Water Quality: Salinity, TDS, and Turbidity Measurements
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Salinity
Concentration of salts in water, affects organisms.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
Measure of all dissolved substances in water.
Hardness
Sum of divalent cations, mainly Ca2+ and Mg2+.
Soft Water
Low TDS and pH, more corrosive to metals.
Hard Water
High TDS and pH, less corrosive.
Practical Salinity Units (PSU)
Measurement of salinity in g/kg.
Turbidity
Clarity of water, affected by suspended solids.
Total Suspended Solids (TSS)
Particles suspended in water, affects clarity.
Titration
Method to measure salinity using AgNO3.
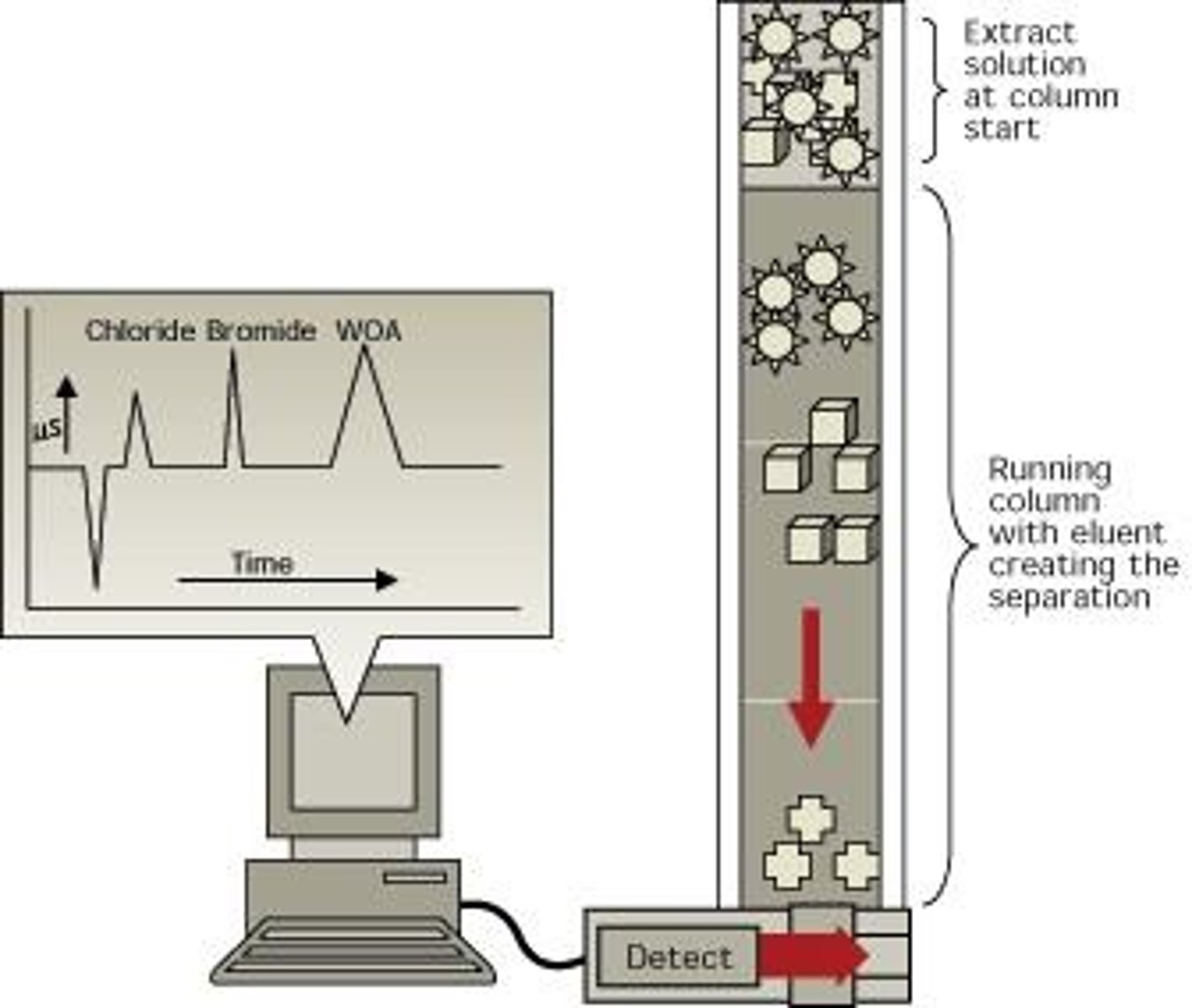
Ion Chromatography
Technique using ion exchange resin for salinity.
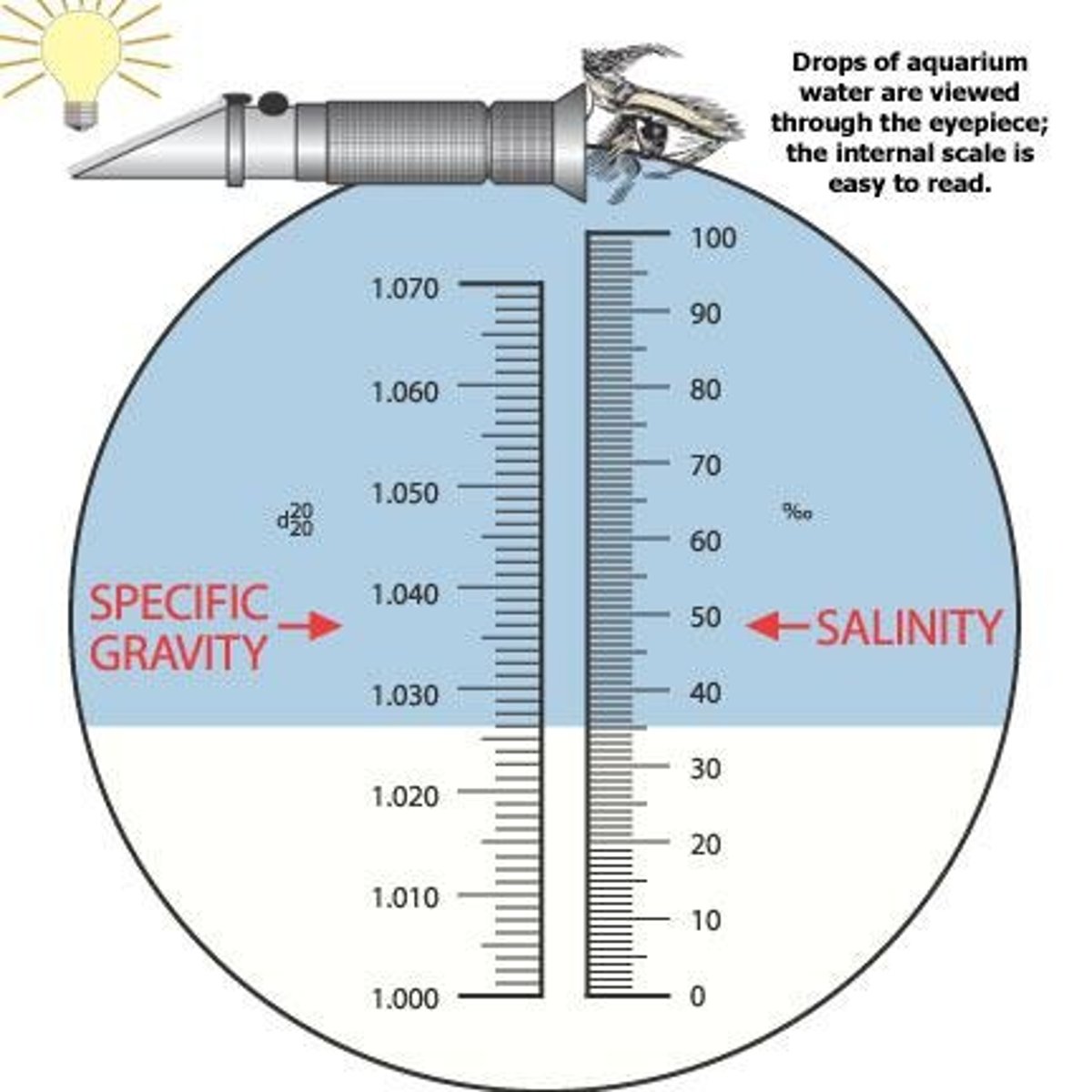
Optical Salinity Refractometer
Measures salinity
Nephelometric Turbidity Unit (NTU)
Unit for measuring turbidity in water.
Sources of TDS
Includes runoff, evaporation, and saline groundwater.
Measuring TDS methods
mass evaporation and conductivity.
Environmental Impact on TSS
Natural and human factors affecting sediment levels.
Bank Stabilization
Methods to reduce erosion and turbidity.
Geology
Type of material affecting stream turbidity.
Seasonal Weather
Spring runoff increases turbidity in streams.
Plant Root Systems
Help stabilize soil, reducing turbidity and erosion
Human Activities
Road building and development increase stream turbidity.
BMP for TSS
Best management practices to control sediment.
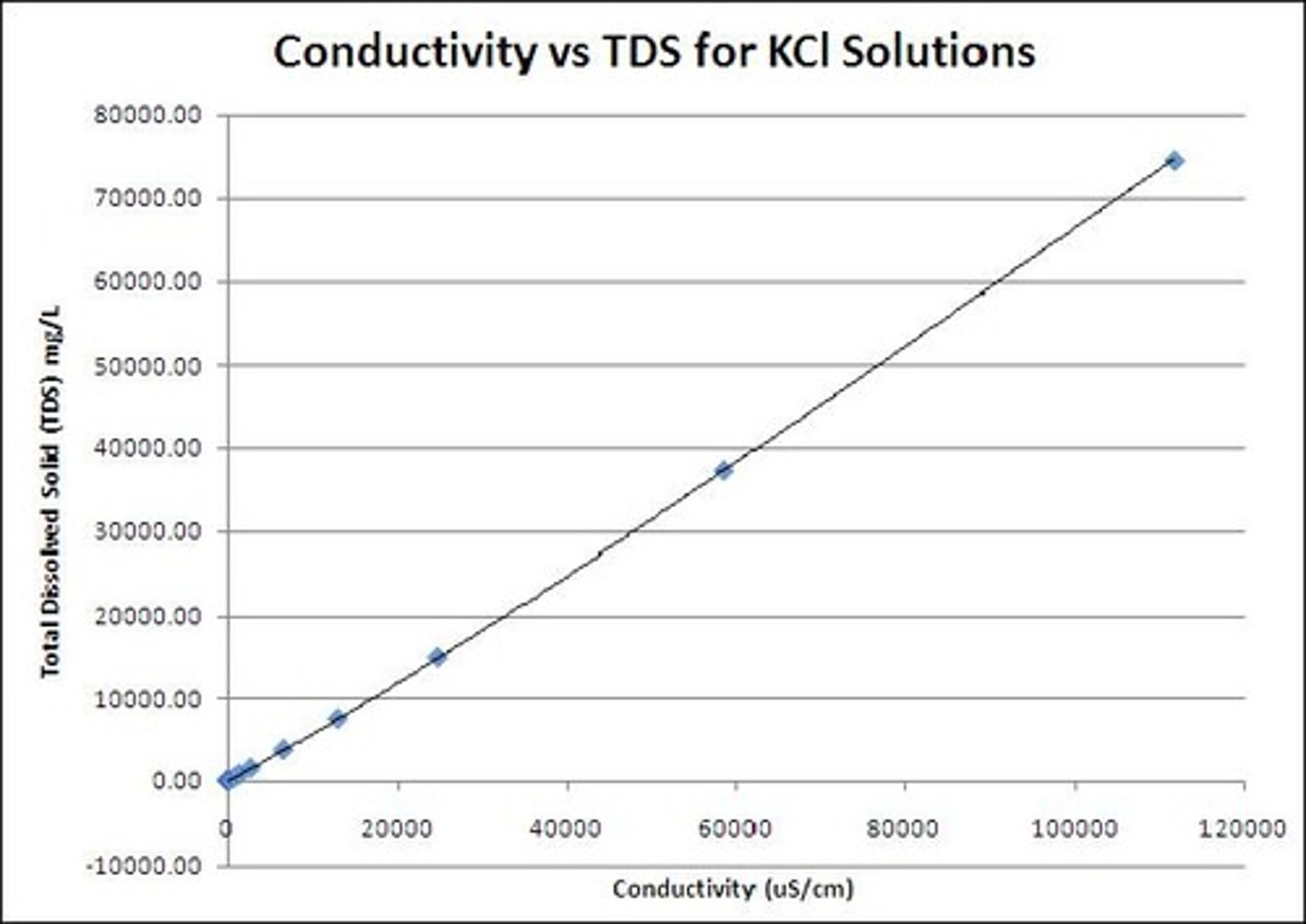
Conductivity Measurement
Reported as µS/cm, highly temperature dependent.

.64
Conversion factor for TDS from conductivity
Lake Okeechobee Example
Hard water lake with high Ca2+ and Mg2+.