Energetics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define exothermic reactions
A reaction that releases heat energy
What happens to the temperature in an exothermic reaction?
The temperature of a substance increases
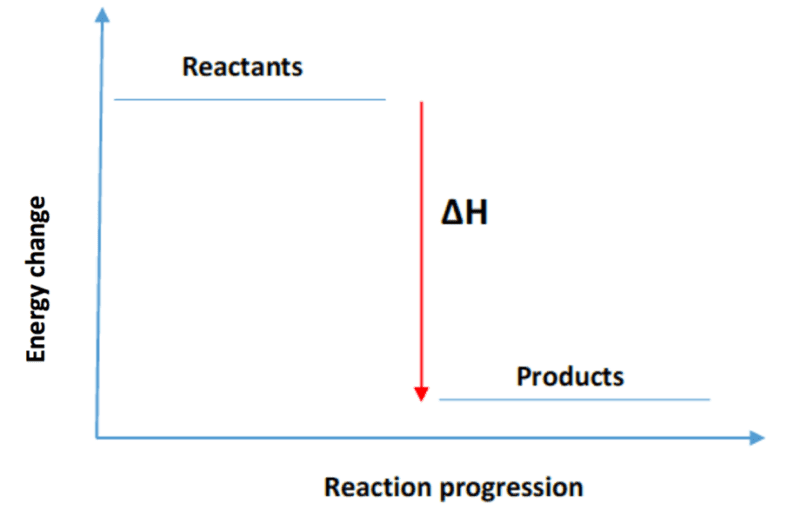
How does a graph for an exothermic reaction look like?
Products are lower than reactants
What are some examples of exothermic reactions?
1) Neutralisation
2) Combustion
3) Displacement (can be endothermic as well)
What are everyday uses of exothermic reactions?
1) Heat pack
Define endothermic reactions
A reaction that takes in heat energy
What happens to the temperature in an endothermic reaction?
The temperature of a substance decreases
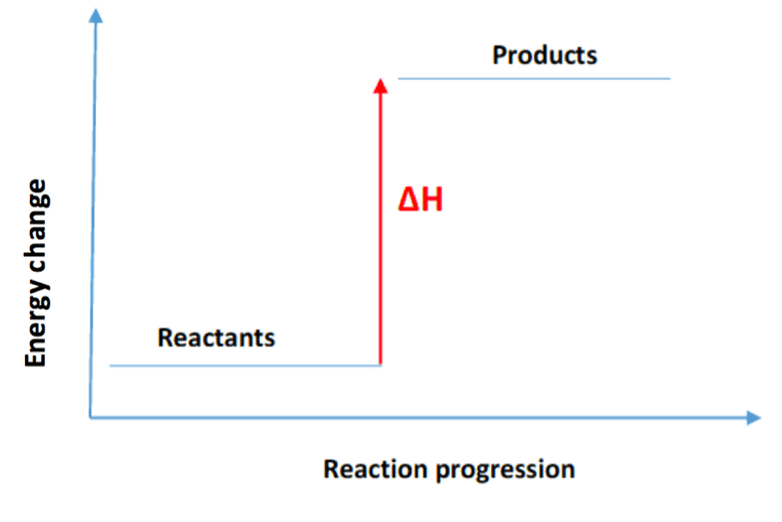
How does a graph for an endothermic reaction look like?
Products are higher than reactants
What are some examples of endothermic reactions?
1) Displacement (can be endothermic as well)
2) Dissolving
What are everyday uses of endothermic reactions?
1) Ice pack
What equation is used to calculate heat energy transferred between two objects?
Q = m c ∆T
Heat energy [J] = mass [g] x specific heat capacity [J/g°c] x temperature change [°C]
What is enthalpy?
Total energy stored within a system (reactants + products of a reaction)
What equation is used to calculate enthalpy?
∆H = Q/mol
Enthalpy = Heat energy/mole [J mol⁻¹]
In what reaction is enthalpy change negative, and why?
Exothermic reactions release heat as bonds are formed in products
Thus, products have a lower enthalpy than reactants started with
ΔH (enthalpy change) = Products - Reactants
→ negative number
In what reaction is enthalpy change positive, and why?
Endothermic reactions take in heat as bonds require breaking
Thus, products have a higher enthalpy than reactants started with
ΔH (enthalpy change) = Products - Reactants
→ positive number
What are the reasons for lower energy released in a calorimetry experiment?
1) Heat lost to surroundings
2) Incomplete combustion
What are the reasons for lower enthalpy change in a calorimetry experiment?
1) Heat lost to surroundings
2) Heat is absorbed by calorimeter
What is the method of the calorimetry experiment for combustion?
Using a measuring cylinder, measure 100 cm3 of water into a copper can
Measure and record the initial temperature of water
Filling the spirit burner with test substance, measure and record its mass
Place burner under copper can and light the wick
Constantly stir the water and heat until temperature rises 20 - 30°C + blow out flame
Measure and record the highest temperature of water
Measure and record the final mass of burner and remaining alcohol
What is the method of the calorimetry experiment for displacement, dissolving, and neutralisation?
Using a measuring cylinder, measure 25 cm3 of Solution 1 into a Polystyrene cup
Measure and record the temperature of Solution 1
Add a measured amount of reactant (solid for dissolving, solution 2 for displacement and neutralisation) into the Polystyrene cup and stir the mixture
Measure and record the highest temperature reached by the mixture