28) AROMATIC CHEMISTRY
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what are arenes?
Hydrocarbons based on benzene
what is benzene?
simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
although benzene is an unsaturated molecule, it is very?
stable
benzene formula
C6H6
what is the structure of benzene?
6 carbon atoms in a cyclic hexagonal ring, one H bonded to each C atom by covalent bonds
what are the lengths of the 6C-C bonds like?
the same length - intermediate between single and double bonds
how is each carbon bonded to another carbon in benzene ring?
covalent bonds
how is a negative charge created above and below the planar benzene ring?
1 electron unused for each C atom in a p orbital
Each p-orbital overlaps with the neighbouring p-orbital to form a 𝝅 bond
the electrons are?
delocalised
how is benzene a stable molecule?
Electrons are delocalised - free to move
They repel each other less by spreading out
why is the melting point of benzene much higher than hexane?
benzene has flat, hexagonal molecules pack together very well in the solid state. They are therefore harder to separate and this must happen for the solid to melt.
what is kekule structure?
Cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene
3 C=C double bonds and 3 C-C with one hydrogen attached to each carbon.
which is more stable, kekule or delocalised structure?
delocalised
what are 3 pieces of evidence that benzene has a delocalised structure rather then 3C=C double bonds?
C-C bond length
addition reactions
enthalpies of hydrogenation (thermochemical evidence)
how do C-C bond lengths prove delocalised structure?
All of the C-C bonds are the same length (intermediate between C=C and C-C)
If it was a triene, the C-C bonds would be longer than the C=C bonds
how do addition reactions prove delocalised structure?
Benzene does not readily undergo addition reactions
Does not decolourise bromine water
A triene would do addition reactions
how do enthalpies of hydrogenation prove delocalised structure?
Triene - releases 360 KJ/mol
benzene - releases 208 KJ/mol
Benzene is 152 KJ/mol more stable
Extra stability is due to the delocalisation of the electrons [delocalisation stability]
enthalpy of hydrogenation of triene
-360 kJ/mol
enthalpy of hydrogenation of benzene
-208 kJ/mol
difference in hydrogenations
152 kJ/mol
benzene is a suffix when?
monosubstitutions and carboxylic acids
phenyl is a prefix when?
Above 2 carbons
Alkenes
Amines
Esters
Alcohol
what are the 2 factors that affect the reactivity of aromatics?
The ring is an area of high electron density because of the delocalised bonding
The aromatic ring is very stable.
why does the high electron density affect reactivity?
induces electrophilic attack
why does the stable ring affect reactivity?
It needs energy to be put in to break the ring before the system can be destroyed- this is called the delocalisation energy
It means that the ring almost always remains intact in the reactions of arenes.
what are most of the reactions of aromatics?
electrophilic substitutions
why do substitution reactions happen over addition reactions?
They leave the aromatic system unchanged
Addition reactions would reduce stability and require the input of the delocalisation energy to destroy the aromatic system.
combustion of arenes
-have flames that are noticably smoky, due to the high carbon:hydrogen ratio compared with alkenes.
a smoky flame suggests an aromatic compound
what happens during electrophilic substitution mechanisms?
H atoms on the ring are replaced by other groups
2 types of electrophilic substitution
nitration
friedel crafts acylation
reagents for nitration
conc HNO3 conc H2SO4
conditions for nitration
50ºC as multiple substitutions would occur if any higher as nitronium becomes too reactive
equation for generation of nitronium ion
HNO3 + H2SO4 →NO2+ + HSO4- + H2O
what are nitrated arenes used for?
explosives (TNT) and formation of amines
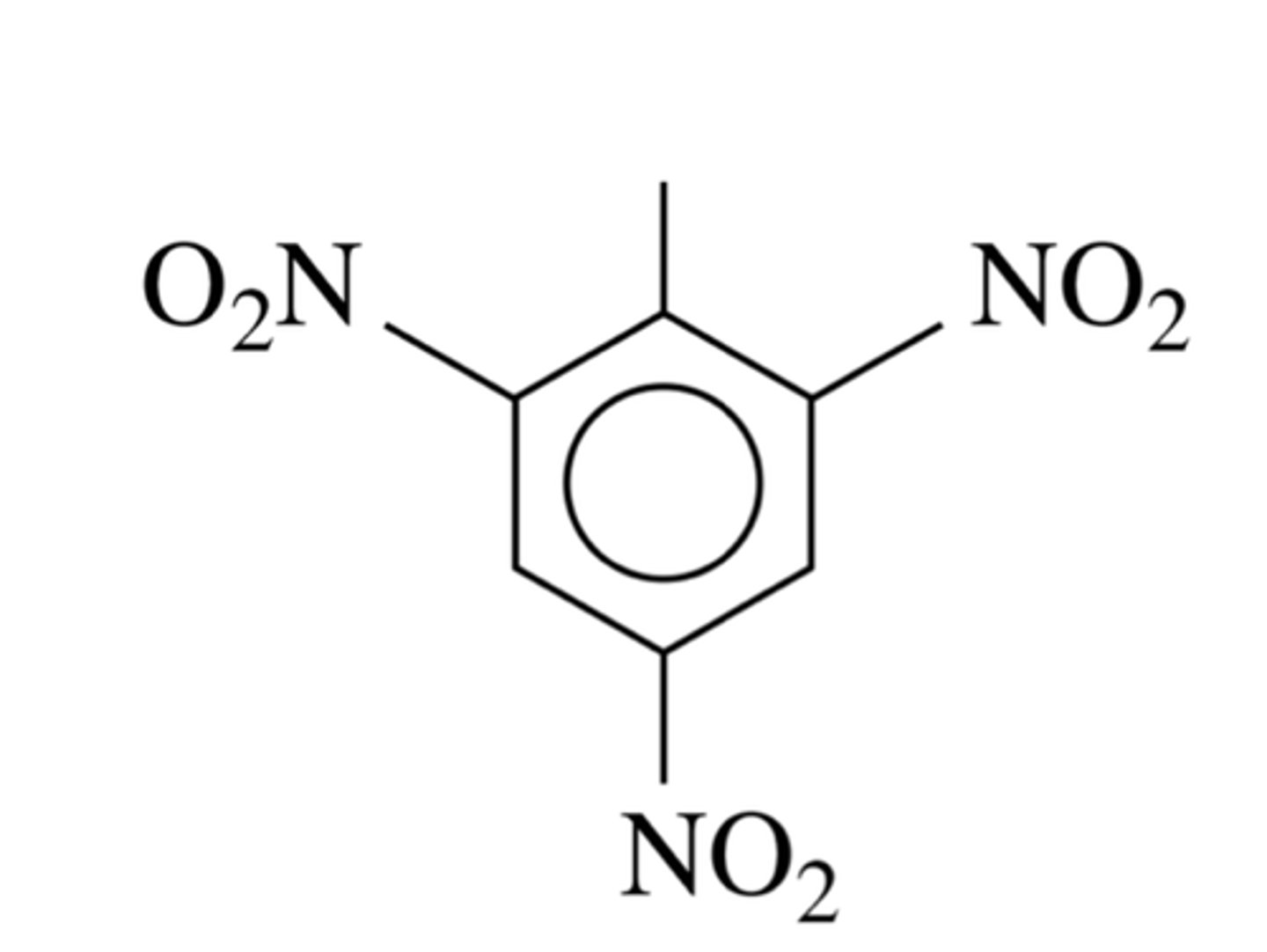
what is formula of TNT
2,4,6-trinitromethylbenzene
how are amines produced from nitrobenzene?
reduction
conditions needed for reduction of nitrobenzene to phenylamine?
HCl and tin catalyst and NaOH
equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene to phenylamine
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
how many [H] needed for reduction of nitrobenzene to phenylamine?
6
reagents needed freidel crafts acylation
acyl chloride or acid anhydride + AlCl3
conditions for freidel crafts acylation
anhydrous to prevent reaction of AlCl3
acylium ion is the?
electrophile
equation for generation of acylium ion using acyl chloride
R-C(Cl)=O + AlCl3 --> R-C+=O + AlCl4-
equation for regeneration of catalyst using acyl chloride
AlCl4- + H+ →AlCl3 + HCl
how to go from methylbenzene to TNT
nitration with conc. H2SO4 conc. HNO3 heat
what is the mechanism name for C6H5CH2Cl --> C6H5CH2NH2
nucleophilic substitution
how to go from chlorobenzene --> benzene
reduction using H2 and Ni catalyst