1-4: Synaptic transmission; structure + function of neurons; nervous and endocrine system
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
What is synaptic transmission?
the way that neurons communicate with each other. It involves a message being passed chemically between neurons (sensory, relay or motor)
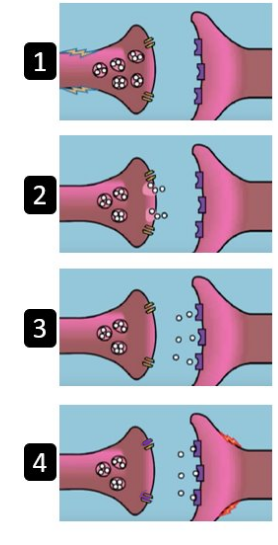
What is happening at step 1?
the electrical signal reaches the end of the presynaptic neuron and it arrives at the terminal button to be passed onto the postsynaptic neuron
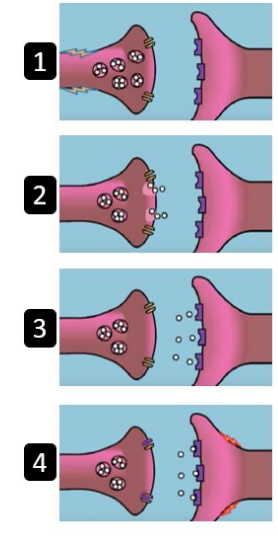
What is happening at step 2?
the electrical signal causes the vesicles to release the neurotransmitters they are carrying into the synaptic cleft ( the gap between the neurons)
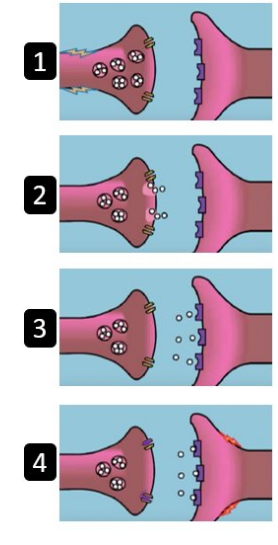
What is happening at step 3?
the neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and makes its way to the postsynaptic neuron. It can only enter the postsynaptic neuron if it fits into the receptor cells (complementary) e.g the neurotransmitter dopamine can only fir into the dopamine receptor sites
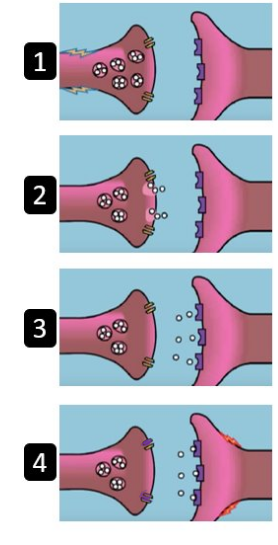
What is happening at step 4?
the neurotransmitter enters the receptor site and causes an electrical message down the postsynaptic neuron, ready to be passed on to the next one. Any neurotransmitters that are left in the synapse might be broken down (by enzymes) or reabsorbed by the reuptake channel so it can be used again
What are the two possibilities of what a neurotransmitter can be?
either excitatory or inhibitory
What is an excitatory neurotransmitter?
one that binds to the receptor sites and increases the chance of the post-synaptic neuron continuing the message to the next neuron as it makes it more likely to fire
What charge does an excitatory neurotransmitter create?
a positive charge
What is an example of an excitatory neurotransmitter?
adrenaline
What is an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
one that binds to the receptor sites and decreases the chances of the post-synaptic neuron continuing the message to the next neuron as it makes it less likely to fire.
What charge does an inhibitory neurotransmitter create?
a negative charge
What is an example of an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
serotonin
Define summation.
a process which decides whether a post-synaptic neuron will fire (pass on the message). This happens by weighing up the amount of inhibitory neurons compared to the excitatory neurons
What will happen if there are more excitatory neurotransmitters than inhibitory?
the post-synaptic neuron will fire
What do sensory neurons do?
Carry information from sensory receptors in the PNS to the CNS
What do relay neurons do?
Connect sensory and motor neurons within the CNS (or to other relay neurons)
What do motor neurons do?
Carry signals from the CNS to effectors (muscles/glands)
What structural features do sensory neurons have?
Long dendrites, short axon
What structural features do relay neurons have?
Short dendrites, short axon
What structural features do motor neurons have?
Short dendrites, long axon
Show the overall structure of a neuron
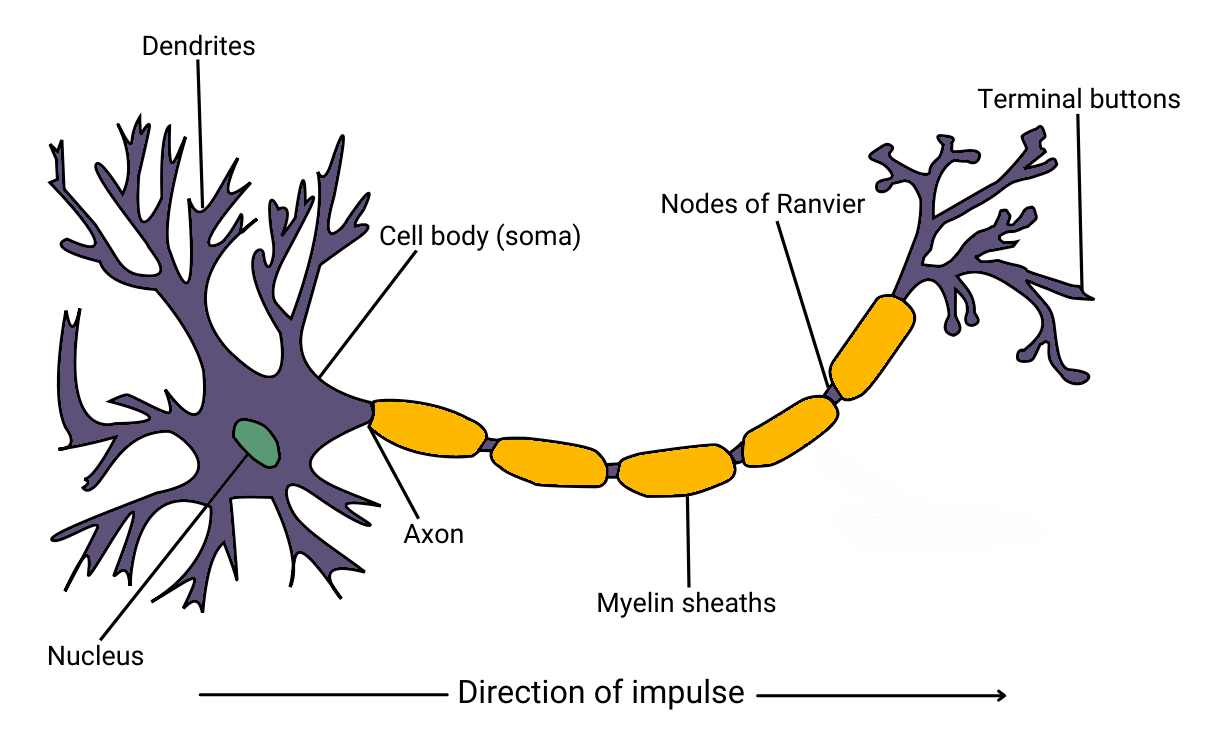
What does the cell body do?
it carries the nucleus
What does the nucleus do?
it contains genetic material (DNA)
What do dendrites do?
receives electrical signals from nearby neurons
What does the myelin sheath do?
protects the axon and speeds up electrical signals
What does the node of Ranvier do?
speeds up electrical signals
What does the terminal button/axon terminal do?
communicates to a nearby neuron
What does the axon do?
carries the message through the neuron
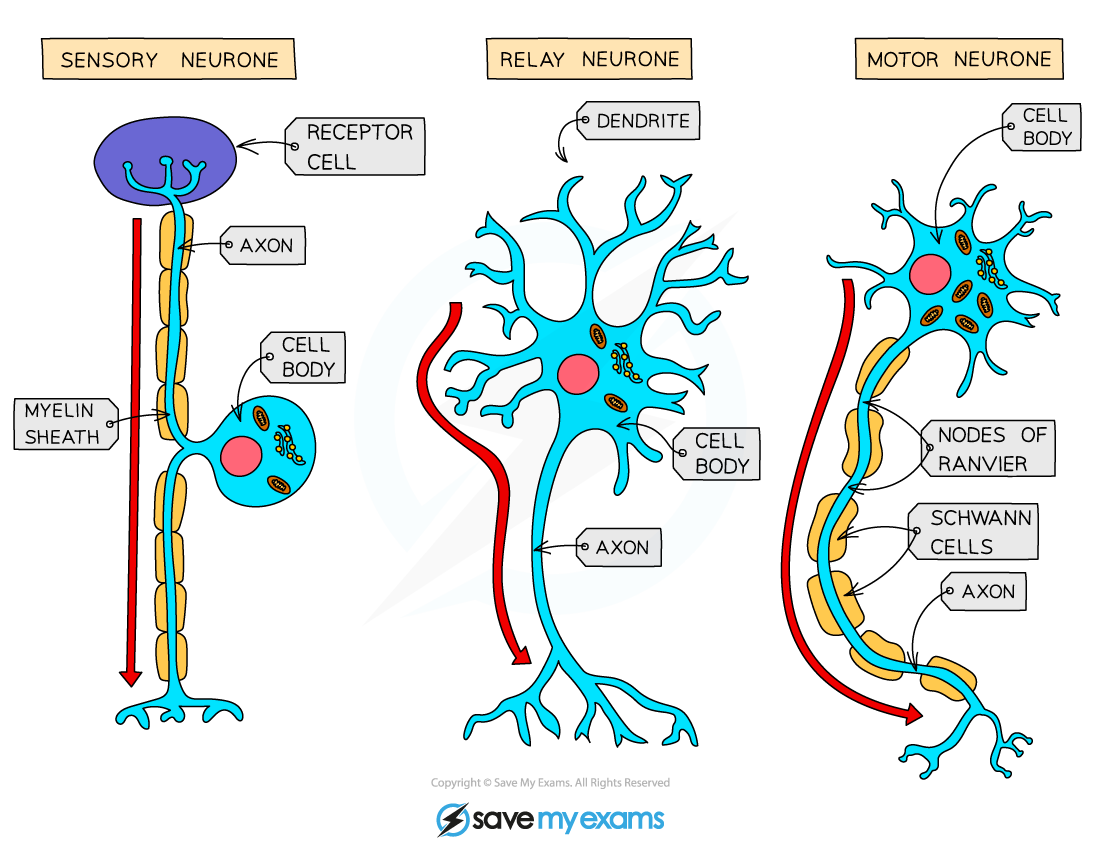
no myelin sheath on relay neuron
What is the nervous system?
a specialised network of nerve cells in the human body. It has two main functions - to collect, process and respond to information in the environment and to co-ordinate the organs in the body
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What structures make up the CNS?
Brain and spinal cord
What is the brain?
all the decision making takes place here. At the base of the brain is the brain stem which controls basic functions. (relay neuron is found here)
What is the spinal cord?
a long structure running down our back. It carries incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and body. (relay neuron is found here)
What is the role of the PNS?
receives and sends messages to the CNS
What are the two divisions of the PNS?
Somatic nervous system (SNS) and autonomic nervous system (ANS)
What is the somatic nervous system?
we have control over this system. It controls our muscle movement and receives information from sensory receptors
What part of the SNS do we not have control over?
our reflexes
What is the autonomic nervous system?
We have no control over this system. It co-ordinates important functions such as breathing, heart rate and digestion.
What are the two branches of the autonomic system?
Sympathetic (arousal) and parasympathetic (rest/digest)
What happens in the body during sympathetic action (fight or flight)
heart rate and breathing increases
pupils dilate
salivation stops
intestine/gut action stops
rectum contracts
What happens in the body during parasympathetic action (rest and digest)?
heart rate and breathing decreases
pupils constrict
salivation resumes
intestine/gut action resumes
rectum relaxes
Define fight or flight.
immediate physiological response of an animal when in danger. The body becomes physically ready to fight the threat or run away from it (flight).
What happens when our brain detects a threat in the activation of fight or flight response?
our hypothalamus identifies the threatening event (perhaps someone jumped out at you) and tells the sympathetic division of the ANS to act
What happens for adrenaline to be released?
the ANS changes from it normal resting state (parasympathetic) to a state of arousal (sympathetic). This releases adrenaline into the bloodstream
What happens during the fight or flight response?
physiological changes occur because of the adrenaline. Your heart rate increases, your pupils dilate (expand), digestion stops and saliva production is stopped. All these changes are designed to help us confront the threat (fight) or run away (flight)
What happens once the threat has passed?
The ANS changes from the state of arousal (sympathetic) back to resting (parasympathetic). Your heart rate slows down, your pupils constrict, digestion and saliva production resumes. This is the ‘rest and digest state’
What is the endocrine system?
a collection of glands that produce hormones which regulate our metabolism, growth, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, mood and more
How do hormones travel?
Through the bloodstream to target organs with specific receptors
What is the hypothalamus?
a small area in the centre of the brain, located above the pituitary gland
What is the pituitary gland?
the ‘master gland’. It is located in the brain
What is the thyroid gland?
a gland located at the front of the neck
Where is the pancreas located?
in the abdomen part of the digestive system
Where is the adrenal gland located?
on top of the kidneys. The cortex is the outer layer of the gland and the medulla is situated within the gland
What are the ovaries?
part of the female reproductive system
What are the testes?
part of the male reproductive system
What hormone does the pituitary gland produce?
none
What is the function of the pituitary gland?
controls hormone secretion in other glands
What hormone does the hypothalamus produce?
none
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
controls functioning of the pituitary gland
What hormone does the thyroid gland produce?
thyroxine
What is the function of the thyroxine?
controls heart rate and metabolic rate
What hormone does the pancreas produce?
insulin and glucagon
What is the function of insulin and glucagon?
stimulates the release and absorption of glucose
What hormone does the adrenal cortex produce?
cortisol
What is the function of cortisol?
controls cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory functions
What hormone does the adrenal medulla produce?
adrenaline and noradrenaline
What is the function of adrenaline and noradrenaline?
prepares the body for fight and flight response
What hormone do the ovaries produce?
oestrogen
What is the function of oestrogen?
regulates female secondary sex characteristics
What hormone do the testes produce?
testosterone
What is the function of testosterone?
regulates male secondary characteristics
What is the SAM pathway?
sympathetic and adrenal medulla
This is the immediate fight or flight response which causes part of the adrenal glands to release adrenaline. Adrenaline causes the responses listed previously e.g increased heart rate
What is the HPA axis?
hypothalamic + pituitary + adrenal cortex
This is the longer-term stress response (not part of fight or flight). At the same time as the signal is sent to the adrenal medulla, a signal is sent to the hypothalamus, which then sends a signal to the pituitary gland which creates the release of the hormone cortisol from the adrenal cortex. Cortisol deals with longer-term stress e.g release of glucose into the blood to provide energy to sustain fight or flight