B2 - Customer-focused business, market segmentation and targeting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a business philosophy?
Business philosophy is a guiding principle for managers on how they should operate their business.
Exists of:
Marketing concept
Production concept
Technology/Product conept
Selling concept
A focal firm is…
A unit in a supply chain that…
Has its own set of competitors
Competes based on a brand (or several brands that logically go together)
Has a leader responsible for strategic planning (and profitability)
Has its own vision or culture (though possibly influenced by higher corporate levels)
Example Nestle
Claim: “as a company, we continuously evolve our product offerings to meet consumer needs and excite consumer preferences.”
This claim can be reached by doing market research to best adres the wants and needs of consumers.
This leads to product development, marketing & food science & technology research. To be able to offer innovative products consumers asked for.
Customer-focused food businesses premises
A customer-focused food business is managed from the marketing concept
The marketing concept is a guideline for management
The marketing concept can be distinguished from the production, product and selling concepts.
Production vs Marketing concepts
Example for Marvel:
Production concept: We make movies
Marketing concept: We entertain people
Example Shell:
Production concept: We provide fuel
Marketing concept: We supply you with energy
Marketing concept
Based on fulfilling “what customers want” or, more precisely, on “what customers value”
Valuing means that the products of a company are worth something for the customer.
Profit is made by satisfying customers.
Production concept
These companies are more orientated towards their internal environment, trying to make their processes ever more efficient, producing offerings at a consistent quality level.
Their risk however is that consumers preferences change and that the company recognizes this too late.
Steps of the selling concept
Main purpose: sell as much as possible and focus lies in the short term. Profit through sales volume.
Emphasis is on making a deal in the short term rather than keeping customers satisfied in the long term.
High switching costs. (for e.g. wifi)

The marketing concept steps.
High competition
Consumers can easily switch products.

Technology/product concept
These companies place a particular emphasis on technology. Believing that if they are the first to come up with a new technology, they will conquer new markets.
Often operate in specialized markets like food for sports, baby food, health food, etc.
Focus is on the long term.
Downside: They may create technology without a demand for it.
Segmentation-Targeting-Positioning (STP) (Segmentation)
Segmentation: A group of customers with relatively similar wants and needs and value of perceptions
About increasing the variance between segments and decreasing the variance within segments
Segmentation-Targeting-Positioning (STP) (Targeting)
Selecting market segments to create value that are attractive for both the customer and the company
To avoid competition: Define customer groups that competitors don’t (yet) recognize
Segmentation-Targeting-Positioning (STP) (Positioning)
Communicating and delivering value to the customer that is unique
Distinguish the product/brand from competitors.
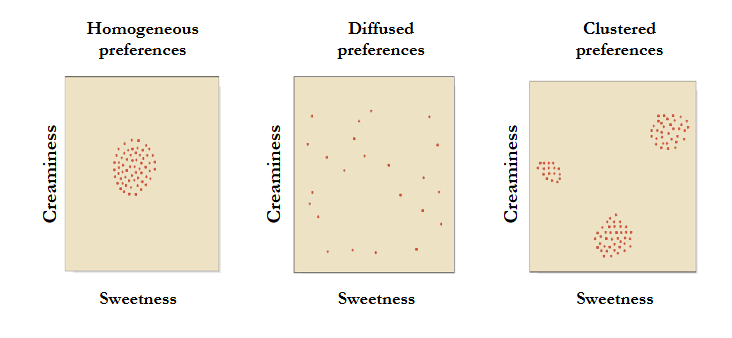
Different types of preferences (e.g. ice cream)
Steps in Segmentation Process
Criteria
Choice and application of segmentation criteria
Assessment
Analysis of the identified segments
Evaluation
Segments on attractiveness
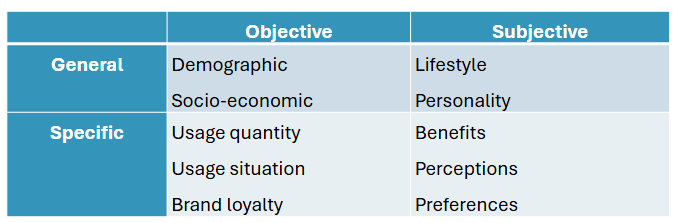
Segmentation criteria split in objective and subjective and general and specific
Demographic segmentation example
Demographic: e.g. age, gender, race, religion
Socio-economic: e.g. income, occupation, education
Brand loyalty segmentation example
Classic loyalty thinking
Potential customer → loyalty strategy: draw them in
Reversing the approach
Giver customer loyalty privileges → customers turn into very interesting customers
Targeting strategies
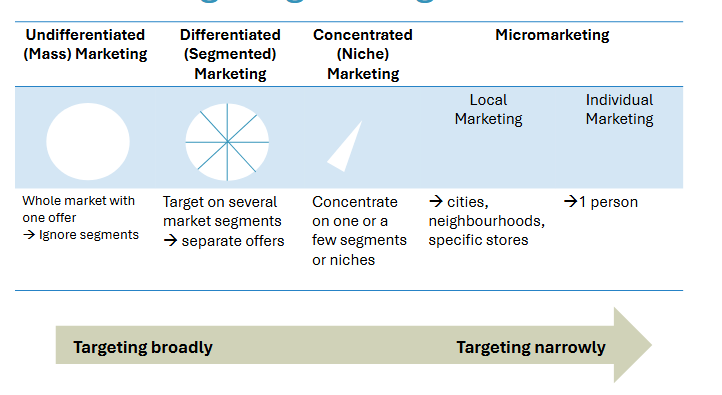
Undifferentiated mass marketing
Undifferentiated mass marketing
Whole market with one offer
no segments
For example gasoline
Differentiated (segmented) marketing
Target on several market segments
Separate offers
e.g. Aldi → aims for low cost customers
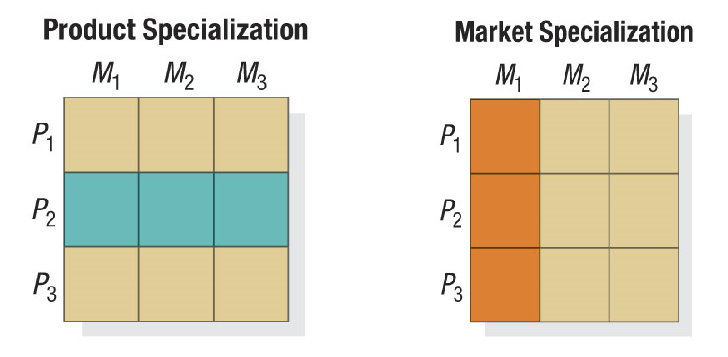
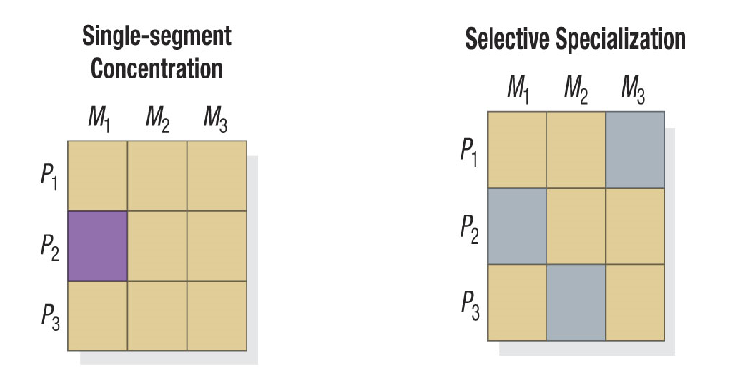
Concentrated (Niche) Marketing
Concentrate on one or a few segments or niches
e.g. Nintendo → aims for gamers.
Selective specialization: One companies with different specialities.
Micromarketing
Exists of local marketing and individual marketing
Local: Cities, neighbourhoods, specific stores
Individual: Buying a house, a realtor will find houses within your budget for example.
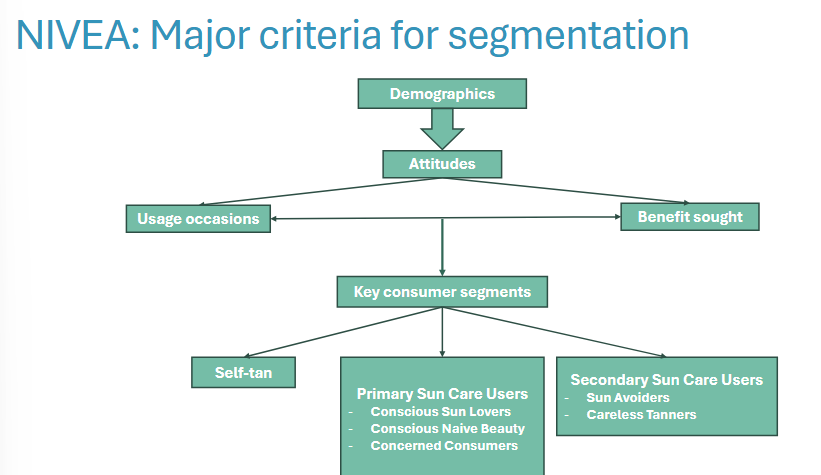
Nivea as an example of market targeting
They have different demographics. One being suncare
Split into amount of usage. Just sunblock or more
Different key consumer segments:
Self-tan
Primary sun care users
Secondary sun care users.
How to segment a market well, segments should be…
Identifiable
measurable
Sufficiently large
Approachable
Homogenous
Stable over time