Stage 2 Instrument
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is an IAP
defined route to take you down to runway
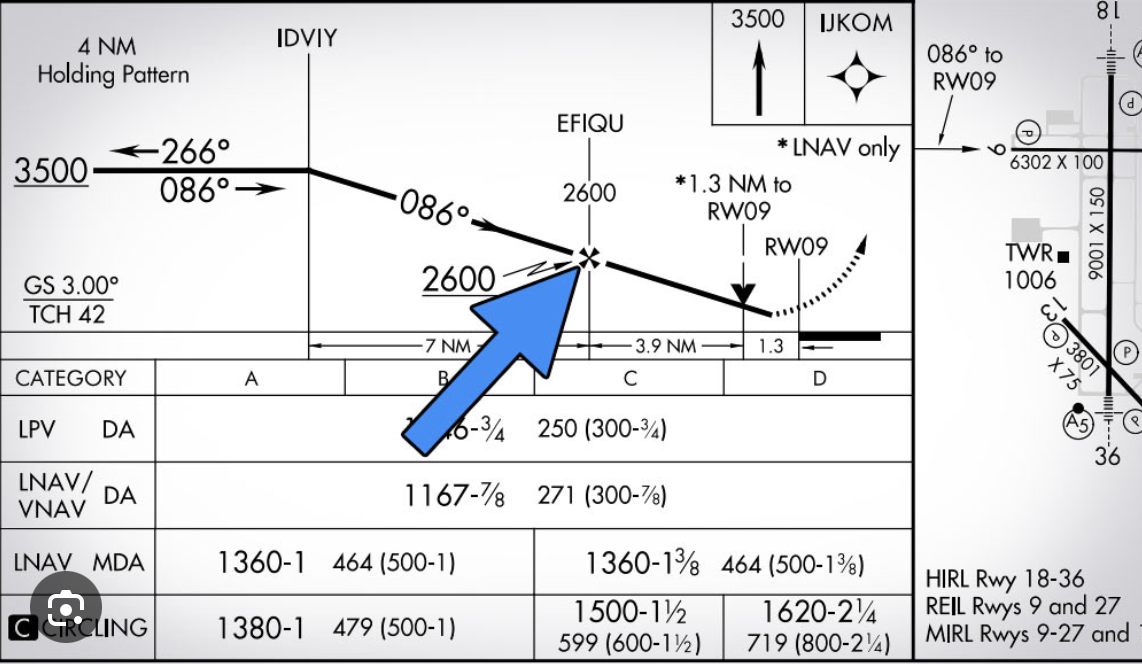
What is the difference between lightning bolt and the Cross on the approach plate
Cross: final approach fix for Non-Precision Approach
Lighting bolt: Glide slope intercept for Approach Procedure with Vertical Guidance (AP-V) & Precision Approach
What is the Missed Approach Point for…
1.) AP-V and Precision approaches
2.)Non precision
1.)Decision height/ Decision Altitude
2.) Labled on approach plate
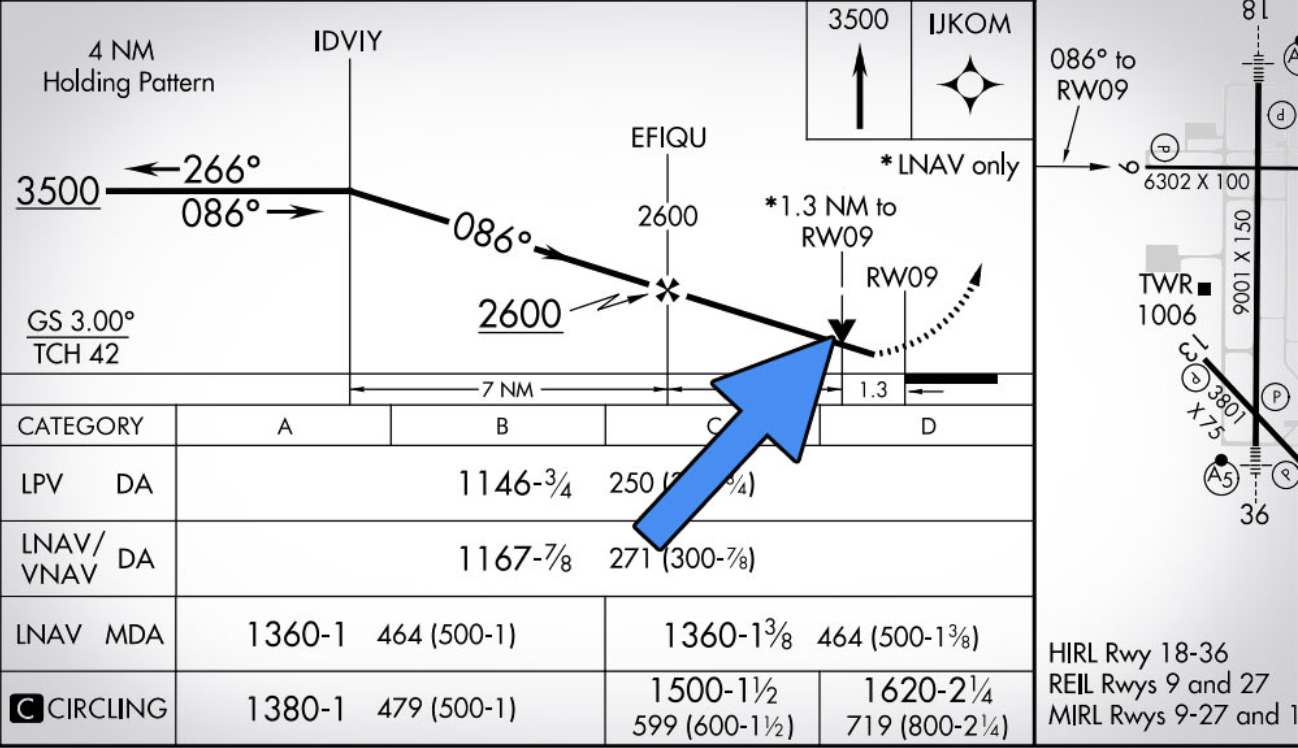
What is the V the arrow is pointing to
Visual Descent Point: defined point on a non-precision approach from which a pilot can begin a normal descent from the MDA to the runway touchdown point, provided they have the required visual references.
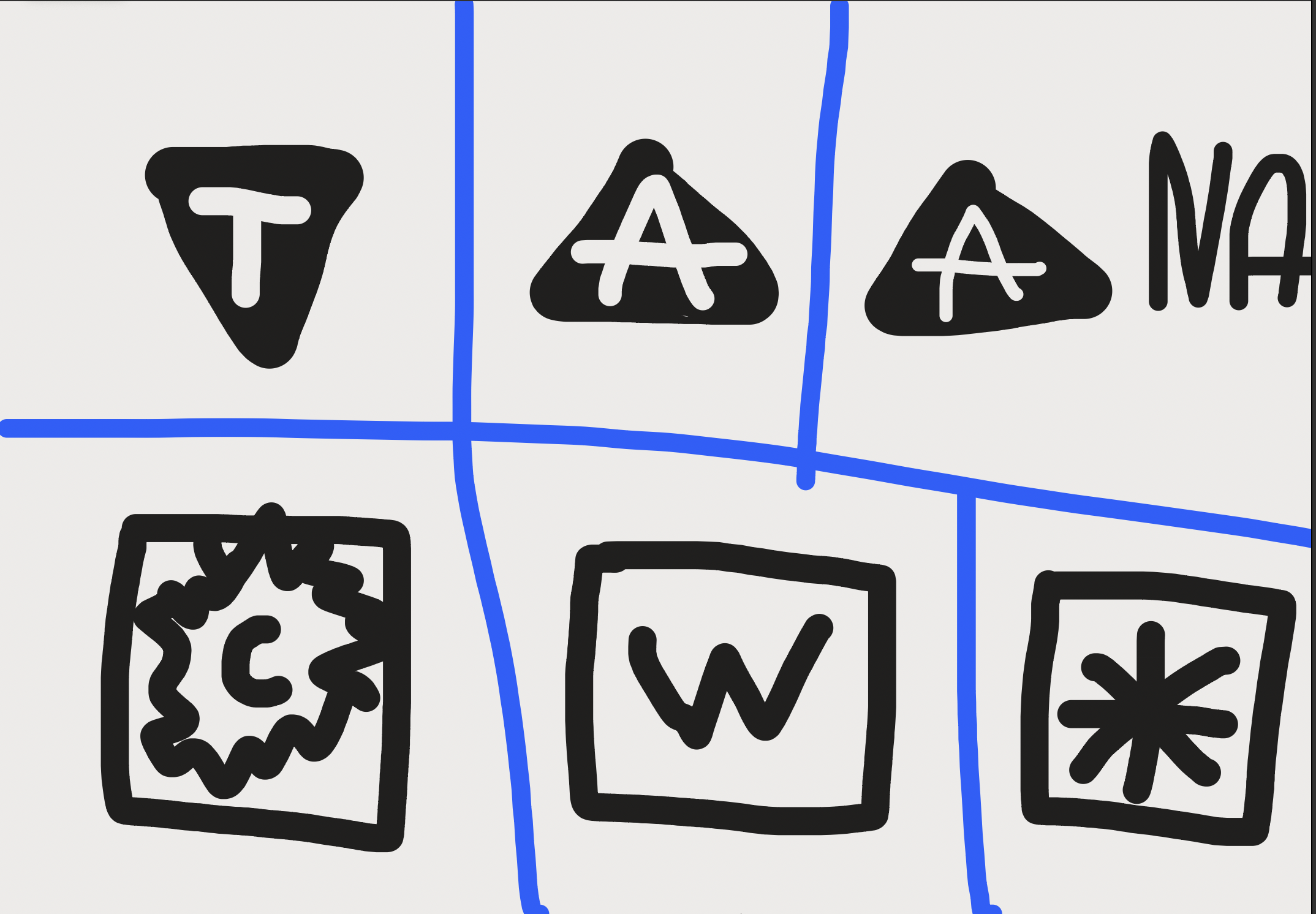
What do each of these symbols mean (the last one is supposed to be a snowflake and the C is supposed to be fully blacked out.)
1.) Nonstandard takeoff mins
2.) non standard alternate mins
3.) Alternate mins not authorized
4.) expanded circling mins
5.) WAAS outage
6.) cold temp correction
What is a…
1.) MSA
2.) TAA
1.) Minimum Safe Altitude: 1000’ buffer within 25nm of nav facility
2.) Terminal Arrival Area: provides transition from en route portion to the terminal environment using RNAV
Decision Height vs Decision Altitude
DH:CAT 2 and 3 approach
-height above touchdown zone
-Need radio Altimeter
DA: in MSL
-CAT 1 APP
When would you not do a procedure turn?
Straight in Approach Clearance
Hold in lieu
Arc
Radar vector
Procedure turn not depicted in chart
Timed approach from hold fix
Teardrop course reversal
a.) If IAF is on airport your outbound procedure turn would be _________ , I its not over air port the turn would be ________
b.) You fly with procedure turn with heading or course?
c.) what is the max distance and speed for a procedure turn?
a.) 2 minute, 1 minute
b.) heading
c.) 10nm and 200kts
a.) What’s the reg that includes operations below DA/DH or MDA
b.) what is required to descend below minimums in CAT 1 (VDP for non precisions and DA for precision)
a.) 91.175
b.) normal manuvers, correct visibility, airport enviorment
What is required to be able to land under IFR.
a.) ALS, except you can’t descend below 100’ above TDZ using approach lights unless you see red terminating bars.
b.) Runway End Identifier lights (REILS)
c.) VASI/PAPI’s
d.) Threshold
e.) Threshold markings
f.) Threshold lights
g.) Runway
h.) Runway lights
i.)Runway marking
j.) Touchdown zone
k.) touchdown lights
l.) Touchdown markings
What are the four steps of aeronautical decision making.
1.) Define problem
2.)create best course of action
3.) Identify the best course of action and review
4.) Implement
1.)What does CRM stand for?
2.) What is CRM?
1.) Crew resource management
2.) Effective use of……..
a.) situational awareness
b.) communication skills
c.)teamwork
d.) task allocation
e.) decision making/error management
What does PAVE stand for? (relating to risk assessment)
Pilot
Aircraft
enVironment
External pressures
List and explain 3 Ps of Risk Management.
Perceive: Gathering information
Process: Analyze information
Perform: execute best course of action
What are the 5 P’s of Risk Management and explain them?
Plan: flight plan, weather, route, fuel requirements, etc.
Plane: aircraft mechanical status, equipment, airworthiness
Pilot: IMSAFE (illness, medication, stress, alcohol, fatigue, emotion/eating (just list eating and emotion because some people learn both)
Passanger: Consider passenger needs, external pressures, potential distractions
Program: use of GPS, autopilot, avionics
List hazardous attitudes, examples, and solution
Resignation— what’s the use— im not helpless I can make a difference
Anti authority—don’t tell me what to do—follow the rules they’re usually right
Impulsivity—do something quickly— Not so fast think first
Invulnerability—it won’t happen to me— it could happen to me
Macho—I can do it——taking chances is foolish
What is the risk assessment matrix?
Tool used to assess risk level of an event by comparing its likelihood to its potential impact
What is the difference between risk and hazard?
Hazard: anything that can cause harm
Risk: likelihood of a hazard causing harm
List and explain the two kinds of IFR clearances
Abbreviated Clearance: Cleared “as filed”
Cruise Clearence: authorization to fly min. IFR altitude down to field elevation and pick any approach, youd get this when the airspace is dead
1.) What does VFR on top mean?
2.) What are the rules of VFR on top
1.) operate VFR in IFR flight plan
2a.) must be below 18000’ MSL
2b.) at or above MEA
2c.) now operate at VFR cruise altitude
2d,) see and avoid
2e.) cannot be assigned by ATC
1.) What is going to be included in a “Vector to Final” approach clearance from ATC?
2.) When ATC provides radar vectors to intercept the final approach course, they should assign the intercept at no more than ________ NM from the Final Approach Fix (FAF)
1.)Position
-Heading
-Altitude
-Clearence
2.) 10
1.) What is a clearance void time?
2.) is this for towered or non towered airport
1.)Time when you must be airborne prior to or your IFR clearance is voided.
2.) non towered
When can you depart if ATC tells you to “Hold for release"?
release time or further instructions.
What is a expect departure clearance time
Time which you are expected to depart within
What is the 123 rule
rule that says “an alternate airport is required if the forecast weather for your destination (one hour before or after your ETA), includes less than 2000’ ceilings or visibility less than 3 sm
What does an IFR flight plan have to include
(Under 91.169)
-91.153
Aircraft ID
Aircraft type
name + address of pilot
point and time of departure
Route, FL, and TAS
First intended landing point + estimated elapsed time over that point
Hours of fuel
# of people
remarks
-alternate
-at least 1 hour before and after ETA celing is at least 2000’ and 3sm visibility
What is required info in compulsory report?
-Aircraft ID
-Position
-Time
-Altitude
-Type of flight plan
-ETA
-Name of next point
-Remarks
1.) List malfunction reports and FAR AIM chapter for it
2.)what do you tell ATC when making this report
1.) 91.187
-navigation
-approach
-communication equipment
2.) Aircraft ID
-Whats wrong
-how it affects your ability to operate IFR
-assistance needed
In lost comms scenario
1.) what altitude should you hold
2.) what route should you fly
1.) Highest altitude between minimum IFR altitude, expected altitude, or assigned altitude
2.)Fly your assigned, vectored, expected, or filed
What ca we expect in ATC IFR clearance
Clearance
Route
Altitude
Frequency
Transponder
What are the ways to close flight plan at controlled and uncontrolled airports.
Controlled: ATC does it for you
Uncontrolled: in the air with ATC or on ground with GCO/ FSS
1.)What is RVSM?
2.) What is needed to operate?
1.) Reduced Vertical Separation Minimums: system that allows for reduction of vert. separation between aircrafts from 2000’ to 1000’ between FL290 and FL410
2.) 2 independent altimeters
-altitude with alerting system
- altitude control system (autopilot)
-mode c transponder
ASOS vs. AWOS
ASOS: Automated Surface Observing System
-controlled airports
-type A B C D
-minute by minute
-detect/ repot significant weather change
AWOS: Automated weather observation system
-20 minute intervals
-types 1 2 3 A
Primary ATC function
collision prevention and control traffic flow
what system does ATC primarily use
Transponder: beacon transmitter will send out continuous interrogation signalsls
Types of transponders and give brief description of each
MODE A: 4 digit squawk code
MODE C altitude reporting + required in A B C airspace
MODE S: permits data exchange
Ways you can file flight plan with FSS
1-800-WX-BRIEF
ground comm outlet
radio comm outlet
List the facilities you go through in an IFR clearance at towered airport
FSS: gives supplementary material
Clearence Delivery: Gives IFR clearance Clearance
Ground: taxi clearance
Approach
Center
Tower: Takeoff and Landing clearance
What is a TRACON?
Terminal Radar Approach Control: FAA facility that houses air traffic controllers who guide aircraft approaching and departing airports within 30nm and up to 10000’
what is a TEC?
Tower enroute control: route within 10000’ or below within terminal environment
What is n ARTCC?
Air Route Traffic Control Center: keeps IFR separation while enroute
What operates as Depart/ Approach control when there is not one avaliable
Center
What is a major task ATC does not do?
Weather avoidance
When can you go off route
-Emergency
-TCAS (Terminal Collision Avoidance System) advises you to
-Amended clearance
-VFR conditions outside of class A
Where do you file a PIEREP to?
Center
what Facilities will you go through on a plan for non towered airports
FSS
CTAF
Approach
Center
At least how long before you fly should you file your flight plan?
30 minutes
1.) How do we file a flight plan?
2.) How do we pickup?
3.) when would we pick up clearence on the ground?
1.) Foreflight, FSS (phone, in person, or WX BRIEF), or in the air
2.) FSS (ground or radio communication outlet), ARTCC, Clearance Delivery, approach
3.) low clouds
Why would you circle to land?
1.) Final approach course is greater than 30º off centerline
2.) Descent gradient is greater than 400’/nm within final approach fix
3.) Runway is not clearly defined
1.) What does a circling approach provide?
2.) What things are required while circling to land?
1.) 300’ minimum obstacle clearance within area
2a.) maintain visual with runway
2b.) maintain minimums until ready to land
2c.) stay within 1.3 mile radius
1.) Two ways you get the category of an airplane for approach
2.)List the Categorys of approaches, speeds, and radius
1.) Vs0 × 1.3 = approach speed
- Vref
2.)
A. 90kts or less 1.3nm
B 91-120kts 1.5nm
C 121-140 1.7nm
D 141-165 2.3nm
E 166+ 4.5nm
1.) What’s the purpose of a contact or visual approach
2.) Contact vs Visual Approach
1.)expedite the flow of traffic
2.) Contact: requested by pilot
-1sm, clear of clouds
Visual: requested by pilot or ATC
-3sm, 1000’ ceilings
When would you go Missed
-hit DA/DH on precision approach
-hit missed approach point on non-precision point
-below MDA
-lose sight of runway on circling approach
-ATC instructed
-unstable
a.) List the three categories of approaches,
b.) which have a minimum descent altitude and which have a decision height/ altitude
c.) which are vertically guided
d.)minimum celing and visibility for each as an alternate
e.)name the specific kinds of approaches that fall under each category
a.) Precision, AP-V, Non Precision,
b.) DA/DH, DA/DH, MDA
c.) Vert. guide, Vert guide, no vert. guide
d.) 600’ 2nm, 800’ 2nm, 800’ 2nm
e.)precision approach radar, ILS, GLS (GBAS + land system)
-LPV., LNAV/VNAV
-VOR, Airport Surveillance Radar, NDB, Localizer, localizer performance, LNAV, Localizer directional aid
1) what are the 4 main components of an ILS
2.) what are a Glideslopes dimensions
2a.) what are a localizers dimensions
3a.)Name the three marker beacons
3b.) How far is each beacon
3c.) What color is each beacon
3d.) What marker is considered the final approach fix?
3e.) What marker is considered point where the aircraft must meet the precision guidance of the Instrument Landing System
1.) Glide slope, localizer, approach lighting system, marker beacon
2.) 1.4 wide and 3º vertically
2a.) width range of 3º-6º, 700’ wide, 35º @ 10 nm, 10º @ 18nm,
3a.) Outer, middle, inner
3b.) outer=4-7 miles, middle=3500’s, inner=beginning of runway
3c.) outer is blue, middle is amber, inner is white
3d.) outer marker
3e.) inner marker
1.)What is a GLS and what does it stand for?
2.) What must you have for this kind of approach
1.) Ground-Based Augmentation System Landing System: uses a ground-based system to strengthen GPS signals, providing accurate lateral and vertical guidance
2.) Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS) and Ground Bbsed Augmentation System (GBAS)
How does ATC see an airplanes position during its approach?
Precision Approach Radar: radar system that provides air traffic controllers with real-time guidance on both the horizontal and vertical position of an aircraft during its approach and landing,
1.) What is an LPV?
3.) Does the sensitivity scale the closer you get?
4.) What kind of approach is it?
5.) How far above the touchdown zone does it bring you
Loacalizer Performance with Vertical Guidance: GPS based approach that gives vertical guidance and lateral course
3.) YES
4.) AP-V
5.) low as 200’
1.) What is an LNAV/VNAV?
2.)Does it require WAAS
3.) Does the sensitivity scale the closer you get?
4.) What kind of approach is it?
5.) how far above the touchdown zone does it bring you
1.) Lateral Navigation/Vertical Navigation: GPS approach that provides lateral and vertical guidance
2.) no
3.) no
4.)AP-V
5.) low as 250
1.) What is an LNAV?
3.) Difference between LNAV and LP
4.) What kind of approach is it?
1.) Localizer navigation
3.) Doesn’t get you as low as LP because it doesnt use WAAS
4.) Non precision
1.) What is an VOR approach?
2.) If you need DME where will it be
4.) What kind of approach is it?
1.) Approach using a VOR that is not aligned to the runway hence its innaccuracy
2.) In the title
4.) non precision
1.) What is an ASR? What does it do?
2.)Precision or non precision
1.)Approach Surveillance Radar, allows ATC to give lateral guidance
2.)non precision
1.) What is an SDF?
2.)What it do?
1.) Simplified Directional Facility
2.)lateral guidance facility that covers large area, its really buns tho
1.) What is an NDB approach?
2.)is it accurate?
1.) Ground based raio transmitter broadcasts signal in all directions and we track using ADF (we dont have ADF we have the RNAV subsititute [ground based dme])
2.)no
1.) What is an LP approach?
2.)Does it require WAAS
1.) Localizer performance
2.)Yes
1.) What is an localizer approach?
2.)What are the dimensions
1.) track localizer inbound
2.) Guranteed accuracy up to 35º at 10nm
-Guranteed accuracy up to 10º at 18nm
What do you do on no gyro approach
ATC will tel you to turn left or right
If there’s no runway number on approach plate what does that mean.
Circling approaches only

1.) List all the lighting systems
2.) What does the dot above them mean
3.) If the signs were blacked out what does that mean
A: ALSF-2
A1: ALSF-1
A2: Short Approach Lighting system
A3: Simplified Short Approach Lighting System
A4: Medium Intensity Approach Lighting System
A5 Medium Intensity Approach Lighting System and RAIL
O: Omni directional lighting system
2.) Sequence flashing lights installed in approach
3.) pilot controlled lighting
List FAR AIM Part 91.167-187 main topics
167:Fuel requirements
169: Flight Plan
171: VOR checks
173: ATC Clearence
175: Takeoff and landing under IFR
176: enhanced flight vision systems
177: Min altitudes for IFR
179: Cruising altitude
180: Reduced Vertical Seperation Min airspace
181: Course to be flown
183: IFR comms
185: Radio fail
187: malfunction reports
Which approach kinds use WAAS?
LPV and Localizer Performance
How does GBAS work?
provides accurate gps signals through a ground station, basically ground based WAAS that shoots out signal that is more accurate
1.)The aircraft must remain within the required RNP value for at least ______% of the flight time.
2.) RNP “distances”
1.) 95%
2.)Enroute: 2miles
-Departure: 1 mile
-Arrival: .3 miles
What is a popup IFR clearence
clearance outside of controlled airspace before preceding into IFR in controlled airspace ,
What can we expect in a clearance for IFR.
Clearance limit
Route
Altitude
Frequency
Transponder
How long after ETA do you have to cancel IFR flight plan?
30 minutes
1.) Mandetory Reporting points
2.) Which ones are non radar
1.) Missed approach
Airspeed ± 10 kts or 5% TAS deviation
Reach holding fix
VFR on top altitude change
ETA ± 2 minutes
Leaveing hold fix
Outer marker inbound
Unforecasted weather
Saftey of flight
Vacateing altitude
Final approach fix inbound
Radio/comm failure
Compulsory reporting points
500’/min climb or descent not attainable.
2.) ETA, Outer marker inbound, Final approach inbound, Compuslory reporting point
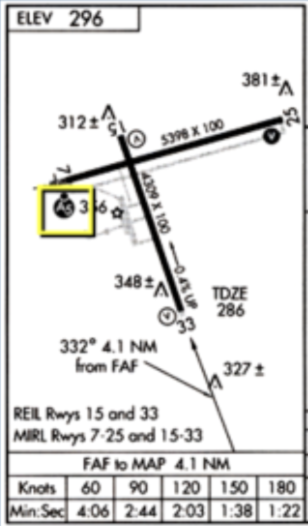
In the box for a missed approach point, is that speed indicated, true, calibrated, or ground speed.
ground speed
What altitude will you fly when you cant see and in an emergency situation
Minimum Safe Altitude
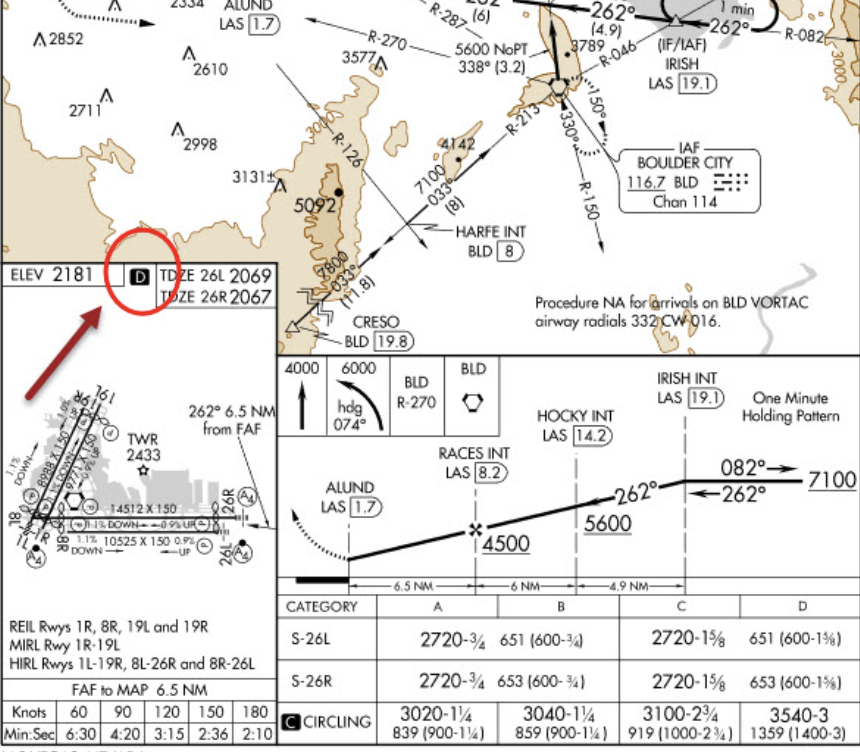
what does the D mean
symbol is shown to indicate runway declared distance information available, you can see appropriate Chart Supplement for distance information.
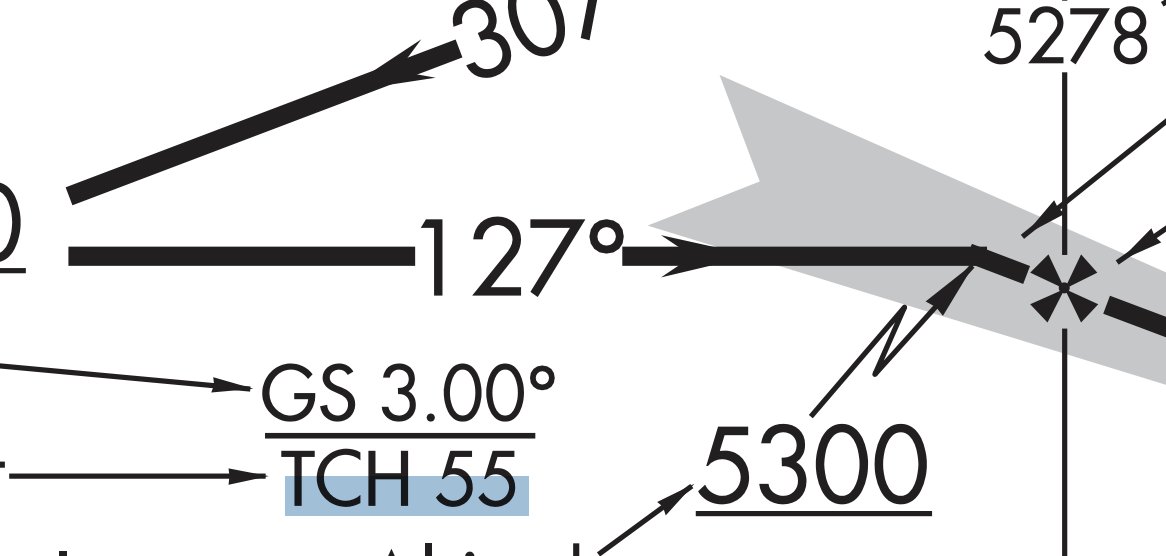
What does the TCH stand for
Threshold crossing height
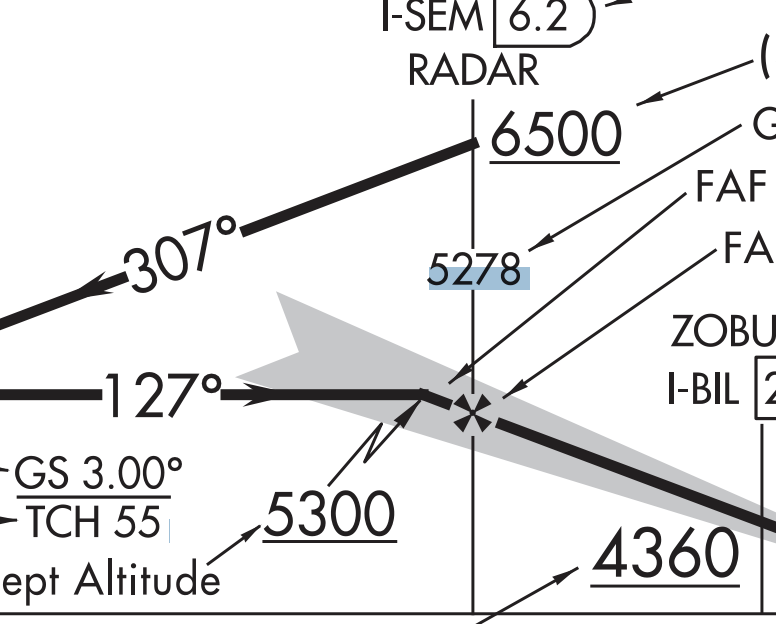
1.) What does the highlighted 5278 stand for
2.) What does the 5300 stand for
1.)Glide Slope Altitude at Outer Marker/FAF
2.) glide slope intercept altitude
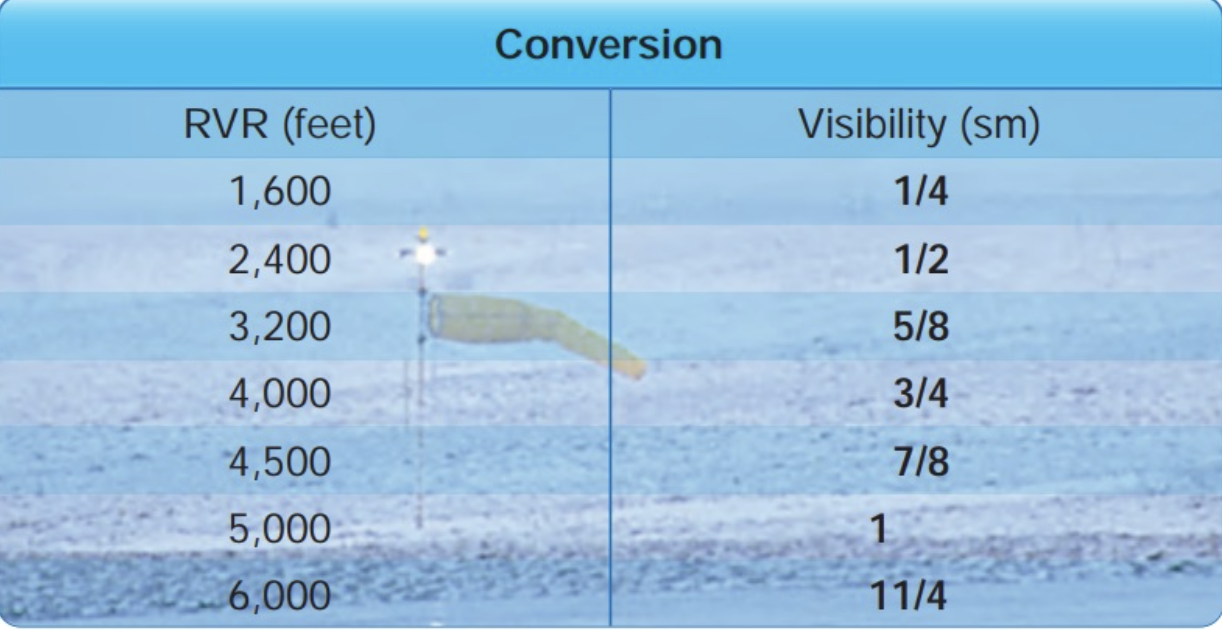
Rvr feet to statute miles
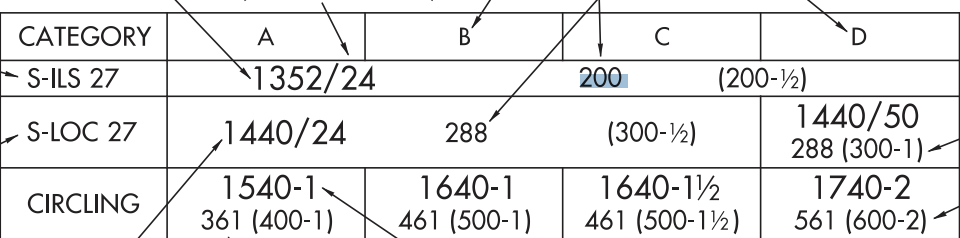
1.) what does the 200 in the S-ILS 27 and 288 in the S-LOC 27 stand for?
2.) what does the 361 stand for in the Circling
3.) what does the 1540-1 stand for in the Circling
1.) Height above touchdown zone
2.) height above airport
3.) MDA is 1540 with 1 sm visibility
If during a Non Precision there is no final app fix what would we use to replae it?
where procedure turn intercepts the course
No procedure turn if…
Straight in approach
Hold in leiu
Arc
Radar vectored
Procedure turn not authorized on chart
Teardrop entry in lieu of procedure turn
Timed approach
what is a microwave landing system
Two beams are scanned, aircraft derives angular information by intercepting the two beams.
Why are APV and percision seperate?
APV did not meet the requirements to meet ICAO standards for precision
1.)Which approaches have WAAS
2.)Which has angular senstivity
1.) LP & LPV
2.) LPV
List Takeoff minimums for part 91, 121 with one engine and two engines.
Part 91: none
Part 121/135:
-one or two engines: 1sm
3+ engines: ½ sm
What are you giving up if you take a contact/visual approach
the ability to re-enter clouds