Lecture 4 :Conjuctiva and lacrimal system
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What are the borders of the conjuctiva borders?
Continuous from eyelid margin to palpebral conjunctiva
Palpebral conjuctiva to fornix
Bulbar conjunctiva to limbus
What cells make up the conjuctiva?
Stratified squamous to columnar non-keratinizing epithelium with underlying substrantia propria. Goblet cells found regionally as well.
What is the physiology of conjuctiva?
Provide smooth lubricated surface for eyelids to contact cornea
Disperse tear film
Remove debris from ocular surface
Produce mucous component of tear film (Goblet)
Protective/immunologic function (Lymphoid follicles, IgA production)
What is the conjuctiva epithelium continuous with?
Cornea
What normal bacteria are found in conjuctiva?
Primarily gram positive, a few gram negative
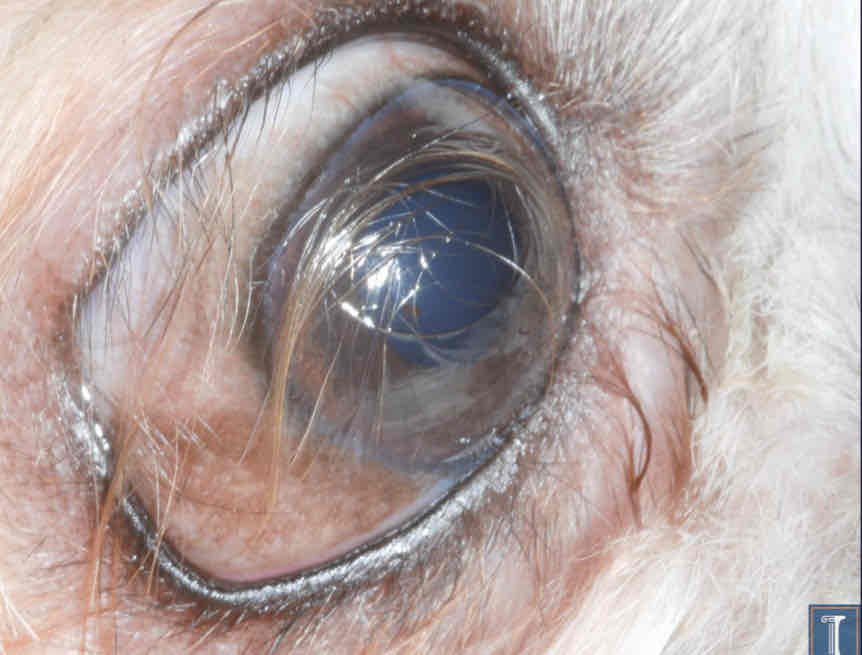
congenital disease
Dermoid
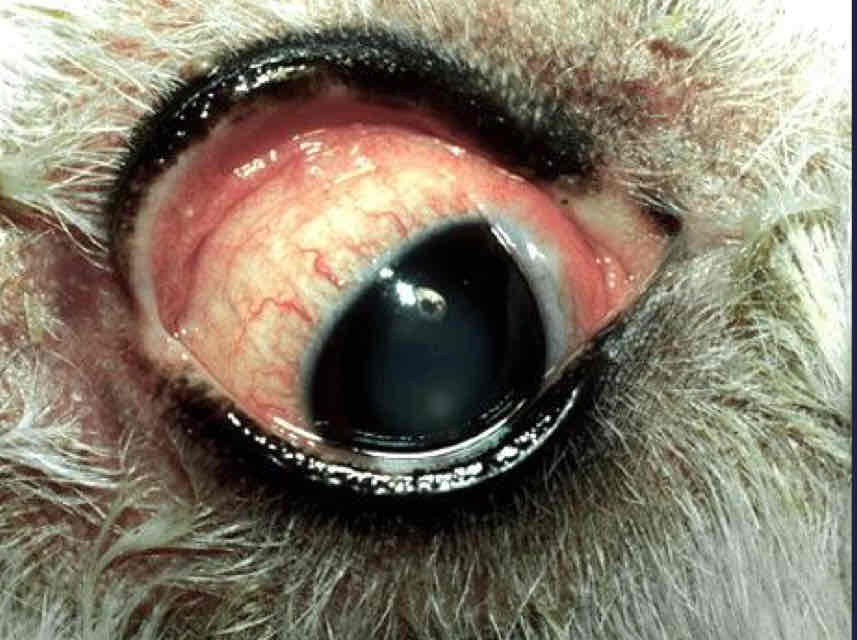
Common in all species
Very NSF
Variable CS:
Conjunctiva hyperemia
Chemosis
Lymphoid follicles
Ocular discharge
Treatment varies by cause
Conjuctivitis
What are the common viral causes of conjuctivitis?
FHV-1 and canine distemper virus
Chlaumdia is the most common cause of conjuctivitis in what animals?
Sheep in cats
What is the most common cause of conjuctivitis in goats?
Mycoplasma
What are some parasitic cause of conjuctivitis?
Thelazia, Onchocera, Habronema, Hepatozoon, Leishmania
Common cause of conjuctivitis in cats
Wide spectrum of CS
Most common in young stressed immunocompromised cats
FHV-1
Treatment of FHV-1
Reduce stress
L-lysine
Cidofovir
Farmciclovir
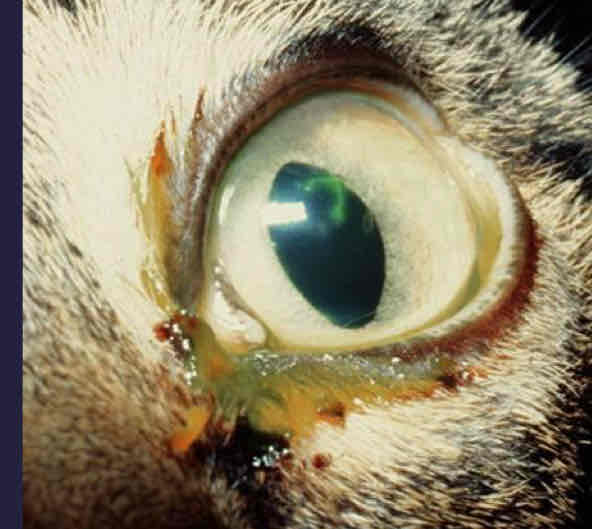
Dendritic ulcer
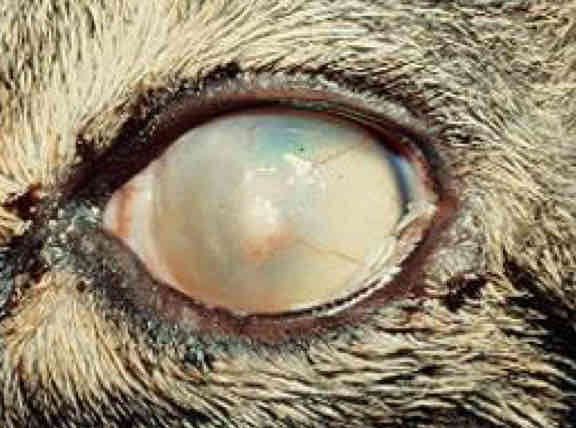
Stormal keratitis
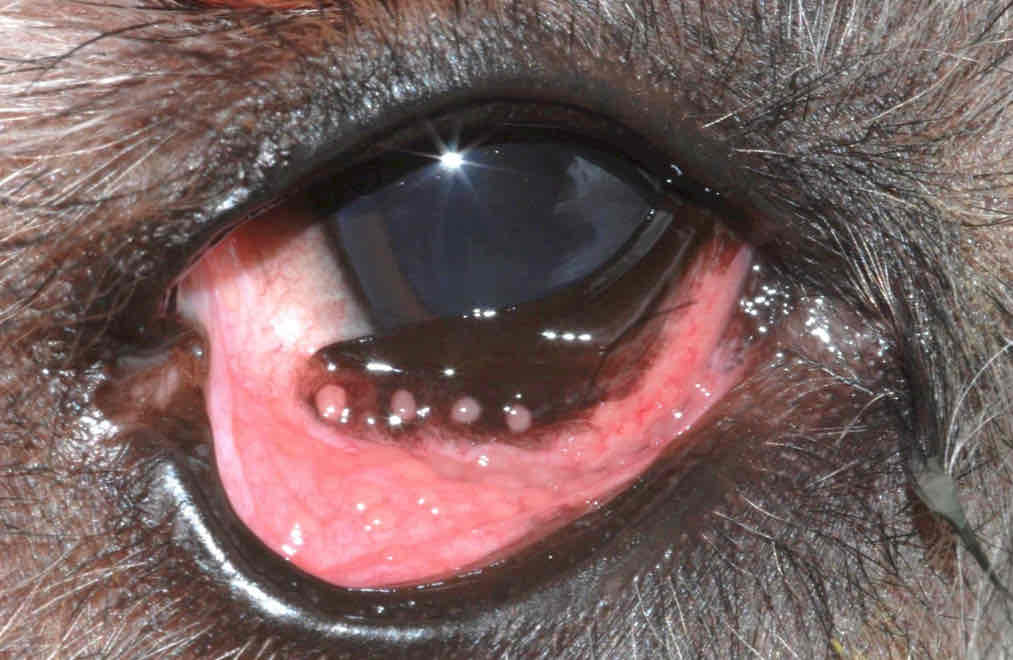
Diagnosis of exclusion
More common in young dogs
May have concurrent skin allergies
Bulbar conjuctival follicles
Epiphora or mucoid ocular discharge
Allergic conjuctivitis
Treatment for allergic conjunctivitis
Topical anti-histamines or anti-inflammatories
Diagnostics for conjuctivitis
Complete opthalmic exam
Culture and sensitivity
Schirmer tear test
Biopsy
Vital stains
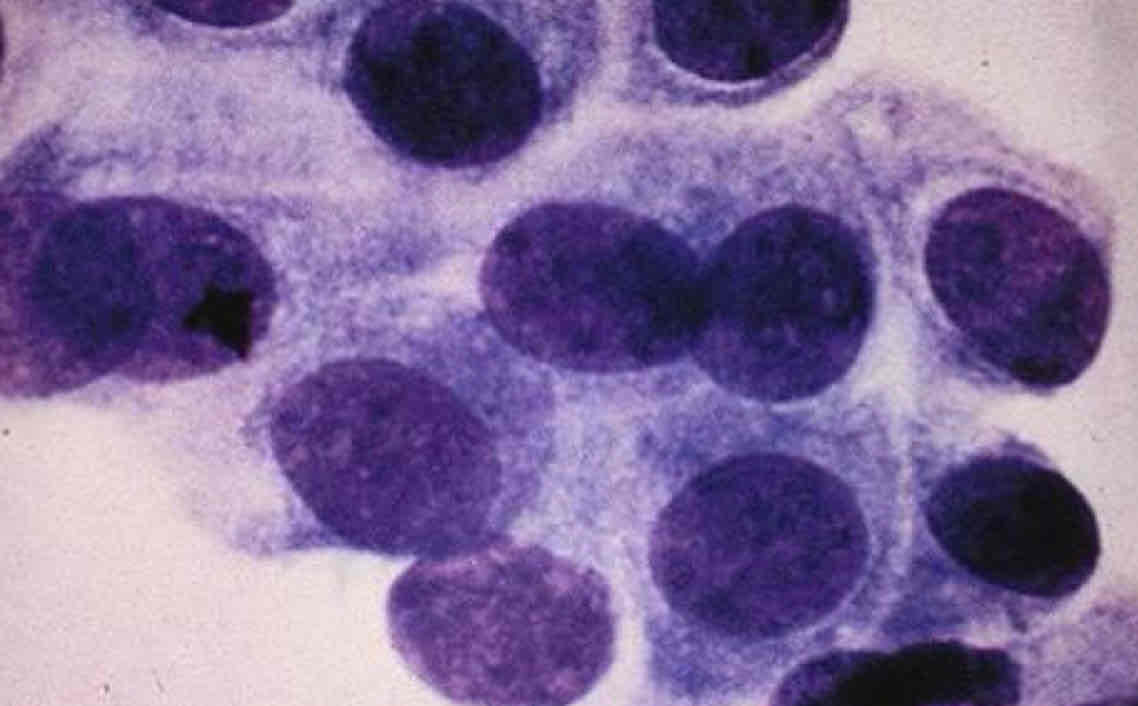
Superficial epithelial from a normal dog
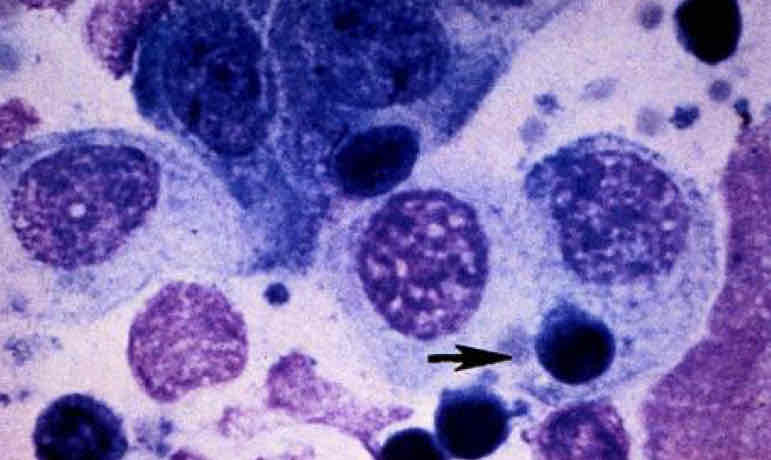
Kitten with FHV-1
Numbers mature lymphocytes are interspersed among and superimposed on the epithelial cells.
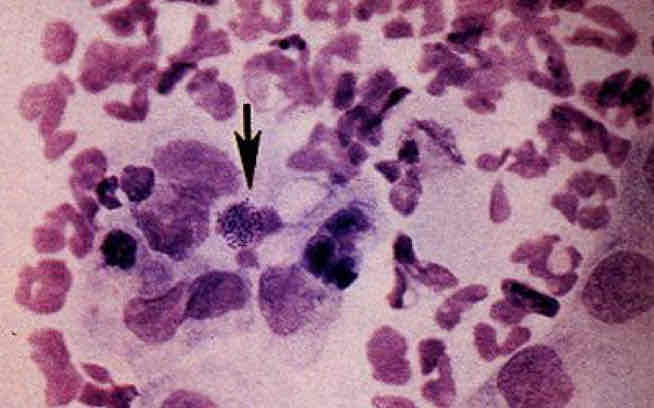
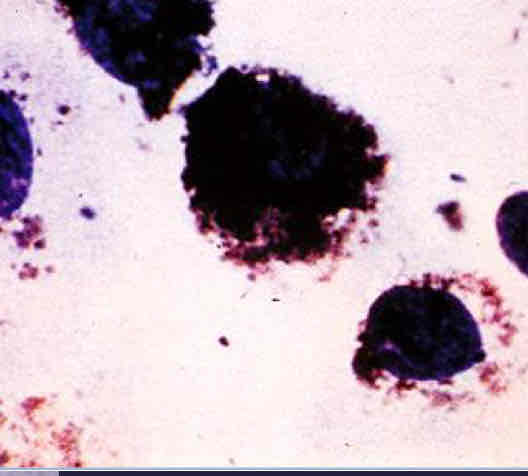
Dog with bacterial conjuctivitis
Note the presence of large numbers of degenerating neutrophils. Microorganisms are present (arrow), Giemsa stain.
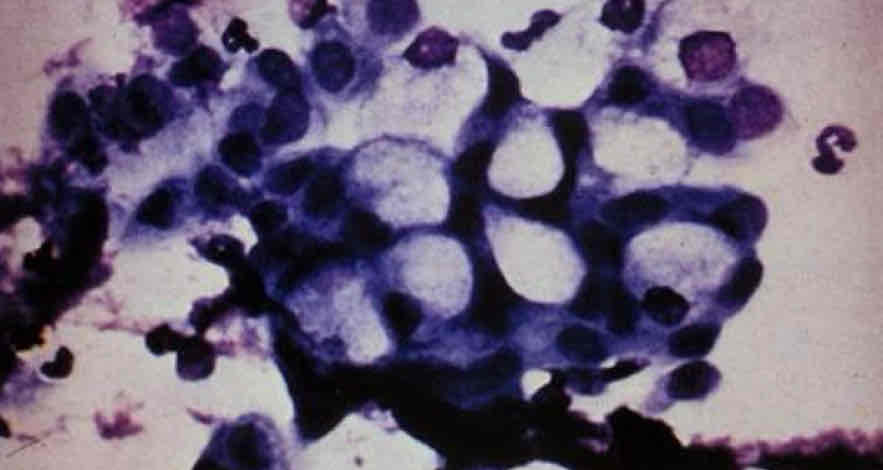
may be recognized by the large amount of mucin which displaces the nucleus to the periphery. Areas of mucus may stain light blue or appear as clear areas. Giemsa stain.
Conjunctival goblet cells
Conjunctival epithelial cells
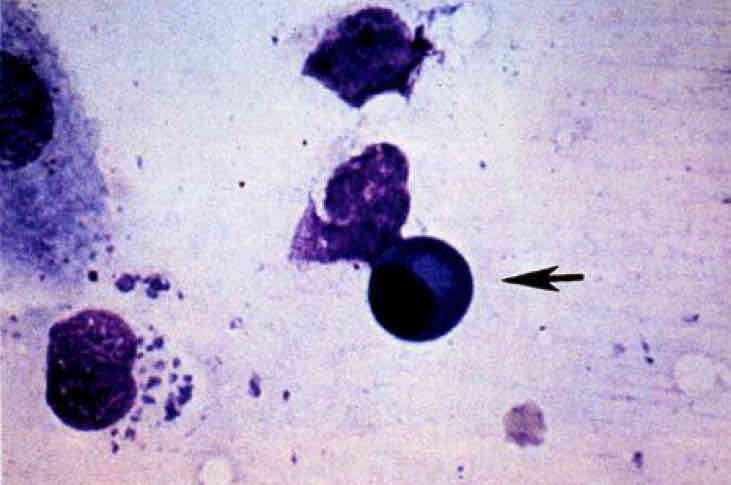
Plasma cell. Indicates an immune-medical response
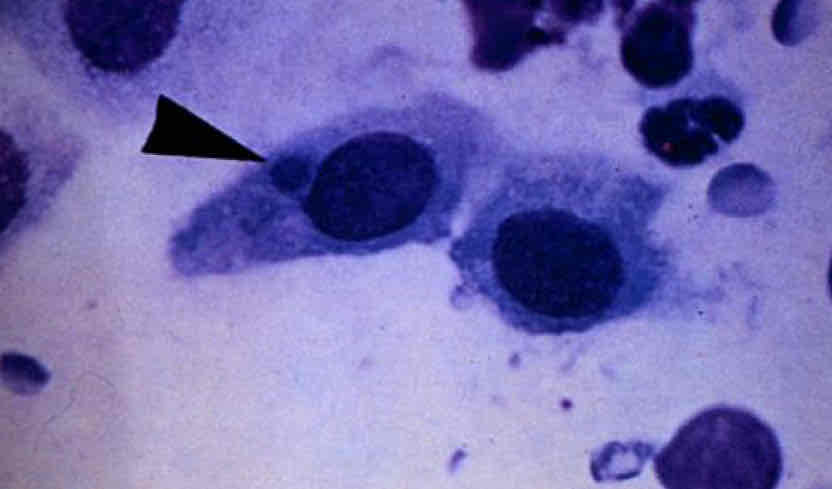
Chlamydia inclusion body
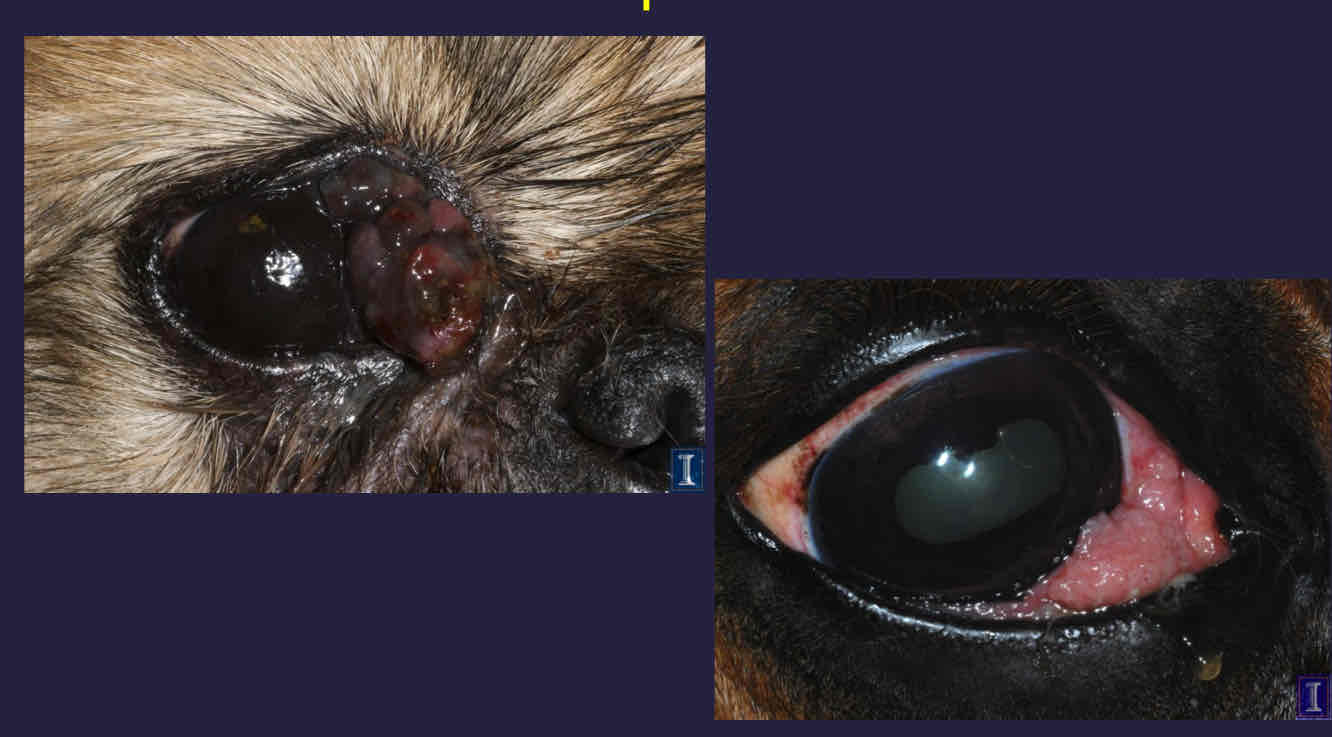
usually primary
Often malignant
FNA or biopsy
Local excision and adjunctive therapy
Conjunctival neoplasia
What is hemorrhage associated with in subconjunctival?
Proposes
Blunt trauma
Strangulation
Coagulopathy
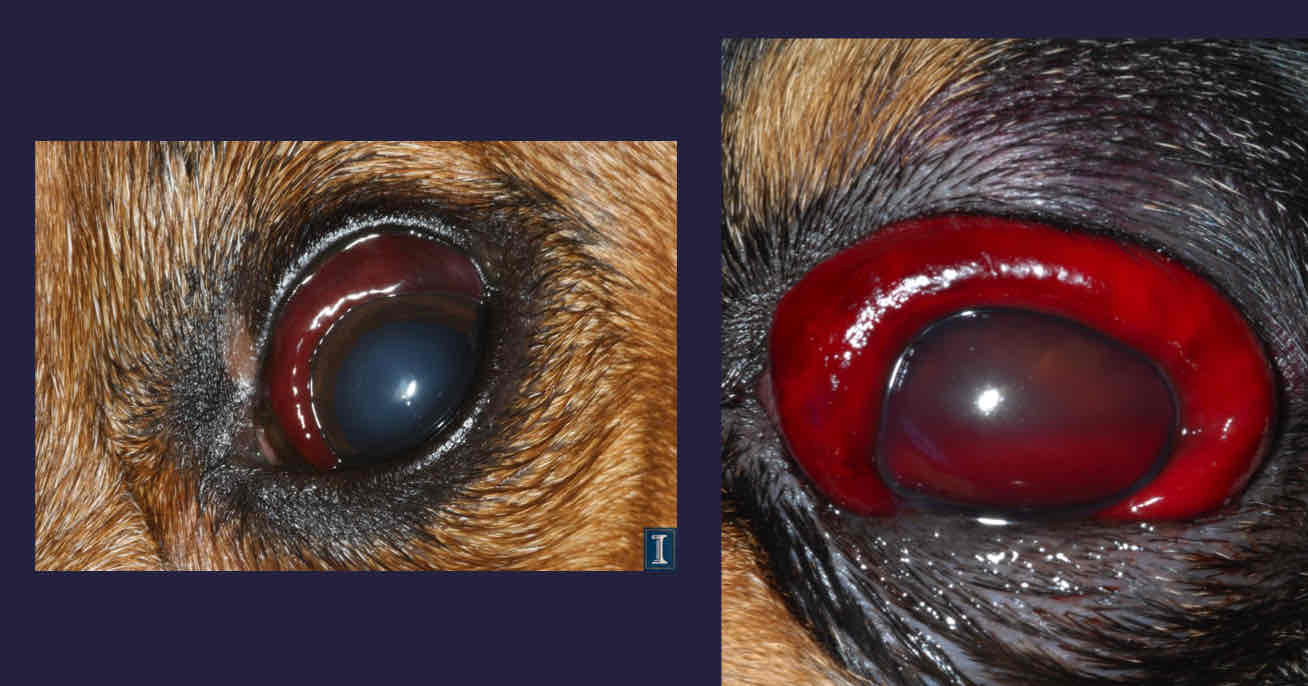
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
What is part of secretory system?
Orbital lacrimal gland
Gland of the 3rd eyelid
What is part of the distrubtion system for the lacrimal system?
Eyelids and third eyelid
Drainage system for lacrimal system?
Upper and lower puncta
Canaliculi
Lacrimal sac
Nasolacrimal duct
What is the order of the lacrimal drainage system?
Punctual → Canaliculus → Lacrimal sac → Nasolacrimal duct → Nasal puncta
What makes the aqueous layer of tear film?
Orbital lacrimal gland and gland of third eyelid
What makes the lipid layer of the tear film?
Meibomian glands
What makes the mucus layer of the tear film?
Conjunctival goblet cells
Name the 7 functions of the tear film
Smooth the ocular surface
Lubriciation of the ocular surface
Provide oxygen and nutritionist to the cornea surface
Remove metabolic by-produces from corneal surface
Give white blood access to cornea
Remove debris from ocular surface
Defend ocular surface from pathogens
How do you test the patent of the nasolacrimal system?
Nasolacrimal flush
How do you perform a nasolacrimal system?
Use 23-27g metal cannula and flush with saline or eye wash
Observe flow out opposite puncta and nares or swallowing
Topical anesthesia is necessary
How do you test patency and function of nasolacrimal system?
Jones test
How do you perform a Jones test?
Instill fluorescent into the eye
Lower head/nose
Observe fluorscein in the nares or oral cavity but does note always occur even in normal patients
What can tear overflow result in?
Overproduction and decreased drainage
Flow of tears onto the face or as a result of decreased drainage of tears
Causes:
Malpositioning of lacrimal puncta
Deep medial canthal pocket
Carbuncular trichiasis
Puncta aretesia
Epiphora
Treatment of epiphora
Surgical correction
Low dose tetracycline/macrolides (not recommended for chronic problem)
Why do tears turn brown on the face?
Porphyrins
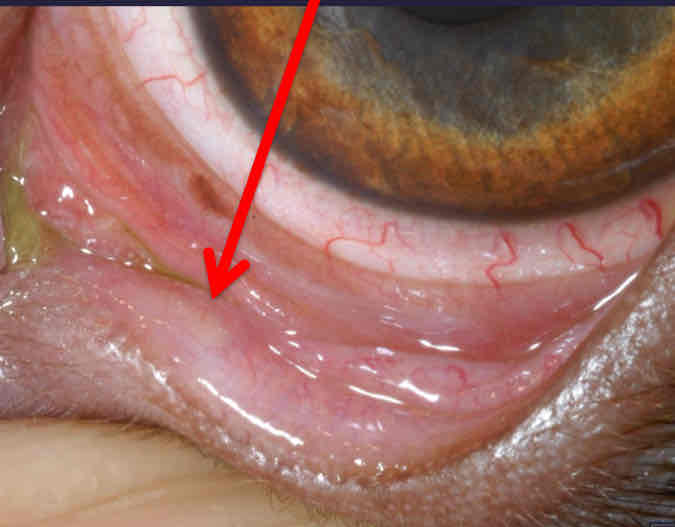
Lacrimal punctal atresia
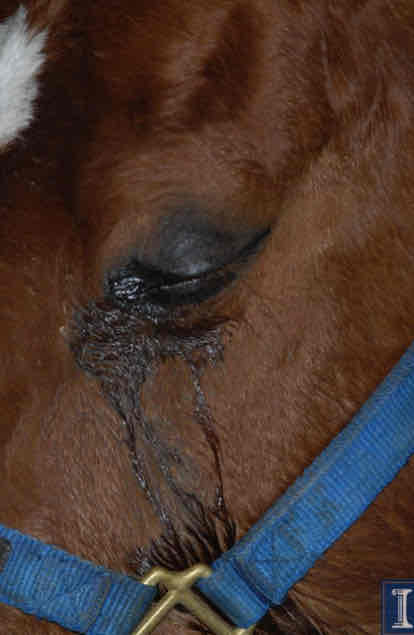
Very NSF of ocular pain
May result from intraocular disease or ocular surface disease
R/out nasolacrimal drainage problems then look for a reason
Hyperlacrimation
What is the most common neoplasia of lacrimal system?
Neoplasia of the third eyelid
CS of lacrimal neoplasia
Strabismus
Globe deviation
Protrusion of 3rd eyelid
Enopthalmos or exothalamus
KCS
Epiphora
Obstruction of nasolacrimal system by FB or inflammation
CS:
Epiphora or mucoid discharge
Negative Jones test
May require aggressive lavage, advanced imaging to locate obstruction
Dacryocystitis
Treatment for dacryocsytitis
Topical antibiotics/anti-inflammatories
Placement of nasolacrimal stent while duct is healing (prevent stricture)
Most common form of keraoconjuctivitis sic is (KCS)
Quantitative- deficiency of aqueous layer.
Less common form of KCS
Qualitative- deficiency of mucus or lipid layers. Treat w/hydaluronic acid based drop
Most common cause of KCS
Immune mediated (T-cell mediated of lacrimal tissue)
KCS CS
Mucoid, ropy, tenacious discharge
Conjunctival hyperemia/conjuctivitis
Corneal vascularization
Corneal pigmentation
Corneal ulceration
Lackluster corneal surface
Blepharitis
Loss of vision
Medical treatment of KCS
Lacrimostimulants (Cylcosporine that inhibits T cells)
Treat replacement
Usually unilateral
Affected animals usually have a dry eye and dry nostril on the same side
Treat with oral or topical pilocaprine
May be self-limiting
Neurogenic KCS
Surgical treatment for KCS
Parotid duct transportation
What are some potential complications you see with parotid duct transposition?
Excessive tear flow and facial dermatitis
Calcium precipitates on the cornea
Sialoliths can cause blockages
What is the main function of the conjunctiva? a) To produce the aqueous layer of the tear film. b) To lubricate the surface of the cornea and spread the tear film c) To provide structural support to the eye. d) To control the amount of light entering the eye
b) To lubricate the surface of the cornea and spread the tear film
Which of the following is NOT a clinical sign of conjunctivitis? a) Hyperemia b) Chemosis c) Miosis d) Ocular discharge
c) Miosis
What is the most common cause of conjunctivitis in cats? a) Bacterial infection b) Feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1)c) Chlamydial infection d) Mycoplasmal infection
b) Feline herpesvirus-1 (FHV-1
What is the primary source of the mucus layer of the tear film? a) Meibomian glandsb) Lacrimal gland c) Goblet cells of the conjunctiva d) Gland of the third eyelid
c) Goblet cells of the conjunctiva
Which nerve provides sensory innervation to the conjunctiva? a) Facial nerve (CN VII)b) Trigeminal nerve (CN V)c) Optic nerve (CN II) d) Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
b) Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
What is a dermoid? a) An inflammation of the conjunctiva b) A type of conjunctival tumor c) Normal tissue at an abnormal location d) A common cause of conjunctivitis in cats
c) Normal tissue at an abnormal location
Which diagnostic test involves placing fluorescein dye in the eye to check nasolacrimal duct patency? a) Schirmer Tear Test (STT) b) Jones test c) Nasolacrimal flush d) Conjunctival scraping
b) Jones test
What is the most common cause of dacryocystitis in dogs? a) Viral infection b) Foreign body obstruction c) Congenital atresia d) Neoplasia
b) Foreign body obstruction
What is the most common cause of KCS? a) Drug toxicity b) Immune-mediated destruction of lacrimal tissuec) Congenital defect d) Viral infection
b) Immune-mediated destruction of lacrimal tissue
Which of the following is NOT a potential cause of KCS? a) Sulfonamide toxicity b) Canine distemper virus c) Glaucomad) Neurogenic causes
c) Glaucoma
Which medication is used to stimulate tear production in KCS? a) Atropine b) Cyclosporine A c) Pilocarpine d) Neomycin
b) Cyclosporine A
What type of cells are primarily involved in immune-mediated KCS? a) B-cells b) T-cells c) Eosinophils d) Basophils
b) T-cells
What is a common clinical sign of allergic conjunctivitis? a) Purulent discharge b) Corneal ulceration c) Pruritus d) Icterus
c) Pruritus
What is a common finding in a conjunctival scraping from a dog with bacterial conjunctivitis? a) Lymphocytes and plasma cells b) Eosinophils and basophils c) Degenerating neutrophils d) Inclusion bodies
c) Degenerating neutrophils
Which of the following is NOT a function of the tear film? a) Providing a smooth surface for refraction b) Controlling intraocular pressure c) Lubricating the ocular surface d) Defending the ocular surface from pathogens
b) Controlling intraocular pressure
What is the purpose of the nasolacrimal flush test? a) To evaluate the quality of tear production b) To test for bacterial infection c) To evaluate the patency of the nasolacrimal system d) To assess the severity of conjunctivitis
c) To evaluate the patency of the nasolacrimal system
What does the Schirmer Tear Test (STT) measure? a) The amount of mucus in the tear film b) The lipid layer of tear film c) Aqueous tear production d) The presence of bacteria in the tear film
c) Aqueous tear production
What is the most common tumor of the conjunctiva in cattle and horses? a) Hemangioma b) Squamous cell carcinoma c) Mastocytoma d) Melanoma
b) Squamous cell carcinoma
Which of the following medications has been associated with neurogenic KCS when used in the ear? a) Doxycycline b) Tetracycline c) Florfenicol, terbinafine hydrochloride, mometasone furoate d) Pilocarpine
c) Florfenicol, terbinafine hydrochloride, mometasone furoate