Lecture 2 - Global structure of chromosomes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is a fractal globule ?
It’s a dense, untangled structure that maintains the ability to fold and unfold.
What is particular about the location of chromosomes during interphase ?
Each chromosome tends to occupy their own territory in the nucleus.
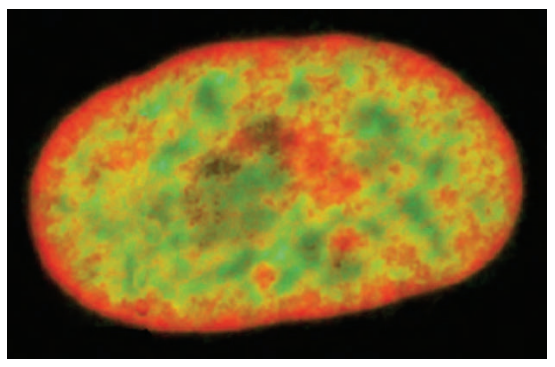
Where are the heterochromatic regions usually found in the nucleus ?
Heterochromatic regions are found in the nuclear lamina (towards the exterior) whereas euchromatic regions are usually more in the interior.
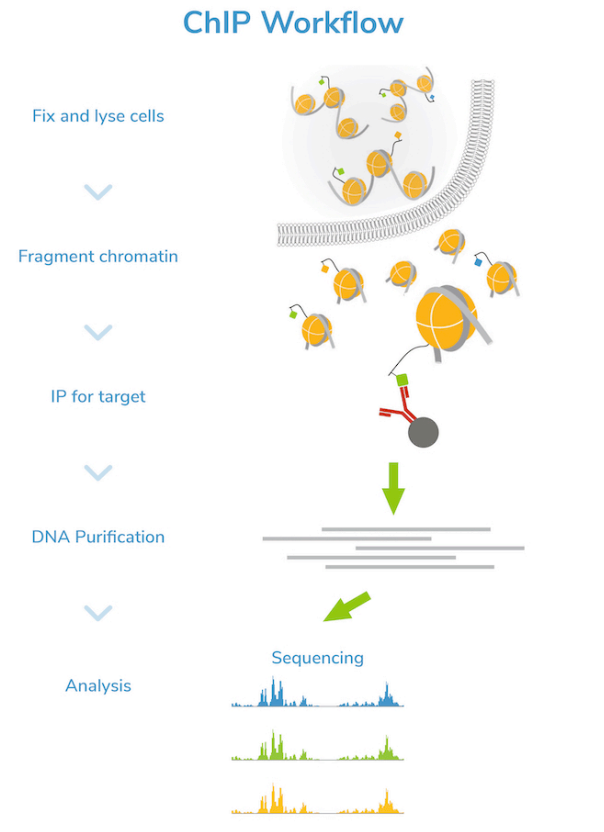
What method is used to determine all the DNA regions that possess a specific histone modification ?
Chromatin Immune-precipitation (ChiP)
Explain how ChiP works
Crosslink histones and DNA (meaning bind histones with DNA).
Fragment chromatin into small pieces.
Select a marker and use the corresponding antibody.
Use Immunoprecipitation (IP) to isolate the fragment of interest.
Purify the DNA. (Get rid of the proteins)
Sequence the DNA.
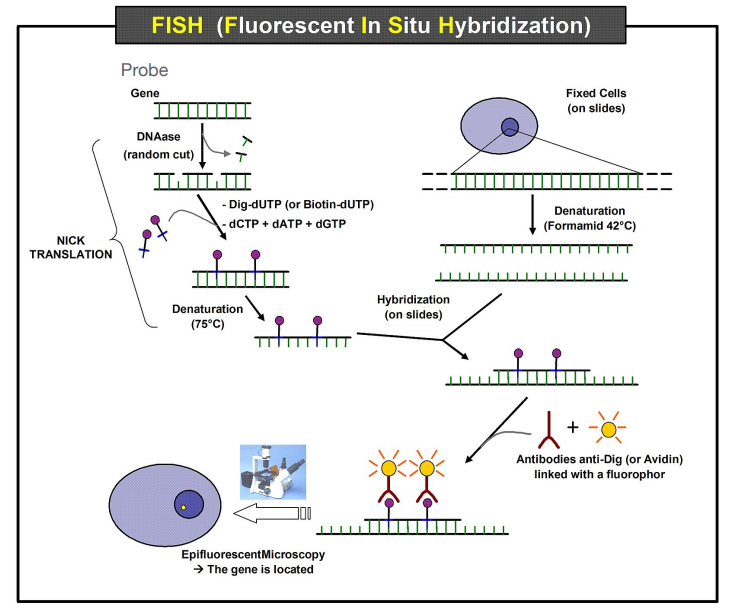
What method is used to detect specific sequences of DNA in situ (in the original location)?
Chromosome painting using FISH (Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization). Allows detection of specific regions in the nucleus.
Explain how FISH works
Fixation of the cell.
A ssDNA probe is produced by inserting Dig-dUTP after random cuts with DNAse (modified nucleotides which substitute for dTTP) enzyme
Denaturation of probes and cell DNA.
Since the probe is complementary to the DNA sequence, it binds to sequence of interest. It is coupled with a fluorescent marker.
Antibody linked with a fluorophore and acts as an anti-Dig.
Location is detected.
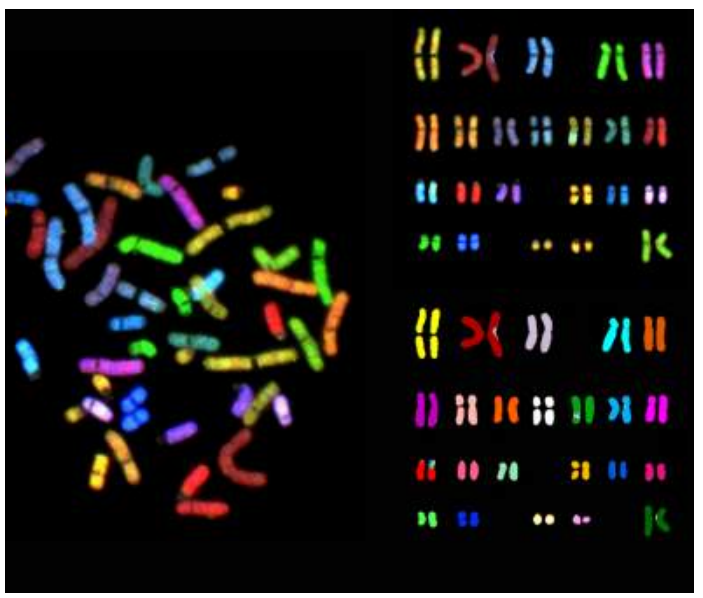
What method is used to detect problems or changes in chromosomes ?
Cytogenic analysis
Explain how cytogenic analysis works
Fix/crosslink the cells.
Use a hypotonic solution to spread at metaphase (solution with a lot of water and low solute. This allows the metaphase chromosomes to spread out.
Hybridization of specific probes leads to fluorescence and downstream analysis.
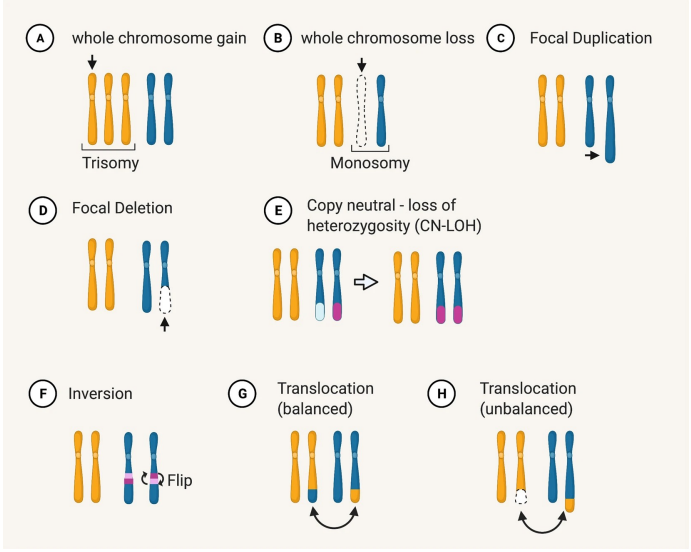
What are the different types of chromosome alterations ?
Deletion (loss of chromosome regions)
Duplications (One or more additional copies of a region)
Translocation (Chromosomal rearrangement)
What is the human genome project ? What did they figure out ?
It’s the sequencing of the entire human genome. They found out that about 90% of it is probably unimportant.
What are exons and what are introns ?
Coding sequences of the genome are called exons and non-coding sequences are called introns.
What information did comparing genomes with other species give us ?
Revealed functional DNA sequences by conservation through evolution.
4.5% of the human genome consists of multispecies conserved sequences.
What are homologous genes ?
They are genetic sequences inherited from a common ancestor. Similar in sequence and perform similar functions Can be in a single organism or in multiple.
How many errors does a gamete have on average ?
About 30.
What are the different types of mutations ?
Simple local changes : point mutations.
Large-scale genome arrangements.
Mobile genetic elements.
What is single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
It’s the substitution of one nucleotide at a given position in the genome. Also defined as a mutation that is present only in a fraction of the population. For it to be considered a SNP, it has to occur in >1% of the population. This is the basis to alleles.
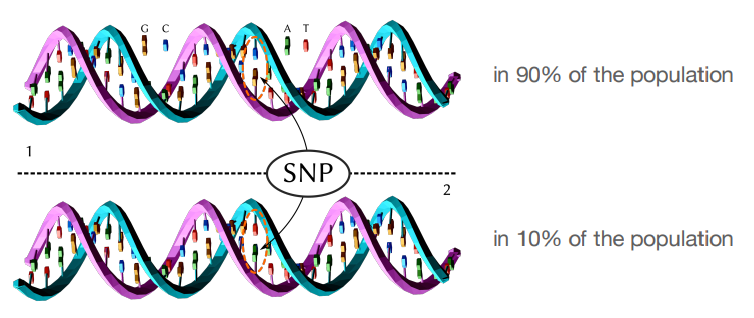
What are the two types of SNPs ?
Synonymous : Amino acid isn’t changed.
Non-synonymous : Amino acid is changed.
What is a GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Studies) ?
It’s a large scale study that scans the genome for SNPs associated with a trait. This gives a list of the SNPs associated with the trait.
How does a GWAS work ?
Collect DNA from thousands of people.
Genotype them with the SNPs.
Use statistics to find the SNPs that occur more frequently in people with the trait.