Biology Unit 3 - Biochemistry
1/259
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
260 Terms
Organic Compound
produced by/occur naturally in organisms
Organic Compound
ex. Breast milk
organic compound
ex. hemoglobin
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur
Six most common elements found in organic compounds?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur
CHONPS
hydrocarbon
chain/ring of carbon atoms w /hydrogen atoms ONLY
substituted hydrocarbon
hydrocarbon w/ one or more “functional groups” replacing hydrogen
Hydroxyl Group
–OH, A single oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom.
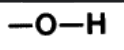
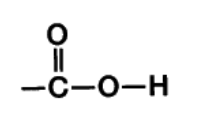
Carboxyl group
–COOH, A carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group.
Carboxyl
which is acidic? Carboxyl group or Hydroxyl group?
hydroxyl
which forms alcohols? Carboxyl group or Hydroxyl group?
Carboxyl groups
which forms acids? Carboxyl groups or Hydroxyl groups?
biological macromolecules
large, complex substituted organic molecules with specific roles in organisms
monomers
single unit building blocks of larger molecules
polymer
long chain of monomers, large molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
4 major groups of biological macromolecules
carbohydrates
composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ONLY, used primarily as a source of energy in cellular respiration
structural compounds
molecules where the arrangement of atoms and bonds determines their properties, often represented by a structural formula that shows how atoms are connected
T
T or F, some carbohydrates function as structural compounds
monosaccharides
simplest carbohydrates, monomers
ose
what do the names of monosaccharides end in?
monosaccharides
single ringed and also called sugars
isomers
two molecules that share the same molecular formula but have different structural formulas
disaccharides
double ringed sugar, not monomer
disaccharides
form through dehydration synthesis
dehydration synthesis
formation of a bond between monomers caused by the removal of water (H20)
hydrolysis
breaking of a bond between monomers by adding water
hydrolysis
opposite of dehydration synthesis
dehydration synthesis
opposite of hydrolysis
polysaccharides
complex carbohydrates/polymers
polysaccharides
made up of chains of monosaccharides
starch, cellulose, glycogen, chitin
four types of polysaccharides:
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
what three elements make up carbohydrates?
1:2:1
what is the ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a monosaccharide
cellular respiration
the main use of carbohydrates in the diet of living things is a source of energy in ______
1
number of monomer units in monosaccharides
2
number of monomer units in disaccharides
10+
number of monomer units in polysaccharides
glucose
example of monosaccharide:
maltose
example of disaccharide of glucose:
glucose polymer (starch)
example of polysaccharide of glucose:
starch, cellulose
name two polysaccharides commonly found in plants:
chitin, cellulose
name two structural polysaccharides:
glycogen
what is another name for “animal starch”?
liver
where is glycogen found?
starch
in what form do plants store excess glucose
starch
molecule in which plants store excess sugar in roots, stems, and leaves?
cellulose
tough, structural polysaccharides found in plant cells walls, can not be digested
in plant cells walls
where is cellulose found?
glycogen
molecule used by animals to store excess sugar in the liver
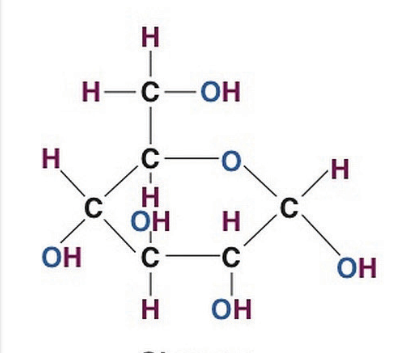
glucose
what does this show
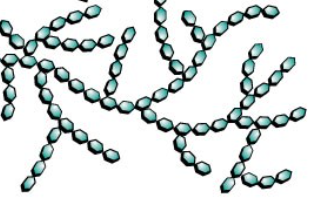
glycogen
highly branched carbohydrate
chitin
tough structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of insects, spiders,crustaceans. found in cell wall of fungi
fibrous
found in hair, nails, feathers, skin, muscle, (structure). what what type of protein?
proteins
perform functions: hormones, antibodies, and enzymes. what biological macromolecule?
protein structure
______ is key to how living things look and function.
amino acids
monomers of proteins
20
how many different types of amino acids are there?
9
how many amino acids are essential, how many need to be obtained through diet, bc human body can’t make.
replacement group
differs between each specific amino acid.
R group
syn for replacement group
amino acids
this is the general formula for what?
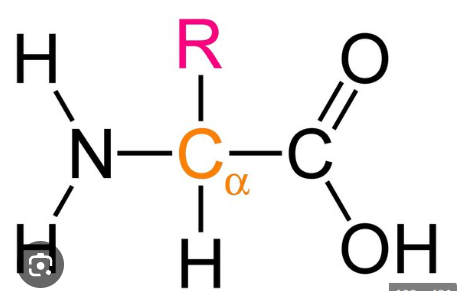
replacement group
what does the “R” in this formula stand for?

polypeptides
polymer, type of amino acid. long chain of amino acids.
polypeptides
range in size from 50 amino acids to 100k
hydrogen bond
weak force of attraction that can form between amino acids
dipeptide
two linked amino acids
peptide bond
name of the special bond that holds together a chain of amino acids.
proteins
one or more polypeptides (long chain of amino acids.) folded into specific shape
enzymes
organic catalysts
ase
what do the names of enzymes end in?
enzymes
react only with a substrate that matches its unique 3D shape
substrate
the specific substance(s) undergoing a chemical reaction. enzymes temporarily bond to this
catalyst
a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed/destroyed itself
Lock and Key theory
describes how enzymes promote reactions
Hydrocarbons
What are the simplest organic molecules?
monomer
What is the general term for a repeating building block unit of a complex macromolecule
proteins
Which group of organic macromolecules includes sucrase?
Carbohydrates
Which group of organic macromolecules includes maltose?
monosaccharide
When starch is broken down by enzymes, what is the specific name for the simplest molecules formed?
polypeptide
What is the general name for a polymer protein?
dehydration synthesis bonds
What is the name for the special bonds that hold together simples sugars in a polysaccharide?
dehydration synthesis
What is the name for the chemical process which results in the formation peptide bonds
enzyme
What specific type of protein is considered an organic catalyst?
functional group
an atom or group of atoms that determines a molecule's chemical properties
functional group
What is the name for a specific group of atoms, such as -COOH, that alters the properties of a hydrocarbon?
Globular
What is the name for the general group of proteins, including hormones and antibodies,whose function depends on their specific shape? adj
Isomers
What is the name given to two molecules with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas?
Hydrogen
What is the name for the type of bond that helps bind the substrate in the correct position with an enzyme to form the activated complex?
Denaturation
The term for the destruction of the normal shape of a protein based on temperature or pH?
glycogen
What is the name for the molecule known as "animal starch" stored in our liver?
4
How many bonds does carbon normally form when it is stable?
replacement group
The general structure of an amino acid is altered by changing a particular group of atoms known as?
chitin
What is the name for the form of carbohydrate that is found in the exoskeleton of insects?
b
In the "Lock and Key Theory" of enzyme function: a) One enzyme can catalyze reactions with many different substrates to promote different chemical reactions, b) An enzyme has a very specific shape and can only accept a very specific shaped substrate; enzymes are therefore substrate specific, c) An enzyme functions to speed a chemical reaction once; the enzyme is destroyed in the process
Cellulose
This polysaccharide resists hydrolysis from enzymes and is utilized by plants to build cell walls.
reaction coordinate
displays the progress of a chemical reaction