Disorders of Hemostasis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Hemostasis
It is the stoppage of blood flow (the process by which the body stops the bleeding after an injury).
Component of Hemostasis: Platelets
Platelets (thrombocytes)
They’re anuclear (does not have a nucleus)
Originate from pluripotent stem cell - myeloid stem cell - megakaryocyte
Thrombopoetin stimulates platelet production → Thrombopoetin is released by the liver
Components of Hemostasis: Plasma Clotting Factors
Factors I-XII are all mostly synthesized by the liver
The Activation Clotting Factors leads to → The Clotting Cascade
Unique Clotting Factors - Factor X
Factor X (both pathways converge here)
Factor I and Factor Ia
Factor I - Fibrinogen; when activated is Factor Ia - Fibrin
Factor II and Factor IIa
Factor II - Prothrombin; when activated is Factor IIa - Thrombin
Factor IV
Calcium
Vitamin K Clotting Factors
The Clotting Factors that need Vitamin K are:
Factor II - Prothrombin
Factor VII
Factor IX
Factor X
Clotting Cascade
Components:
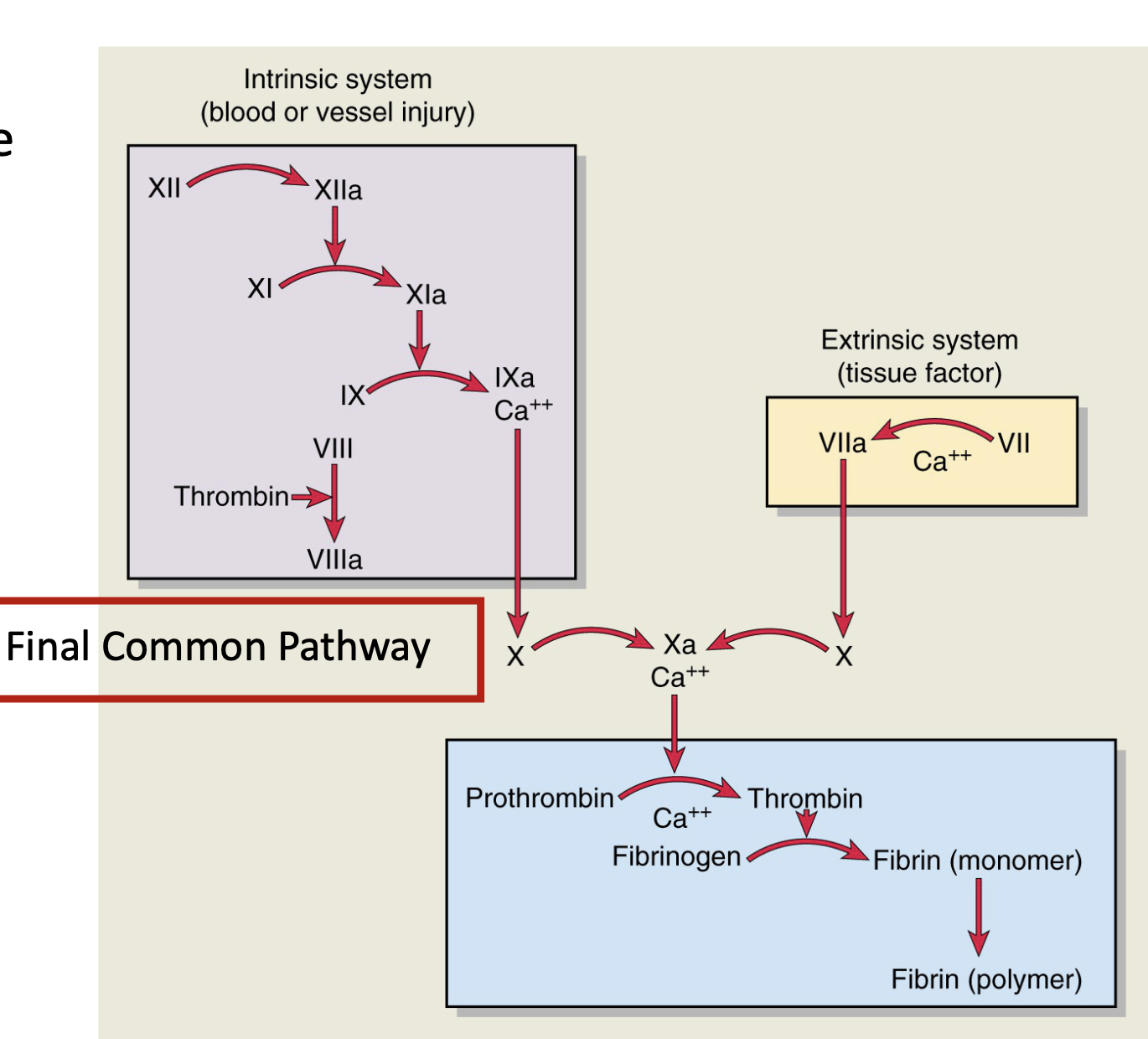
INtrinsic Pathway - slow (1 to 6 mins), happens when damage to the blood vessel wall is done). First factor to activate → Factor XII
EXtrinsic Pathway - faster (15 secs); happens outside the blood vessel wall. First factor to activate → Factor III: Tissue Factor
Both pathways converge at factor X - Factor II → Factor IIa (Prothrombin → Thrombin), Factor I → Factor Ia (Fibrinogen → Fibrin)
Be able to explain the Clotting Cascade
5 Steps of Hemostasis
Vessel Spasm/Vasoconstriction
Formation of Platelet Plug
Blood Coagulation (Clotting Cascade)
Clot Retraction
Clot Dissolution
Vessel Spasm/Vasoconstriction
a. Immediate response to vessel injury.
b. Smooth muscle in the vessel wall contracts → reduces blood flow and limits blood loss.
c. Mediated by endothelin, thromboxane A₂, and neural reflexes.
Formation of Platelet Plug
Platelet Plug Formation
a.Platelets adhere to exposed collagen via von Willebrand factor (vWF).
b. Activated platelets release ADP, thromboxane A₂, and serotonin → recruit and activate more platelets.
c. Platelets aggregate to form a temporary plug.
(Coagulation) Clotting Cascade
Coagulation Cascade (Secondary Hemostasis)
a. Intrinsic pathway: triggered by contact with exposed collagen (Factors XII, XI, IX, VIII).
b. Extrinsic pathway: triggered by tissue factor (Factor III) and Factor VII.
c. Both converge on the common pathway: Factor X → Xa → converts prothrombin (II) to thrombin
Clot Retraction
Clot Retraction
a. Platelets contract, pulling fibrin strands together.
b. This reduces clot size and brings wound edges closer.
c. Fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells migrate in for tissue repair.
Clot Dissolution (fibrinolysis)
Fibrinolysis (Clot Removal)
a.Once healing begins, the clot is dissolved.
b. Plasminogen is activated to plasmin, which digests fibrin.
c. Prevents excessive clotting and restores normal blood flow.
Bleeding Disorders: Thrombocytopenia
caused by decreased in circulating platelet count (< 150,000/μL)
increases the risk of bleeding
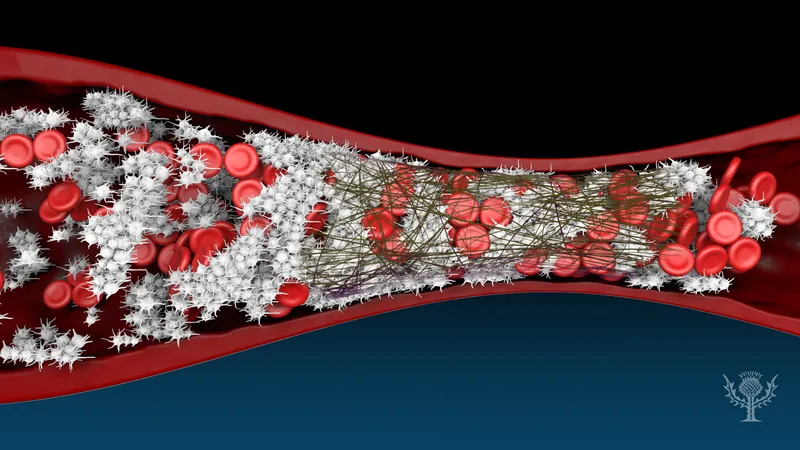
Thrombocytopathia
there are plenty of platelets, they are just not working
caused by the use of aspirin (ASA) and NSAIDs
can be caused by disorders of adhesion (von Willebrand disease)
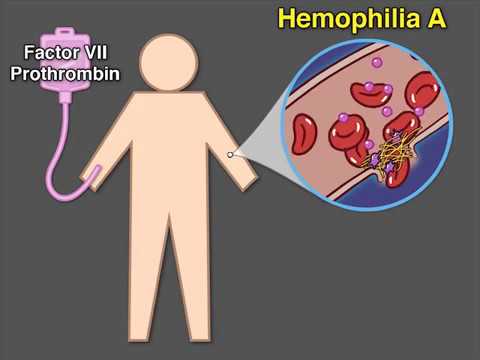
Coagulation Disorders: Hemophilia A
X-linked recessive disorder
Factor VIII deficiency
Treatment: Factor VIII replacement therapy
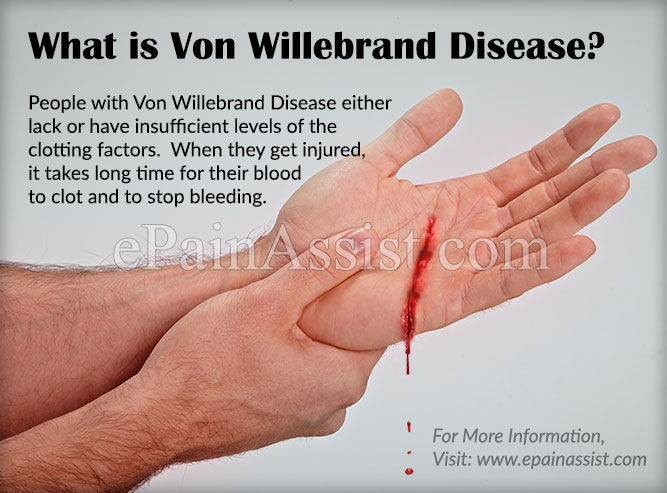
Coagulation Disorders: von Willebrand Disease
Autosomal Dominant Disorder
Deficiency or defect in von Willebrand Factor (vWF)
Treatment: mild- moderate bleeding: DDAVP (desmopressin acetate), analog of vasopressin (ADH)
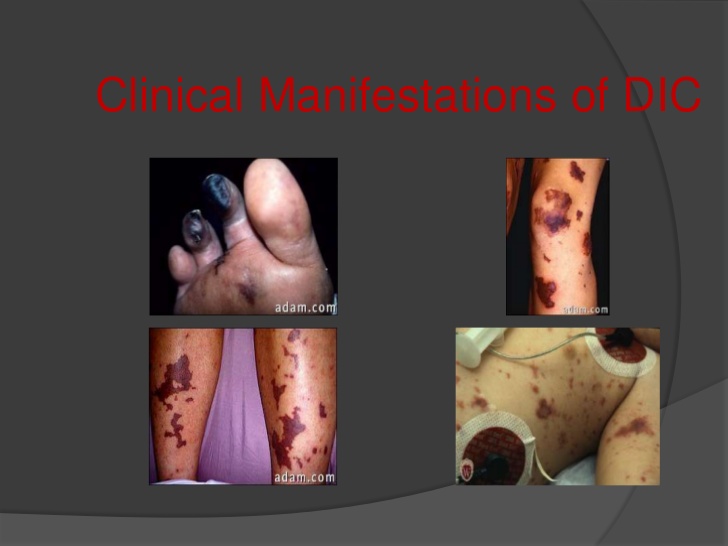
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
First problem: clotting then bleeding (clotting, bleeding, clotting, bleeding pattern)
clotting comes first as a result of excessive thrombin generation
basically, steps 3 and 5 of hemostasis are repeated over and over until all platelets and clotting factors have been used up
Manifestations: bleeding (their organs are being filled with tiny blood clots), hypoxia, and organ damage