3.5 alevel biology flashcards
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is ecology ?
The study of how living organisms interact with their surroundings and eachother
What are abiotic factors?
Physical factors such as light intensity , soil , ph and temperature
what are biotic factors ?
biological factors such as pathogens and bacteria
What is an ecosystem ?
Made up of the community , biotic component , habitat and abiotic component
What is a community ?
It is made up of the different populations of species in a habitat
What is a population ?
Interbreeding group of organisms of the same species occupying a particular habitat
What is a habitat ?
the place where an organism lives
What determines the size of the population ?
Birth rate
Death rate
Immigration
Emigration
Factors affecting population growth
biotic potential
Environmental resistance
Carrying capacity
What is biotic potential ?
the maximum rate at which it can reproduce when given all the resources it needs
What is environmental resistance ?
all factors that could limit the growth of a population
What is carrying capacity ?
The maximum number around which a population fluctuates in a given environment
Population growth curve
for equilibrium species
Sigmoid shape
Has 4 phases
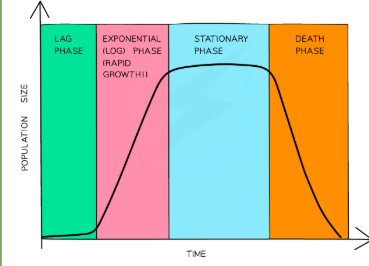
Phases of population growth curve
Lag phase
Log phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
What is the lag phase ?
preparation and adaptation for growth
Intense metabolic activity
little or no increase in population
What is the log phase ?
population growth increases rapidly
Rapid rate isn’t maintained as long as the effcets of environmental resistance kick in
What is stationary phase ?
Birth rate = death rate
Population number fluctuates around carrying capacity
What is death phase ?
-factors limiting growth becoming significant -death rate exceeds birth rate
What are environmental factors ?
all factors that could limit the growth of a population
What are the types of environmental factors ?
Density dependent
Density independent
What are density dependent factors ?
factors tha vary in effect based on population size
always biotic
What are density independent factors ?
affect all plants and animals regradless of population size
Tend to be abiotic
What is a niche ?
The role an organism plays in its environment
What is succession ?
Transition between one stage and the next
What is primary succession ?
starting from bare rock , sand or water
Takes place in stages - called “sere”
First stage of primary succession
pioneer species
first species to colonise an area
Able to withstand desiccation, extreme temperatures, and low nutrient levels
Second stage of primary succession
Pioneer species penetrate and break up the rock. Freeze-thaw erosion occurs here
Pioneer species die and decompose, and humus builds up
Simple plants, such as ferns and mosses, can now grow
Third stage in primary succession
Mosses and ferns cast a shadow to prevent lichens from further growth
roots are longer and further break up the rock
Organic material increases as these palnts die.More water is retained by this so grasses , small flowering plants and shrubs can now grow.
Fourth stage of primary succession
Growth of larger plants and animals would make further changes in soil and light conditions
The shading effect by plants causes soem smaller plants to die
last stage of Primary succession
Climax community
when the area is colonised by a dominant species
What is secondary succession ?
Occurs when a current seral stage is removed abruptly
What happens in secondary succession ?
Succession occurs quickly, as there is soil and probably seeds present
What is delfected succession/disclimax ?
when a climax community is not reached
This can be due to human activity of limiting factors in teh surrounding environment
Types of organisms involved in the decay of dead organisms
detritivores
Saprophytes
What are detritivores ?
animals with a tube gut that feed on dead organic materials
They help to speed up decomposition by increasing the surface area of the dead organic material for the action of saprophytes
What are saprophytes ?
Fungi and bacteria that carry out extracellular digestion of the organic material to obtain nutrients
Decompose dead material
Three key processes in carbon cycle
Photosynthesis
Respiration
Combustion
How does photosynthesis impact carbon cycle ?
Photoautotrophs remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and “fix” it into organic molecules
How does respiration impact carbon cycle ?
Returns carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
How does combustion impact carbon cycle ?
plant material and fossil fuels releasse carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
Global impacts of carbon cycle impacted by human actions
Melting polar ice caps and rising sea levels
Increased frequency of extreme weather
Increased desertification and soil erosion
Increased extinction rate
Changes in the distribution of disease vectors, such as mosquitos
How does farming have a high carbon footprint ?
The production of farm tools
The production of insecticides, fungicides, and fertilisers
Farm machinery, powered by fossil fuel
Transport of the produce
Key processes of Nitrogen cycle
Putrefaction
Nitrification
Nitrogen fixation
Denitrification
What is putrefaction done by ?
Decomposers
organisms that feed on dead organic matter and faeces saprophytically
Process of Putrefication
Proteins and nitrogen containing compounds are broken down into smaller soluble compounds
These are absorbed by organisms
Any excess nitrogenous compounds are converted into ammonium and excreted by the micro-organism
nitrogenous compounds are converted into ammonium in the soil
What is nitrification ?
The process by which ammonium is oxidised into nitrite and then nitrate by bacteria
What happens in nitrification ?
The nitrogenous compounds ammonium and nitrite are being used as a source of energy by bacteria
These are nitrifying bacteria
What is nitrobactor ?
converts nitrite to nitrate
What is nitrosomonas ?
Converts ammonium into nitrite
What is nitrogen fixation ?
The conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonium which is carried out by nitrogen fixing bacteria .
Types of bacteria involved in nitrogen fixation
Azotobacter
Rhizobium
What is Azotobacter ?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria that is free living in the soil
What is Rhizobium ?
Nitrogen fixation occurs in the roots of legumes
Live in a mutually beneficial relationship
How does Rhizobium function ?
bacteria invade in the roots of plants and the plant repsonds by forming a nodule where the bacteria can live
NItrogen gas diffuses into the nodule from the soil
The nitrogen gas is then utilised by bacteria to make ammonium and amino acids
Excess ammonium and amino acids are exported to the plant for protein synthesis
Rhizobium gains sugars for respiration from the plant
Conditions of nitrogen fixation
anaerobic environement
Plant produces leghaemoglobin
This takes up oxygen in the nodule and removes it from bacterial environment
Farming activities that aim to improve soil fertility
Adding chemical fertilisers (ammonium nitrate)
Adding manure (animal waste)
Adding treated sewage (human waste)
Planting legumes such as clover
Ploughing or draining to improve aeration
Human activity causing nitrogen pollution
Excess nitrates on grassland leads to increased growth of weeds, such as nettles, this
decreases biodiversity due to competition for resources
Draining wetlands destroys unique habitats
Nitrate pollution (excess fertilisers, manure, etc) in waterways causes eutrophication
– ultimately causing a decrease in dissolved oxygen and a decrease in biodiversity
What is denitrification ?
Pseudomonas
Use nitrate to provide oxygen for respiration
The nitrogen atoms remaining are converted to nitrogen gas
Conditions of denitrification
anaerobic
Usually due to water logging - air spaces in soil filled with water
Water logged soils - defecient in nitrates and soil fertility decreases
How do farmers try to avoid water logging ?
Ploughing
Mixes soil with air
Oxygen from the air inhibits the denitrifying bacteria (Pseudomonas)
Encourages the growth of Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter, and Rhizobium Nitrosomonas
What plant lives in water logged conditions ?
Carnivorous plants
gain carbohydrates from photosynthesis
Gain nitrogenous compounds from digestion of invertebrates