Unit 3 Environmental Science test
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Which of the following are the two most significant abiotic factors in determining biomes?
temperature and precipitation
What is the effect of increasing latitude on temperature and primary productivity?
both decrease
What is the name for a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar communities?
Biome
A combination line/bar graph that show trends in temperature and precipitation over a typical year in a biome is known as
Climatograph
A tropical grassland is also known as a
savanna
A polar forest is also known as
boreal
What is the key difference between primary and secondary succession?
primary succession occurs where no life existed before; secondary succession follows a disturbance
Which of the following would most likely be considered a pioneer species in primary succession?
lichens and mosses
Why does secondary succession typically proceed faster than primary succession?
because the soil remains intact, allowing for quicker plant regrowth
Which of the following is not a freshwater inland ecosystem
estuary and deltas
bog, swamp, and marsh are all freshwater inland ecosystems
In ocean ecosystems, the region where the depth of the water increases quickly is known as
continental slope
What is the name given to tides that occur when the sun's gravitation field and the moon's gravitational field are in alignment?
spring tides
What is the order of things in the biosphere from most specific to braodest
organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, and biosphere
What is precipitation and temperature influenced by?
Latitude, altitude, and wind
What is latitude?
the distance from the equator, measured in degrees north or south
As latitude increases what tends to decrease due to the changing sun angle?
temperature and primary productivity
What is primary productivity?
the amount of energy produced by plants
What is altitude?
it is the elevation above sea level
As altitude increases what tends to decrease?
average temps and primary productivity
What are prevailing winds?
regions where the wind tends to blow from a certain direction
What are trade winds?
from the tropics southwest or northwest towards the equator
What are westerlies
come from the subtropics west towards the midaltitudes
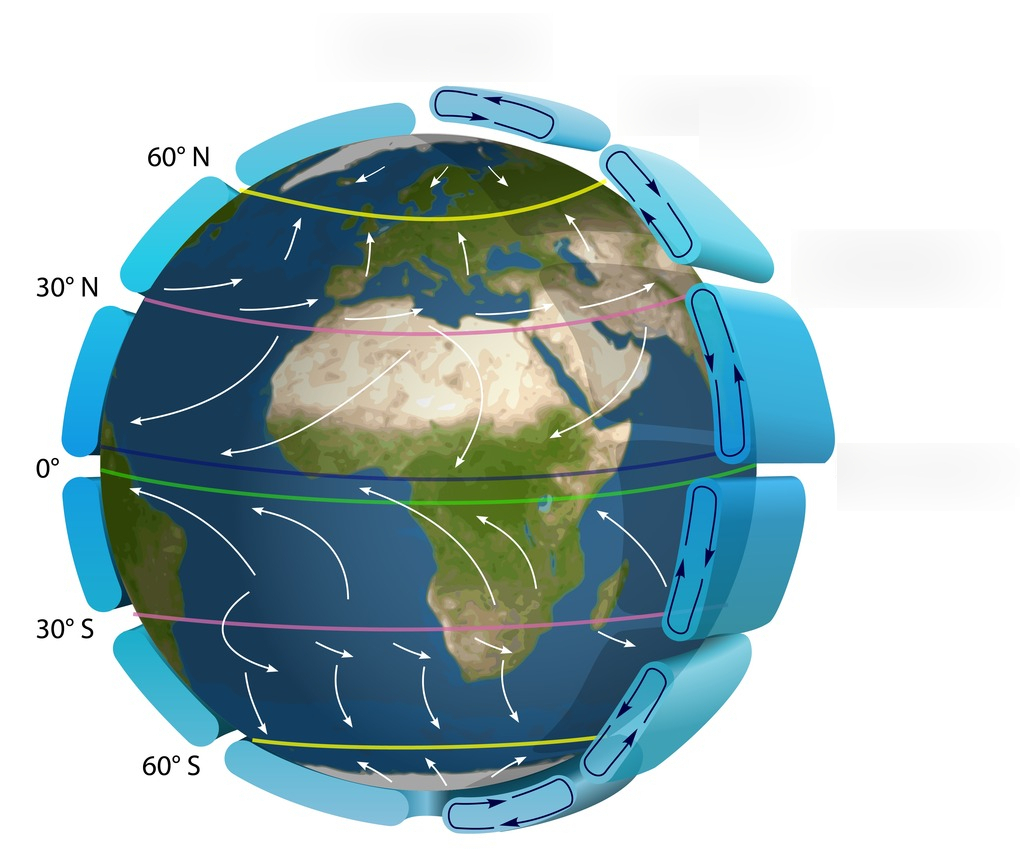
Label where the polar easterlies, prevailing westerlies, and trade winds are on this map - on the right side going from top to middle then they start over again.
polar esterlies
prevailing westerlies
trade winds
trade winds
prevailing westerlies
polar easterlies
What is the rainshadow effect?
it is a decrease in precipitation on the side of a mountain facing away from prevailing winds - on the leeward slope
all the clouds gather at top of mountain and rains on top of mnt then nothing left of the other side
What is the windward and leeward slope?
Windward slope of a mountain faces winds and ocean, receives more precipitation
Leeward slope is on the none ocean side of the mountain that has reduced precipitation due to the rainshadow effect.
A biome is defined as
a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar communities
How many biomes are there in the world?
8
What are the 8 biomes?
Tropical rainforest
savanna
desert
chaparral
temperate grassland
temperate forest
taiga (boreal forest)
arctic tundra
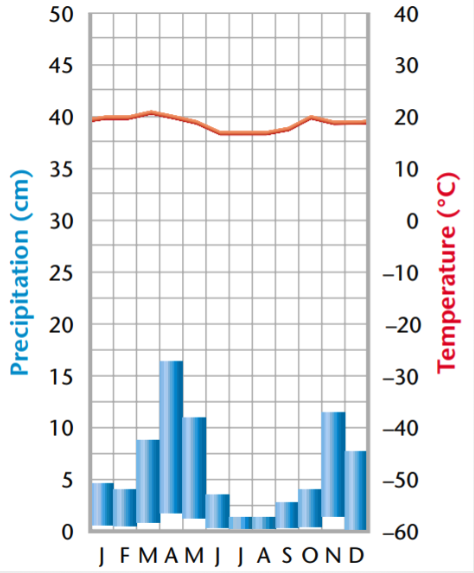
Define Arctic Tundra
a cold, treeless biome with permafrost and short growing seasonsD
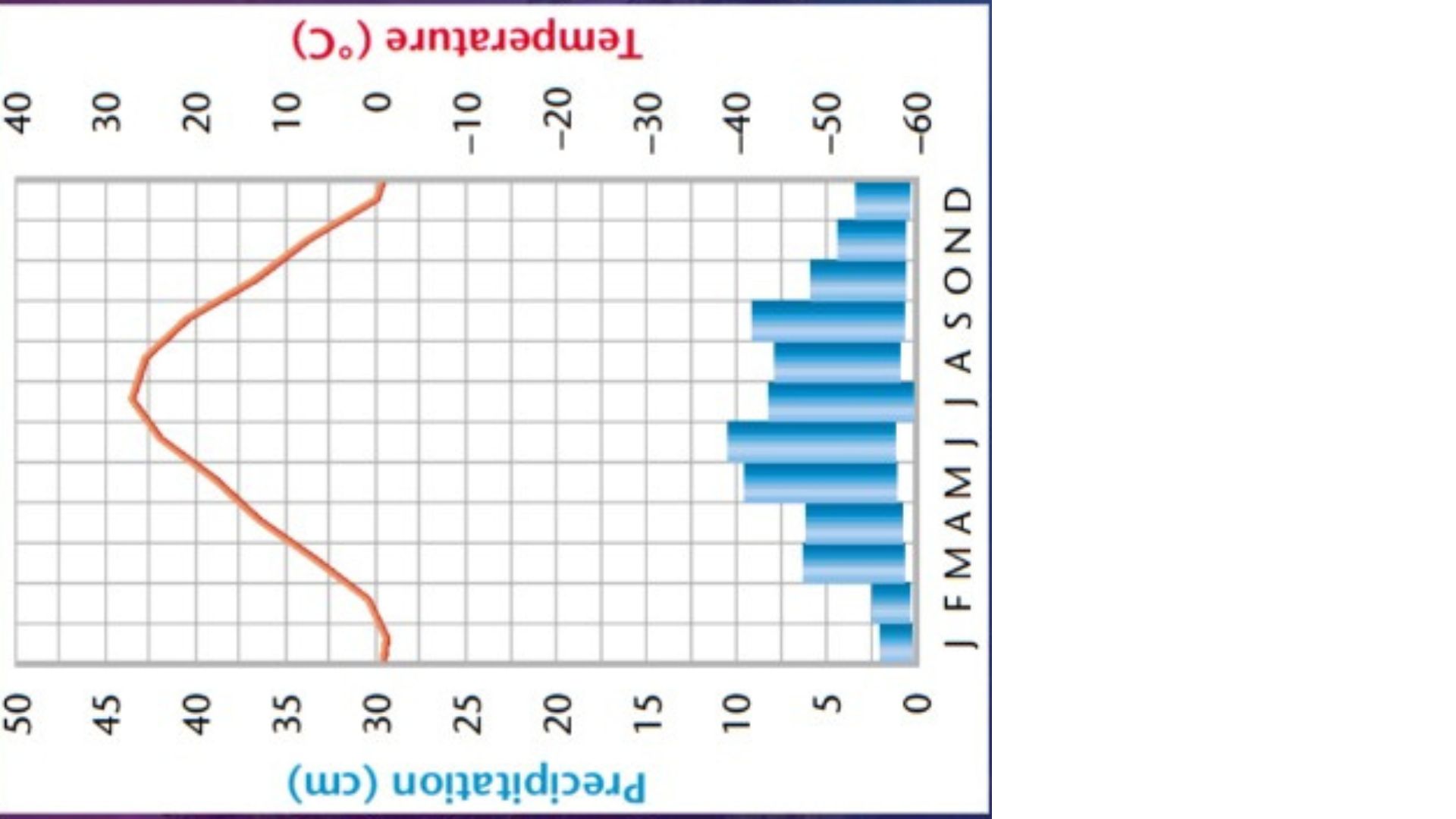
Define Taiga/Boreal forest
a coniferous only forest biome with long, cold winters and short, cool summers
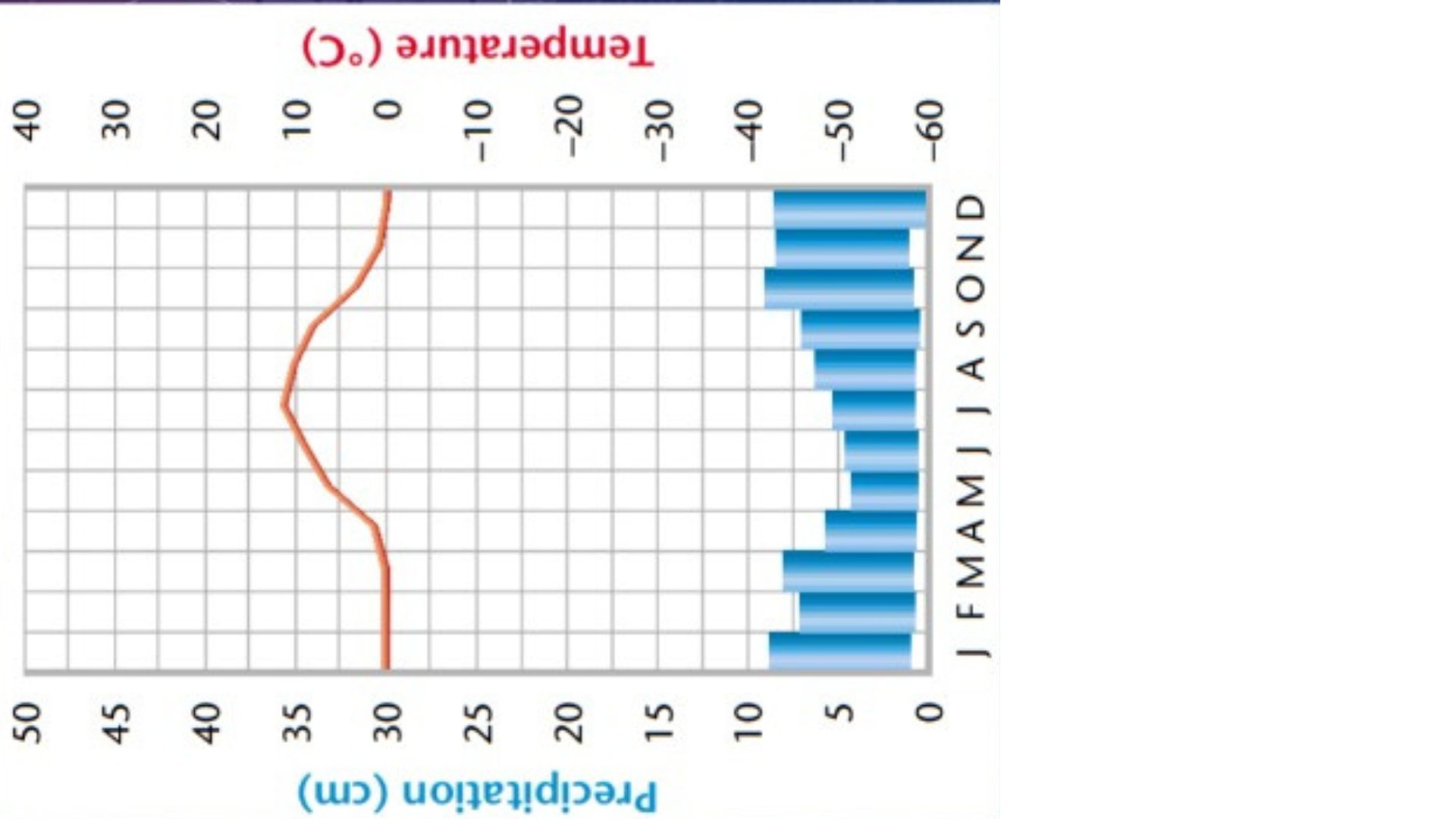
Define temperate forest
a forest biome with deciduous trees, moderate rainfall, and distinct seasons
Define temperate grassland
a grassland biome with moderate rainfall, warm summers, and cold winters
Define Chaparral
a shrubland biome with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, often found near Mediterranean climates
Bible lands right?
Define Desert
a dry biome with little precipitation, supporting specialized plant and animal life
Define Savanna
a grassland biome with scattered trees and shrubs, found in regions with seasonal rainfall
Define tropical rainforest
characterized by high rainfall, warm temperatures, and dense, diverse vegetation.
The above is an example of what kind of grassland?
Savanna
the above is an example of what kind of grassland?
prairie
the above is an example of what kind of grassland?
Tundra
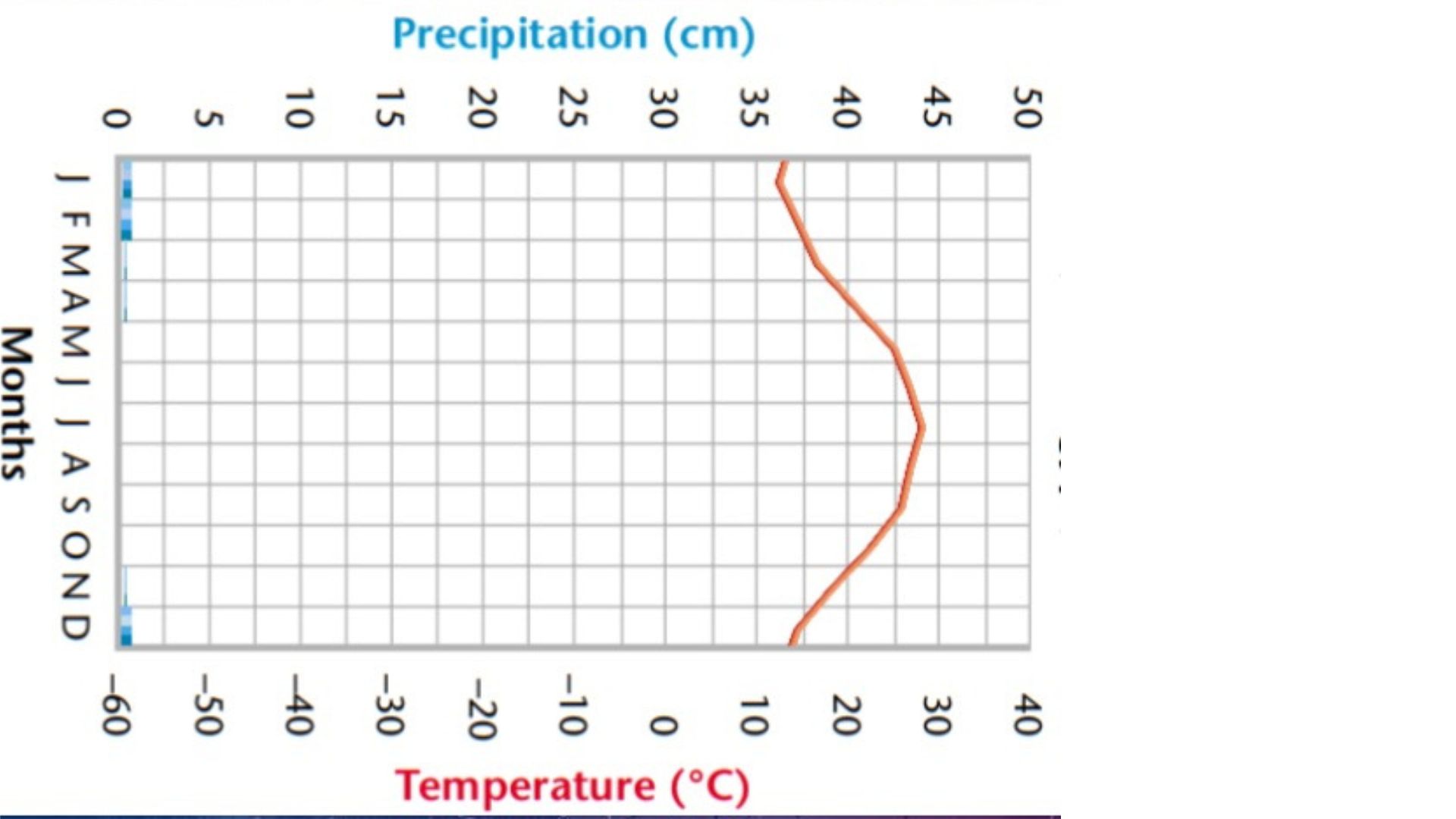
the above is an example of what kind of biome?
Desert
The upper-most layer of a forest is known as the
what are the next layers in order
emergent layer
canopy
understory
Which tends to arrive first in the process of primary succession>
annuals
Which of the following is not an abiotic factor that differentiates aquatic ecosystems?
latitude - geographical not latitude
Which section of a river has high dissolved oxygen and low nutrients?
headwaters
What type of freshwater wetlands is characterized by floating mats of plant matter?
Bogs
What are the three types of freshwater wetlands? and desribe each
Marsh - low lying treeless areas
Bogs - have floating mats of plant matter that living plants grown on
Swamps - low lying wetlands dominated by trees
The part of the ocean characterized by little sunlight, hydrothermal vents, and benthic creatures?
abyssal plain
True or false
The aphotoic zone has sunlight
False
True or false
90% of ocean biodiversity is found in the open ocean
false
What type of ecological succession begins on bare rock after a volcanic eruption?
Primary succession
Which biome is known for permanently frozen soil called permafrost?
tundra
What is the main reason deserts are often found around 30 degree latitude
sinking dry air creates dry climates
in a freshwater lake, which zone is closest to the shore and supports rooted plants?
Littoral zone
What type of tree is most common in Boreal forests (Taiga)
coniferous trees
Which of the following best describes an estuary
a place where freshwater mixes with saltwater
What type of lake has low nutrients levels, clear water, and limited algae growth
oligotrophic lake
Difference between abiotic and biotic factors
abiotic is non-living
biotic is living
Define the subtropical deserts
forms between the tropics and equator
results of sinking air around 30 degrees n/s moving back equaotrward
Define a rainshadow desert
moisture is squeezed out on the windward side of a mountain leaving little moisture for precipitation on the leeward side
Define temperate deserts
seasonal temperature variations - has some green in it
Define polar deserts
consistently cold and dry
What are the adaptations needed for organisms living in the desert
ability to store water
reduced growth rate and or herd size
spikes and camouflage for defense
dormancy
deep taproots
Define what grasslands are
Moderate or seasonal precipitation
warm or seasonal temperatures
moderate net primary productivity.
Fire is important here
Rainfall is 10-30 inches per year
What are the four types of deserts
subtropical
Rainshadow
temperate
polarW
What are the three types of grasslands?
Tundra/polar
prairies/temperate
savannas/tropical
Define Savannas (tropical grasslands)
located near the equator between tropical forests and subtropical deserts.
Temp - consistent
Precip - seasonal
Define Prairies (temperate grasslands
found in midaltitiudes
temp - seasonal
precip - moderate
Defin tundras
have short growing seasons and permanently frozen soil called permafrost.
temp - consistently cold
precip - moderate
What are the adaptations needed for plants living in the grasslands
Prairie plants have deep/complex root structures that allow them to recover from drought, wild fire, cold winters, and grazing animals
Tundra plants are low-lying due to permafrost and mature rapidly in the short growing season
Define what a forest biome consists of
moderate to high precipitation that support tree growth
warm or seasonal temps
high net primary productivity across many layers
What are the four types of forests?
tropical rainforests
temperate forest/deciduous
Boreal forest/taiga
Mediterranean forests
What type of trees are in the topical rainforest
broadleaf trees only
wide and flat to maximize sun absorption
prone to moisture loss via transpiration
shed in winters or prolonged dry seasons
What type of leaves do Boreal or taiga forests have
CHRISTMAN TREES
coniferous trees only
narrow, wax-caoted leaves
absorbs less sunlight but transpire less water
not shed during cold or dry seasonsWhat
What type of leaves do temperate forests have
mostly broadleaf that shed each winter
what type of leaves do Mediterranean forests have
small confierous trees and shrubs
What are ecoregions(ecozones)?
areas within ecosystems that vary by quality, quantity of environmental resources
This is from the state map we colored in lab
What is ecological succession?
The process for change in the abiotic and biotic factors of an ecosystem over time
What is primary succession
when a new ecosystem was created where no prior life existed
like a volcanic island
What plants grow in each of the three stages of primary succession
First stage - rock is weathered into soil - growth of lichens and mosses - pioneer species
Middle stages - grasses and wildflowers - seeds carried over by wind and animals
Late stages - formation of climax communityW
What is climax community?
highly stable ecosystems that will remain until a disruption occurs
What is pioneer species
the first organisms to appear in a new ecosystem
What is secondary succesion
occurs when an existing ecosystem undergoes a disruption - like fire, flood, volcanic eruption, ect.
What are the abiotic and environmental factors that differentiates aquatic ecosystems?
Temperature
Availability of sunlight
salinity
nutrients - nitrates and phosphate that runoff from land - needed for algae growth
turbidity
pH - acidity or alkalinity of water
What is turbidity
measures water cloudiness and increases with soil runoff
What are the biotic factors found in aquatic biomes
Plankton - small, free-floating or weekly swimming
Phytoplankton - plantlike
Zooplankton - animal-like
Pelagic - large, independent swimmers - fish and shrimp
Benthos - bottom dwellers - many don’t move or seldom doWhat
Define lakes and ponds
areas naturally filled with water
lentic - nonflowing
What are the zones of freshwater biomes (lakes) and describe them
Riparian - terrestrial but soggy - plants give habitat for animals that like to be in water but can’t breath it - filters runoff and stabilizes bank
littoral - nearest the shore - water is warm, shallow, and sunlit - emergent plants live here
Limnetic - open water area too deep for emergent plants
Photic zone - warm and sunlit, supports phytoplankton
Aphotic zone - deep, dark, and cold
What are emergent plants
plants that root at the bottom and pass through the waters surface
What are the two types of lakes and define them
Oligotrophic - have water with low turbidity and nutrient levels - limits algae growth
Eutrophic - water has high turbidity bc of high nutrient levels and excessive algae growth (neighborhood lake)W
What is a stream?
a narrow channel that carries runoff water towards riversW
What are rivers?
wider than streams and carry more water
Lotic - flowing
What is the difference between lotic and lentic?
Lotic - flowing
lentic - non-flowing
What are the three different sections of the river?
Headwaters
transition zone
mouth
What are the headwaters?
Headwaters - river source
comes from melting ice on mountains ice bergs snow ect.
high dissolved oxygen, low nutrients
cold water temps
low turbidity
no salinity
What is the transition zone of rivers?
The middle where it widens and deepens
warmer
decreased dissolved oxygen
increases nutrient levels
Here we see the fertile floodplains
What are floodplains?
The area around a river where the river will flood with high rain, so the soil is great for farming
What is the mouth of the river section?
where it enters the ocean
low dissolved oxygen
high nutrients
warm water temps
high turbidity
moderate salinity
What are wetlands?
areas containing soils that are usually waterlogged
soil tends to be oxygen poor due to the lack of air exposureW
What adaptations are needed for wetland organisms?
Marshes
Floating - fewer vascular tissues since water is plenty - making them lighter
Carnivorous - captures and digest insects to increase nitrogen and phosphorus levels - fly traps
Emergent - empty spaces in tissues to allow oxygen flow through plant and into the submerged roots
What are the 6 costal ecosystems
estuaries
coastal lagoons
tidal flats
deltas
salt marshes
seagrass beds
mangrove forests
last three are wetlands