Era 1, 1200 - 1450 CE: The Mighty Aztecs/Incans/Mayans (Quizlet #3)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1. Era 1 Overview, 1200 - 1450 CE
-Era 1 from 1200 - 1450 CE saw a rise in several important Land-Based Empires, as well as a huge increase in trade and travel;
-CRITICAL ERA 1 EMPIRES TO KNOW:
-Song Dynasty in China/East Asia
-Mayans, Incans, and Aztecs in the Americas
-The disintegration of the Abbasid Caliphate into several smaller Turkic empires in the Middle East/South Asia
-The Islamic Delhi Sultanate in South Asia
-Great Zimbabwe in Africa
-Feudalism and decentralization (no empire) in Western Europe
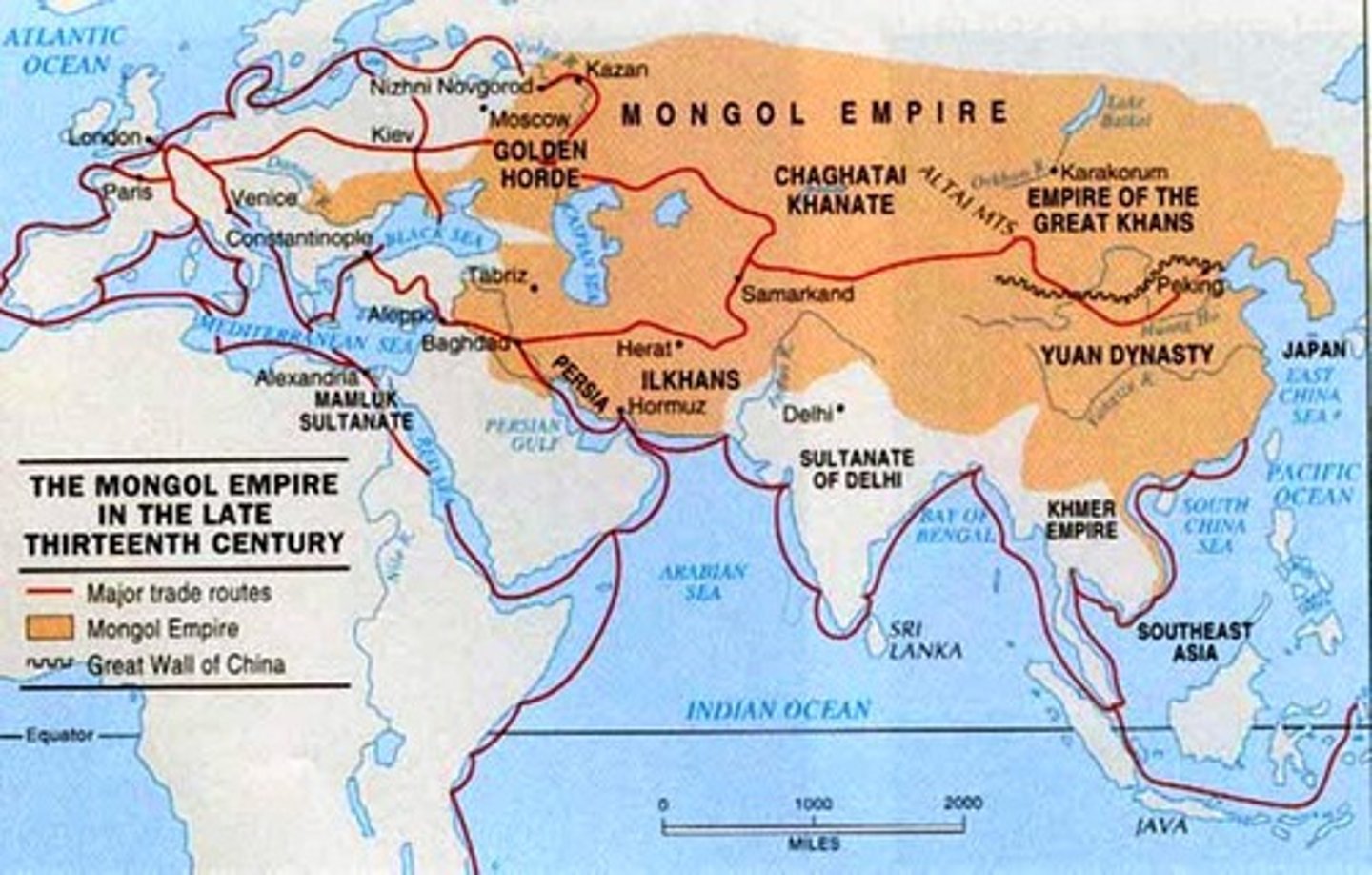
-The Mongol Empire in Asia/Middle East; they come in at the end and knock many empires down!
TRADE also massive. BIG FOUR ERA 1TRADE NETWORKS TO KNOW:
-Silk Roads in Eurasia/Middle East
-Trans-Saharan Routes in Africa
-Indian Ocean Basin trade
-Mediterranean Sea Trade
2. The Mayans, Incans, and Aztecs
-In the Americas /Mesoamerica during Era 1, 1200 - 1450 CE, there were three major Empires that sprang up and became very powerful
-Incans were centered around the Andes mountains in South America
-The Aztecs and Mayans were in Mesoamerica (essentially modern day Mexico and Central America)
-These empires were known for their powerful political, trading, and military systems
-Built long systems of roads and conducted trade
-complicated, complex civilizations with record keeping systems and beautiful artwork and culture
-complex religions that could include human sacrifice
-Wealthy empires that had large amounts of gold and silver; stunning feats of architecture and engineering
-systems of education, cleanliness, lack of homelessness
-Ended with the invasion of the Spanish Conquistadores in the late 1400's/1500's
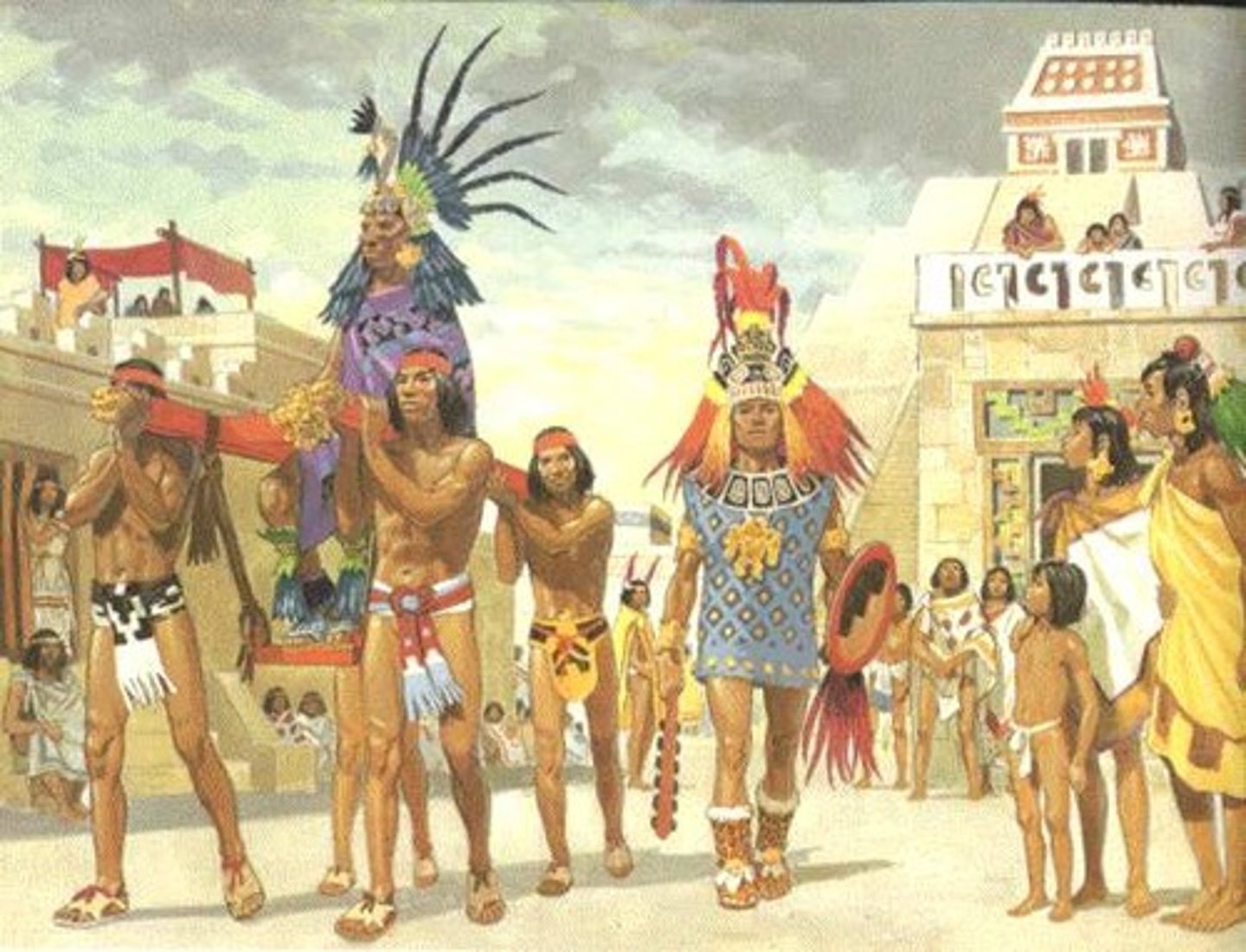

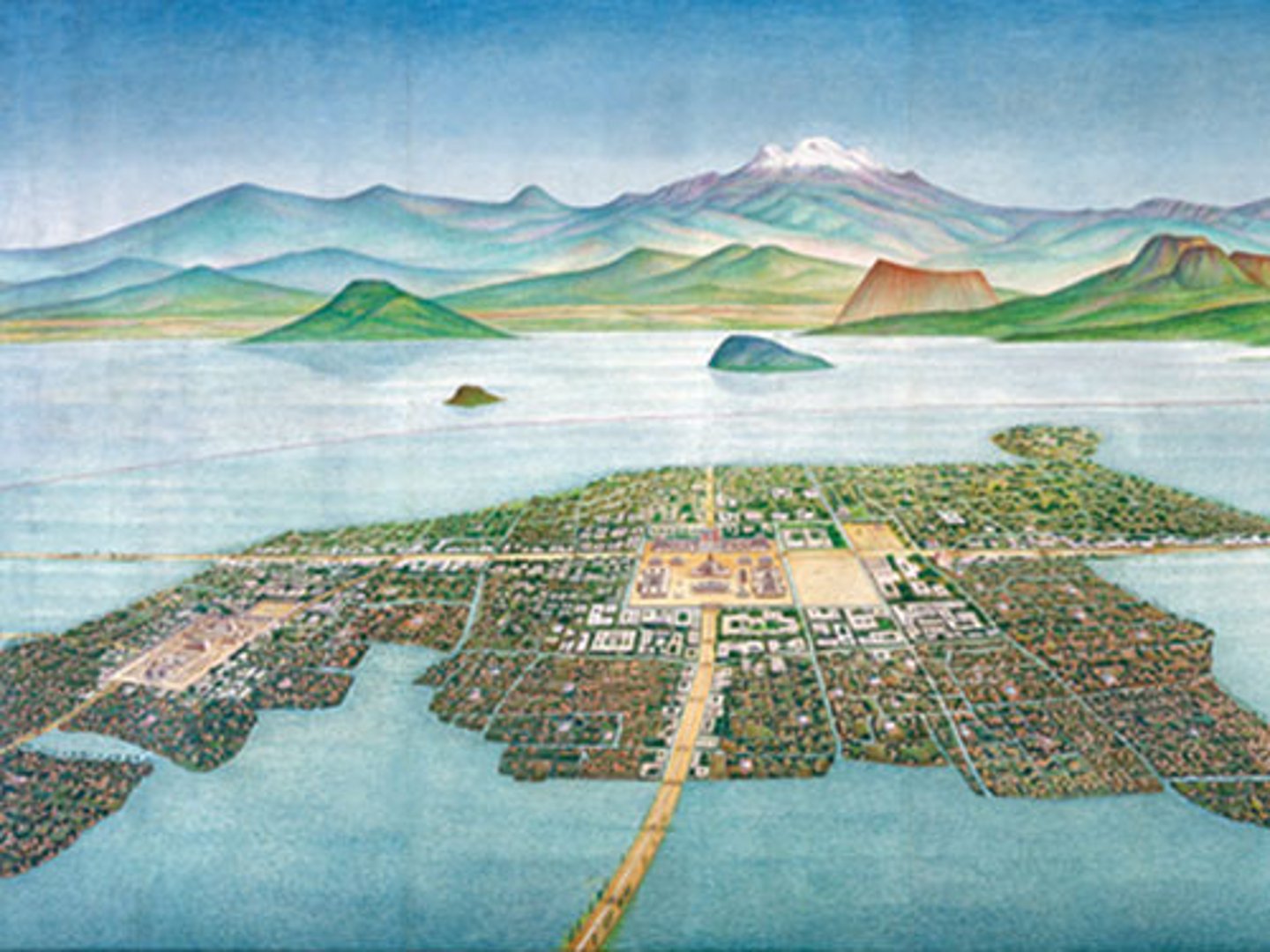
3. The Aztec Empire in Mesoamerica 1430 CE to 1520 CE
-Huge Empire in Mesoamerica ( modern day Mexico) started by the Mexica people in 1430 CE
-They built a massive capital city of Tenochtitlan on an island in the marshy region of a lake; was known as an extraordinarily beautiful city, the Spaniards were astonished when they saw it; this showed their brilliant engineering and architecture
-had complex systems of agriculture like the chinampa field system, and record keeping, as well as complex religions
-strong systems of education, strong standards of personal hygiene and cleanliness
-Very warlike people, conquered far and wide, they used a large system of slavery to enslave other native tribes in the area. Some enslaved persons [slaves] would be used for human sacrifice. Neighboring tribes paid tribute [trade goods] to the Aztecs
-Brought down by the Spanish Conquistador Hernan Cortes in 1520 CE
![<p>-Huge Empire in Mesoamerica ( modern day Mexico) started by the Mexica people in 1430 CE</p><p>-They built a massive capital city of Tenochtitlan on an island in the marshy region of a lake; was known as an extraordinarily beautiful city, the Spaniards were astonished when they saw it; this showed their brilliant engineering and architecture</p><p>-had complex systems of agriculture like the chinampa field system, and record keeping, as well as complex religions</p><p>-strong systems of education, strong standards of personal hygiene and cleanliness</p><p>-Very warlike people, conquered far and wide, they used a large system of slavery to enslave other native tribes in the area. Some enslaved persons [slaves] would be used for human sacrifice. Neighboring tribes paid tribute [trade goods] to the Aztecs</p><p>-Brought down by the Spanish Conquistador Hernan Cortes in 1520 CE</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4ab26779-1aa5-4b2a-8998-742bf482a407.jpg)
4. The Mexica
-The most dominant tribe in the Aztec Empire. The Aztec Empire was really formed by the Mexica tribe, who allied with a few other tribes.
-Incredibly feared as warriors
-Once they established the Aztec Empire, the Mexica ruled over 5 million people in Mesoamerica or modern-day Mexico.

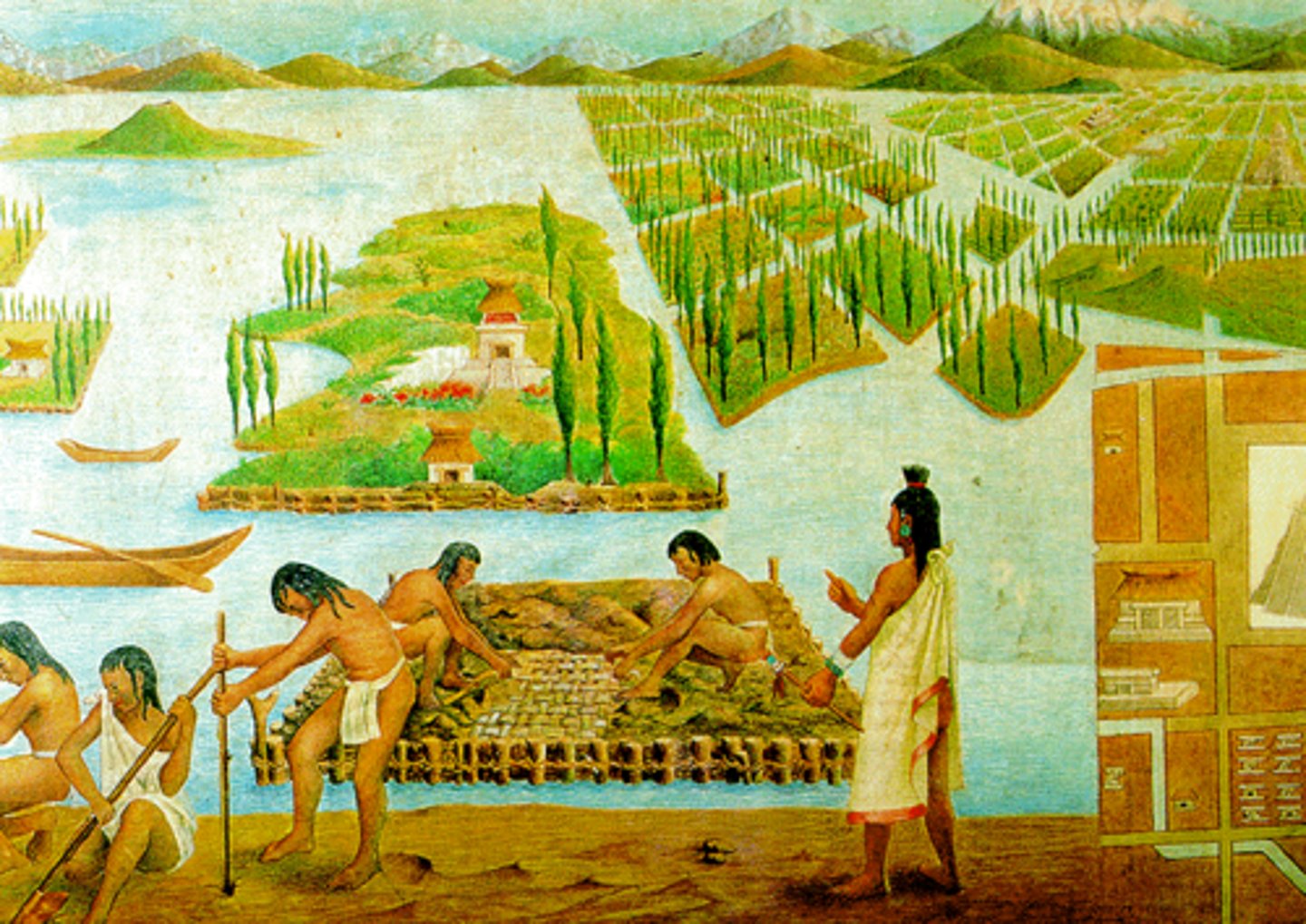
5. Tenochtitlan
-Capital City of the Aztec Empire in Mesoamerica, the Aztecs built this city on an island in the middle of a lake surrounded by marsh
-the lake fed them and allowed them to develop the "chinampa" system of agriculture where they grew maize (corn) year around
-The lake also served as a defense, as warriors constantly patrolled the bridges leading to the city.
-________________ was a massive center of trade; the Aztecs made all of the neighboring tribes pay them tribute, so the neighboring tribes were always sending them textiles (cloths), jewelry made out of gold and silver, and food
-the Spaniards were astonished by the beauty of the city when they saw it with Conquistador Hernan Cortes
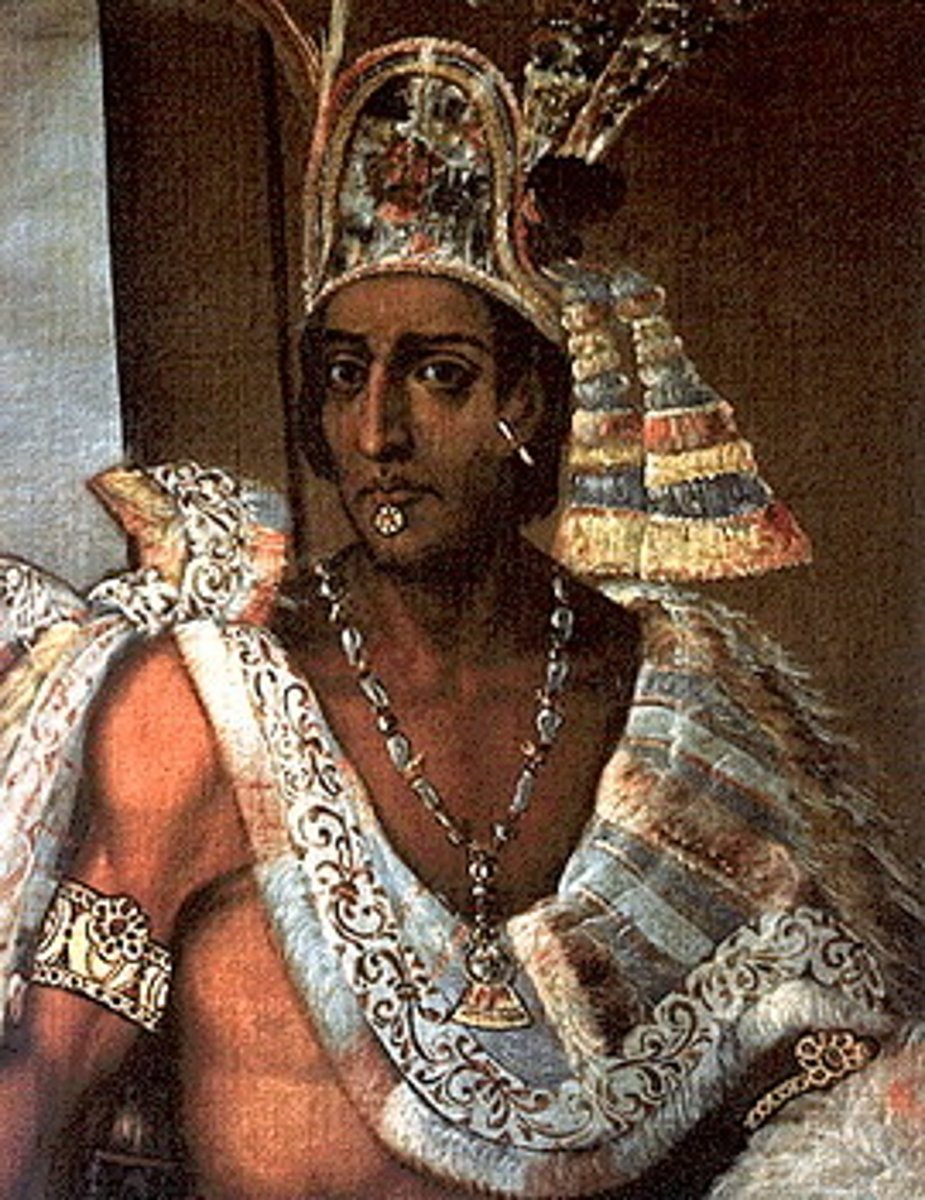
6. Moctezuma
-Aztec ruler who was taken captive by Spanish Conquistador Hernan Cortes, he actually "ruled" from captivity before being killed
-He is THE Major ruler you need to know for the Aztecs
-Before Cortes, conquered far and wide and expanded the Aztec empire
-Was incredibly rich, tons of gold and other goods
-As with most Aztecs, noted for personal cleanliness and hygiene, often bathed twice a day with natural soaps and herbs

7. Tribute
-Once they conquered a tribe or city state, the Aztecs made their subjects pay ______________
-The tribes and city states the Aztecs conquered were forced to give them things like food crops, rabbit-fur blankets, jewelry, and obsidian knives
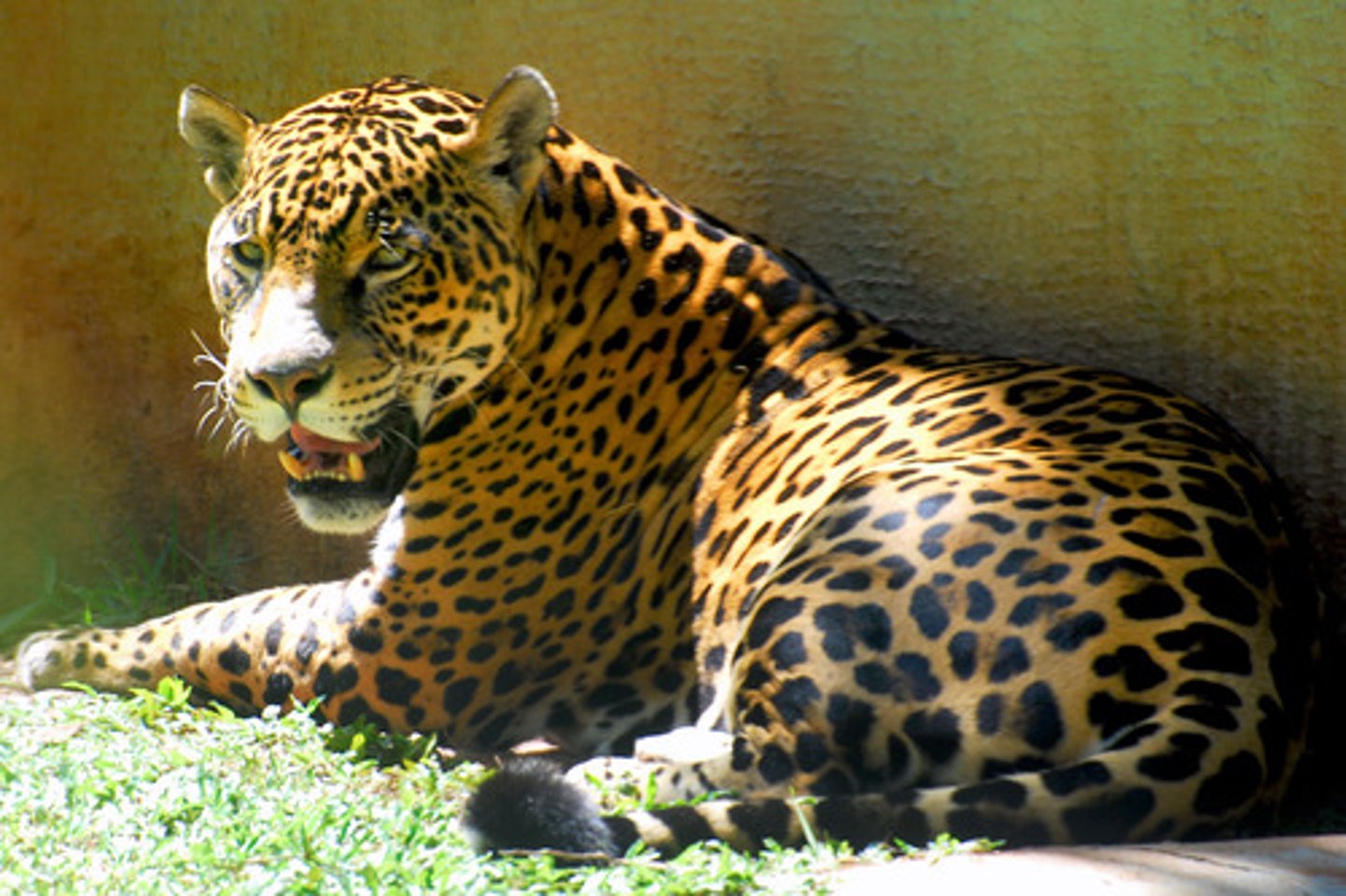
-One of the most valuable things subjects had to give the Aztecs was jaguar skins, as jaguars were the most powerful and dangerous animals in the jungle
-At the height of their power, 500 city states paid tribute to the Aztecs, with over 5,000,000 people governed

8. Aztec Trade in Mesoamerica
-The Aztecs made all of their subjects pay them tribute in the form of goods
-This meant that trade was really increased in the Aztec Empire, helping spread goods, technology, and other things in Mesoamerica
-Some of the common goods traded were textiles (cloth), jewelry, shells, pottery, food crops such as maize
-One of the most prized trade item was jaguar skins, as they were the most dangerous and feared predator in the jungle. Other luxury items were bird feathers and gold
-The center of trade was the massive capital city of Tenochtitlan

9. Aztec (Mexica) Political Control
-Unlike the Incans, the Aztecs didn't use government officials or bureaucrats
-Basically all they did was conquer people and then make them pay tribute
-The Aztecs would conquer neighbors and enslave them. The enslaved persons [slaves] would build pyramids and other stuff for the Aztecs
-Also unlike the Mayans and Aztecs, there was no city-states or local government. Once a tribe was conquered, a tribe could still keep its own government as long as it payed tribute on time
-If any tribe rebelled, they would be crushed by the Mexica/Aztec warriors
-At its high point, 500 city-states sent tribute in to Tenochtitlan
![<p>-Unlike the Incans, the Aztecs didn't use government officials or bureaucrats</p><p>-Basically all they did was conquer people and then make them pay tribute</p><p>-The Aztecs would conquer neighbors and enslave them. The enslaved persons [slaves] would build pyramids and other stuff for the Aztecs</p><p>-Also unlike the Mayans and Aztecs, there was no city-states or local government. Once a tribe was conquered, a tribe could still keep its own government as long as it payed tribute on time</p><p>-If any tribe rebelled, they would be crushed by the Mexica/Aztec warriors</p><p>-At its high point, 500 city-states sent tribute in to Tenochtitlan</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/234ade08-ff1c-47bb-8295-94021fb47735.jpg)
10. Tenochtitlan's Market
-Because of the Tribute System, neighboring tribes always had to send goods to the Aztecs. So there was always things like textiles (cloth), gold and silver jewelry, food crops like maize, and jaguar skins being sent to the Aztecs
-Enslaved persons [slaves] were bought and sold here. The Aztecs conquered neighboring tribes and enslaved them. Some of those enslaved persons could be used in human sacrifice
-In this market in Tenochtitlan, you would see trade in textiles (cloths), gold and silver jewelry, and food like maize
-You would also smell fresh herbs, hot beverages and clean soaps and medicinal herbs
![<p>-Because of the Tribute System, neighboring tribes always had to send goods to the Aztecs. So there was always things like textiles (cloth), gold and silver jewelry, food crops like maize, and jaguar skins being sent to the Aztecs</p><p>-Enslaved persons [slaves] were bought and sold here. The Aztecs conquered neighboring tribes and enslaved them. Some of those enslaved persons could be used in human sacrifice</p><p>-In this market in Tenochtitlan, you would see trade in textiles (cloths), gold and silver jewelry, and food like maize</p><p>-You would also smell fresh herbs, hot beverages and clean soaps and medicinal herbs</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ad287783-3761-4ccd-b8c8-8c5e703ec575.jpg)
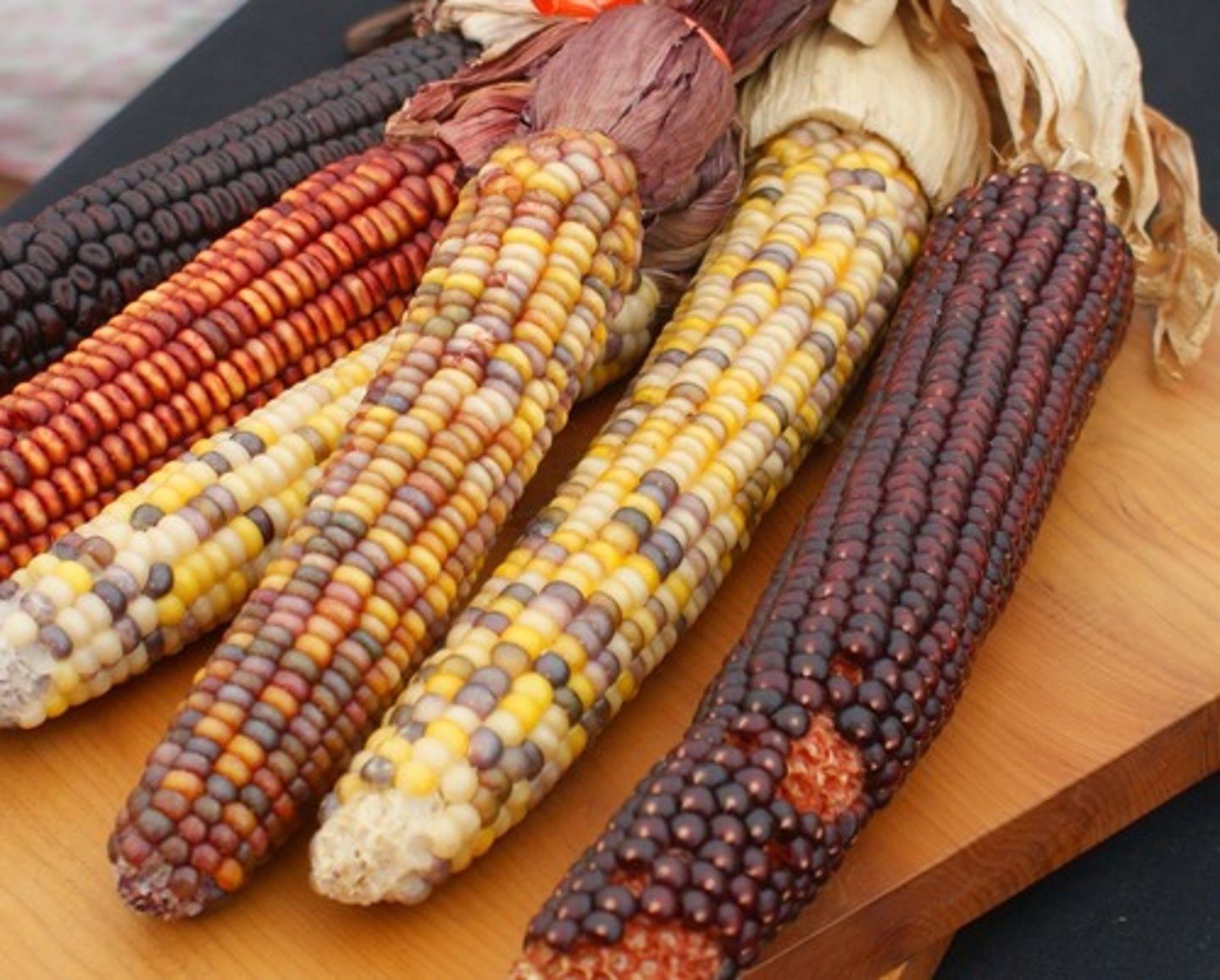
11. Maize
-The major food crop that spread through the Mayan, Aztec, and Incan empires through trade
-A type of corn, this was the most important food crop in Mesoamerica
-High in calories, it helped native populations to grow.

12. Human Sacrifice
-The Aztecs, Incans, and Mayans all did this to varying degrees [different amounts]
-In particular, the Aztecs believed that this was necessary to please the gods and keep the crops growing
-Captured warriors or conquered tribespeople would be killed in a religious ritual in order to please the gods
-Their blood would be seen as a symbol of giving moisture to the earth for crops; when it wasn't raining, sacrifices would increase with the hope that sacrifice of blood would please the gods who would make it rain
![<p>-The Aztecs, Incans, and Mayans all did this to varying degrees [different amounts]</p><p>-In particular, the Aztecs believed that this was necessary to please the gods and keep the crops growing</p><p>-Captured warriors or conquered tribespeople would be killed in a religious ritual in order to please the gods</p><p>-Their blood would be seen as a symbol of giving moisture to the earth for crops; when it wasn't raining, sacrifices would increase with the hope that sacrifice of blood would please the gods who would make it rain</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c513c97b-2c40-4199-9d66-c324d4026ebc.jpg)
13. Aztec Personal Hygiene + Cleanliness
-The Aztecs were remarkable for their personal hygiene and cleanliness.
-The Aztecs went to great lengths and used engineering to provide clean water for regular drinking and bathing for their people, using natural herbs and soaps such as the amolli plant to bath daily
-The Aztecs employed over a thousand public servants to sweep the streets and clean the city of Tenochtitlan every night
-used steam lodges called temazcal for further cleaning
-This was in contrast to the Europeans at the time, who were known for lack of hygiene/disease carrying. The Spanish were shocked at the cleanliness of the Aztecs when they arrived in what is now known as Mexico

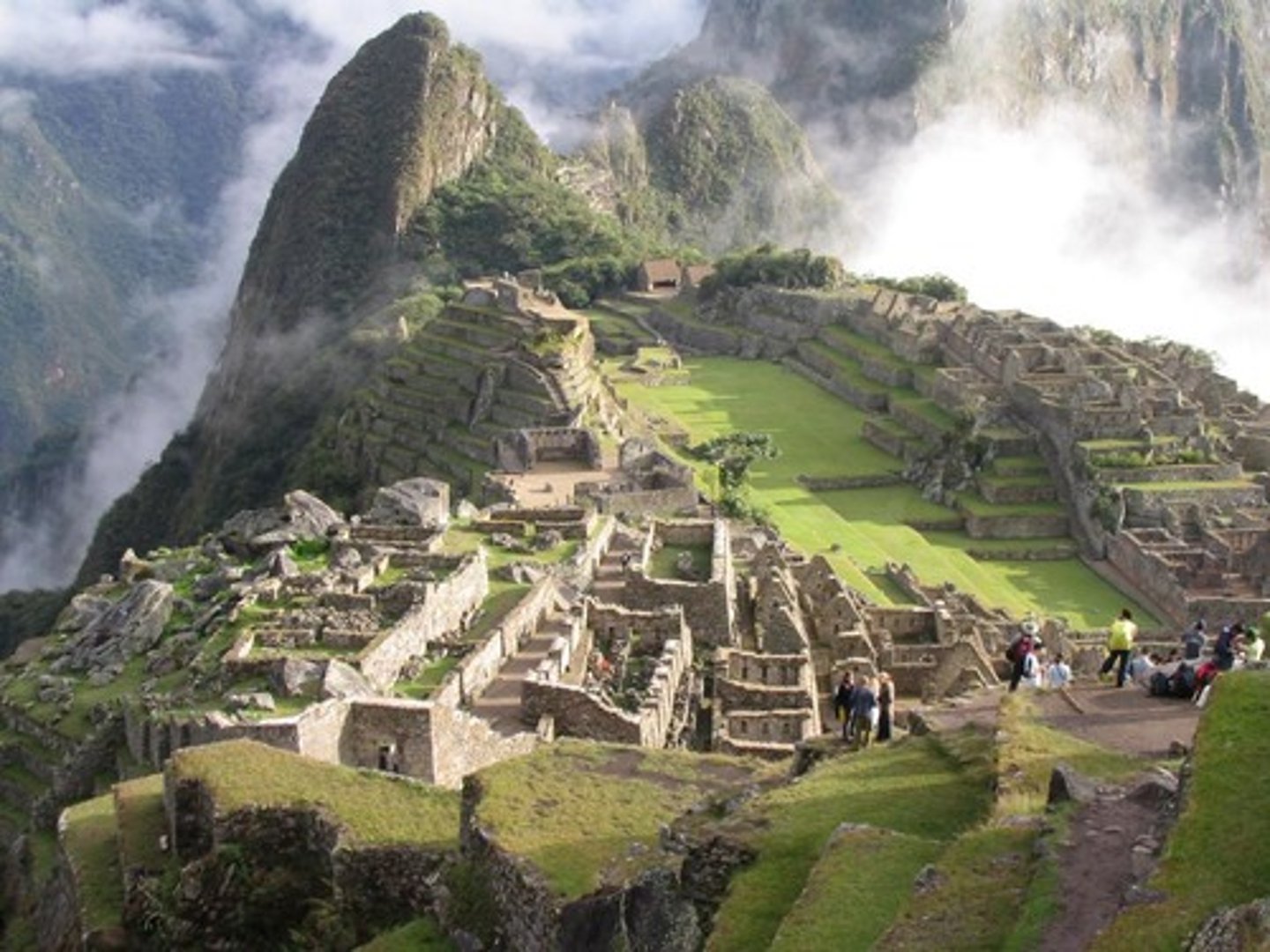
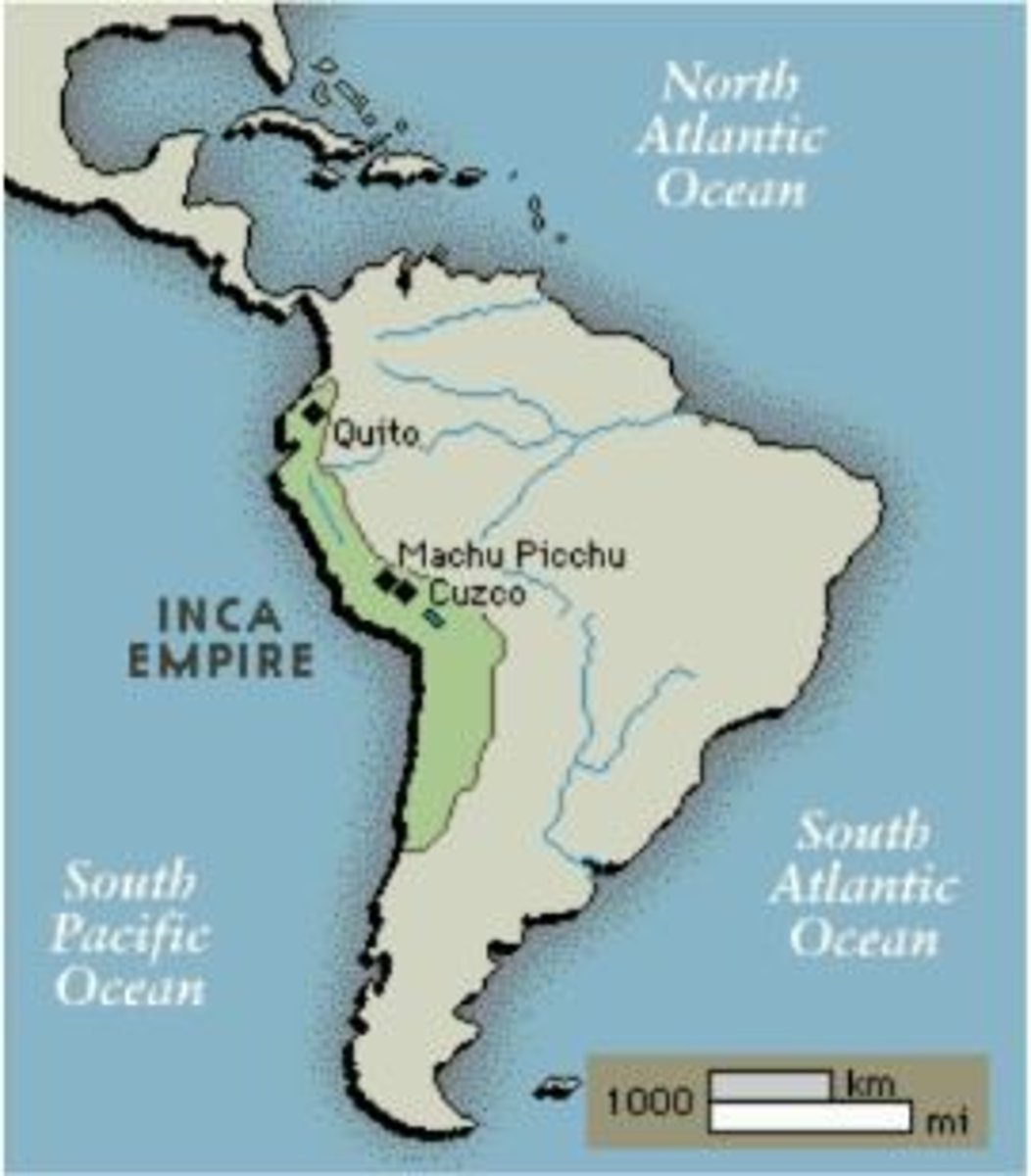
14. The Incan Empire 1430 - 1530 CE
-Largest empire in South America during Era 1, 1200-1450 CE
-Known for its great system of roads, architecture and engineering, advanced record keeping and medical practices, and very belligerent [warlike] people
-Letter "D" on the map image
-Strict social structure and social classes
-Used the Quipu system of record keeping to keep track of economy and politics
-Beautiful legendary city at Machu Picchu and Capital at Cuzco
-Very rich, lots of silver + advanced architecture and engineering [building large structures]
-Brought down by the Spanish Conquistador Francisco Pizarro
![<p>-Largest empire in South America during Era 1, 1200-1450 CE</p><p>-Known for its great system of roads, architecture and engineering, advanced record keeping and medical practices, and very belligerent [warlike] people</p><p>-Letter "D" on the map image</p><p>-Strict social structure and social classes</p><p>-Used the Quipu system of record keeping to keep track of economy and politics</p><p>-Beautiful legendary city at Machu Picchu and Capital at Cuzco</p><p>-Very rich, lots of silver + advanced architecture and engineering [building large structures]</p><p>-Brought down by the Spanish Conquistador Francisco Pizarro</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c266e029-0321-4961-aa8f-ca50e910913a.jpg)
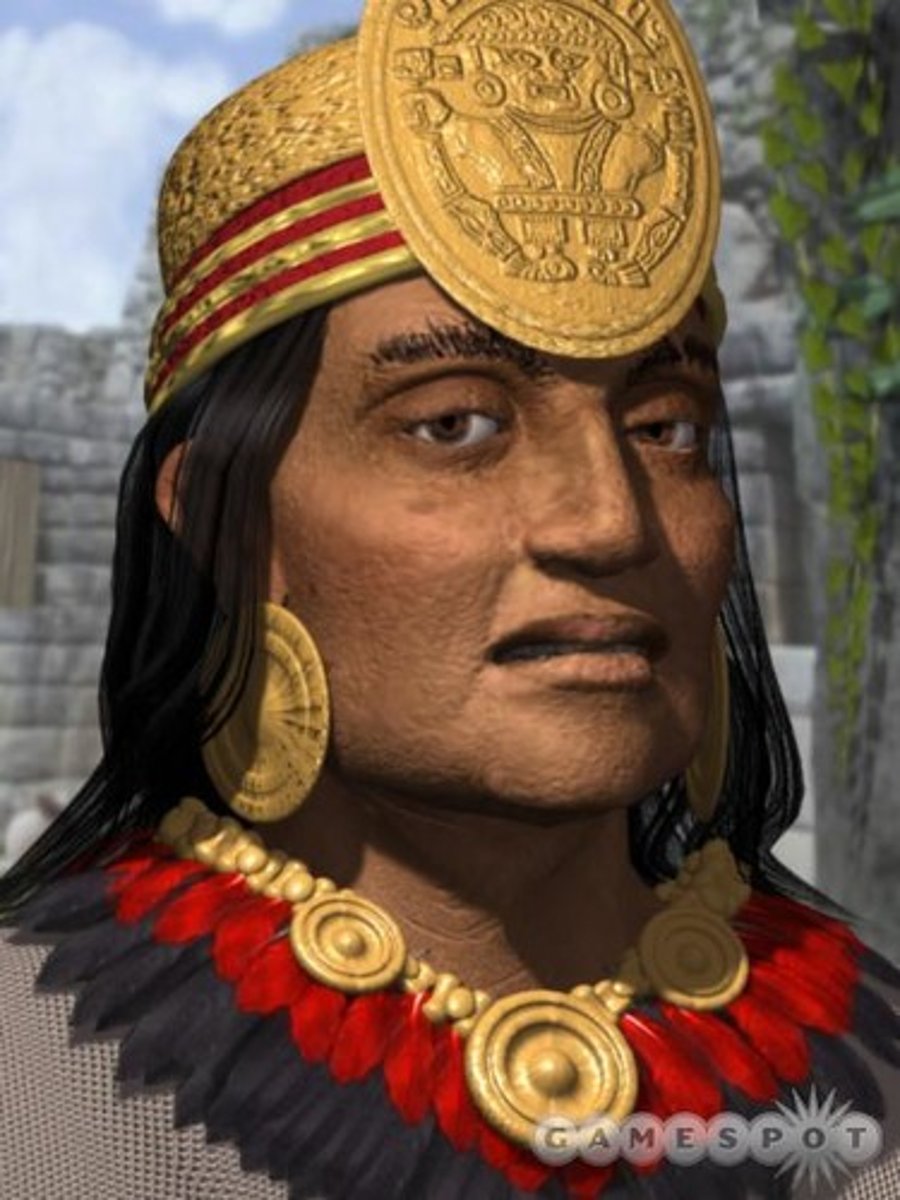
15. Pachacuti
-Founding ruler of the Incan empire in 1430
-Great military general and leader, took over several kingdoms and launched an empire
-the famous, beautiful mountain city of Machu Picchu may have been built as his estate
-Helped start the Incan cult surrounding the sun
-Established Cuzco as capital city

16. Incan Political Control
-The Incans ruled as a military elite separate from the people they conquered
-they made the people they conquered fight for them
-The Incans weren't that numerous. If people rebelled against them, they tried to crush them or made them go live in distant parts of the empire
-The Incans used a large number of bureaucrats (government officials) who used a system called "quipu" to help them keep track of responsibilities

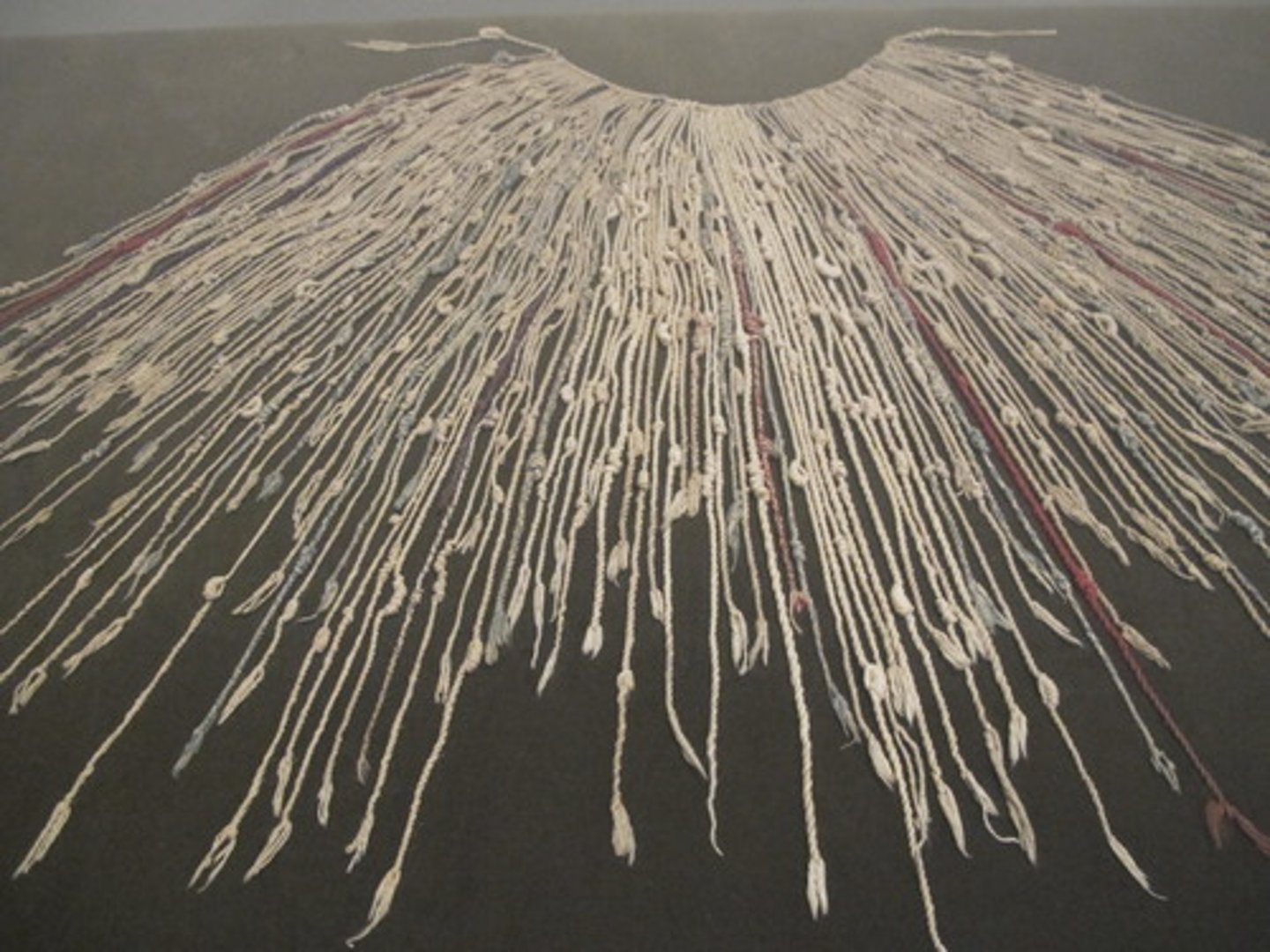
17. Quipu
-This was a system used by Incan bureaucrats (government officials) that helped them keep track of responsibilities and records
-it was a string of cords of different lengths and colors. Officials would tie knots on certain cords in order to help them keep track of population sizes, taxes, and labor services that were owed to the government

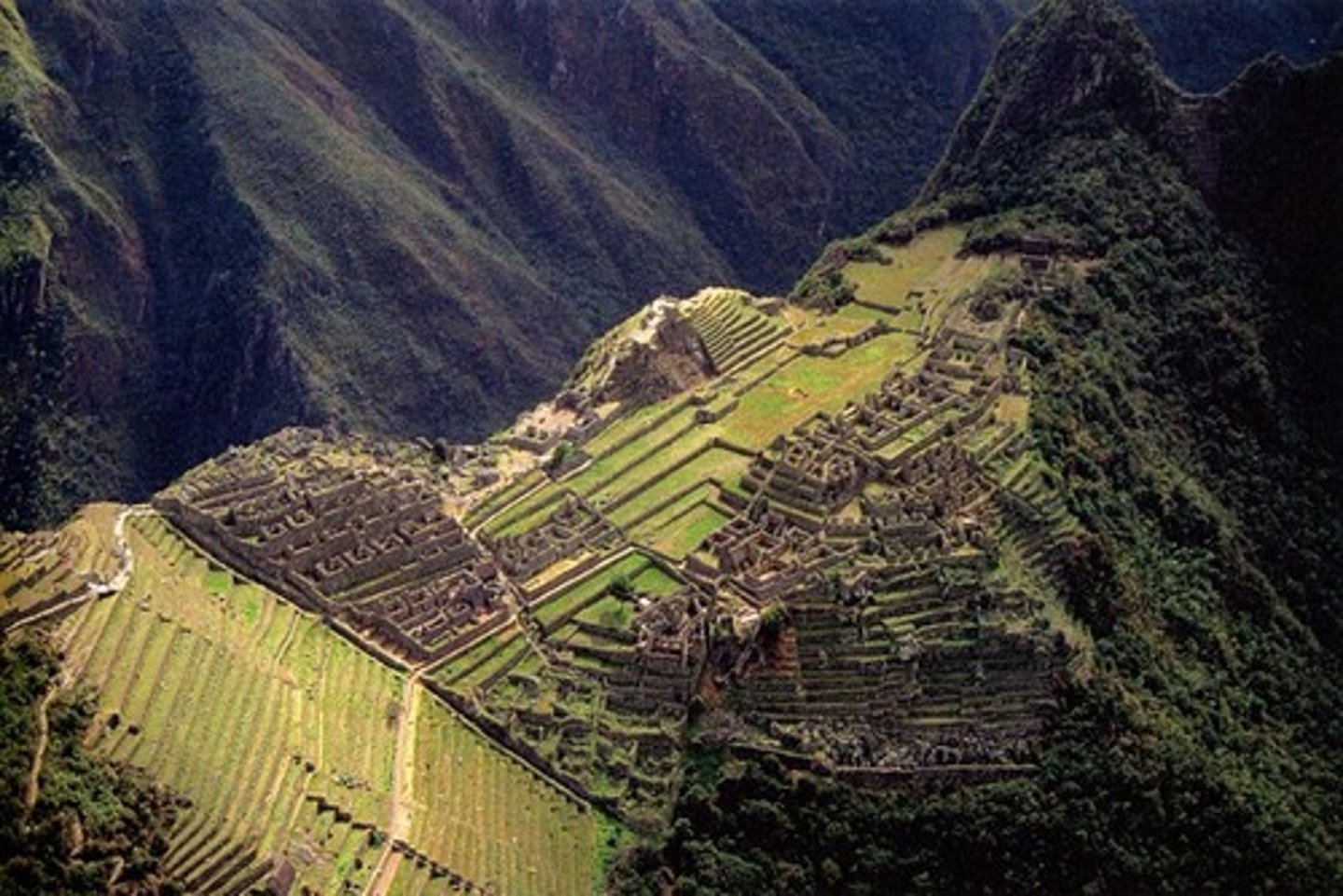
18. Cuzco
-Capital city of the Incan Empire, it was the religious and ceremonial center of the empire
-population over 100,000 people
-This is where the Incan rulers and nobles lived in grand palaces
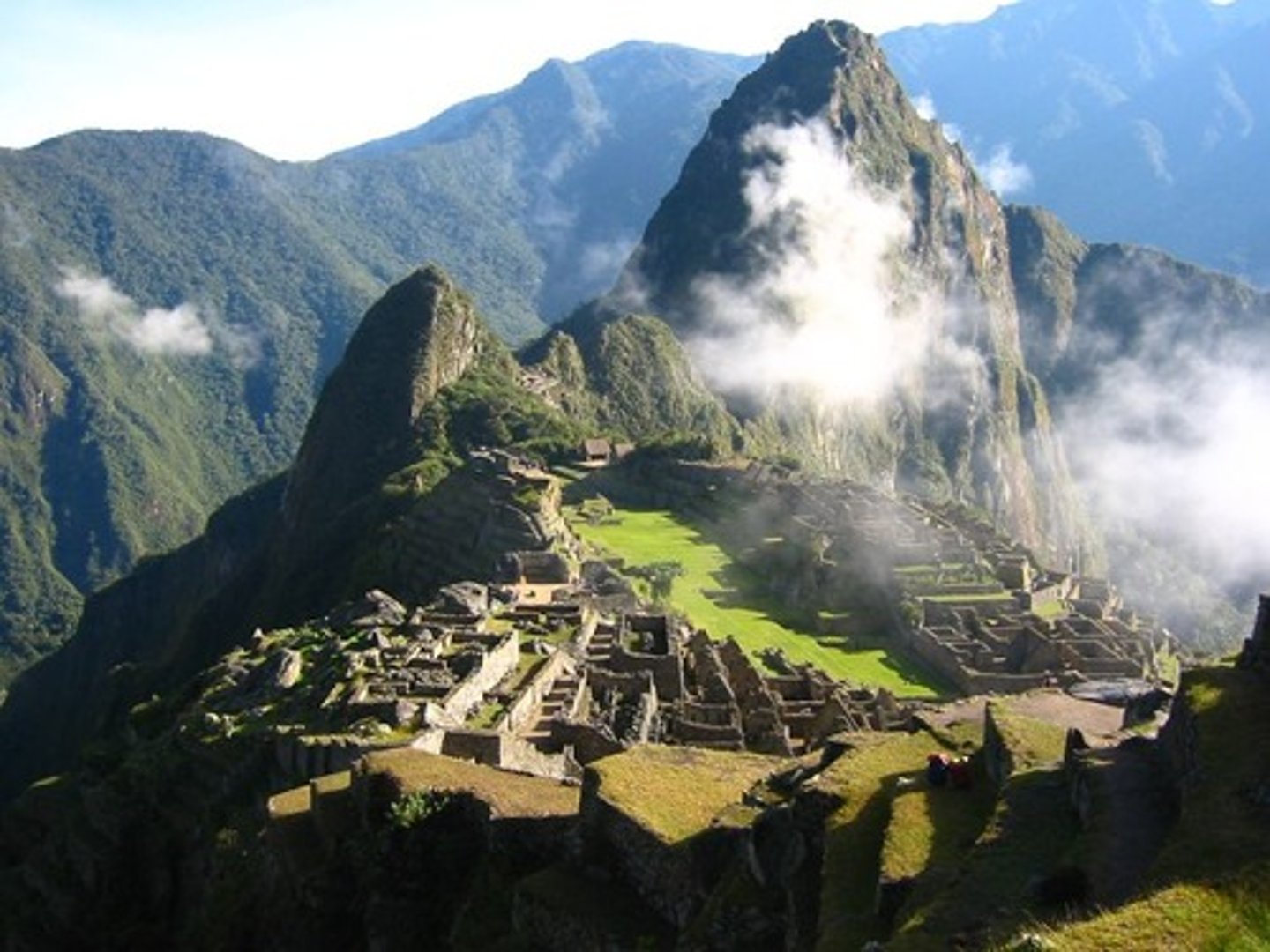

19. Incan Roads
-The Incans built the best ______________ in all of the Americas
-These _______________ were over 25,000 miles long and were HUGE for helping with trade in the empire
-When the Spanish came in the 1500's, they were amazed at how nice and wide they were, shaded by trees
-If an Incan ruler wanted fresh seafood, runners were sent from Cuzco for 320 miles along these ________ and they had their fish in two days

20. The Mit'a System
-The Incans forced every tribe they conquered to give up some of their men for a period of time each year to complete projects building roads, cities, and temples
-After the Spanish conquered the Incans then used the same system to get labor for silver mining
-One out of every Seven men in a tribe had to go work for four months out of the year as enslaved persons [slaves] in the silver mines
-Any town who didn't send 1/7th of their male population would be severely punished
![<p>-The Incans forced every tribe they conquered to give up some of their men for a period of time each year to complete projects building roads, cities, and temples</p><p>-After the Spanish conquered the Incans then used the same system to get labor for silver mining</p><p>-One out of every Seven men in a tribe had to go work for four months out of the year as enslaved persons [slaves] in the silver mines</p><p>-Any town who didn't send 1/7th of their male population would be severely punished</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ebde0c03-620b-4eb3-add9-449c4ce46980.jpg)
21. Incan Trade
-Under the Incans, trade moving from north to south through along the Andes mountains increased dramatically
-Pottery, textiles (cloth), and gold and silver jewelry, food goods, and animal furs traveled along the Incan trade routes in the Incan Empire
-There were no merchants in the Incan Empire; all of the trade in the Incan Empire was run by the government
22. Chosen Women of the Incas
-Aklya Kona or "Virgins of the Sun," in Inca religion, women who lived in temple convents under a vow of chastity
- Their duties included the preparation of ritual food, the maintenance of a sacred fire, and the weaving of garments [clothes] for the emperor and for ritual use.
-At the time of the Spanish conquest in the early 1500's the Chosen Women numbered several thousand and were governed by a high priestess, the Coya Pasca, a noblewoman who was believed to be the earthly lover of the sun god.
-The Chosen Women, not of noble birth, were village girls selected by officials for their beauty and talent; they were chosen at the age of 8 or 10 and closed up in the temples, which they were not allowed to leave for six or seven years.
-Of these girls, some became sacrificial victims, whereas others were sometimes made imperial concubines [girlfriends to the Emperor] or the wives of nobles.
![<p>-Aklya Kona or "Virgins of the Sun," in Inca religion, women who lived in temple convents under a vow of chastity</p><p>- Their duties included the preparation of ritual food, the maintenance of a sacred fire, and the weaving of garments [clothes] for the emperor and for ritual use. </p><p>-At the time of the Spanish conquest in the early 1500's the Chosen Women numbered several thousand and were governed by a high priestess, the Coya Pasca, a noblewoman who was believed to be the earthly lover of the sun god. </p><p>-The Chosen Women, not of noble birth, were village girls selected by officials for their beauty and talent; they were chosen at the age of 8 or 10 and closed up in the temples, which they were not allowed to leave for six or seven years. </p><p>-Of these girls, some became sacrificial victims, whereas others were sometimes made imperial concubines [girlfriends to the Emperor] or the wives of nobles.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff77ab60-cfc2-415b-8ee1-5164e5aecb19.jpg)
23. Hernan Cortes and Francisco Pizarro, Invasion of the Spanish Conquistadors in 1520
-During Era 1, 1200 CE to 1450 CE, many empires fell due to invasion
-This happened and the Incans and Aztecs both were taken down
-the Conquistadors Cortes and Pizarro invaded and allied with local tribes that didn't like the Aztecs and Incans
-Cortes brought down the Aztecs; Pizarro invaded and brought down the Incans in 1530;
-Both Spanish Conquistadors
-Both used steel, horses, guns, and alliances with local peoples who already had resentment against the Aztecs and Incans
-Collision at Cajamarca--famous battle between ______________________ and the Incans where a much smaller Spanish forced used steel and horses to overcome a much larger Incan army
-Once this happened, the Incans and Aztec Empires were devastated by diseases and then defeated by superior weapons

24. Mayan City-States
-The Mayan Kingdom was divided into dozens of city-states; this meant that there was a central city, with a population of people organized around the city in the surrounding area
-The largest city-state was Tikal, with a population around forty thousand people
-Each city state had it's own king and usually each city had large religious temples to the gods
-The city-states would often war and fight with each other; when one city-state would conquer another, the losers would be enslaved and turned into enslaved persons [slaves]; some enslaved persons would have to work in agriculture, while others could be sacrificed at the temples as part of religious ceremonies
-Most Mayan kings of the city-states were named after the most dangerous predator of the jungle, the Jaguar. Jaguar Paw, Shield Jaguar, Bird Jaguar, etc.
-THe populations of the city-states were usually between ten and thirty thousand people
-City-states is a similar political structure to ancient Mesopotamia, which had twelve city-states
![<p>-The Mayan Kingdom was divided into dozens of city-states; this meant that there was a central city, with a population of people organized around the city in the surrounding area</p><p>-The largest city-state was Tikal, with a population around forty thousand people</p><p>-Each city state had it's own king and usually each city had large religious temples to the gods</p><p>-The city-states would often war and fight with each other; when one city-state would conquer another, the losers would be enslaved and turned into enslaved persons [slaves]; some enslaved persons would have to work in agriculture, while others could be sacrificed at the temples as part of religious ceremonies</p><p>-Most Mayan kings of the city-states were named after the most dangerous predator of the jungle, the Jaguar. Jaguar Paw, Shield Jaguar, Bird Jaguar, etc.</p><p>-THe populations of the city-states were usually between ten and thirty thousand people</p><p>-City-states is a similar political structure to ancient Mesopotamia, which had twelve city-states</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/802536f9-db6f-4b21-9e23-ed575f7882d2.jpg)
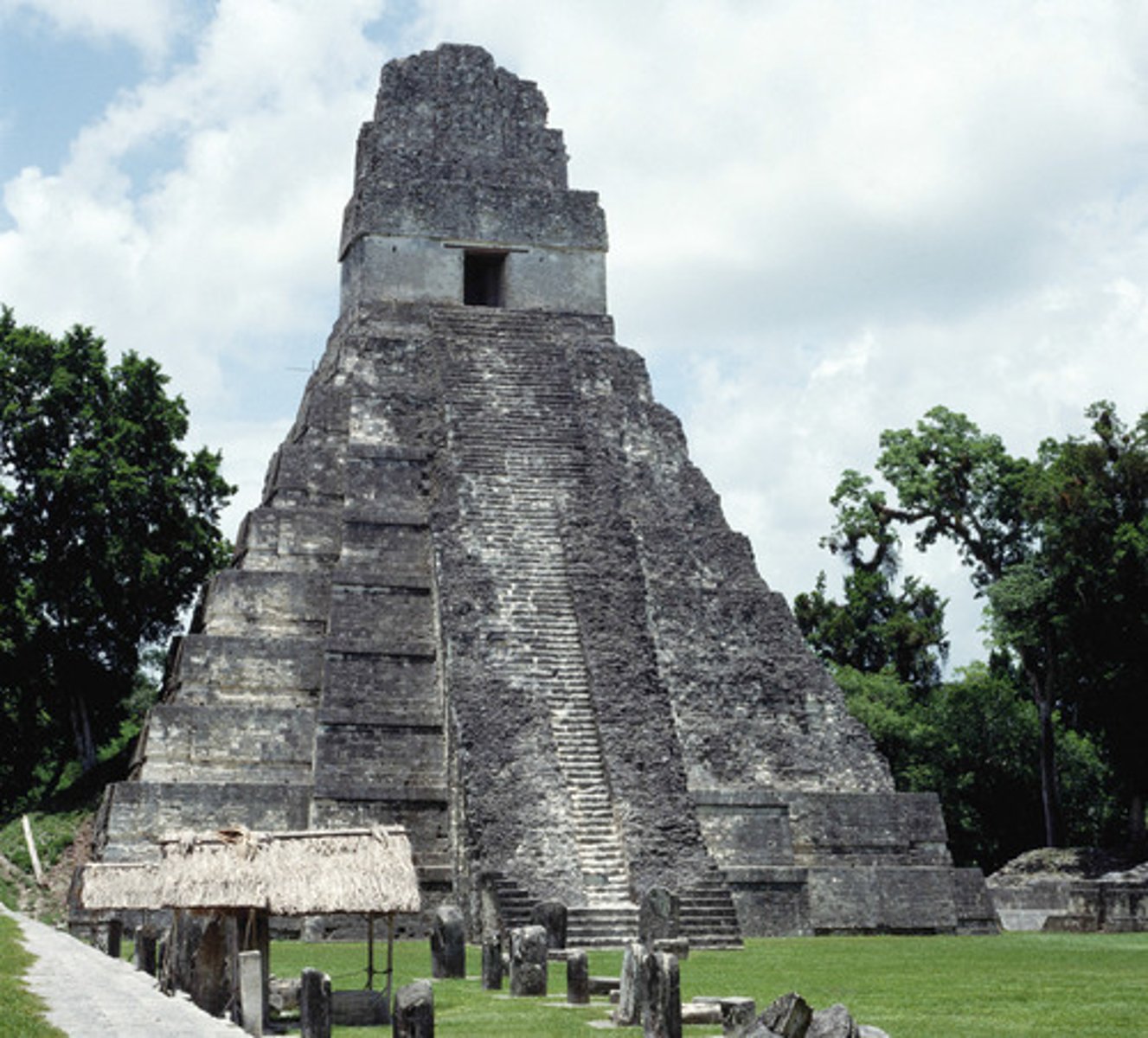
25. Tikal
-Capital city of the Mayan empire
-filled with massive temples along with 40,000 people
-Included massive Temple of the Giant Jaguar
-also had enormous plazas, trading centers, was a big religious and cultural center
-Center of the biggest Mayan City-State
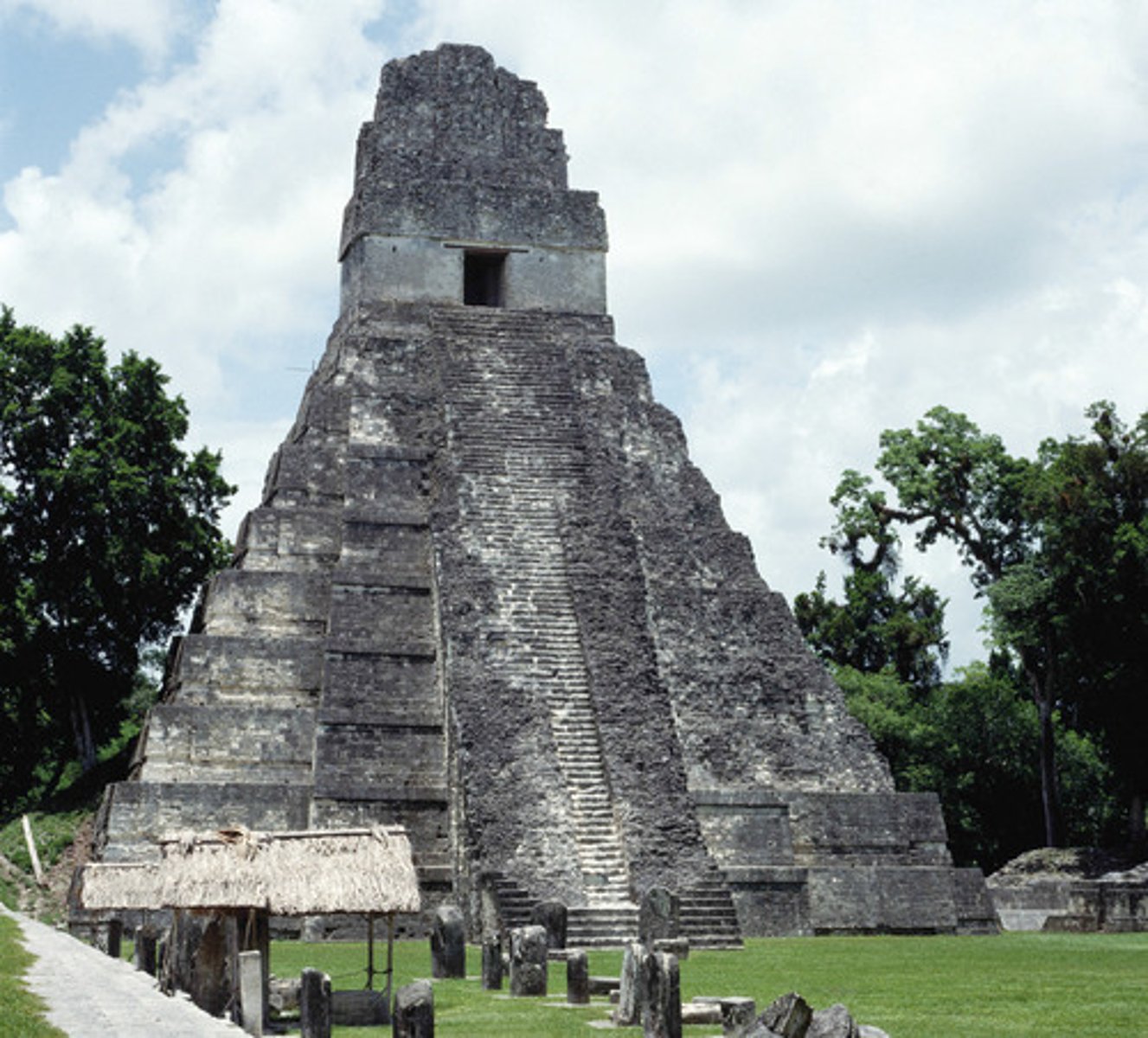

26. Temple of the Giant Jaguar
-Giant Mayan temple in the capital city of Tikal
-Over 150 feet high, worshipped by population of 40,000
-Center of the biggest Mayan City-State
