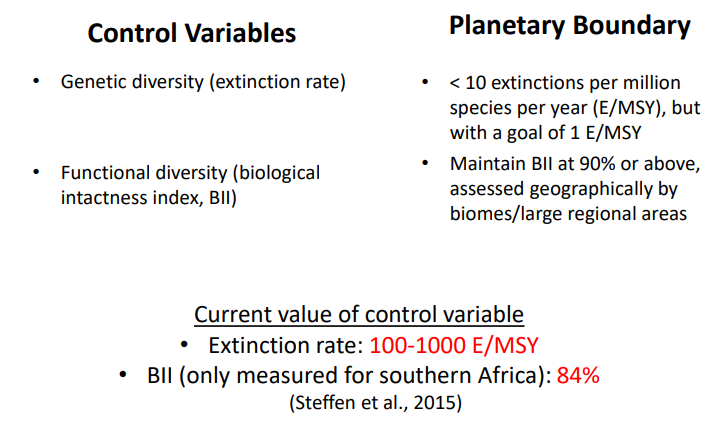
Has the Planetary Boundary been crossed?
What is An Ecosystem?
An integrated system defined by its biotic community of organisms, abiotic environmental conditions, and their dynamic interactions all functioning as a unit. We often put arbitrary spatial boundaries on ecosystems – but they are nested within each other!
Ecosystem Functions may include:
The flow of energy and nutrients (productivity, decomposition, cycling) Species interactions How species use resources & interact with habitat
How does the biosphere function?
Through two fundamental processes: • Energy flow • Nutrient/ Biogeochemical cycling
ENERGY RELATIONSHIPS WITHIN ECOSYSTEMS
–Autotrophs are capable of photosynthesis, and so can ‘feed themselves’
–Heterotrophs must feed on biomass produced by other organisms
Habitat
the physical environment where a species typically lives.
Niche
the role a species plays in its ecosystem; not only its habitat requirements, but also how it acquires energy and nutrients, and how it interacts with other species, and non-biotic parts of its ecosystem.
Keystone species
a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment compared to its relative abundance.
When a keystone species is removed, the ecosystem may change drastically, even if the species removed was a “small” part of the entire ecosystem
Trophic Cascade
Occurs when the impact of a predator on its prey affects one or more trophic level.
• When the apex predator is removed, the lack of population control at the next trophic level down can affect the populations at the trophic level below.
• Trophic cascades must occur across a minimum of three trophic levels (e.g. secondary consumer, primary consumer, and producer).
• Trophic cascades can also happen from the bottom up; for example, the removal of a producer may affect population sizes in the trophic levels above it
The best way for an ecosystem to be resilient?
Biodiversity:
• The degree of variation of life.
• Affects ecosystem function and ecosystem services.
biodiversity loss
The loss of even one species can disrupt an entire ecosystem, from specific organism populations, to the movement of matter and energy (ecosystem functions).
• Every piece of an ecosystem is interdependent.
• More biodiverse ecosystems are usually more resilient to other pressures on the Earth system.
TROPHIC LEVELS
