Early Empires in West Asia and the Mediterranean | Quizlet
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Consolidated Empires
Succesful Empires
Aspirational empires
Lasted just for a few decades
Empires as participatory systems
They only operate if people actually become part of it
Empire definition by Smith and Montiel 2001
"states incorporating several previously independent and culturally distinct nations the ruler of which could style himself as 'kings of kings'"
Empire definition by Tilly 1994
"Concatenating central military organizations, thin regional administrations, trading networks, and organizations of tribute in which local and regional rulers - often maintaining cultural identities distinct from that of the empire's centre - enjoyed great autonomy in return for collaboration in the collection of tribute and support in the empire's military campaigns."
Institutionalized perspective on empires
Standardized weights, distances, people and taxes
The imperial capital
A feature of an empire
- Large complex urban centre with proclamations of imperial ideology
Domination of territory
A feature of an empire
- Economic control with exchange between capital and provinces and the political and military control
Projection of influence in a larger international context
Economic influence through trade with extraimperial regions
Political and military influence along enemy borders
Cultural influence by adoption of imperial gods or rituals
Hegemonic empire
Remains in hands of original rulers who become vassals.
Less expensive, less stable.
No need to create an entirely new infrastructure
Territorial control
High investment and high revenues
Bootom-up perspective on empires
The new imperial histories
Shift to local and embedded research
Can territorial empires have vassal states?
Yes
The model put forward by Smith and Montiel
contains many criteria that are not unique to empires
Why do network models of ancient empires compare well with examples from the modern world?
Transnational military infrastructures tend to take the form of networks
In the new imperial history empires are studied as
produced in the course of daily interactions in imperial provinces and peripheries
Impact by colonial rule on
Family structures, sexual practices gender roles
Imperial power
Shift from homogenously run centrist states to heterogeneous and dynamic patchworks of imperial configurations
Self-evident empires
Empires with written source context
Study of Empires in Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica
Difficult to study
Hegemonic in character
Definition of empire and imperialism by Doyle (1986)
Behavioural definition of empire as effective control, whether formal or informal of a subordinated society by an imperial society.
4 intersecting sources account for the imperial relationship
The Metropolitan Regime
The peripheral political society
The transnational system
The international context
The Hittites
Major state of Anatolian people between 1400 - 1180 BC
Akhenaton
Charismatic leader who moves the Egyptian capital to Amarna
The Amarna letters
International correspondence between the Great kings (Hittites, Babylonians, etc.)
Letter from Mittani to Pharaoh of Egypt
Marriage between families
Pleasant letter
Letter from King of Byblos to King of Egypt
Showing respect
The Battle of Kadesh
1275 BC - Ramses II vs Muwatallis
Big battle between Egypt and Hittite Forces
Engineering Metropole in Hittite Empire
> circular fortifications
> The development of Hattusa
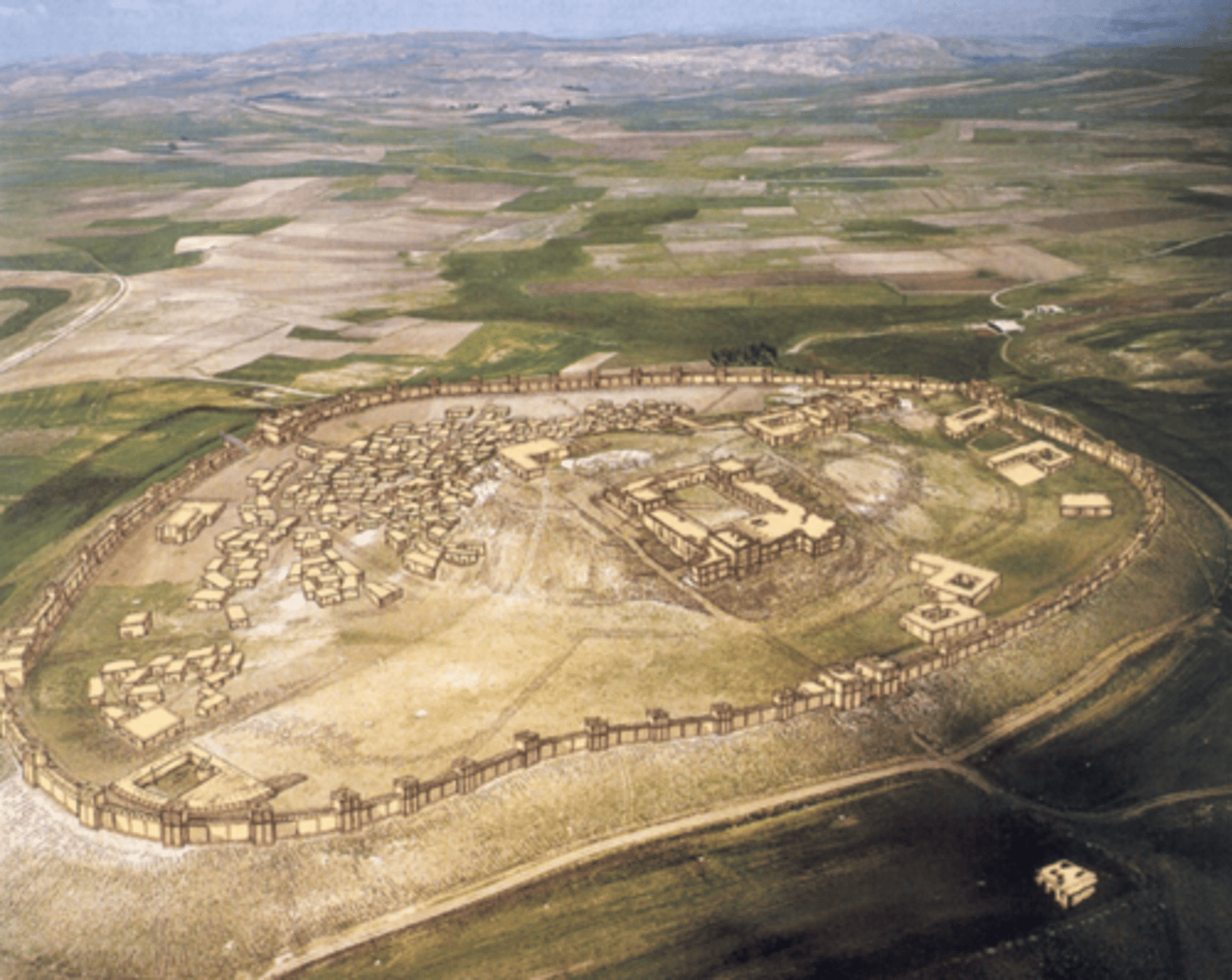
Hattusa
capital of Hittite empire
Land of a thousand gods
Continuous settlement with profound structural and functional changes
Old Assyrian Trade routes
Between Upper-Mesopotamia, Assur and central Anatolia
> Metals, textiles
Karum-Hatus houses
Courtyard buildings and trading station
Citadel of Büyükkale
Steep natural fort
Godnapping in Hattusa
Taking statues of gods to take them to Hattusa
Temples of Hattusa
Major economic institution
Supply rooms for goods and huge granaries
Structure of Hittite Temples
Modular rooms arranged
Central courtyard for offerings
Back of temple for statues
Rituals in a small room
Hittite Fortification problem
Upper city on flat terrace, walk in from south to north
Poterne
Little tunnel made of stone
For passage use when at peace
The Gates at Hattusa
Statuary iconography
Lions Gate/ Kings Gate
Mountain God
Son of Main God
Seal of King Muwatallis
Close link between king and deities
King responsibilities in cult and has special connection

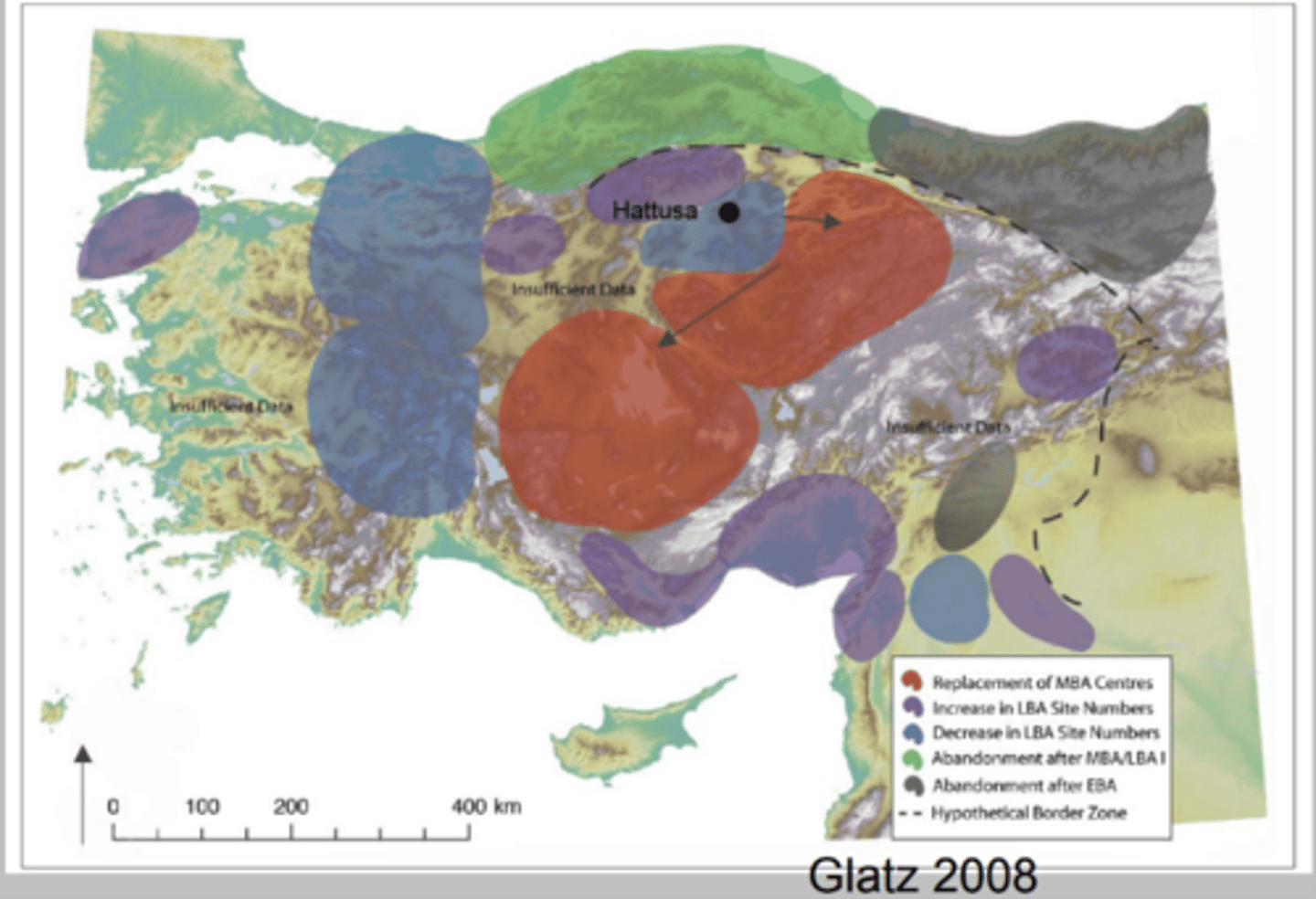
Hittite abandonment of cities
Decrease in LBA in settlement numbers
Harvesting people by conquering areas
Taking people back to Hittite land for farming
Kusakli-Sarissa
New centre built of 18 ha with c. 5000 people?
Temples, fortifications, gates, large monumental structures
Local administration by Hittites

LBA-NCA ceramics
Anatolian ceramics
At various sites found
Mainly in central highlands
Hittite Seals
At Troy, Levant and Cyprus
Do they represent only the Hittites or further as well?
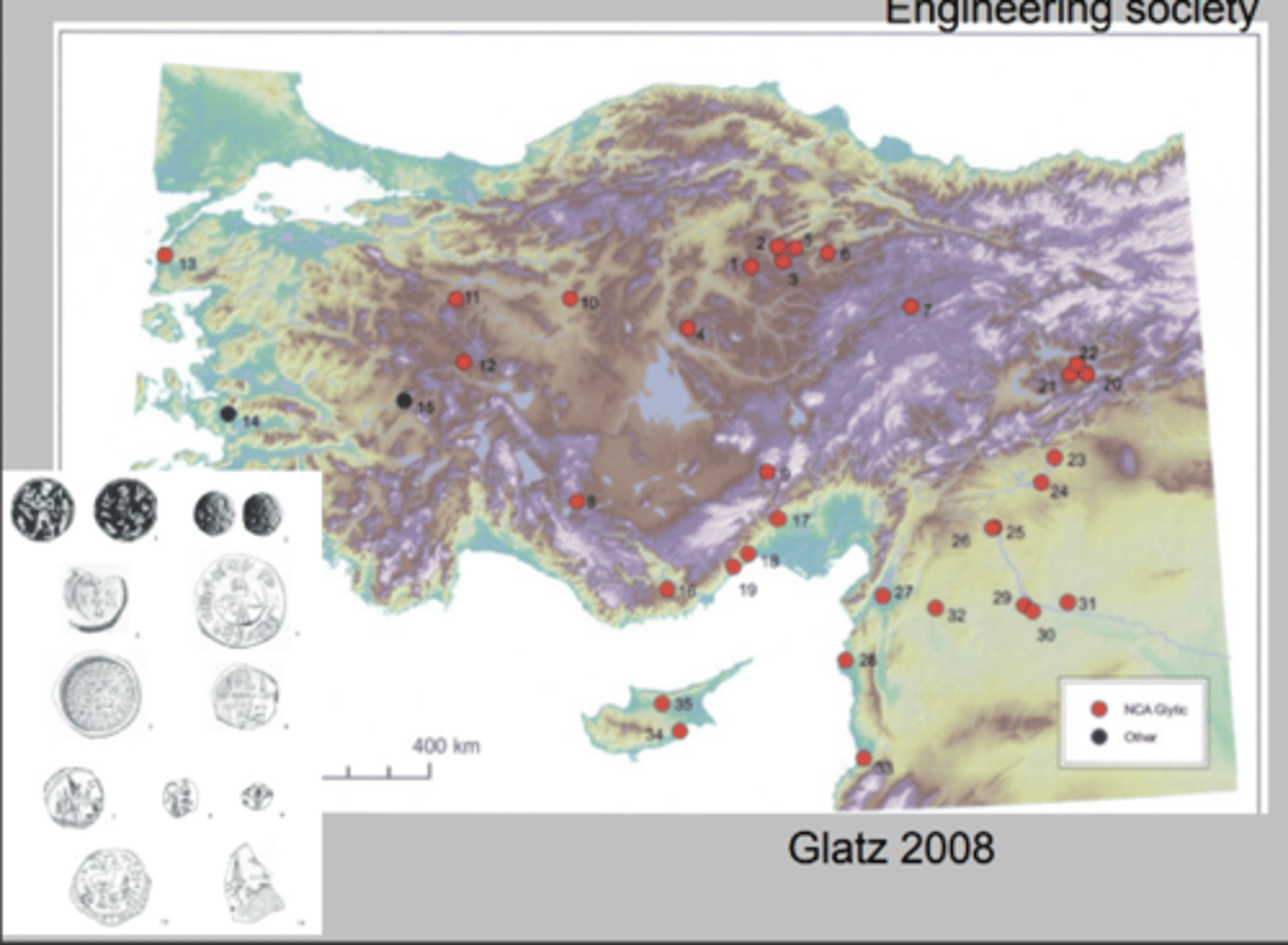
Engineering Subsistence Hittites
> Large-scale granaries
> Low-intensity farming
> Taxed yields
Hittite: Large Granary
capacity of 7000-9000m3
Landscape Change in Hittite Period
Oaks present in landscape with drop in LBA
Steppic herbs and grass increased in LBA
Engineering Space: Hittites
> Rock art monuments
> Design of religious and public spaces to reflect and enforce Hittite cultural and religious norms.
> Significant changes in landscape to support the agricultural and religious needs.
The Amarna archive is of great importance because
it provides us the correspondence between the pharaoh and his vassals as well as his peers
The first attestation of the Hittites occurs in
the trade archives at Kanesh
The site of Hattusa was chosen for
its historical importance
The Hittite capital was
a religious nexus for the empire
The Hittite Empire (quiz)
had diverse practices of rule
The Great Temple (Hittite)
Bogazköy
Constructed in the early Old-Hittite period
Symbolises the unification of the Hittite pantheon
Settlement sites (Hittite)
Typically on high plateaus or mountainous areas
Supra-regional exchange system
Vitaly for settlements in Hittite empire
> Extended influence beyond immediate constraints
Urban developments in Hittite
Rugged terrains needed new urban structures
13th c. BC changes in Hittite Empire
Major refurbishment and transforming central temple areas into representative quarter
The Assyrian Empire period
From c. 1350-612 BCE
The Assyrian Empire
First empire that doesn't have any competitors at the same level
Replaced by the Mitanni
The Assyrian Empire range
Assur - Sabi Abyad - Babylon - Memphis - Thebe
Augustan threshold
The point where an empire begins to stabilize through bureaucracy and integration
Propaganda used by the Assyrians
Orthostats
The Bible
Obelisks
Royal Annals
Orthostat
Slabs of stone with low relief with themes such as war scenes
The bible in Assyrian propaganda
Depopulation, the moving of people from one place to another
Assur
Ancient city of the Assyrian Empire
60 ha in total
Trade centre
Northern side had official monumental buildings
Southern side was the residential part
Distinct cultural traditions
Assur meaning
City/god/land (Assyria) / People (Assyrians
Anu-Adad temple
Key temple in Assyria
Only foundation is left
Middle Assyrian Palace
Remained central to kingship
Royal tombs for Assyrian kings
City layout of Assur
Buildings on open squares
Densely build up
Capitals of Assyrians
Needed bigger place so new capitals are being build
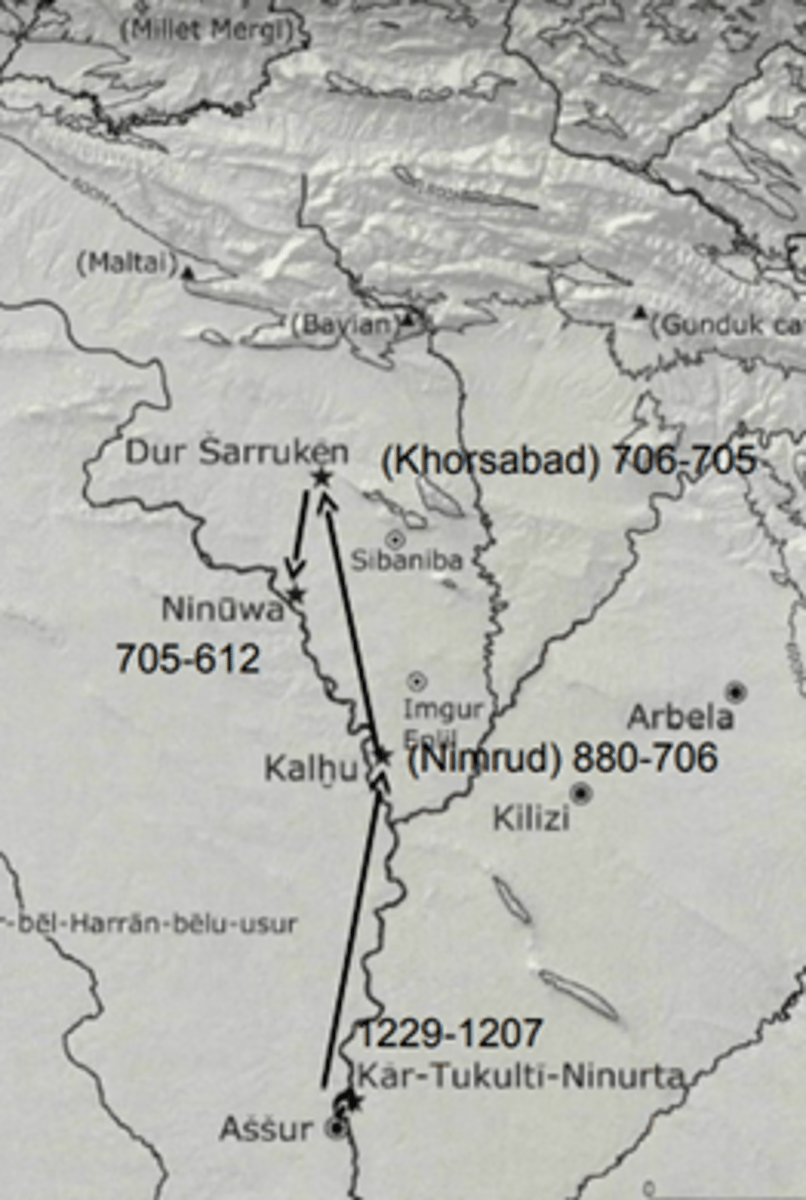
Kar-Tukulti-Ninurta
Capital of Assyria from 1229 - 1207 BC
240 ha
Failed only lasts 22 years
Has a city centre
Kalhu (Nimrud)
Capital of Assyria from 880 - 706 BC
Lasted the longest
was 300 ha
Dur Sarruken
only lasted one year from 706 - 705 BC
Ninuwa
Capital in the last years of Assyria from 705 - 612 BC
700 ha
Engineering Space: Assyrian Empire
> Establishment of fortified cities
> The use of monumental art to depict the power of the Assyrian state, reinforcing the empire's dominance over its territories.
The land of Assur and the yoke of Assur
Work by Nicholas Gate
The land of Assur - The heartland of Assyrian Empire
The Yoke of Assur - Broader imperial reach of Assyria
Engineering Society: Assyrian Empire
> Massive depopulation policies
> Resettlement of conquered peoples, which helped to integrate diverse groups into the empire and secure its borders.
Chariots in Assyrian Empire
Lightweight with 2 horses in front
Speed of transporting military personnel and trade
Engineering subsistence: Assyrian Empire
> Sophisticated irrigation systems
> Canals and aqueducts to support agriculture in the arid regions of the empire.
Agricultural system in the Upper Tigris (Assyrian)
Areas previously barren were cultivated
3 fundamental traits of empires
> Resource control
> Rapid expansion and decline
> Consolidation for stability
2 strategies used by imperial authorities in administering subject territories
Invasive restructuring
Coercive exploitation
3 overarching themes of Neo-Assyrian model of Imperialism
> Agricultural colonies establishment
> Use or enforcement of buffer zones between frontier provinces and hostile neighbours
> The discontinguous nature of imperial control
Assyrian Imperial Period
900 - 600 BC
Early Iron Age (1050-882 BC) Tigris River Valley
10 villages, 9 hamlets
Evenly spaced out villages
Loosely integrated villages
Early Iron Age Corrugated Wares (Assyrian)
Corpus of Ceramics
Handmade, low-fired
Bag-shaped jars
Local workshops
Ashurnasirpal besieged two sites of Upper Tigris River Valley before reaching town of Tusshan
Village of Mariru where assyrians carried off oxen and sheep
Town of Tela where Assyrians received oxen and cat
The Rassam Obelisk
Made by Ashurnasirpal
Visual representation of inhabitants of region
Tribute in form of textiles, cauldrons, logs
Kenan Tepe
Early Iron Age, Indigenous Anatolian small village
High mound with large stone structure
animal husbandry and cereal cultivation
Gre Dimse
Tell of 4 ha mound
Loose internal organization
Metalworking evidence and two EIA burials
Ziyaret Tepe
EIA occupation high mound (32 ha)
Substantial fortifications
Two monumental buildings
Tax collector room
Boztepe
Low mound
Part of domestic structure
House with several rooms centred around central courtyard
Liverani's network model
Empire is not a spread of land but a network of communications over which the material goods are carried
Postgate's territorial model
Inner core of provinces surrounded by vassal states
Parker's study on Upper Tigris
Assyrian impact varied greatly depending on agricultural potential and pre-existing social structures
Non-Assyrian participations
Non-Assyrian elites often adopted Assyrian identities to secure their status
Deportees in Assyria
Not seen as slaves but as dependents with certain rights and responsibilities
The Roman Empire start
509-27 BCE