Biological Molecules
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Give examples of some polymers:
DNA, RNA, proteins, Starch, glycogen, Cellulose
What is a condensation reaction?
The joining of two molecules by forming a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a water molecule.
What is a Hydrolysis reaction?
Breaking a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule.
What are the functions of Lipids?
Can be used as respiratory substrates which provide energy for cells, form a bilayer in cell membranes and make up some hormones.
Glucose is a hexose sugar which can form two isomers: what is an isomer?
Two or more compounds with the same molecular formula but a different structure and different properties.
Give examples of monomers:
Monosaccharides eg glucose, fructose and galactose, amino acids and nucleotides.
What is the function of Carbohydrates?
Respiratory substrates which provide energy for the cells, also used for structure in cell membranes and cell walls in plants .
What is the function of proteins?
Main component of many cellular structures, form enzymes and chemical messengers.
What is the function of Nucleic Acids?
Form polymers (DNA and RNA) which make up the genetic material of organisms. Code for the sequence of amino acids which make up all proteins.
What evidence supports the theory that all animals and plants share a common ancestor?
All organisms use the same nucleic acids as genetic material, use the same 20 amino acids to build up proteins and use lipids and carbohydrates as energy stores and to make up their cell membranes and cell walls.
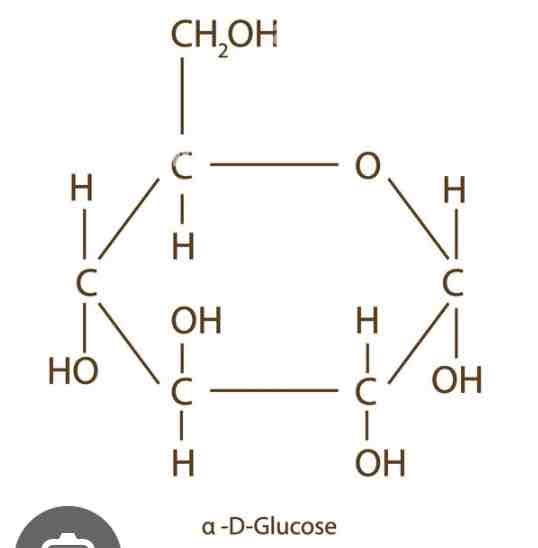
What does alpha glucose look like?
See image:
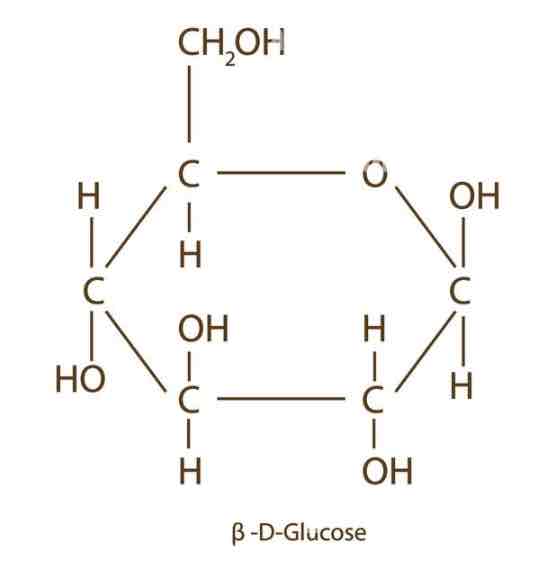
What does Beta glucose look like?
See image:
Why is glucose extremely soluble in water?
Glucose contains large amounts of hydroxyl groups. Hydroxyl groups are polar as they have a small negative charge on the oxygen atom and a small positive charge on the hydrogen atom. This means that hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. (Hydrophilic).
What is the function of starch?
Plants store excess glucose as starch in the leaves. Starch is too large to leave cells and insoluble (doesn’t dissolve in water- doesn’t affect water potential). Starch can be hydrolysed to release glucose for respiration.
How do you test for a non reducing sugar?
Add dilute hydrochloric acid to the sample and heat using a water bath.
Then add an alkaline solution to neutralise.
Heat with Benedicts solution and if there is a non reducing sugar present, there will be a red precipitate.
Use of a colorimeter would improve the repeatability of the results. Why?
It gives quantitative data which standardises the method.
Two differences between glycogen and cellulose.
Cellulose is a straight chain whereas glycogen is highly branched.
Cellulose is made up of beta glucose whereas glycogen is made up of alpha glucose.
Features of Starch that make it a good storage molecule:
Starch is insoluble in water so doesn’t affect water potential.
Starch is a coiled alpha helix to make it more compact so it can store many molecules in a smaller area.
Branched to create lots of terminal ends for rapid hydrolysis and enzyme action.
It is a large molecule so cannot leave the cell.
Suggest how glycogen acts as a source of energy
Glycogen is hydrolysed to glucose. Glucose is used in respiration.
What is the difference between alpha glucose and beta glucose?
The position of the hydrogen groups and hydroxyl groups on carbon 1 are inverted.