week 5 ischemic heart disease
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
one of the most common indications for an echo for a pt with IHD is to
assess left ventricular function
what 2 things are we looking at in the ventricle wall
thickening and motion
can we see coronary arteries well on echo
no :(
why is it important to ER pt’s with chest pain to assess wall motion
CAD
Diagnostic test for IHD
EKG
Excercise stress test
Nuclear stress test
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac Cath
Echo
Excercise stress echocardiogram
What is Myocardial ischemia
lack of O2 to the heart muscle by blockage in coronary arteries
% Cornoary artery blockage for myocardial ischemia
70% narrowing
what are some onsets for ischemia
increased demand for O2
Excertion
emotional stress
coronary arteries cant supply enough blood to muscle
hypokinesis
change in wall motion of affected area
is hypokinesis permanent
no
wall motion returns to normal when demand for O2 returns to normal
Angina def
chest discomfort due to ischemia (lack of O2 to myocardium)
angina symptoms
chest tightness, pressure, heaviness
radiating pain to left arm, jaw and back
WOMEN
Nausea
vomiting
SOB
General uneasiness
sequence of myocardial ischemia
perfusion abnormalities
observed by NUCLEAR IMAGING
Diastolic and STRAIN abnormalities
Wall motion abnormalities
Echo
ECG change and ANGINA
EKG
Cardiac enzyme release
what is a Myocardial infarction
when occlusion in 1 or more of the coronary arteries leads to irreverable damage to myocardium
MI AKA
Heart attack
signs and symptoms of MI
Angina
chest heaviness, aching, pinching, squeexing, tightness, pressure
nausea, vommiting
numbness
dizziness / fainting
diaphoresis (Excessive unexplained sweating)
Palpitations
Radiating arm, back, shoulder, jaw pain
dyspnea
HF (SOB, Edema, cough)
Sudden cardiac death
ECG Changes
WOMEN
Nausea, vommiting, SOB, General uneasiness, feeling unwell
causes of MI
Rupture of atherosclerotic plaque
SCAD (spontaneous coronary artery dissection)
more common in women
coronary spasm
EKG for acute MI
ST Elevation
EKG for old MI
Q Waves
leading cause of death in men and women
MI *o*
echo for acute MI
Normal wall thickness
reduced / absent endocardial motion & wall thickening
ST Elevation on ekg
echo for old MI
Thinning and increased echogenicity due to scarring and fibrosis
abnormal motion and absent wall thickening
Q Waves on the EKG
progression of MI
heart muscle is affected
hypokinetic
akinetic
normal thickness
myocardium becomes thin and scarred (fibrotic) over time and appear brighter on echo
normal wall motion implies no ischemia at the time of imaging
Dresslers syndrome
form of pericarditis
small pericardial effusion after MI
Usually 1 - 12 weeks post MI
What is the best test for post MI patient with a murmur and what is assessed
echo
MR
VSD
Ventricular rupture with pseudoaneurism
Ischemic MR after MI
MC COMPLICATION OF MI***
Ischemia and dialated cardiomyopathy
cause by papilary muscle displacement and dilation of the annulus
severe MR can occur with papillary muscle rupture
tenting of MV LEAFLETS
(Normal closure is at the annulus)
VSD after MI
Rupture of part of the IVS
Evaluate using color looking for high velocity flow from left to right
left to right because of increased LV Pressure
obtain peak velocity using CW in MULTIPLE WINDOWS
Pseudoanuerism AKA
Contained rupture
What is a pseudoanurism
aneurism caused by a rupture
qualities of a pseudoaneurism
narrow neck (<0.5cm) and lined with pericardium
NOT LINED WITH MYOCARDIUM
may have thrombus
Perform off-axis magnified imaging (improved near field resolution)
surgical repair recommended
True anuerism characterics
Diastolic contour abnormality
outward bulging of the wall in a severyly infarcted area
systolic dyskinesis
wall moves out while the other walls contract in
Lined by thin myocardium
Smooth transition from normal myocardium to thinned area
MOST COMMON IN APICAL OR INFEROBASAL WALLS
Wide neck
GREATER THAN 0.5 cm
may have thrombus
perform off-axis magnified imaging (improved near field resolution)
pericardial Effusion
can occur after MI
Dresslers syndrome
Non-specific response
Usually benign but can indicate pericarditis, possible dissection or LV Rupture
sometimes can develop tamponade physiology
Right ventricular infarction
most common with INFERIOR MI
RV Hypokinesis
Variable degrees of dilation
Left Ventricular thrombi
clotting formation in area of low flow
low flow examples increasing risk of LV Thrombi
Severly reduced akinetic area
aneurism
appearance of spontaneus echo contrast (smoke)
where do you have to image very carefully for left ventricular thrombi and why
LV and APEX
Can be small or large
can be confused with other structures
trabeculation, tendon, chord
use high res settings for better near field resolution
use off axis planes (short-axis apical views)
use multiple imaging planes
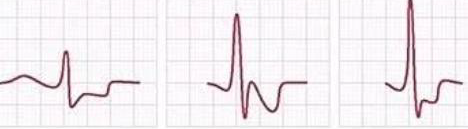
ST Depression
Ischemia
Normal sinus rythym
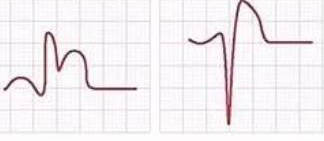
ST Elevation
acute MI
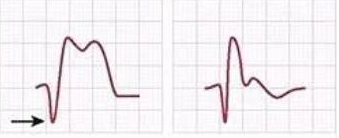
Q Waves
OLD MI
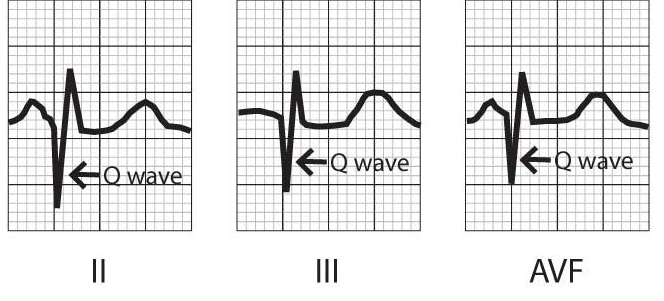
Q Waves after an inferior MI
(Usually RV)
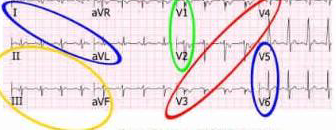
what is each color
blue- lateral
I, aVL
V5, V6
yellow - inferior
II, III, aVF
Green - septal
V1, V2
Red- Anterior
V3, V4
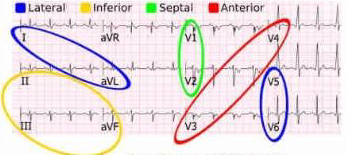
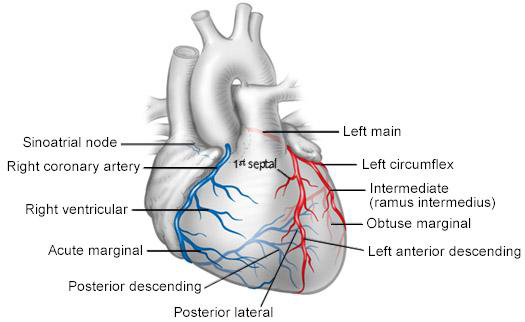
LAD Occlusion will cause MI and Akinesis of
anterior septum
anterior wall
apex
Right coronary artery occlusion will cause MI and Akinesis of
Inferior septum
Base and mid
Inferior wall
Circumflex artery occlusion will cause MI and Akinesis of
Anterolateral wall
(Lateral wall)
Inferolateral wall
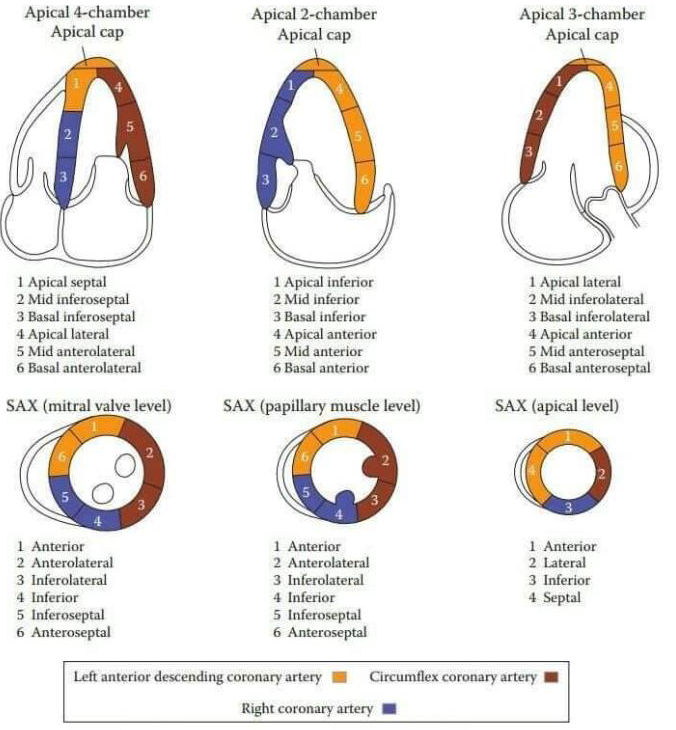
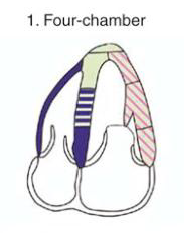
A4C
Inferoseptal wall
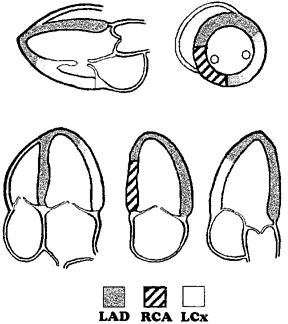
APICAL Septal - LAD
Mid - RCA or LAD
Basal - RCA
Anterolateral
LAD or CX
RV Free wall
RCA
Apical tip
LAD
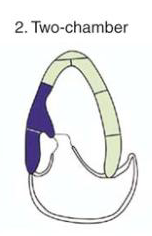
A2C
Anterior wall
Apical- LAD
mid - LAD
Basal- LAD
Inferior wall
Apical - LAD
MID -RCA
Basal - RCA
RV Free wall
RCA
Apical tip
LAD
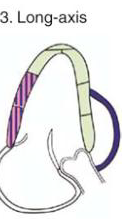
ALAX (A3C)
Anteroseptal
LAD
LAD
LAD
Inferolateral (posterior)
Apical - LAD
Mid - RCA or CX
Basal - RCA or CX
RV Free wall
RCA
Apical tip
LAD
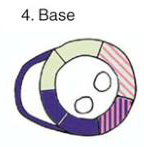
LAD
Anterior
Anteroseptal
RCA
Inferior
Inferoseptal
Antero lateral
LAD or CX
Inferolateral
RCA or CX
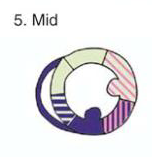
LAD
Anterior
Anteroseptal
RCA
Inferior
Antero lateral
LAD or CX
Inferolateral
RCA or CX
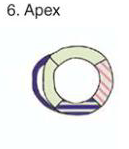
RV Free wall
RCA
anterior
LAD
septal
LAD
inferior
LAD or RCA
Lateral
LAD or CX
Regional heart motion abnormalities:
a segment of the heart does not thicken, contract, and move inward during systole
Possible causes of regional wall motion abnormailities in ABSENCE OF CAD
wall thickening / timing
wall thickening is preserved, although its timing may differ from normal
Possible causes of regional wall motion abnormailities in ABSENCE OF CAD
Abnormal electrical conduction
conduction abnormalities
LBBB
Ventricular pacing
ventricular pre-excitiation
post-pericardiotomy state
pericardial constriction
right ventriular pressure and volume overload
external compression
nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy
stress cardiomyopathy
systemic disease such as sarcoidosis or hemochromotosis
avoid ________ in apical views
FORESHORTENING
How to avoid foreshortening in apical views
endocardial definition may be difficult due to attenuation from lung
Change patient position
Respiratory manuveurs
5 tips for imaging in apicals
avoid foreshortening
obtain extra views at different depths
perform off axis views of the APEX when wall motion abnormalities are present
Magnify of the APEX using high resolution to evaluate thrombus
Use contrast
benefits of contrast in apicial view
aid in endocardial defintion
presence of thrombus especially when wall motion abnormalities are pressent
qualitative evaluation of global & regional function in CAD
Visual assessment of global and regional wall motion and systolic function
Estimate (eyeball) ejection fraction EF
Use all windows and many tomograophical views
semi-quantitative evalutation - wall motion score index 1-4
normal
endocardial inward motion and thickening and of wall in systole
hypokinetic
reduced endocardial motion and wall thickening in systole
Akinetic
absense of inward endocardial motionor wall thickening in systole
Dyskinenetic
outward motion “bulging” of the segment in systole, usually associated with thin, scarred myocardium
how to get an overall wall motion score
divide the sum of scores for each segment by the number of segments evaluated
what MUST be visualized to evaluate wall motion score
ENDOCARDIUM!!!
wall motion criteria for normal or hyperkinetic
normla thickening (usually 30% thickening from end diastole
wall motion criteria for hypokinetic
reduced thickening (usually10-30% thickening from end diastole)
wall motion criteria for akinetic
markedly reduced or no thickening (<10% thickening from end-siastole)
wall motion criteria for dyskinetic or aneurismal
dyskinesia:
aneurism:
dyskinesia: paradoxial thinning and / or outward motion during systole
Aneurism: diastolic deformation of the shape with dyskinetic movement
wall motion score for:
normal or hyerkinetic
hypokinetic
akinetic
dyskinetic or aneurismal
normal or hyerkinetic
1
hypokinetic
2a
akinetic
3
dyskinetic or aneurismal
4
quantitative evaluation of ventricular function
bi-plane tracing of the endocardium at end-systole and end-diastole in the apical views
must have optimal ENDOCARIAL DEFINITION
Method of discs- Simpsons
More accurate and preffered method as long as good imaging of the ENDOCARDIUM
Stress echo for CAD
Echo alone can not assess for CAD
What does a stress echo use to diagnose ischemia
Echocardiography (wall motion)
Electrocardiogram
to diagnose ischmia
2 types of stress echoes:
both aim to do what?
excercise
debutamine (pharmalogic)
Both aim to raise HEART RATE and PRIODUCE ISCHEMIA
What will develop if ischemia is present in a stress echo
wall motion abnormalities
reduced O2 to the area means less contraction and thickening
what do we need to evaluate during ischemia
WALL MOTION!!!
When are pressure gradients obtained
PEAK STRESS***
(Stenosis, Obstruction)
What is assessed on ALL Stress echos
PAP!!
what is echo used for to determine in the ER
Suspected MI or CHEST PAIN
Echo can indicate complications from the following conditinos (3)
Regurgitation, effusion, ruptiure
echo can determine _____ and _____ of wall motion abnormalities
location and severity
echo is used to re-evaluate after what procdures
CABG
Coronary artery bypass graft
Stent
Balloon angioplasty
presense of wall motion abnormalities can help distinguish between?
CAD or Dilated cardiomyopathy
End-stage ischemic cardiac disease
Global LV dysfunction develops due to multiple infarcts with some regional variation in wall motion
at end-stage it is difficult to differentiate between?
Dilated cardiomyopathy and end-stage ischmic cardiac disease
Dilated cardomyopathy usually affects
BOTH VENTRICLES
Dilated cardiomyopathy usually preserves
Function at the base
basal posterior wall and lateral wall move best
Ischmic disease echo symptoms
definte areas of akinesis or wall thinning
normal right ventricuklar size and function, unless it had an infarct