A101 Part 2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Dynamic Mic
Moving coil mic moves magnet (engine) makes signal through air pressure. Also doesn't need phantom power.
Ribbon Mic
Type of dynamic mic. Uses vertically suspended foil between 2 magnets. Has natively figure of 8 polar pattern
Condenser Mic
Mic has two front plates, with one flexible one being hit with pressure waves. Because signal is low, needs capacitor and phantom power to boost signal.
Omnidirectional
Polar pattern with equal sensitivity to sound from all directions
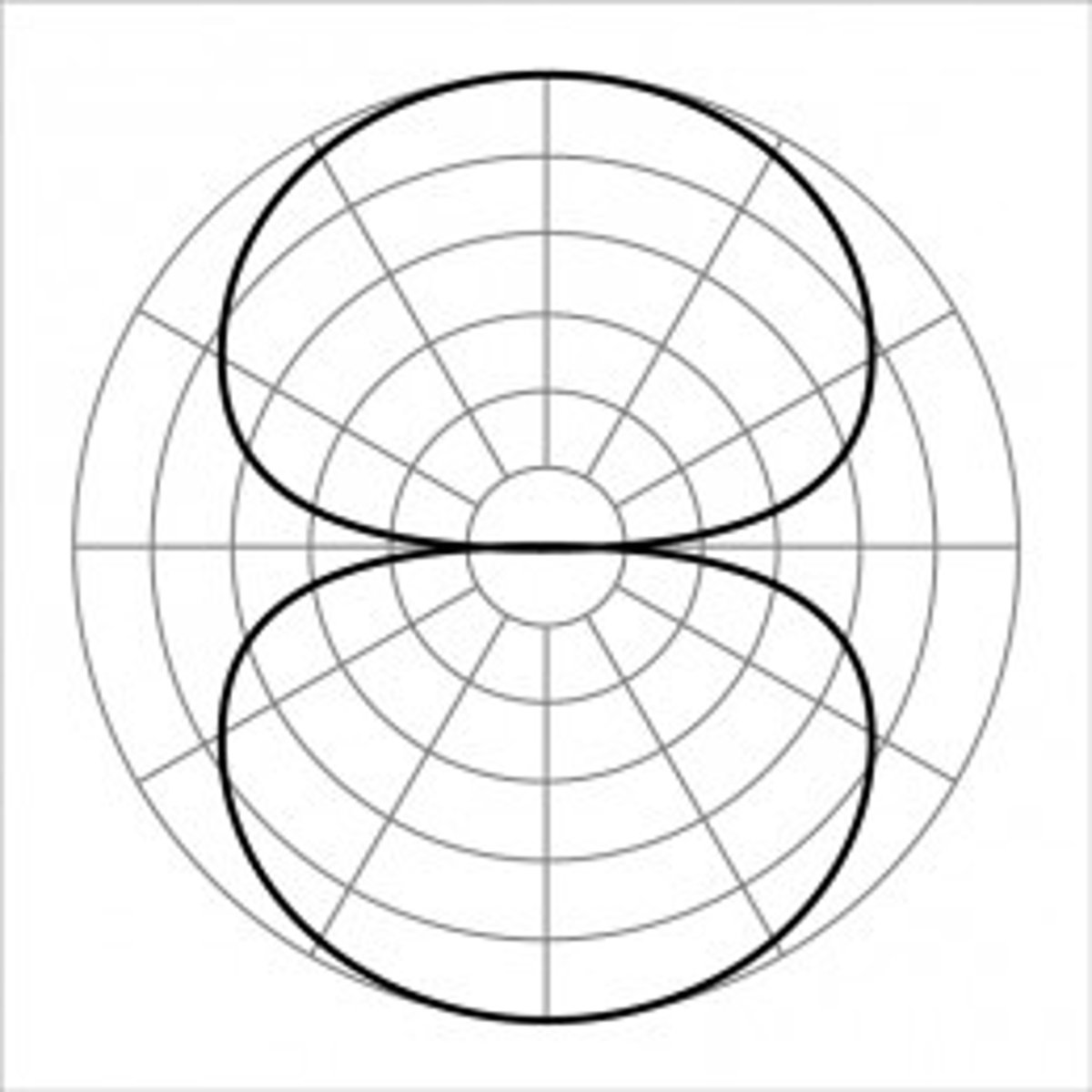
Figure of Eight
Polar pattern sensitive to sounds coming from front and rear
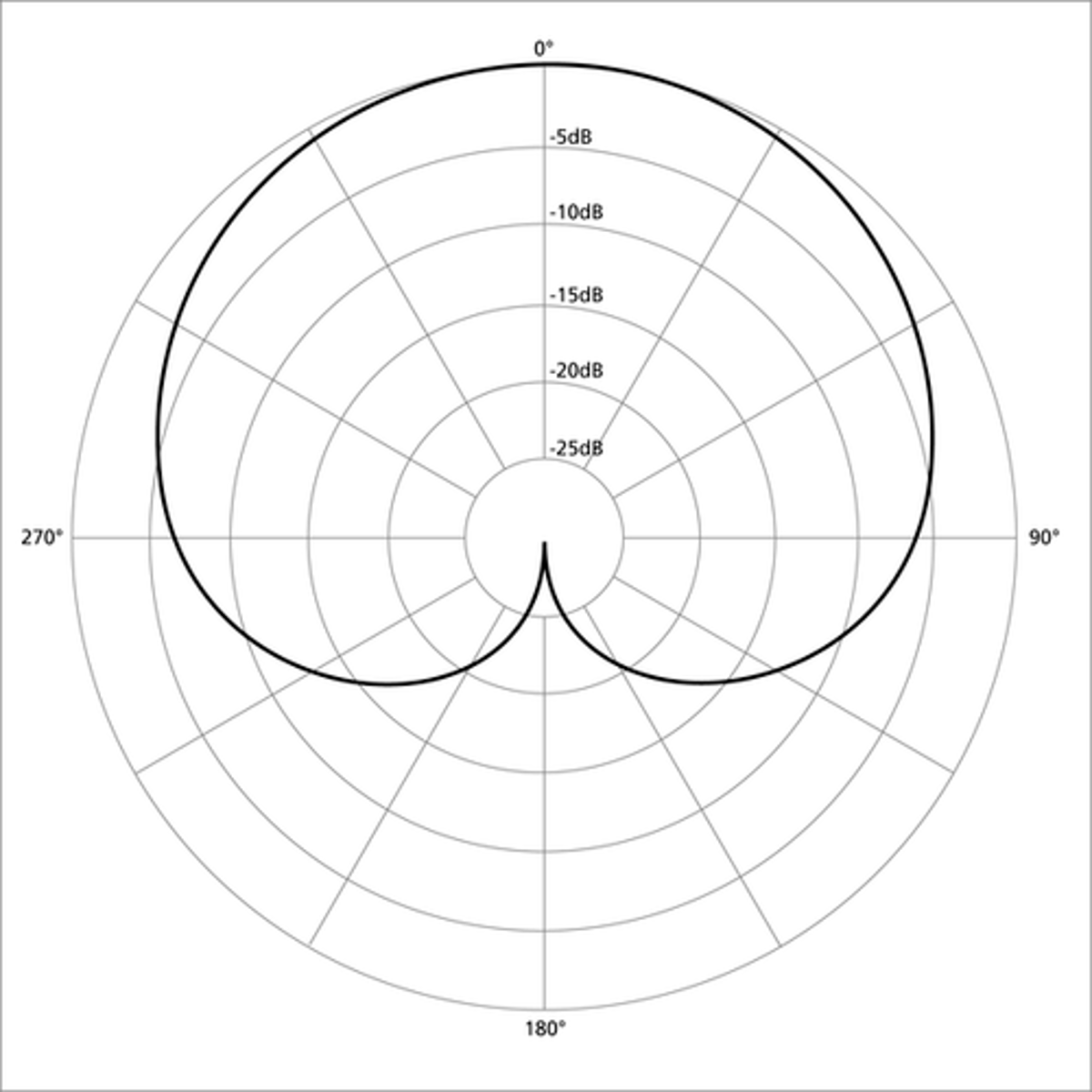
Cardioid
Polar pattern sensitive to sounds mainly from the front
Creating Cardioid Patterns
1: Combining an omnidirectional and a figure of 8 pattern together produces a cardioid pattern because the negative back lobe cancels with omnidirectional back, making it directional.
2: Create acoustic labyrinth behind a diaphragm to create an inverted signal to cancel out back sensitivity
Sub-, super-, hyper-cardioid
Cardioid polar patterns with varying back lobes
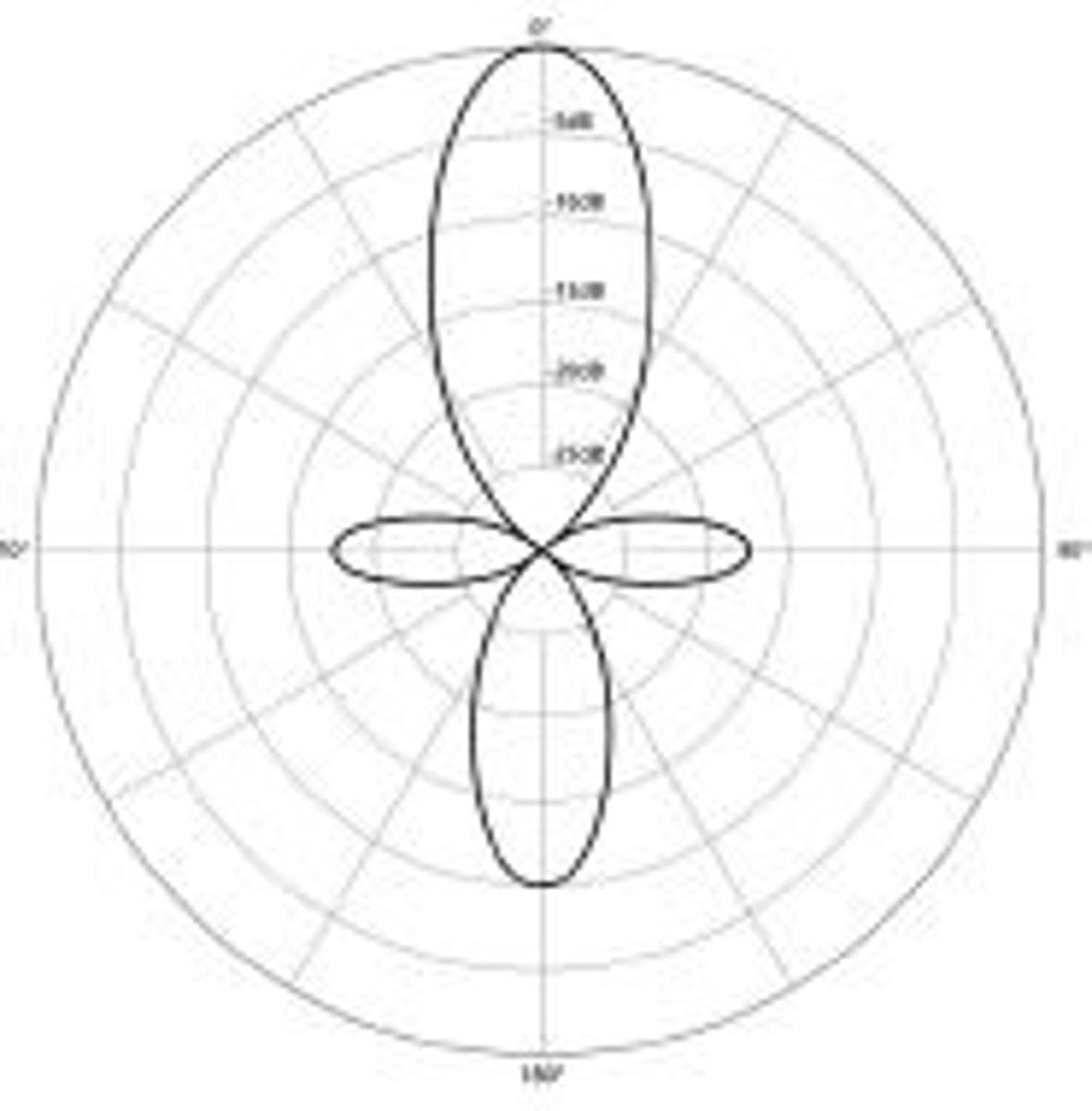
Shotgun
"Lobar" polar pattern, mainly sensitive to front and back, with very limited side sensitivity
What is the head related transfer function?
The shape of the listener's skull effects the sound signal passing through it.
What is phantom image?
sound sources that are perceived where there is none present
What is the advantage of a balanced line?
It rejects noise on a microphone line. It creates this by running a "hot" and an inverted "cold" line, which is then reinvented at the end, cancelling out the noise at the end.
What is phantom power?
A 48V DC current used on condenser mics
Impedance
Combination of resistance and reactance in whole circuit
How much impedance should an output have relative to the input?
About 10x the impedance
What is interaural time difference?
The difference between when sound waves reach one ear before the other determines the direction of the sound
Why does The Microphone Book recommend angling coincident cardioids at 135 degrees?
A wider configuration is more beneficial than a center heavy configuration.
what happens when spaced microphones are placed too far apart?
A "hole in the middle" of the phantom imaging will appear.
What is interaural level difference?
difference between the amplitude level at each ear determines the direction of the sound source.
What are the main 3 sound localization cues?
ITD, ILD, & Sight
Mid-side array
uses forward facing cardioid and a side facing figure of eight microphone.
Spaced stereo array
The stereo image may not be localization precision.
Near-coincident stereo array
Combines amplitude and delay cues to create a stereo image
Coicident stereo array
Responds to amplitude cues only to produce a stereo image
Dynamic Range
6 dB/bit
Quantization distortion
The difference between the actual voltage and the quantized voltage
32 bit float
32-bit float recording is recording a 24-bit audio signal with an additional 8 bits that allow the signal to 'float' louder or softer to retain resolution without clipping. It is a computer format that is used by DAWs when processing audio, it allows signals louder than 0dBFS to be resolved without clipping internally where the audio might clip when output to a 24-bit ADC. There is also a 32-bit float file format that allows resolution to be retained when storing audio. It uses about 50% more space than a 24-bit file and is not compatible with many audio players
Dither
Noise added at the level of the least significant bit to eliminate quantization noise and decorrelate it from the signal. Can increase dynamic range by 2 - 3 bits
Digital clipping
Square wave distortion and aliasing (due to distortion products being greater than the Nyquist frequency)
dBFS
decibels in reference to full scale where 0 is the maximum level
Sample Rate
Frequency Response
Sound cues
Below 700hz = phase difference
Above 2kHz = amp difference
Omnidirectional polar pattern
Cardioid polar pattern
Supercardioid polar pattern
Hypercardioid polar pattern
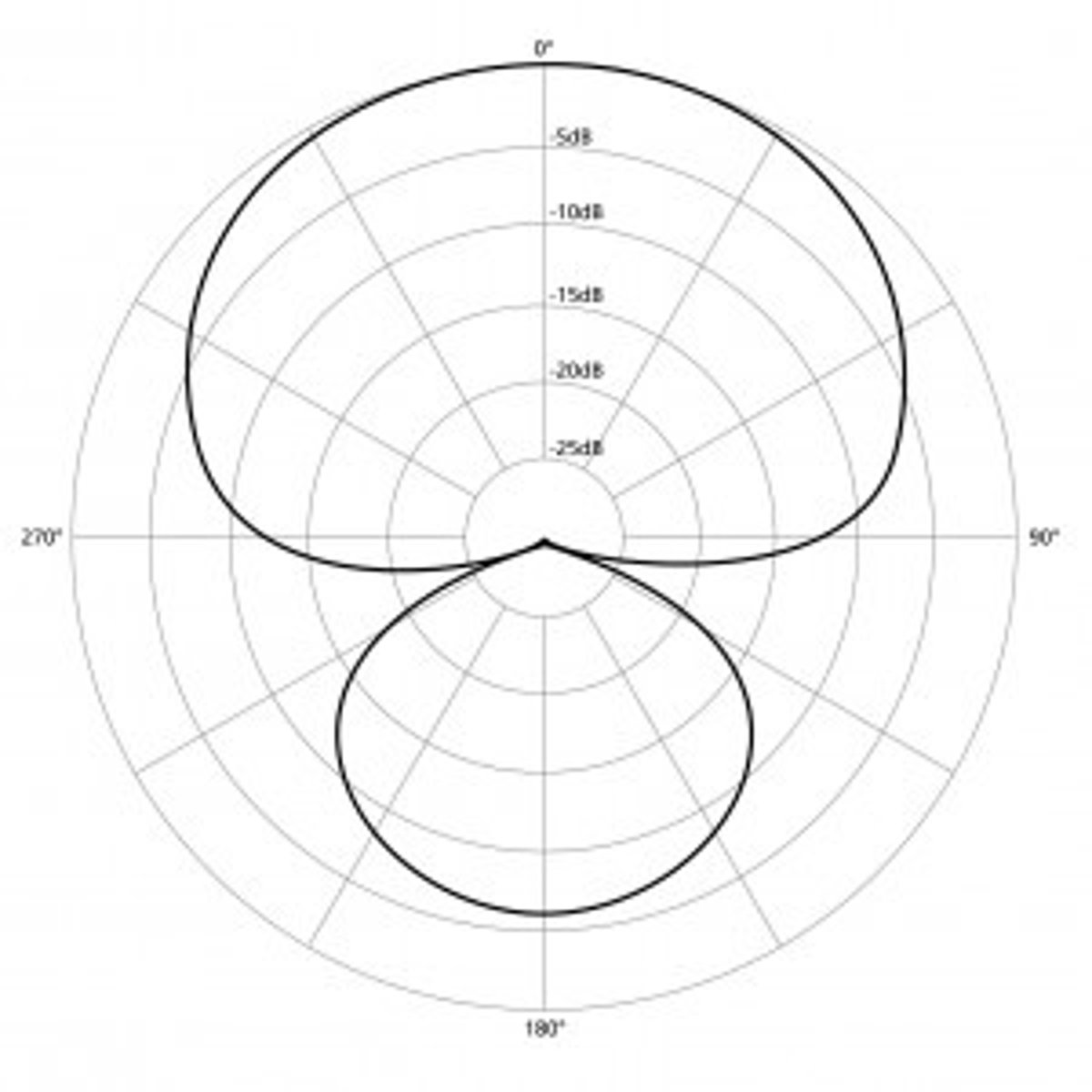
Bidirectional polar pattern
Shotgun polar pattern
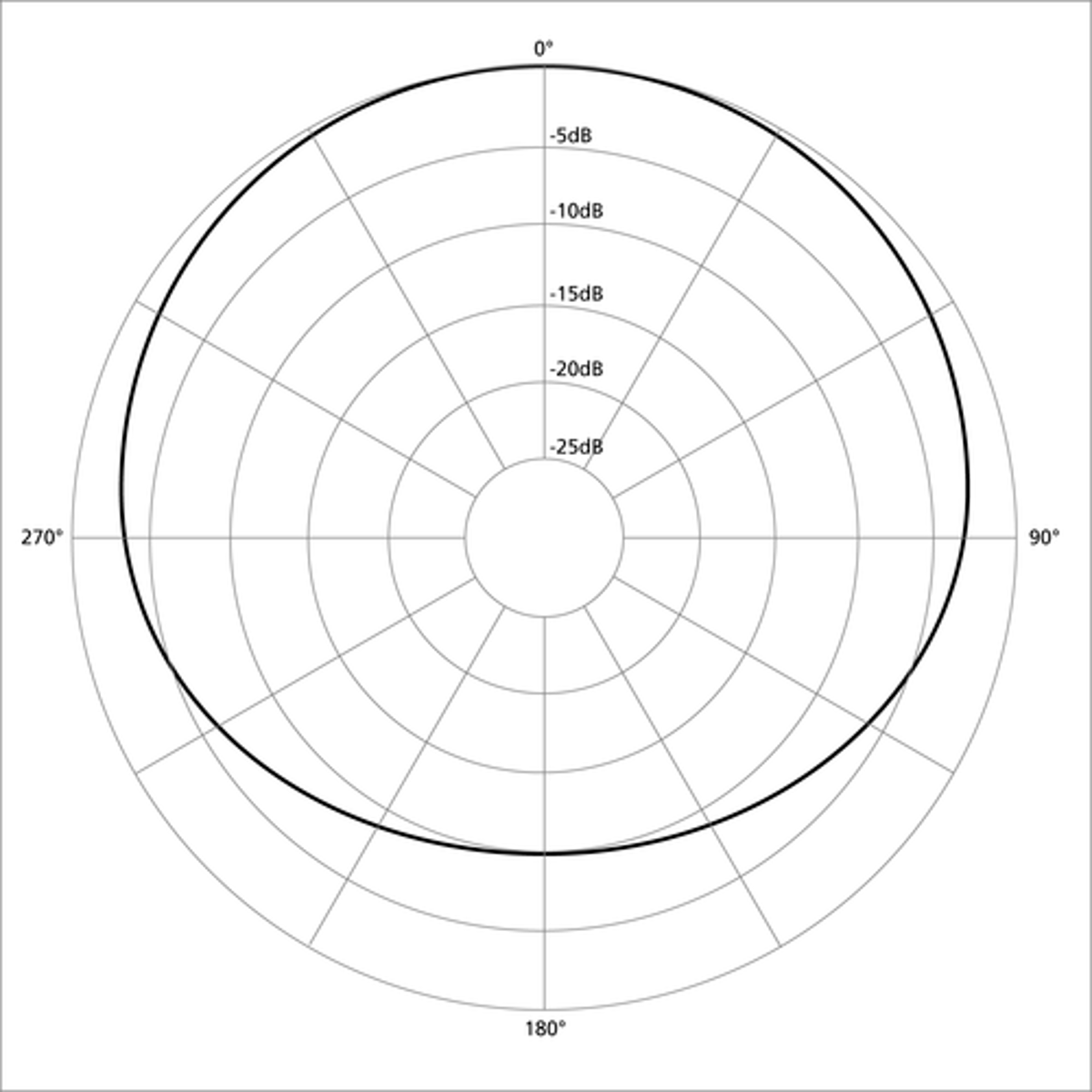
Subcardioid
Nyquist Frequency
1/2 sample rate
Aliasing
'Phantom' frequencies created when a signal above half the sample rate is allowed into, or created within, a digital system.
Quantization
Dynamic Range
Nyquist Theorem
1.For periodic functions, if you sample at a rate that is at least twice as fast as the signal of interest, then no information (data) will be lost upon reconstruction.
2.If you restrict the input signal's bandwidth to less than one-half the sampling frequency, then no errors due to aliasing are possible.
How do we perceive sound cues differently below 700 Hz and above 2 kHz?
Below 700 Hz we perceive a phase difference, above 2 kHz we perceive an amplitude difference
Nominal operating level of dBFS
-20 dBFS
Speaker diagram
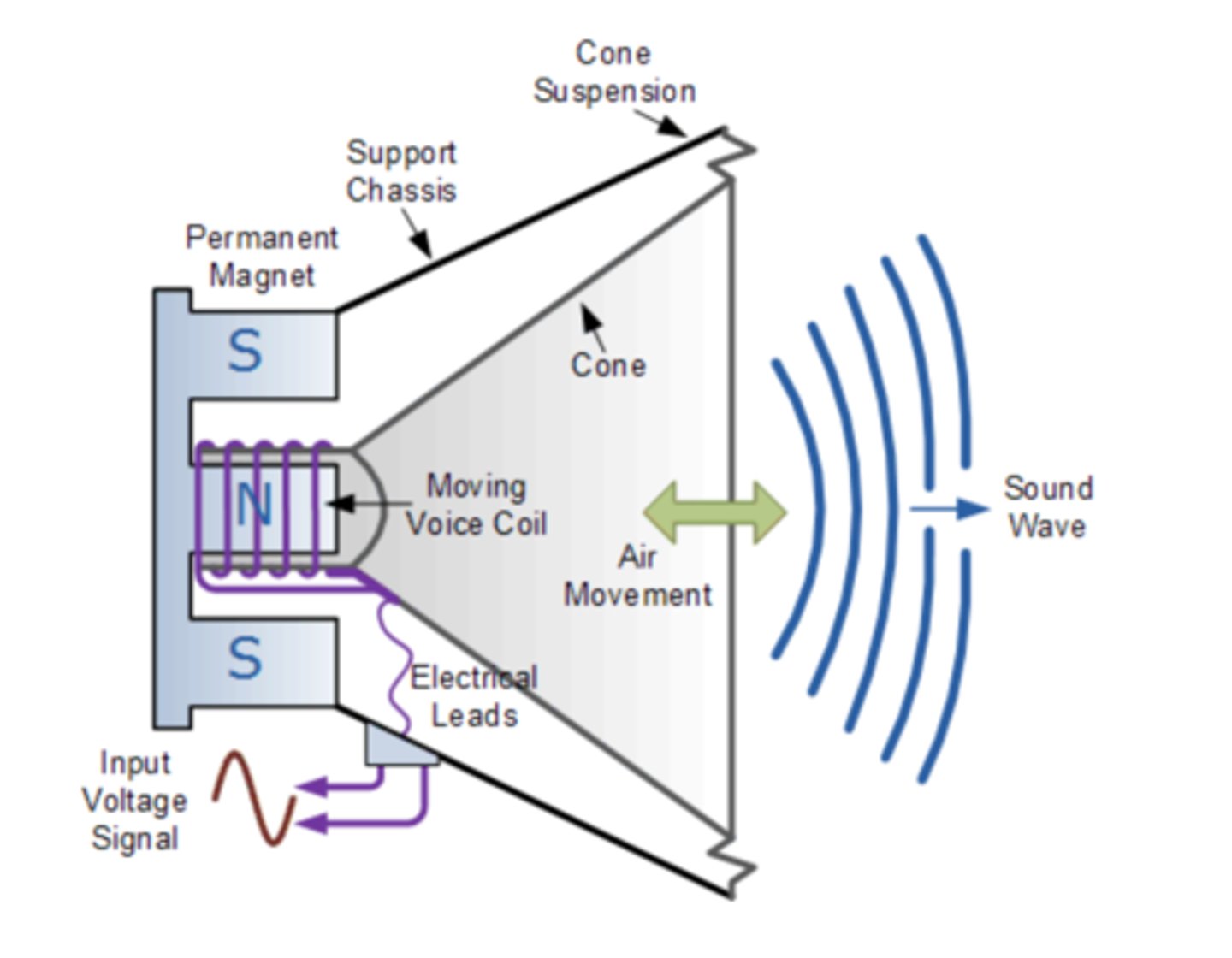
What is a bass reflex speaker?
It has a tuned port mounted in the cabinet
What is a two-way loudspeaker and how does it works?
Woofer is responsible for low frequencies up to 3khz + Tweeter is responsible for the high frequencies up to 20khz
What would a loudspeaker not mounted in an enclosure sound like?
It would sound thin because the low frequencies would cancel out
What are the differences between large and small diaphragm microphones?
small diaphragm off axis frequency response is flatter than large diaphragm
Large diaphragms have greater output level than small diaphragms
Which of the following statements are true regarding microphone polar patterns?
ribbon microphones are natively figure-of-eight
condenser and moving coil microphones are natively omnidirectional
What are the three classic stereo recording techniques?
Coincident, near-coincident, spaced pair