C3.1 Integration of body systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
System integration
All org - use multiple systems → perform various fun of life
Requires coordination of diff systems via comm (chem + electrical)
Ex. Nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory, etc. system
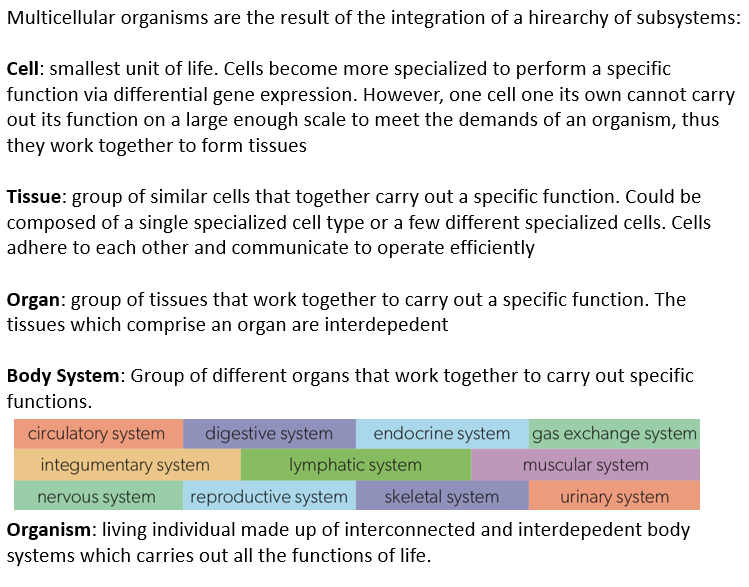
Hierarchy of body systems
Cell → smallest unit of life
Grouped tgt → form tissue
Tissue
Similar cells carry out specific func
Grouped tgt → organ
Organs → tissues work tgt → carry out specifc body func
Tgt → form body sytem
Body system → Diff organs work tgt
Organism
made of interconnected + interdependent body systems → carry out func of life
Emergent property
Multic org → capable of completing func
Char of system → arise from interaction btwn indiv components
not present in components themselves
Ex.
tissues have properties cells do not
Organs have properties tissue don’t
Ex. Cheetah
Cell - Provide blueprint for body shape and fur - create spots for camo
Tissue - loose hips + shoulder joints → flexible spint for running
Organ - enlarged heart → ensure effective deliverly of glucose and o2 to muscle for rapid physical respone
Body system → respiratory system → rapid delivery of o2 to muscle, etc.
Organism → built for chasing prey. narrow paws → minimal contact w ground (run faster)
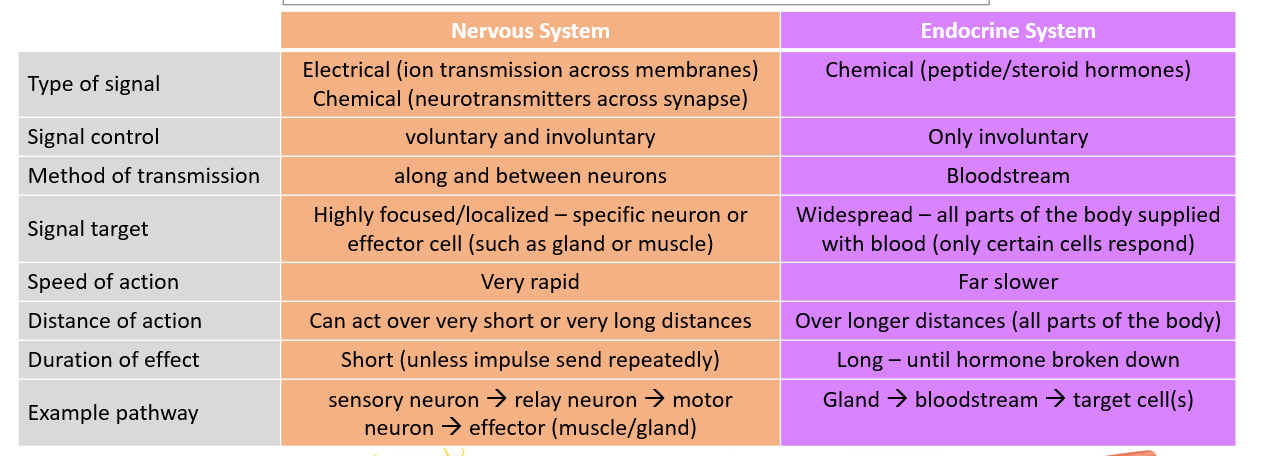
Nervous vs endocrine system. Role of blood in transport of material + e btwn organs
Refer to photo
Transport of materials and e
blood
transport nutrients, o2, etc. (o2 required for cellular respiration in cells)
remove waste product (co2, urea)
Flow maintained by circulatory system + pumping of blood
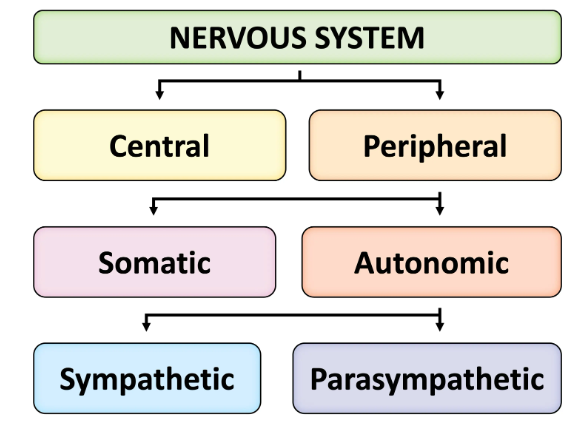
Nervous system
Complex network - control + coor body actions + sensory info
CNS
Brain
Spinal cord
PNS
Neuron - relay signal btwn CNS + organs of body
Ex. Sensory, motor neuron
Somatic (voluntary) or autonomic (involuntary)
Autonomic output
Sympathetic (Fight or flight)
Mobolise body for action
Parasympathetic (rest and diegest)
Promote e conservation
Brain
Central info of integration organ
Function
Receive info
Process info
Stores as memory or send instruction to trigger response
Memory
Capacity to store and retrieve info
Sources of info input
Sensory receptors
Envt
Spinal cord - Unconscious vs Conscious
CNS - Brain + spinal cord
Spinal cord
integrating centre for info processing
Does so unconsciously
unconscious
when awake/asleep
Involuntary
Coor - brain and spinal cord
Ex. Contraction of muscle, release of hormones
Conscious
Awake
Voluntary
Brain - cerebral hemispheres
Ex. Thought, swallowing food
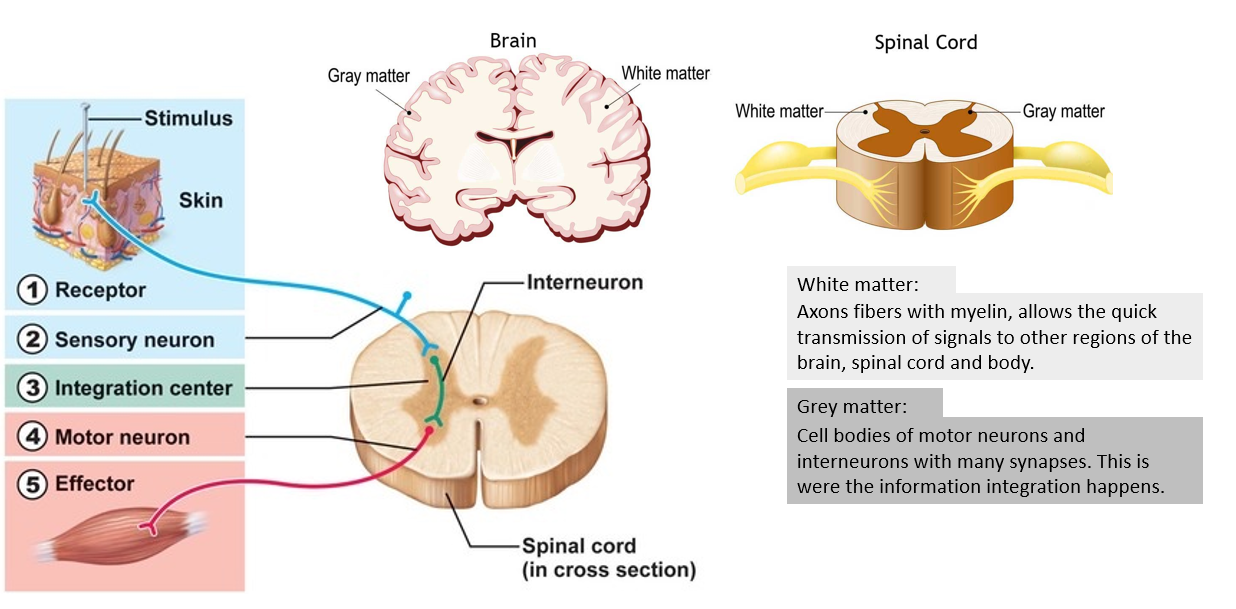
Structure of brain
Cerebral hemisphere
Cerebrum
Control muscle func, speech, thought, emotions, reading, writing, learning
Structures
Right cerebral hemisphere
Muscle on left side of body
Left CH
Muscle on RHS of body
Pri motor cortex
Control voluntary mvt to skeletal muscle (via motor neuron) → cause contract → bones move
Cerebellum
Coor skeletal muscle contraction
Maintain balance
Motor memory
Ex. Riding a bike
Grey matter
Cell bodies of motor + relay neuron w many synapses
Info integration occurs
White matter
Axon fibres w myelin
Allow quick transmission of signal to brain, spinal cord, etc.
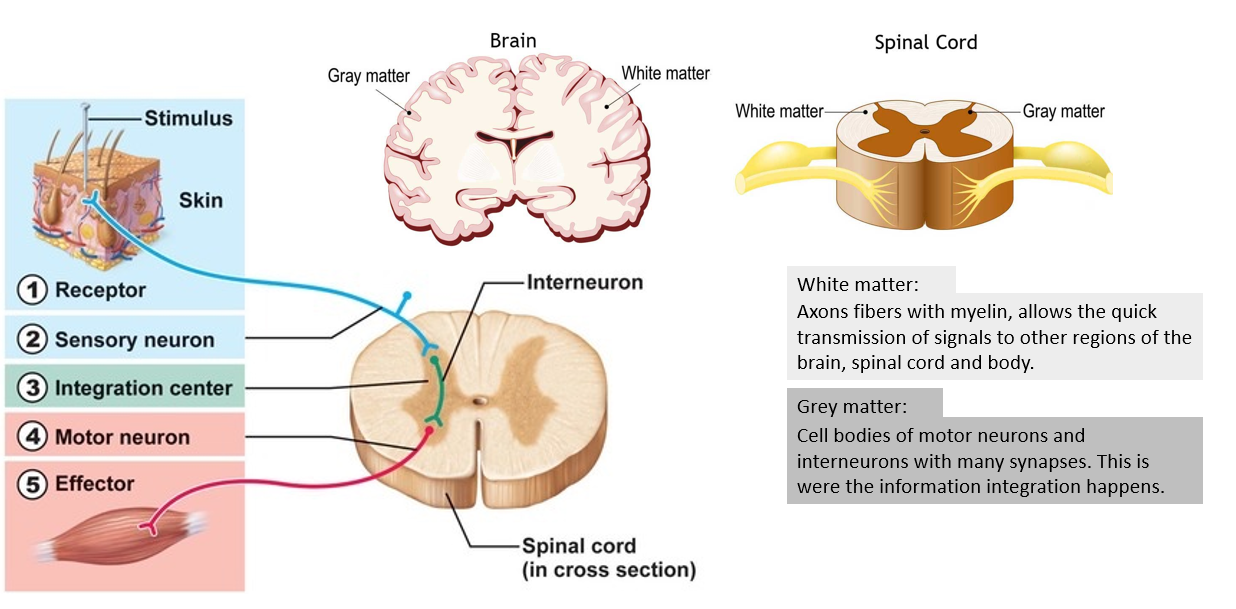
Nervous system - sensory neuron (PNS)
sensory neurons
Signal wn body tissue - detected by receptor → transmitted to CNS via sensory neuron
Ex. Photoreceptor, Chemoreceptors
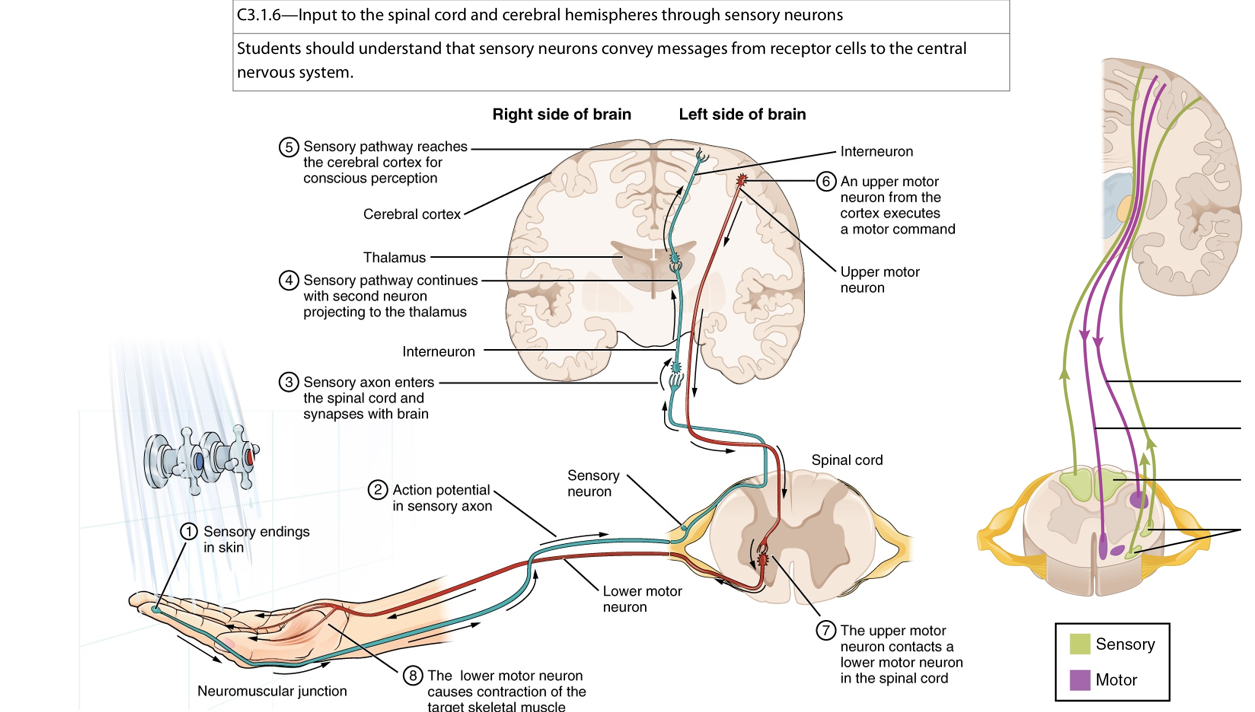
Nervous system - Motor neuron (PNS)
Transmit nerve impulse from CNS → transmitted to effector via motor neurons → result in mvt
Nerve
Bundle of nerve fibre - Sensory, motor, myelinated, unmyelinated neuron
enclosed within myelin sheated
Facfilitate comm w specific region of body
Nerve fibre
Afferent neuron - send signal to CNS via sensory neuron
Efferent neuron - send signal away from CNA via motor neuron
Hypothalamus vs Pituitary gland
Hypothalamus → homeosttic control → regulate hormonal secretion via pituitary gland
produce releasing factors → trigger release of hormones synthesised in pituitary gland
Produce hormones → directy released from pituitary gland
Pituitary gland → adjacent to hypothalamus
Anterior and posterior lobe
Control secretion of hormones from endocrine glands
Reflex arc
Involuntary response - allow allow fast action by activating spinal motor neuron instead of sending signal to brain
Pain stimulus deteced by receptor
Nerve impulse initiated in sensory neuron
Sensory neuron carry signal from sensory receptor to spinal cord
Synapse with relay neuron in grey matter
Relay neuron w motor neuron - leave spinal cord
Motor neuron - synapse with effector
Cause contraction → remove limb from pain stimulus
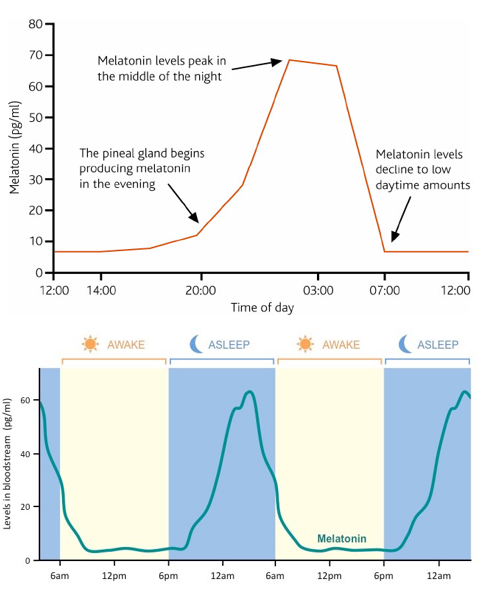
Circadian rhythm
Body normal physiolocal response to 24h day-night cycle
driven by int circadian clock
Melatonin
hormone - produced by pineal gland wn brain
responsible for synchronising circadian rhythm
Regulate body sleep schedule
Synced by light and dark
High secretion in dark → cause drowsiness + promotes sleep
Low secretion in light → promote waking up
Effect:
Reduce bp, urine production
Drop core body temp
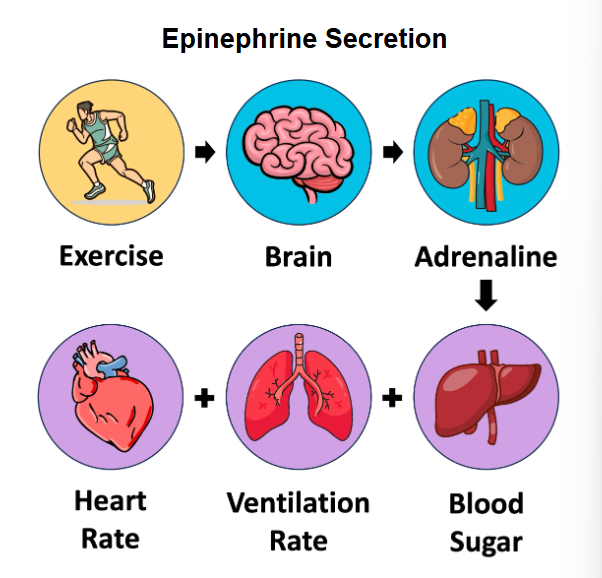
Epinephrine and effect on body
Amygdala → send stress signal to hypothalamus → initiate fight/fight response
Hypothalamus → stimulate release of epinephrine from adrenal gland above kidneys
Effect:
Heart rate - elevated, strength of cardiac contractions increase
Greater blood flow from heart
More blood sent to skeletal muscle - o2 + glucose needed for a/anr respiration
Bronchioles widen → improve uptake of GE
Liver → convert glycogen to glucose for transport to muscles
Cardiac output
Cardiac output
auto controlled by medulla oblongata
varies accor to physiological requirements
Baroreceptor
Location: Aortic walls + carotid arteries
Monitor bp → send neural signal to medulla oblongata accor to changes in bp
Chemoreceptor:
Location: Aortic walls carotid arteries
monitor blood pH + conc of o2 and co2 → stimulated when changes are made to pH → send neural signal to medulla oblongata
Process of cardiac output
Based on signal sent to medulla oblongata from baro/chemoreceptor
cardiovascular centre in MO
process input → cause change in heart rate
bring pH, conc of o2 and co2 back to target levels
Signal sent to SA and AV node → increase/decreate rate of heart beat
I/D vol of blood entering lungs → I/D GE → I/D conc of o2+co2 in blood
Feedback control of ventilation rate
Ventilation → change in repsonse to physical activity, body e demnads increase
ATP production → co2 produced as waste prodcut
co2 → lower blood pH (via carbonic acid) → change in ph (deteced by chemoreceptor in medulla oblongata)
Exercise intensity increase, co2 level increase, need for GE increase, increase in ventilation
Medulla oblongata
signal to lungs + surrounding system to increase ventilation via:
Increase ventilation rate (more breaths) + volume (deeper breaths)
ENS and CNS role in digestive system
Enteric nervous system
neural pathways → coor digestion
Both autonomic and somatic motor pathways (involuntary + voluntary)
Swallow food + egestion of faeces
voluntary action - controlled by CNS
Peristalsis
involuntary action - controlled by ENS
Mechanism - enable food mvt along alimentary canal
ENS coor circular + longitudinal muscles → create wave-like contractions → push food forward
Phytohormones
Signalling chem - produced by plants
regulate growth + dev processes
Examples:
Auxin - growth
Ethylene - ripening
Cytokinin - flowering
Gibberellins - trigger germination
Abscisic acid - leaf shedding + stomatal closure
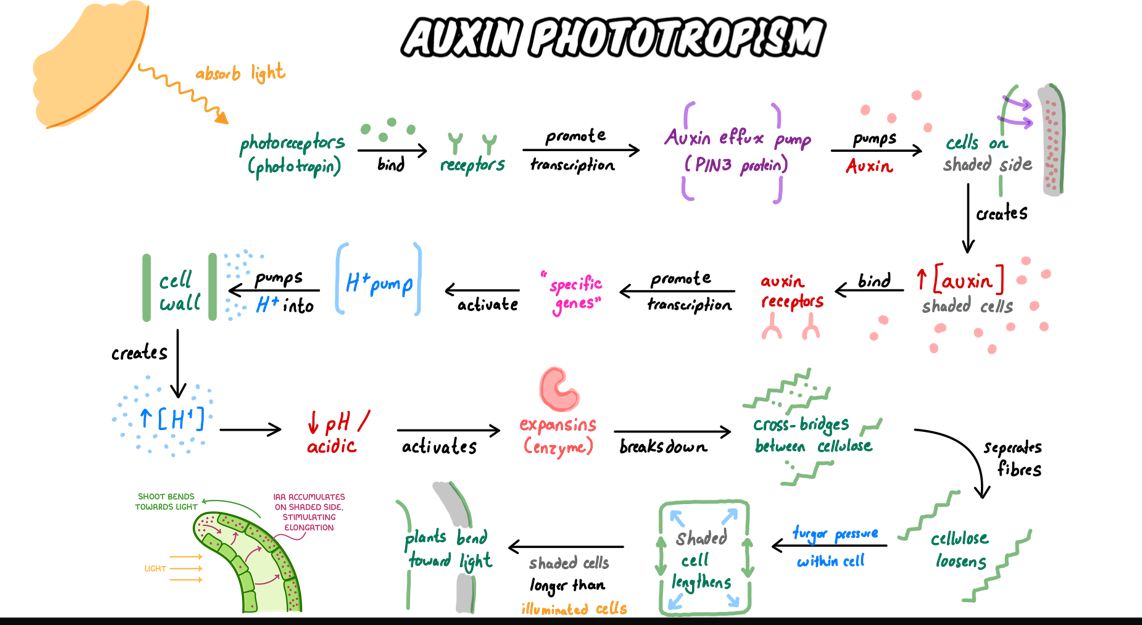
Promotion of cell growth by Auxin
Plant hormone - increase flexibility of cell wall
promote growth via cell elongation
Produced in apical meristem
Process:
Activates protein pump in plasma membrane
Secrete H+ ions into apoplast
pH of apoplast drops → Cell wall is being acidified
Activate expansins - enzyme
Break cross link btwn cellulose fibre
Cell wall becomes more flexible + stretchable
Trigger K+ channel to open
Influx of K+ enter cytoplasm
Lower WP inside cell
h20 enter via osmosis (through aquaporin)
Increase pa wn cell
Cause cyto to expand
Wall stretches
Lead to cell growth
Auxin Efflux Carrier (AEC)
Auxin
Freely diffuse INTO plant cell
Cannot EXIT without specialised protein
Role of AEC:
When inside the cell auxin becomes ionised in cyto → Prevents it from diffusing out
To move auxin out of cell → rely on AEC
Specialised membrane proteins → AT charged auxin m across plasma membrane into cell wall
Process:
Auxin freely enter plant cell via diffusion
Undergo change in ionisation state → prevent passive efflux
Auxin efflux carrier
Transport auxin out of cell
Regulate auxin distribution
Plants
Able to position AEC on one side of cell
Create conc gradient of auxin wn cell
Auxin - actively transported from cell to cell through plant tissue
become conc in particular region of plant
Phototropism
Growth mvt of plant - respond to unidirectional light source
Process:
Phototropins (light receptor)
More light on one side
Phototropin on lit side activated, trigger redistribution of auxin to dark side of plant
Via coor positioning of auxin efflux carrier
Auxin
promote cell growth + elongation of shaded cell
Cause shaded side of plant - become longer than lighter side
Shoot tip bends towards light source (+ve phototropism)
Light → AEC moves to shaded side → Auxin builds up on shaded side →
H⁺ pumps activated → Cell wall acidifies → Expansins loosen wall →
Water enters → Cell elongates → Shoot bends toward light
Apical growth
Growth at tip of plant shoot + roots
Controlled by following hormones:
Hormones need to be transported to region of plant they are NOT produced in
Auxin
responsible for cell elongation
Produced in shoot tip of plant
Transported from plant → root (downward) via phloem
Cytokin
Responsible for cell division
Produced in root tip of plant
Transported from roots → plant (upwards) via xylem
Interactions btwn phytohormones
ensure root + shoot growth → regulated
Auxin
Promote root growth, inhibit shoot growth
Cytokines
Promote shoot growth, inhibit root growth
Differing conc
Allow plant to adapt growth to diff envt + nutrient availability
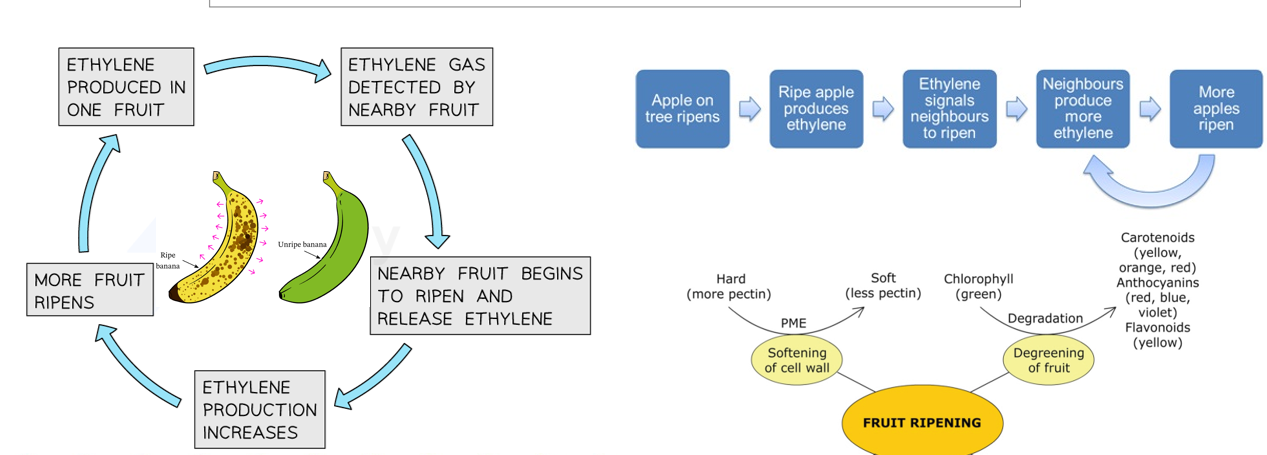
Ethylene
Phytohormone
maturation + ripening of certain types of fruits
Sync ripening of fruit on plant
Gas (produced as fruit begins rippening) - released from one plant → influence growth and maturation of another plant (allelopathy)
Produce more ethylene in turn
Ensure ripening process - rapid, not prolonged