Molecular Evolution and Mutation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
How can you predict divergence times?
Fossil evidence is sparse and imprecise (or non-existent) so predicting divergence times is done by comparing molecular data
What is molecular evolution?
It integrates evolutionary biology, molecular biology, and population genetics:
Describes the process of evolution (changes in time, being vs becoming) of DNA, RNA, and proteins
Includes the study of rates of sequence change, the relative importance of adaptive and neutral changes, and changes in genome structure
Deals with patterns (diagrams, models) and studies the evolution of genes, genomes, proteins, introns, chromosomal arrangements, organisms and species, systems that coevolve, ecological niches, migration patterns using molecular data
What can DNA comparisons be made between?
Individuals, populations, and species
How do genes change?
Occasionally the DNA sequence changes through mutation (about 1.5×10^-8 per base pair per generation in humans). Most of these mutations will be lost from the population by chance or driven out by selection. But some will also increase in frequency and ultimately become fixed (if they are advantageous)
What are the mutations of molecular evolution?
Mutation, insertion, and deletion
What are the types of mutations?
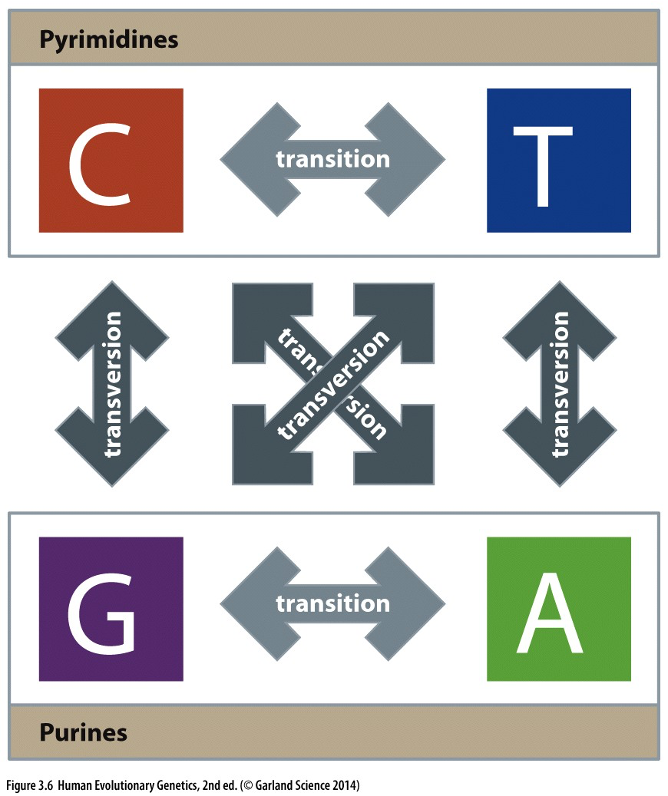
Transition (A←→G)
Transversion (purine ←→pyrimidine)
What doe modelling evolution of a single nucleotide look like?
At a single nucleotide, there are only four states (T, C, A, G)
Multiple rates of change from each nucleotide to every other one (some mutations are more likely than others)
What is the central problem of history?
History cannot be observed, only end products
What forms the basis of genomic evolution?
DNA alterations
What is a synonymous mutation?
It does not change the amino acid
What is a non-synonymous mutation?
It changes the amino acid
What is a nonsense mutation?
A point mutation resulting in a pre-mature stop codon
What is a missense mutation?
It results in a different amino acid
What is a frameshift mutation?
The insertion/deletion of 1 or 2 nucleotides
What is a silent mutation?
The same as a synonymous mutation
What is a neutral mutation?
The mutation has no fitness effects. It’s invisible to evolution (neutrality is usually hard to confirm)
What is a deleterious mutation?
It has detrimental fitness effect
What is a beneficial mutation?
It increases fitness
What is fitness?
The ability to survive and reproduce