HumanA&P 7: Bones
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Bone Tissue Composition
o Bone tissue (osseous tissue)
o Dense regular & irregular connective tissue
o Bone marrow (mix of tissue types)
o Epithelium
o Adipose tissue
o Nervous tissue
7 Bone Functions
Protection
Mineral Storage & Acid-Base Homeostasis
Blood Cell Formation
Fat Storage
Movement
Support
Hormone Production: Osteacalcin
2 Divisions of Skeletal System
Axial Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
80 bones that lie around longitudinal
axis of human body:
the bones of the skull, auditory ossicles (ear bones), hyoid
bone, ribs, sternum, and vertebrae.
Appendicular Skeleton
126 bones of upper and lower
limbs or appendages plus the bone groups called girdles
that connect the limbs to the axial skeleton.
6 Bone Classifications
Sutural Bones
Irregular Bones
Short Bones
Flat Bones
Long Bones
Sesamoid Bones
Long Bones
Longer than they are wide
Most bones in arms & legs
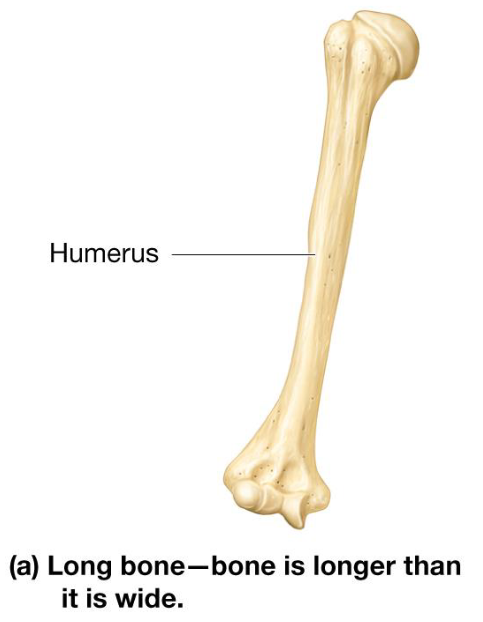
Short Bones
Roughly cube-shaped
Includes carpals & tarsals
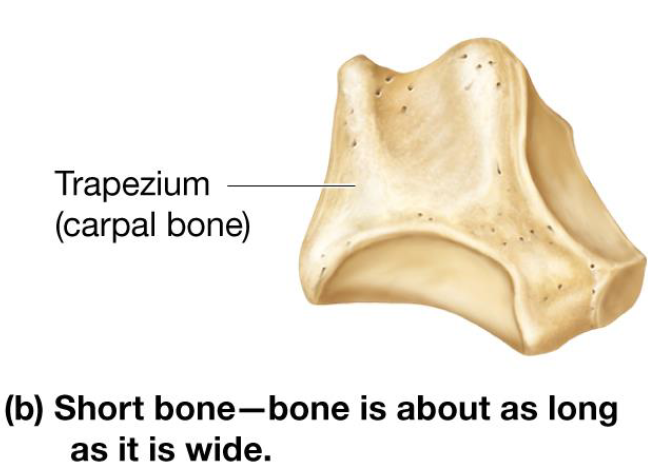
Flat Bones
Thin & broad bones
Include:
ribs
pelvis
sternum
skull bones
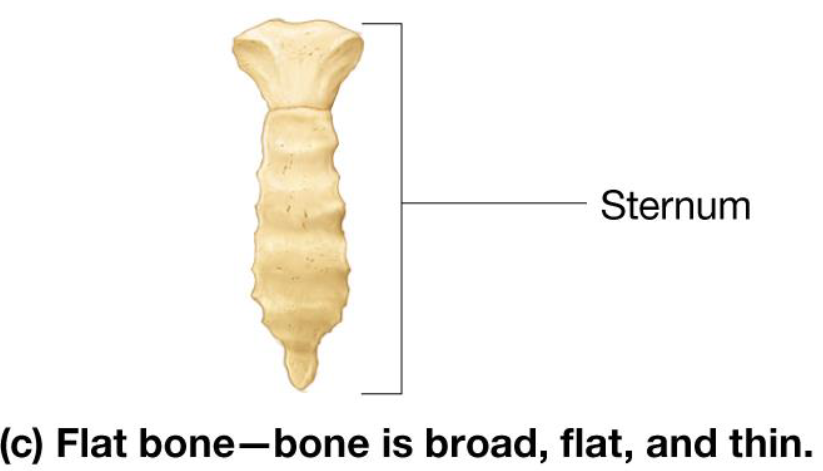
Irregular Bones
Irregular shape
Include vertebrae & skull bones
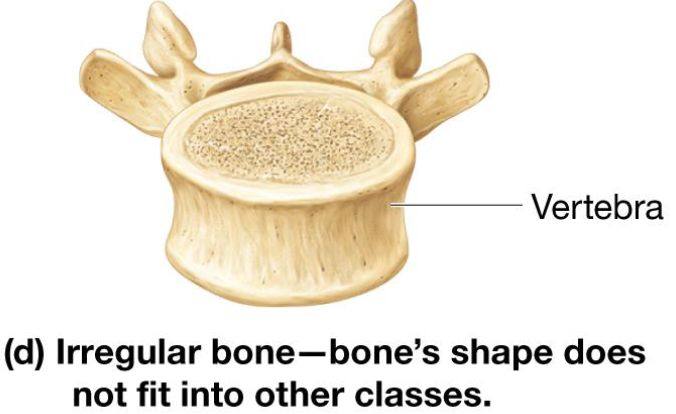
Sesamoid Bones
Specialized bones located within tendons
Usually small, flat, oval shaped
Gives tendons mechanical advantage
Appositional Cartilage Growth
Cartilage-forming cells in perichondrium secrete matrix against external face of existing cartilage
New matrix laid down on surface of cartilage
Interstitial Cartilage Growth
Chondrocytes within lacunae divide and secrete new matrix, expanding cartilage from within
New matrix made within cartilage
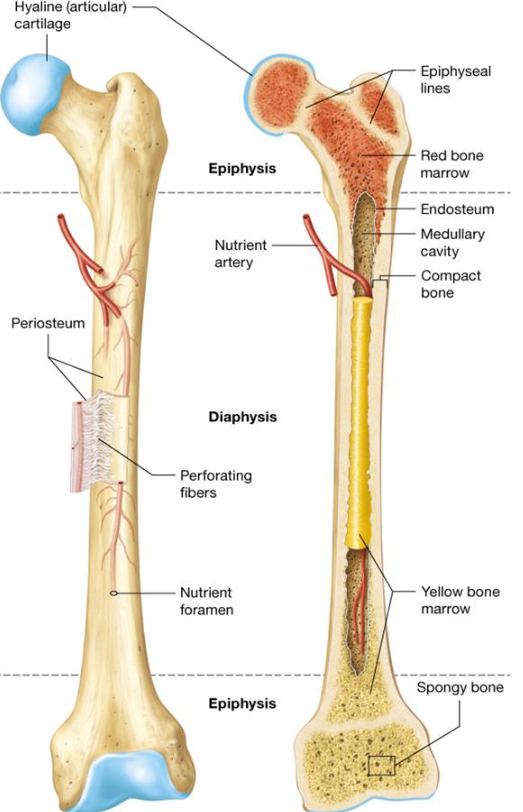
Anatomy of Long Bones
Diaphysis
Epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
Periosteum
Medullary Cavity
Endosteum
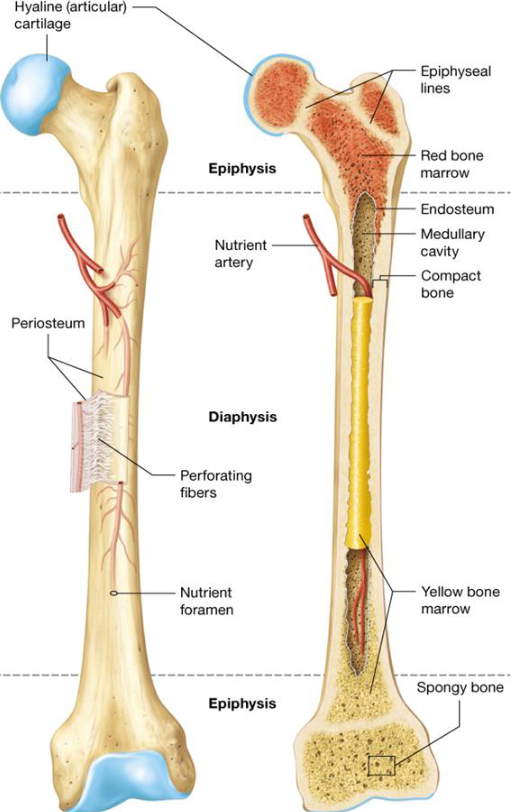
Diaphysis
Long bones
Middle shaft of long bones
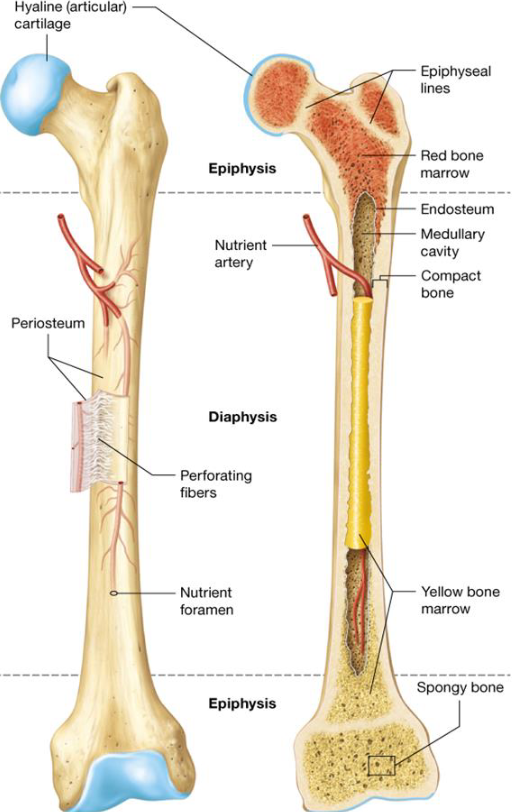
Epiphysis
Long bones
2 rounded ends of long bones
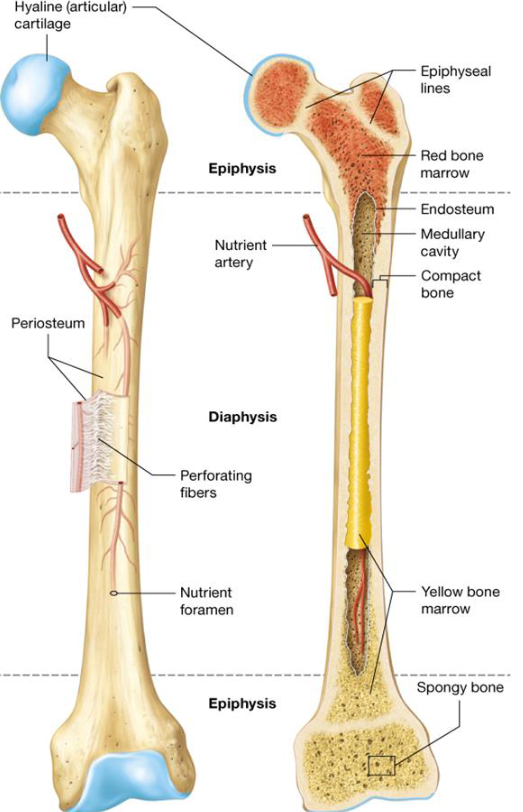
Articular Cartilage
Long bones
Thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering regions of the epiphysis where bone articulates with other bones
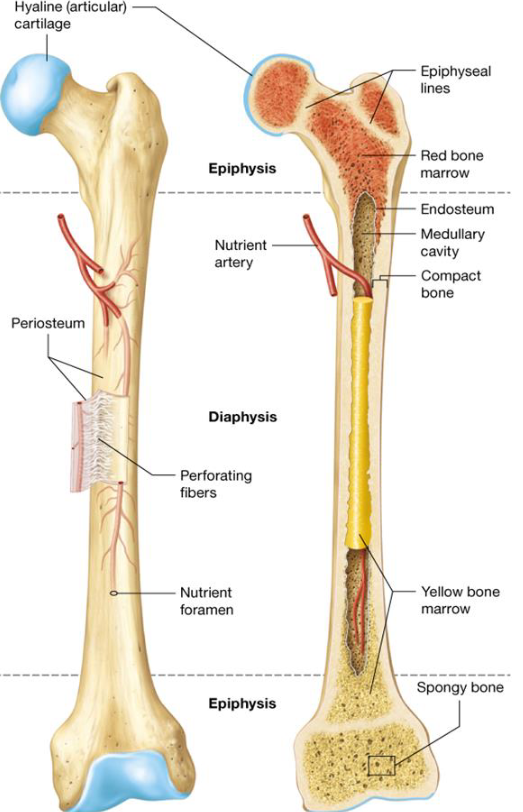
Periostium
Long bones
Sheath of dense irregular connective tissue and blood vessels surrounding parts of the bone outside of the articular cartilage
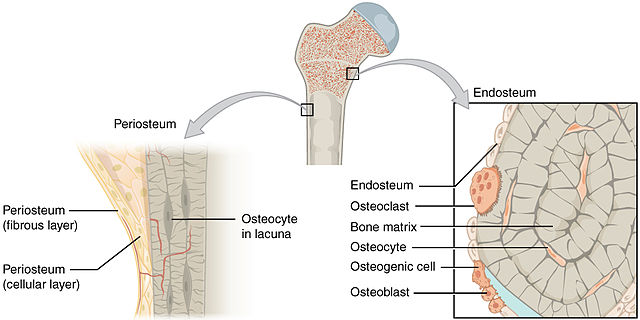
Endosteum
Long bones
Thin membrane that lines medullary cavity in
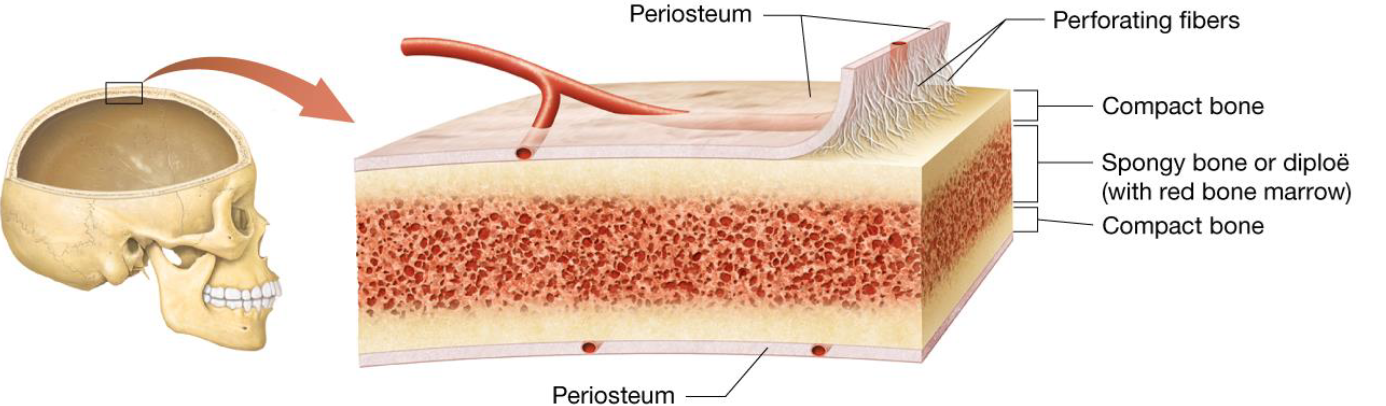
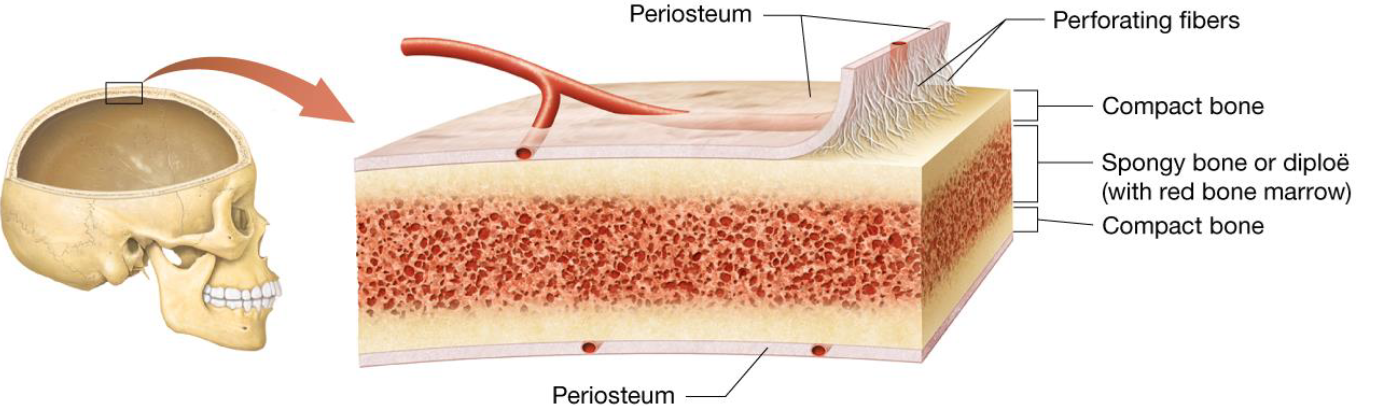
Anatomy of Short, Flat, Irregular & Sesamoid Bones
No diaphysis, epiphysis, or medullary cavities
Covered by periosteum, perforating fibers
Internal structure:
2 outer layers of thin, compact bone
Middle layer of spongey bone
Red bone marrow
Blood Supply to Long Bones
1/3 from periosteum
2/3 from nutrient arteries through nutrient foramen
Blood Supply to Short, Flat, Irregular & Sesamoid Bones
Provided mostly from the periosteum
Red Bone Marrow
Loose connective tissue
Blood-forming hematopoietic cells
Amount decreases with age
Yellow Bone Marrow
Triglyceride storage
Blood vessels
Adipocytes
Microscopic Bone Structure
Osseous tissue composed mostly ECM with small population of cells scattered throughout
Extracellular Matrix of Bone
Inorganic materials: minerals 60% of bone weight
Organic materials: Collagen fibers & usual ECM components make up the rest
Inorganic Bone Matrix
Predominantly calcium salts
Stores around 85% of calcium ions, lots of phosphorus
Ca + P = hydroxyapatite crystal
Makes bone hardest substance in body
Bicarbonate, potassium, magnesium, sodium
Bone shatters easily without it
Organic Bone Matrix
Osteiod
Consists of:
protein fibers
proteoglycans
glycosaminoglycans
bone-specific proteins
collagen
Bone cannot resist compression without it
4 Bone Cells
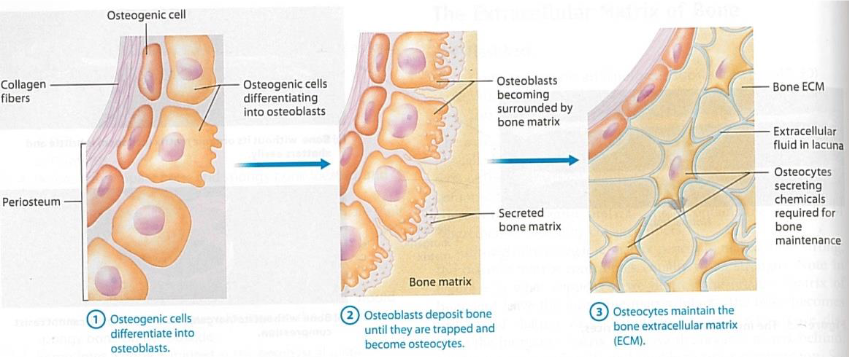
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
Osteoclasts
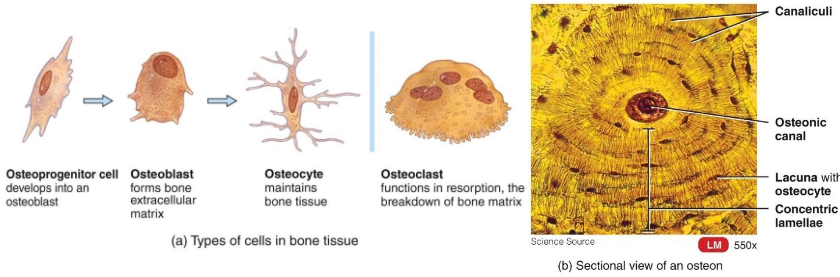
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Stem cells that develop into osteoblasts
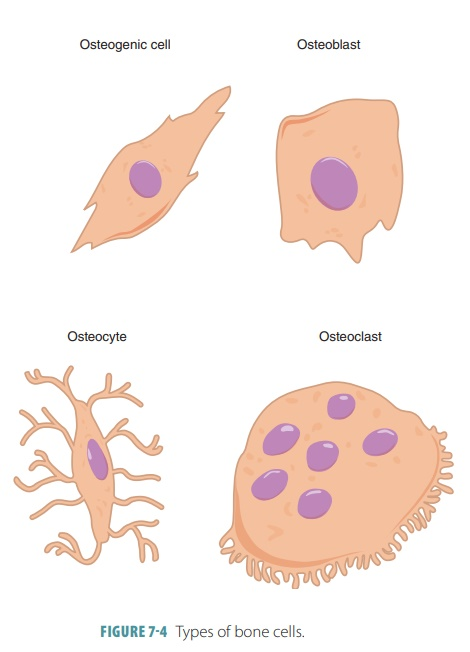
Osteoblasts
Bone deposition
Synthesize & secrete ECM that calcifies into bone
Eventually surround themselves with matrix in lacunae and become osteocytes
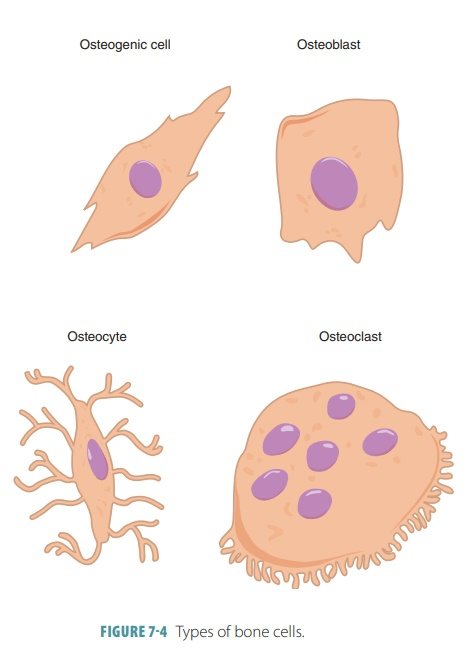
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells
Most numerous cells in bone tissue
Maintain bone tissue
Monitor mechanical stress
Help repair damaged bone
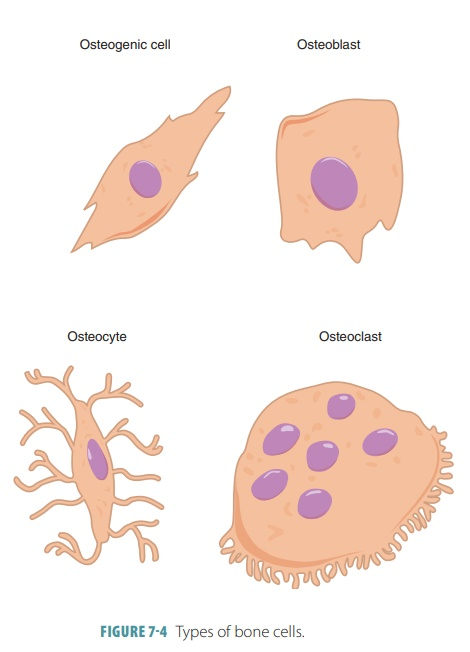
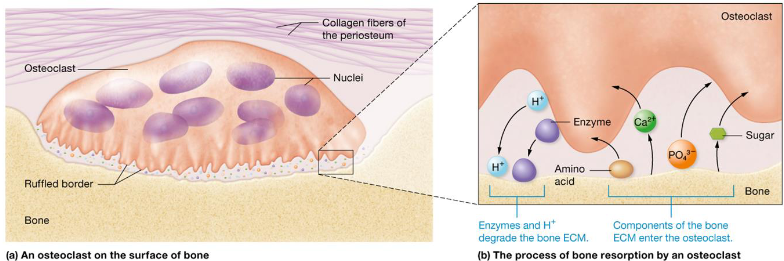
Osteoclasts
Bone reabsorption
Secretes H+ and enzymes to break down materials
Large multinucleated cells
Break down ECM to release nutrients
Help bones grow & heal
Osteogenic Cells
Immature cells that differentiate into osteoblasts when stimulated by specific chemical signals
3 Steps of Osteoblasts —> Osteocytes
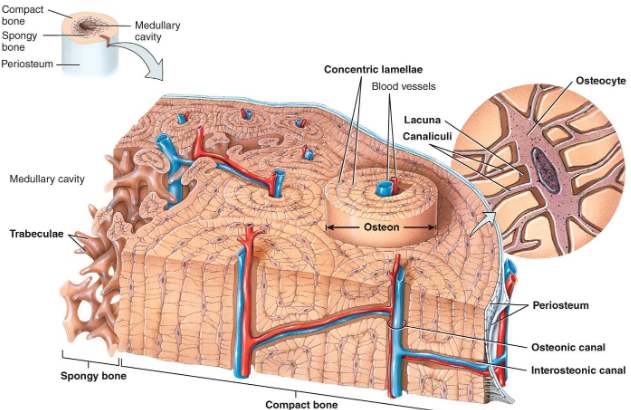
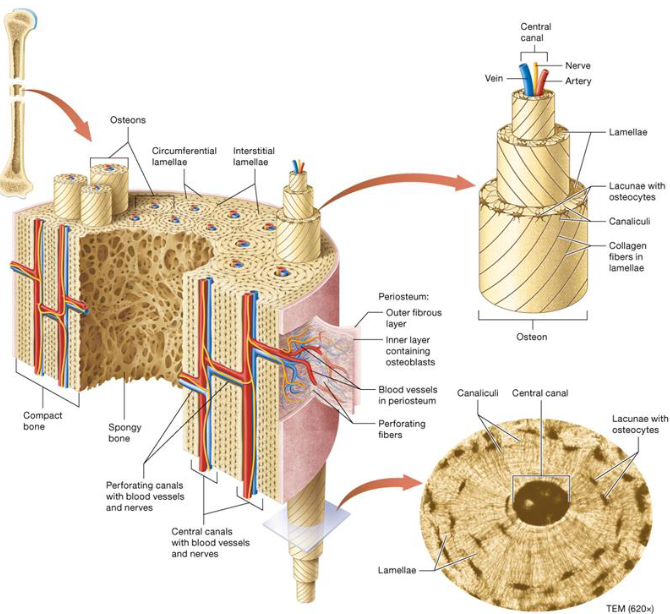
Bone Histology
Hard outer compact bone
Organized by osteons
Inner layers called lamellae
Porous inner spongy bone
Trabeculae
Lacunae
Small cavities or spaces
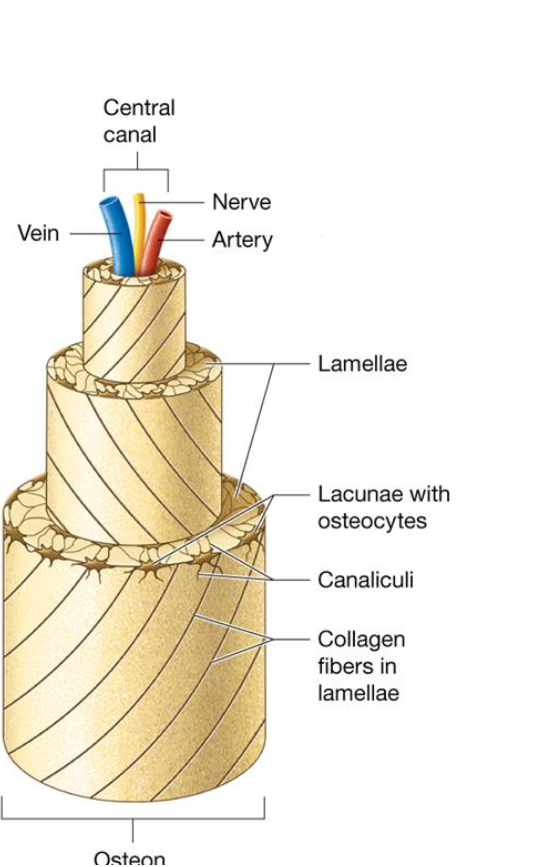
Osteon Structure
Osteon contains 4-20 lamellae ring structures that make the bone strong
Central canal contain blood vessels & nerves
Osteocytes reside in lacunae
Canaliculi are extensions of osteocytes that connect lacunae together
Spongy Bone
Resists forces from multiple directions
Made of trabeculae: projections of bone making “web”
Made of lamellae with osteocytes localized to lacunae that communicate through canaliculi
No osteons
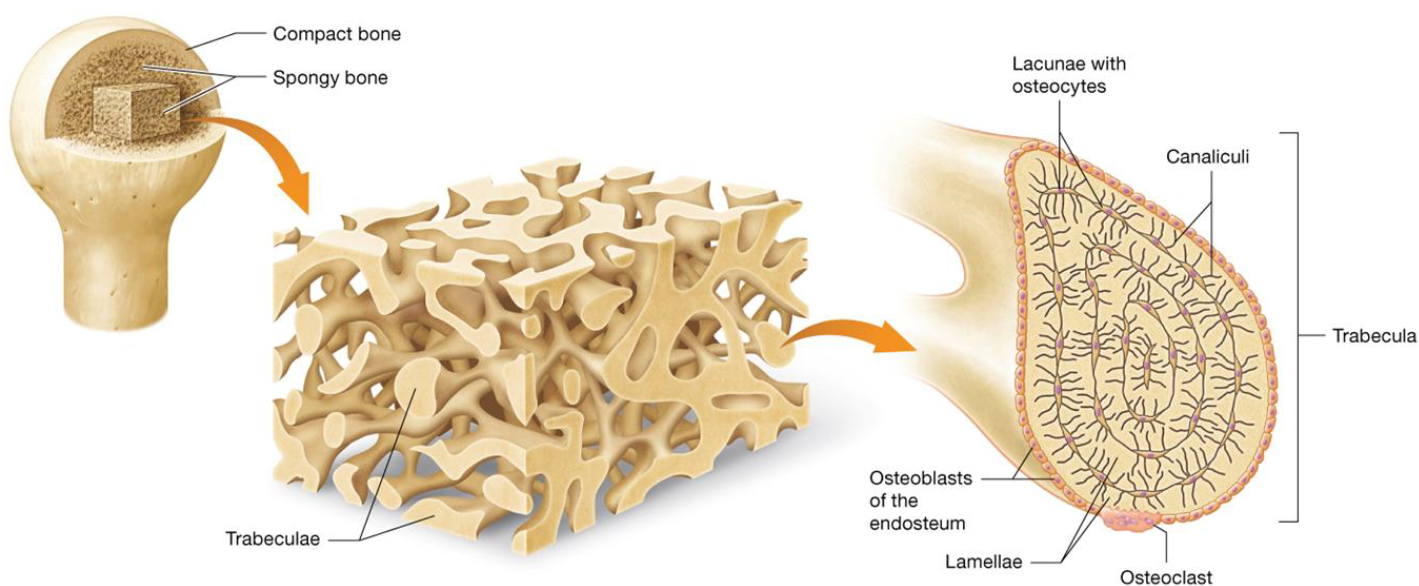
Bone Density
Compact Bone:
Denser, arranged into osteons with osteonic canal
Concentric lamellae, lacunae within
Spongy Bone:
No osteons
Arranged in trabeculae
Cavities are filled with red bone
Factors Affecting Bone Homeostasis
Require multiple factors to be successful:
Adequate minerals
Vitamins A, C, D
hGH & insulin-like growth factors
Weight-bearing exercise that stresses bones
Growth driven by hormone increases, repair/remodeling occur throughout life
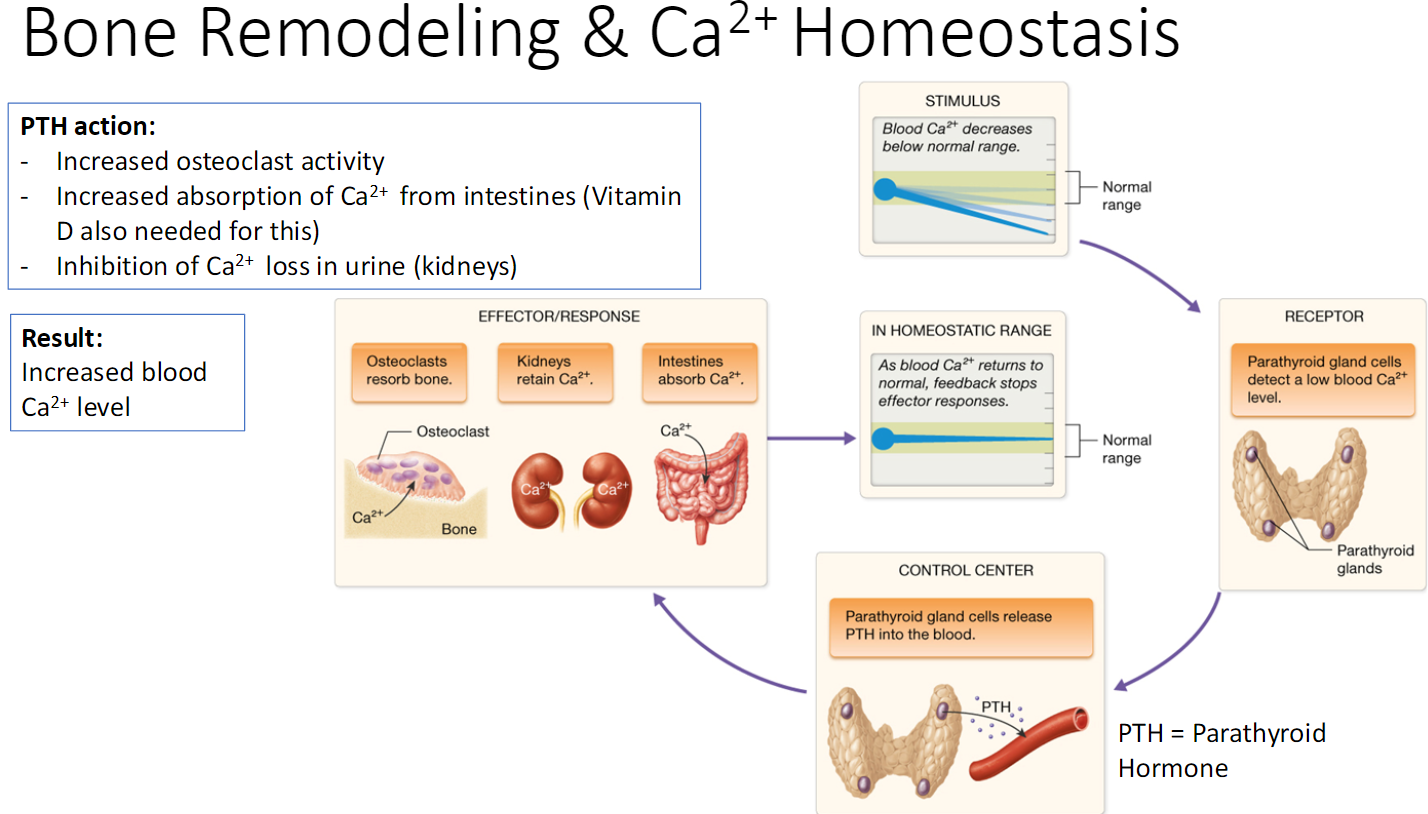
Parathyroid Hormone
Higher levels stimulate osteoclasts to break down more bone matrix, lower levels slow activity
Bone Resorption
Removal of minerals and collagen by osteoclasts
Bone Deposition
Addition of minerals & collagen by osteoblasts
Bone Remodeling
Continuous process, old tissue replaced
Absorption & deposition
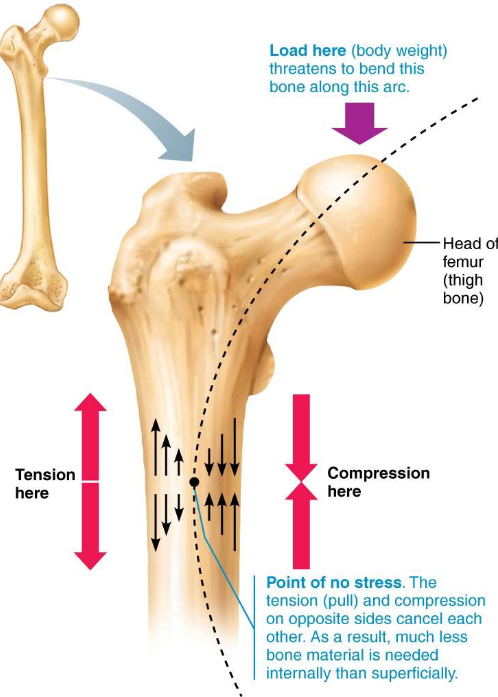
Blood Ca levels determine when matrix is broken or formed
Gravity & muscles determine where matrix is broken or formed
Bone Remodeling & Ca2+ Homeostasis
Bone Spurs
Growth of bone from excessive rubbing on the bone
Can cause problems if they end up rubbing on other structures
4 Types of Bone Fractures
Partial: incomplete break
Complete: bone is broken in 2 or more pieces
Closed (simple): bone does not break through skin
Open (compound): bone protrudes through skin
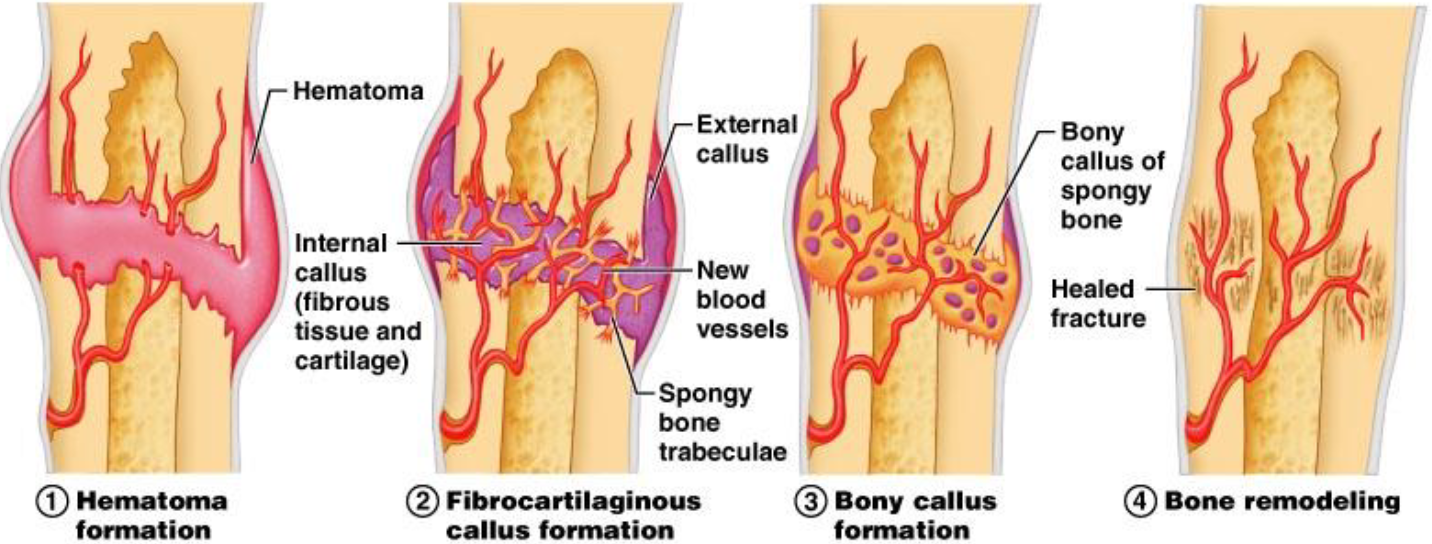
4 Steps of Bone Formation After Fracture
Exercise & Bone Tissue
Bone becomes stronger when placed under stress
Osteoporosis
Long term lack of calcium
Age-related osteoporosis linked to reduced estrogen during menopause
Related to overactive thyroid, parathyroid, or adrenal glands