Ecology.
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Ecology
the branch of biology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings
Organisms depend on their environment for:
food
shelter
breeding site
Species
A group of organisms that can potentially interbreed to produce fertile, viable offspring
Population
A group of organisms of the same species, living in the same area at the same time
Community
A group of populations living together and interacting with each other within a given area
Habitat
The environment in which a species normally lives, or the location of a living organism
Ecosystem
A community and its abiotic environment (i.e. habitat)
Biomass
•The total mass of a group of organisms – consisting of the carbon compounds contained in the cells and tissues
Biotic factors
Other living things in the environment
mates
prey
predators
Abiotic factors
Non-living factors in the environment
Physical: •Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide ,Light Intensity and Water Availability
Climatic: temperature, humidity
Autotrophes
•organisms that make their organic molecules out of inorganic molecules (plants and some bacteria, via photosynthesis)
Heterotrophic organisms
•Organisms that get their organic molecules by eating other organisms, (animals, fungi and certain bacteria)
Trophic levels
The position an organism occupies within a feeding sequence
•Producers always occupy the first trophic level in a feeding sequence
•Primary consumers feed on producers and hence occupy the second trophic level
- Further consumers (e.g. secondary, tertiary, etc.) may occupy subsequent trophic levels
Heterotrophy - consumers
Ingest organic matter which is living or recently killed
Heterotrophy - detritivores
Ingest non-living organic matter
Heterotrophy - Saprotrophs
Feed on non-living organic matter by secreting digestive enzymes and absorbing the products
Food chain/web
A food chain shows the linear feeding relationships between species in a community
Rule of 10
Energy transfer between organisms is never 100% efficient, usually, the energy transfer from one trophic level to the next is 1/10 of the previous one.
Mutualism
Both species benefit
Commensalism
One benefits, one doesn’t care
Parasitism
One benefits at the other’s expense
Ecological pyramids
Quantitative representations of energy flow
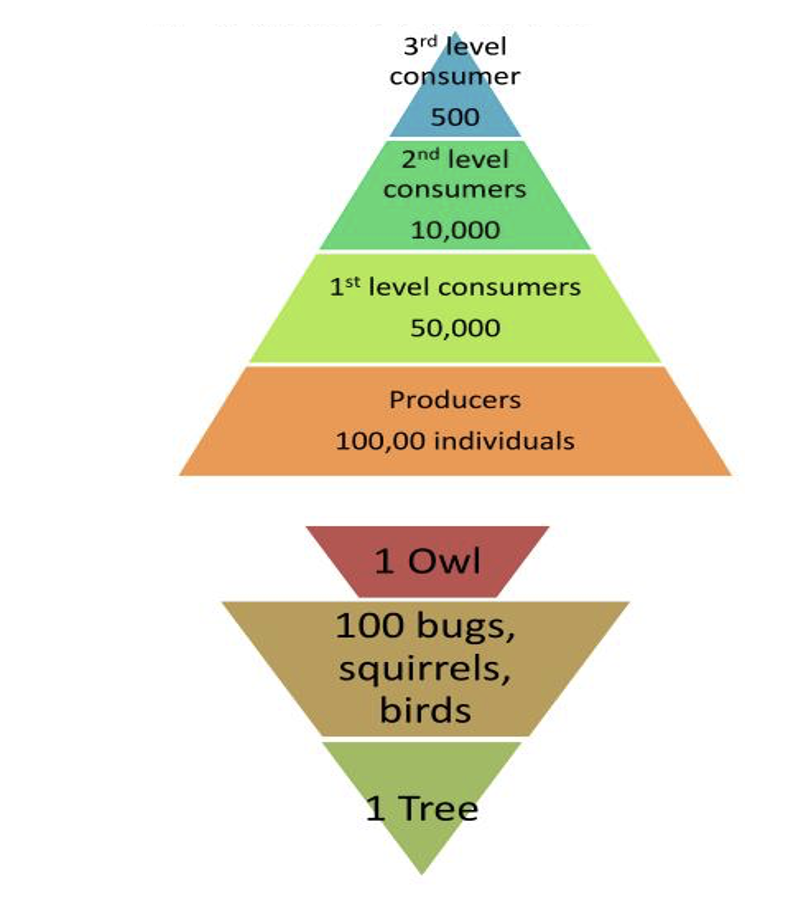
Pyramid of numbers
The relative number of organisms at each stage or trophic level.
Problem: Pyramid can look odd, due to difficulties drawing to scale and enormous numbers of some organisms.
Pyramid of biomass
The total mass of organisms at each stage of a food chain
Each level in the pyramid will be roughly one tenth the size of the preceding level as energy transformations are ~10% efficient
Pyramid of energy
Shows the amount of energy trapped per area in a given time period at each stage of a food chain
These pyramids are always upright in shape, as energy is lost along food chains (either used in respiration or lost in digestion)
Carbon
•Raw material for growth of the cells (fats and proteins)
•Source of energy ( released via oxidisation during respiration eg: carbohydrates and fats)