1.4 Genetics and Growth of Prokaryotic Cells
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
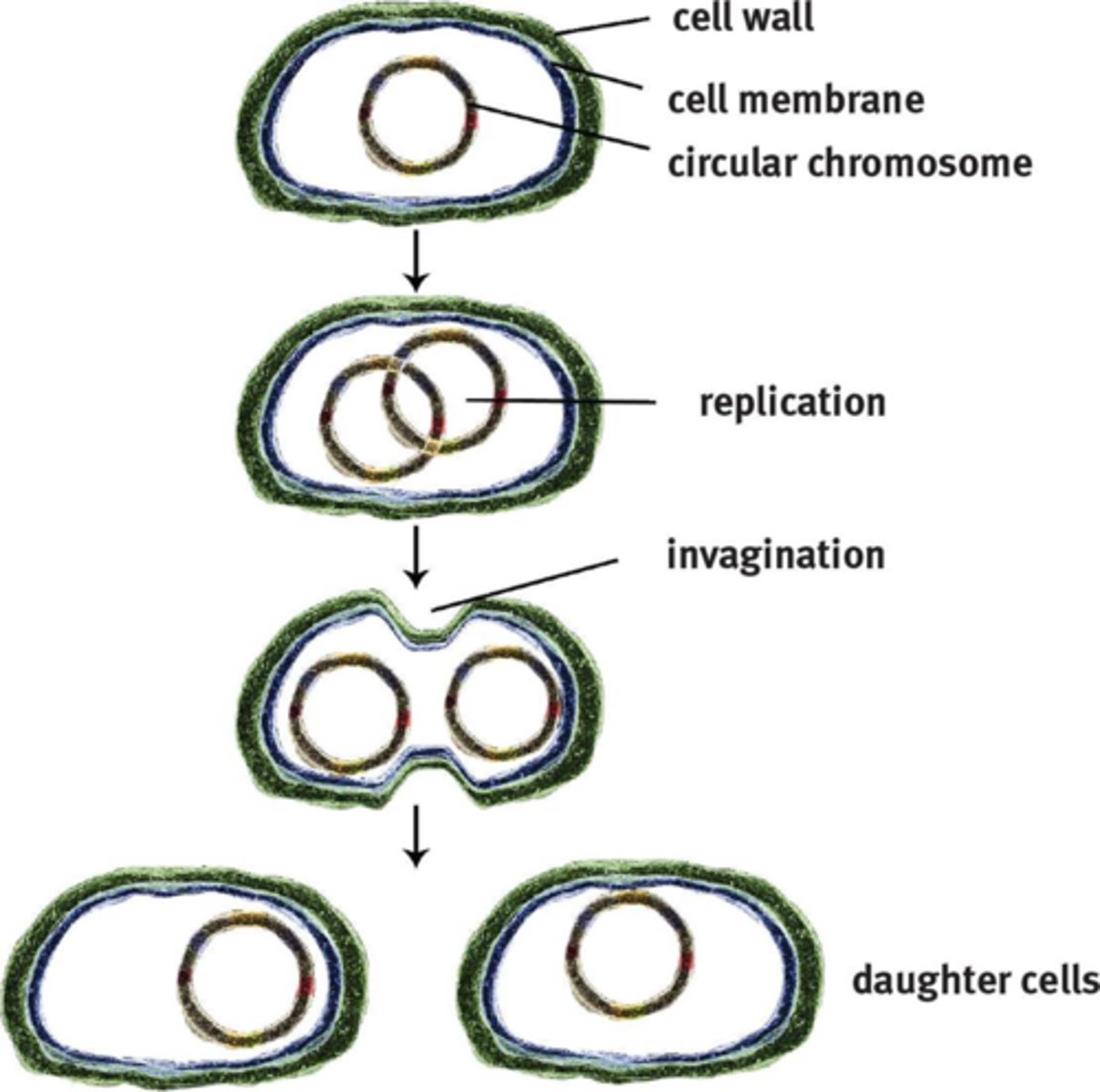
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes.
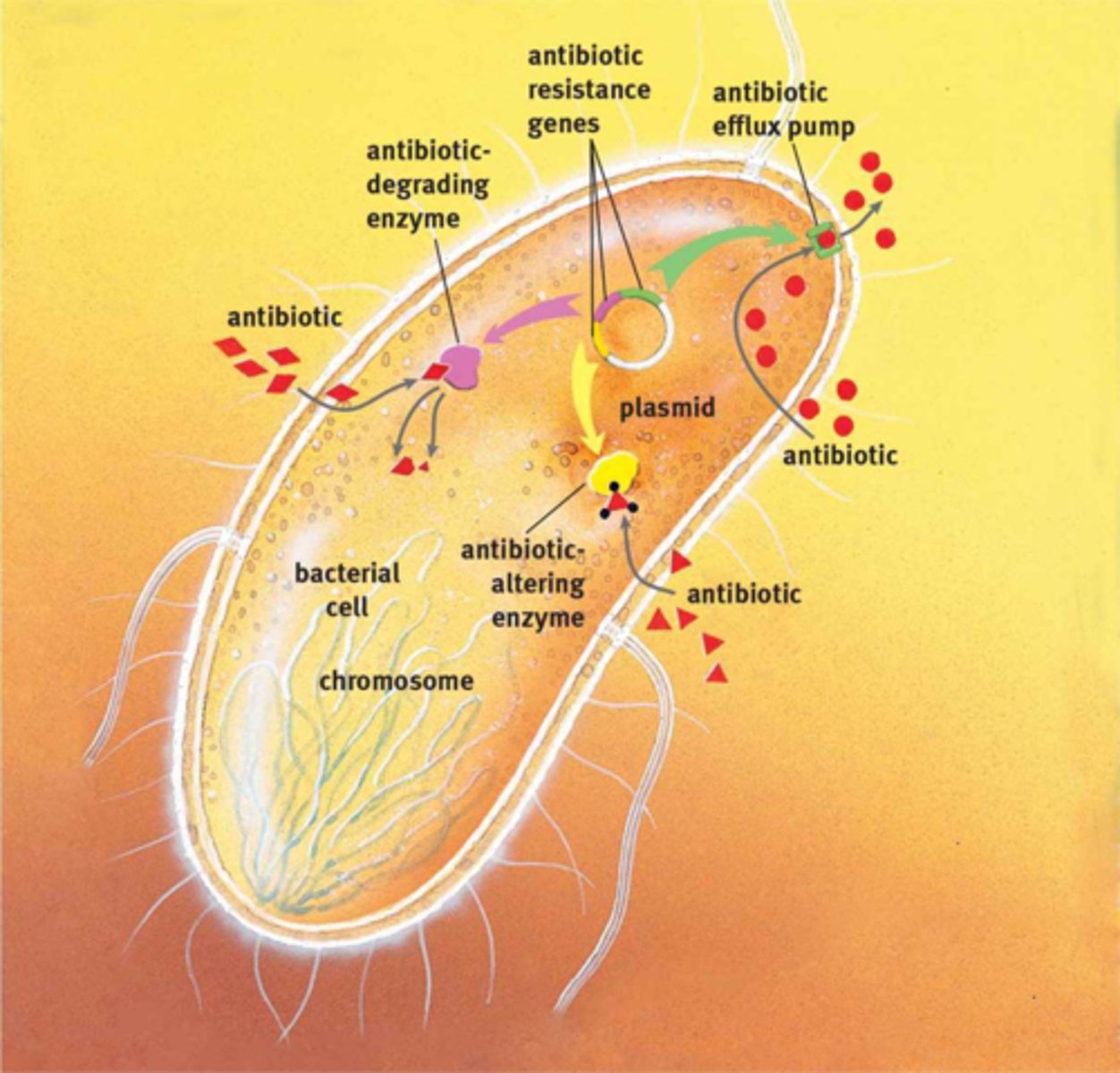
Plasmids
Extragenomic genetic material in prokaryotes.
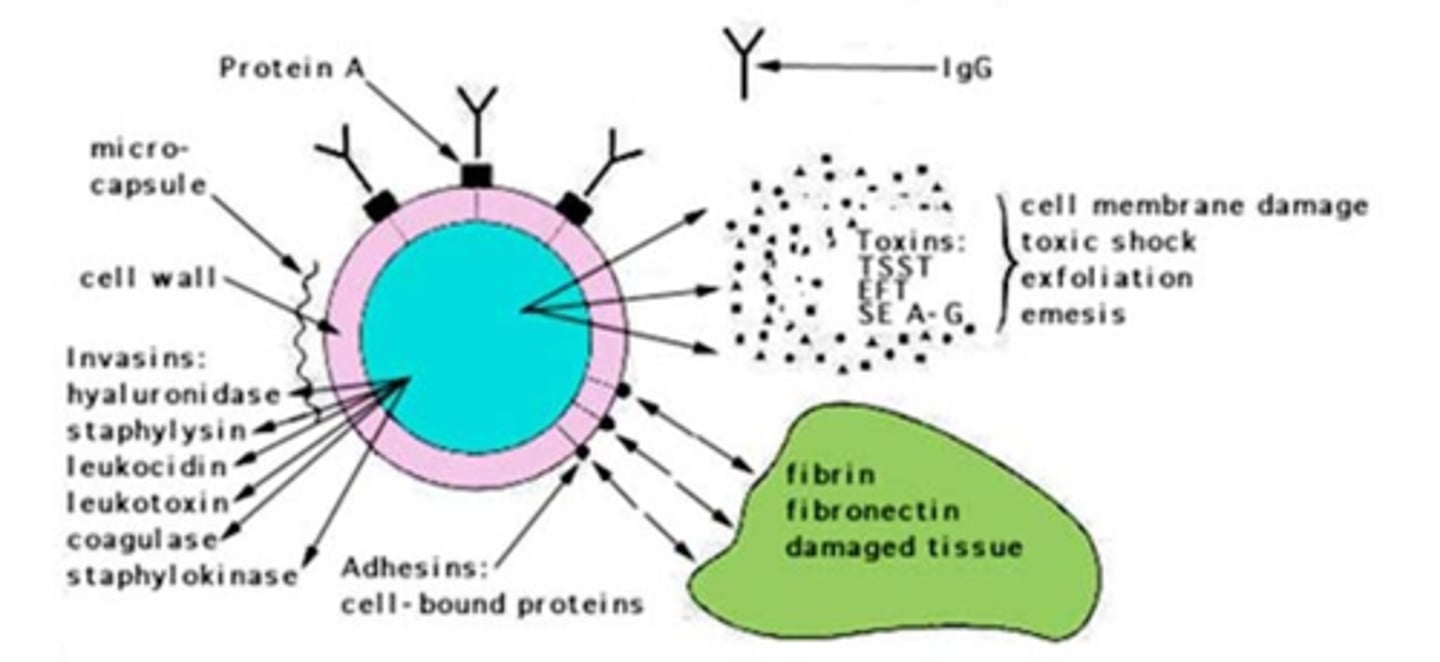
Virulence Factors
Traits that make bacteria more pathogenic.
Episomes
Plasmids that can incorporate into the genome.
Antibiotic Degradation, Antibiotic Alteration, Antibiotic Efflux Pumping
Bacterial mechanisms of antibiotic resistance.
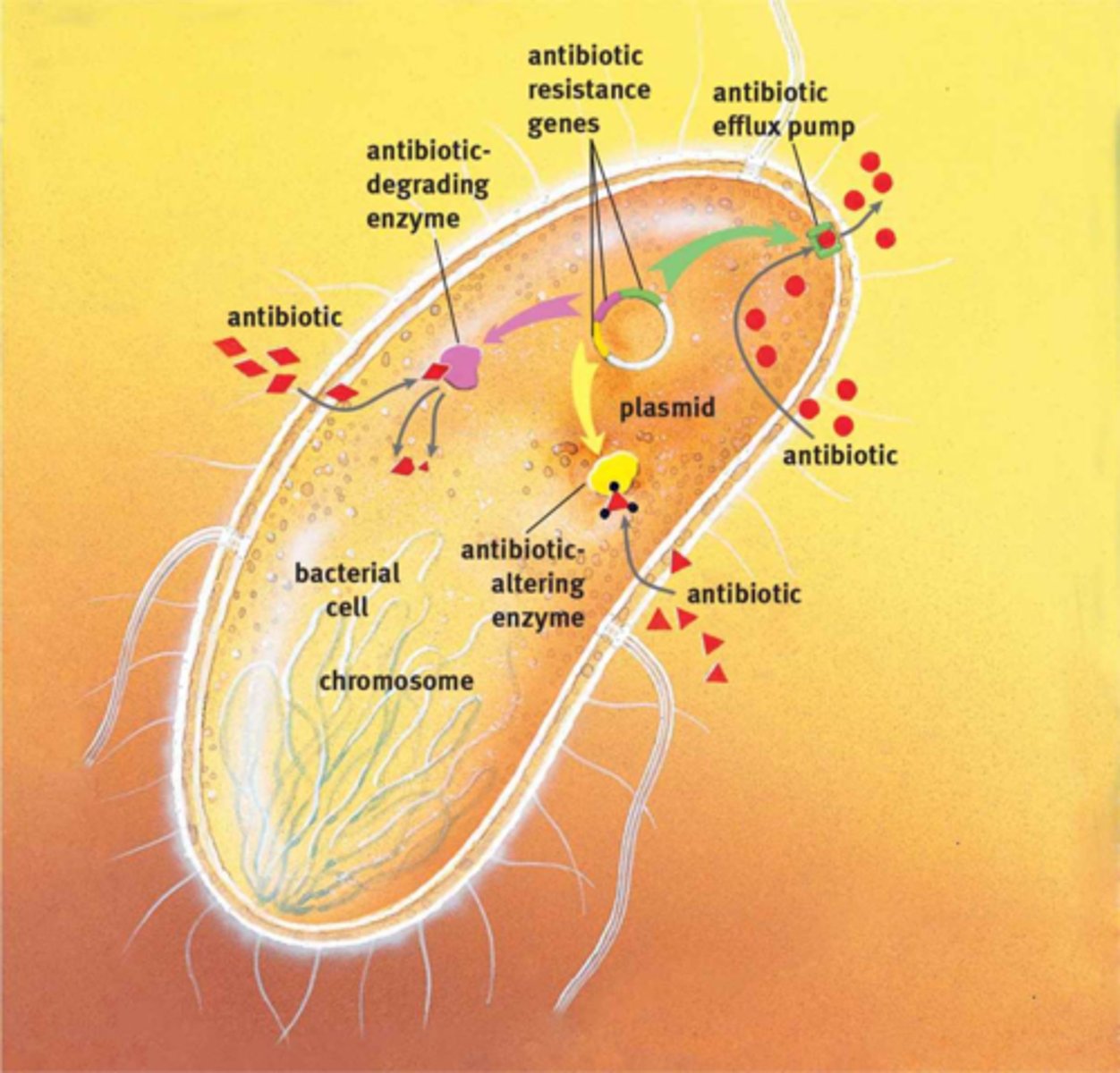
Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction
Mechanisms through which bacteria recombine genes.
Transformation
The process of incorporating foreign genetic material into the host genome.
Many gram-negative rods are capable of doing this.
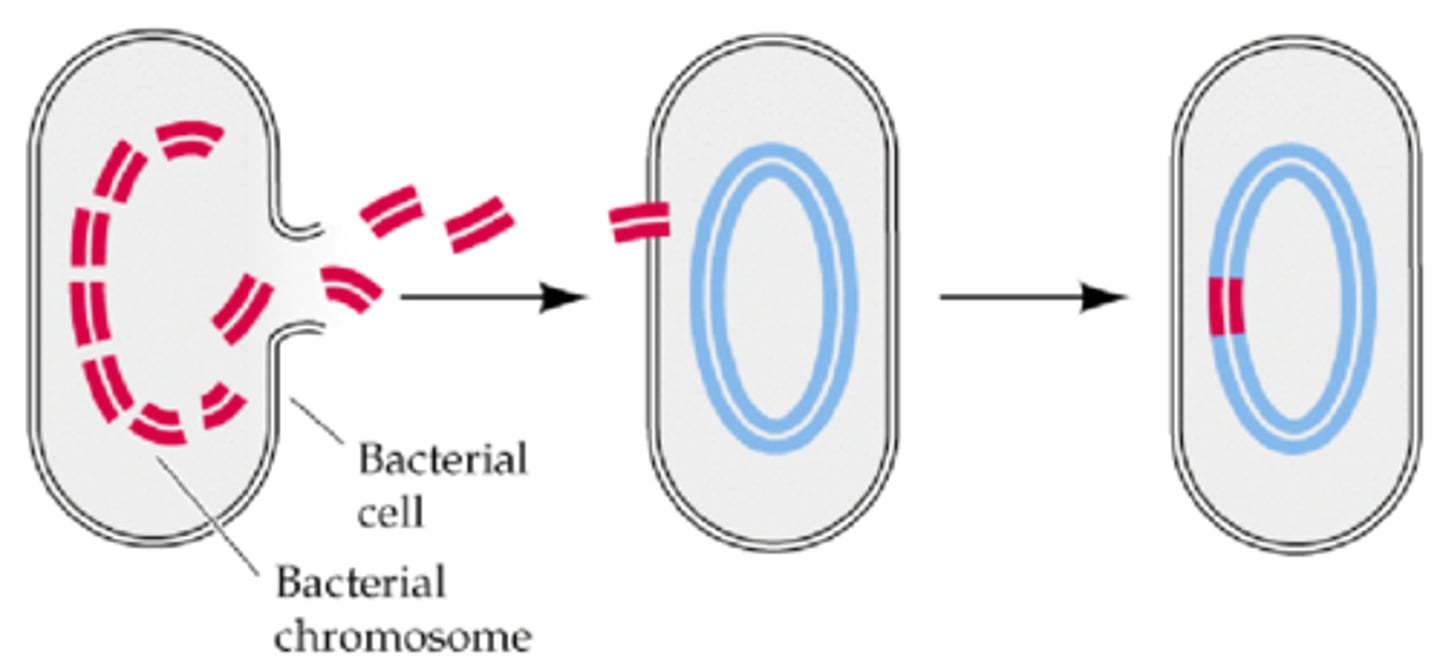
Gram-Negative Bacilli
Many of these rod-shaped bacteria are capable of transformation.
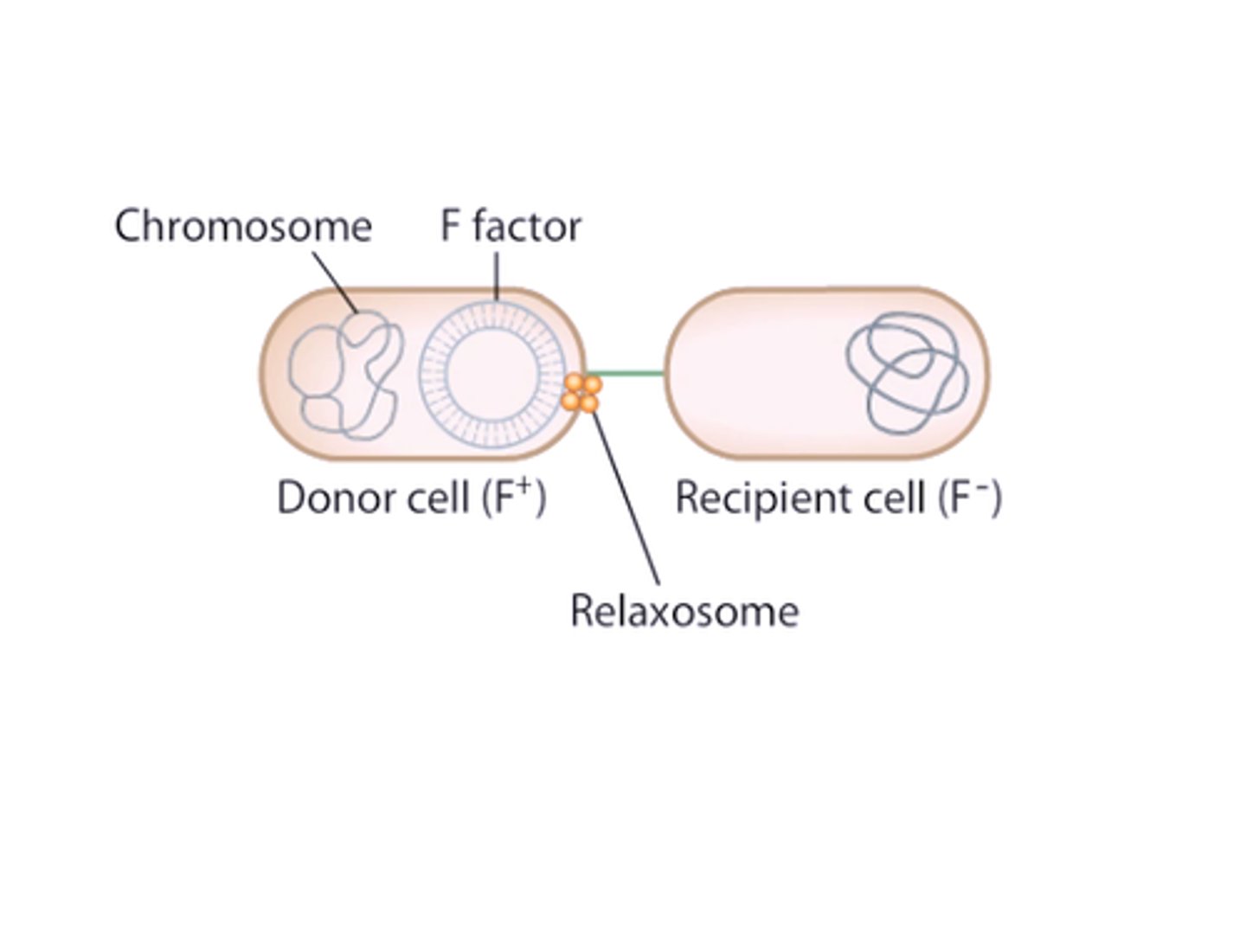
Conjugation
Mating of bacteria.
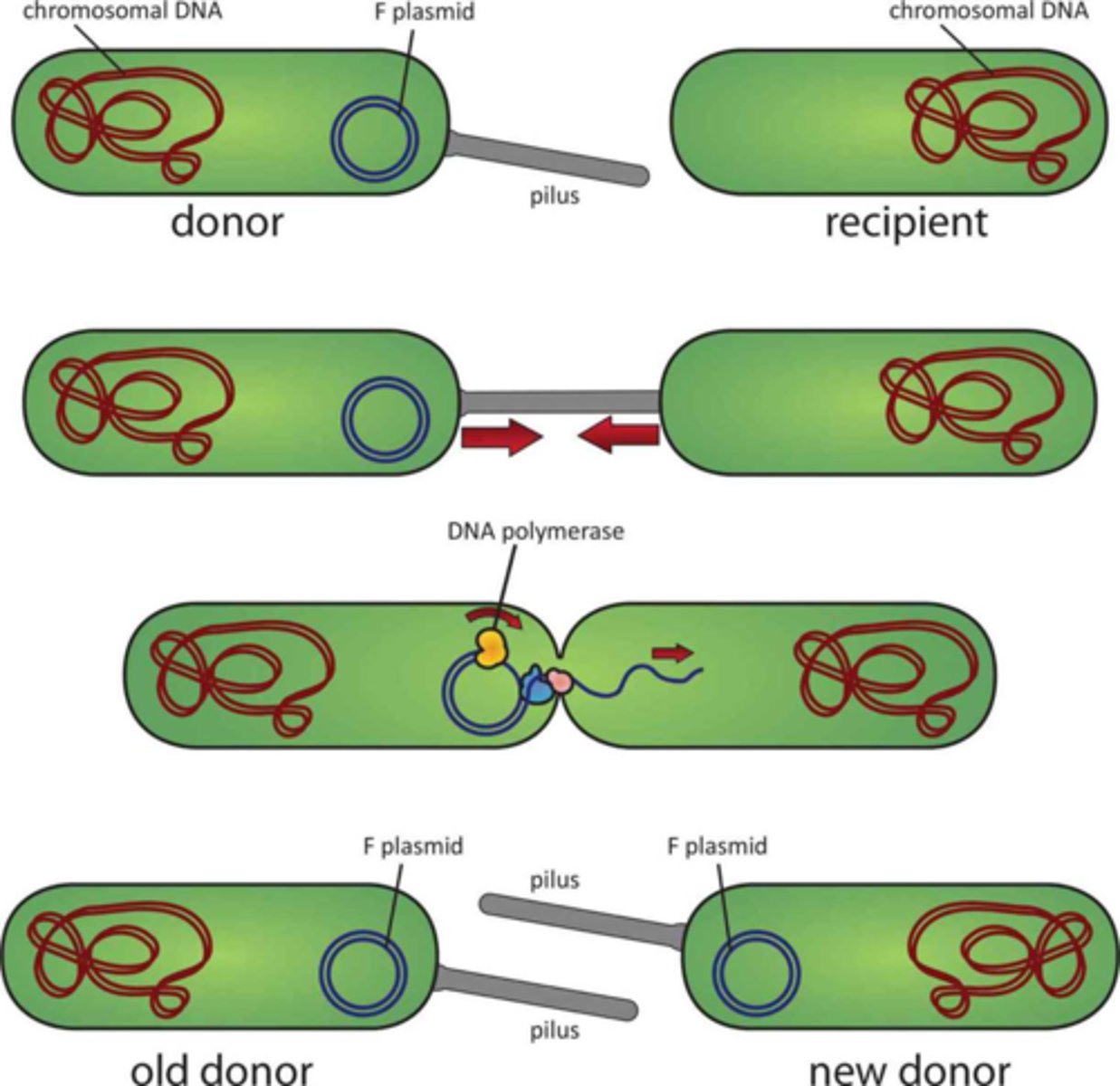
Conjugation Bridge
Forms between conjugating bacteria that facilitates the transfer of genetic material.
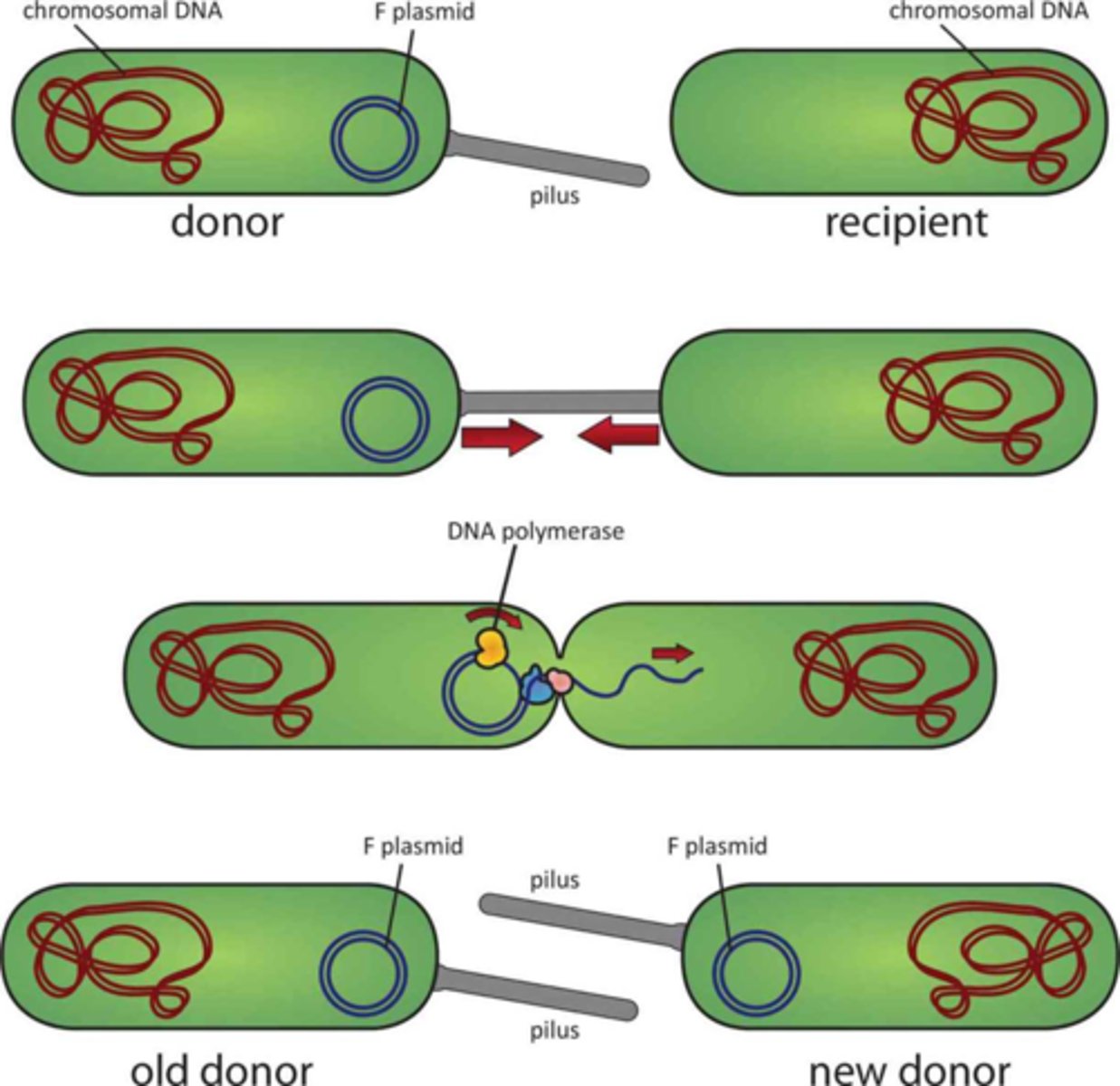
Unidirectional Transfer
Bacteria send the genetic material in one direction, from the donor male to the recipient female.
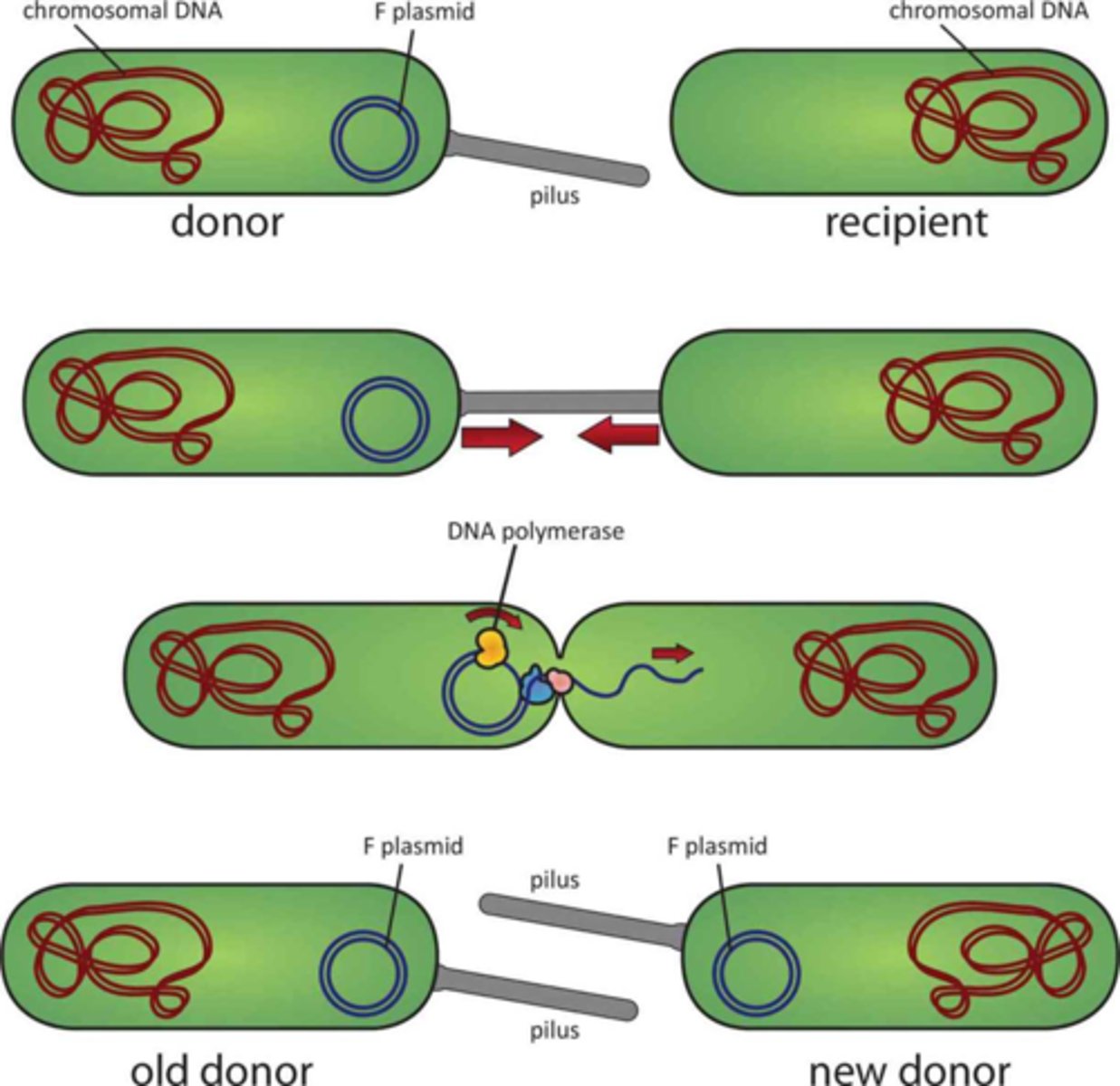
Sex Pilli
Appendages on the male bacterium that form the conjugation bridge.
Sex Factors
Plasmid genes that encode the necessary material to form the sex pilli. Though it is a plasmid, it can be incorporated through transformation.
Fertility Factor
Common sex factor which define E. coli as F+ or F-.
Hfr
Cells that transform the sex factors are said to have a high frequency of recombination.
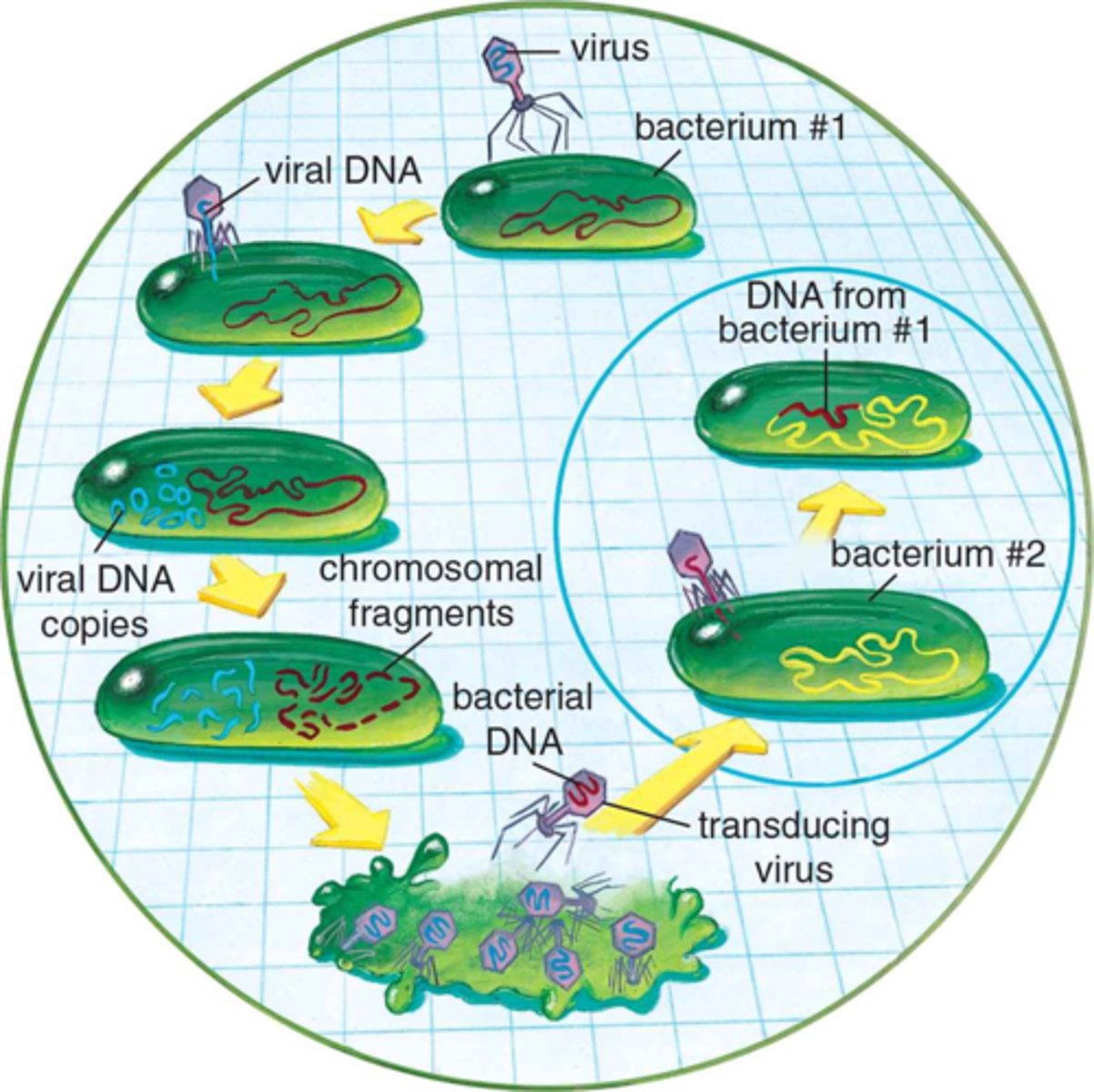
Transduction
Genetic recombination process that requires a vector.
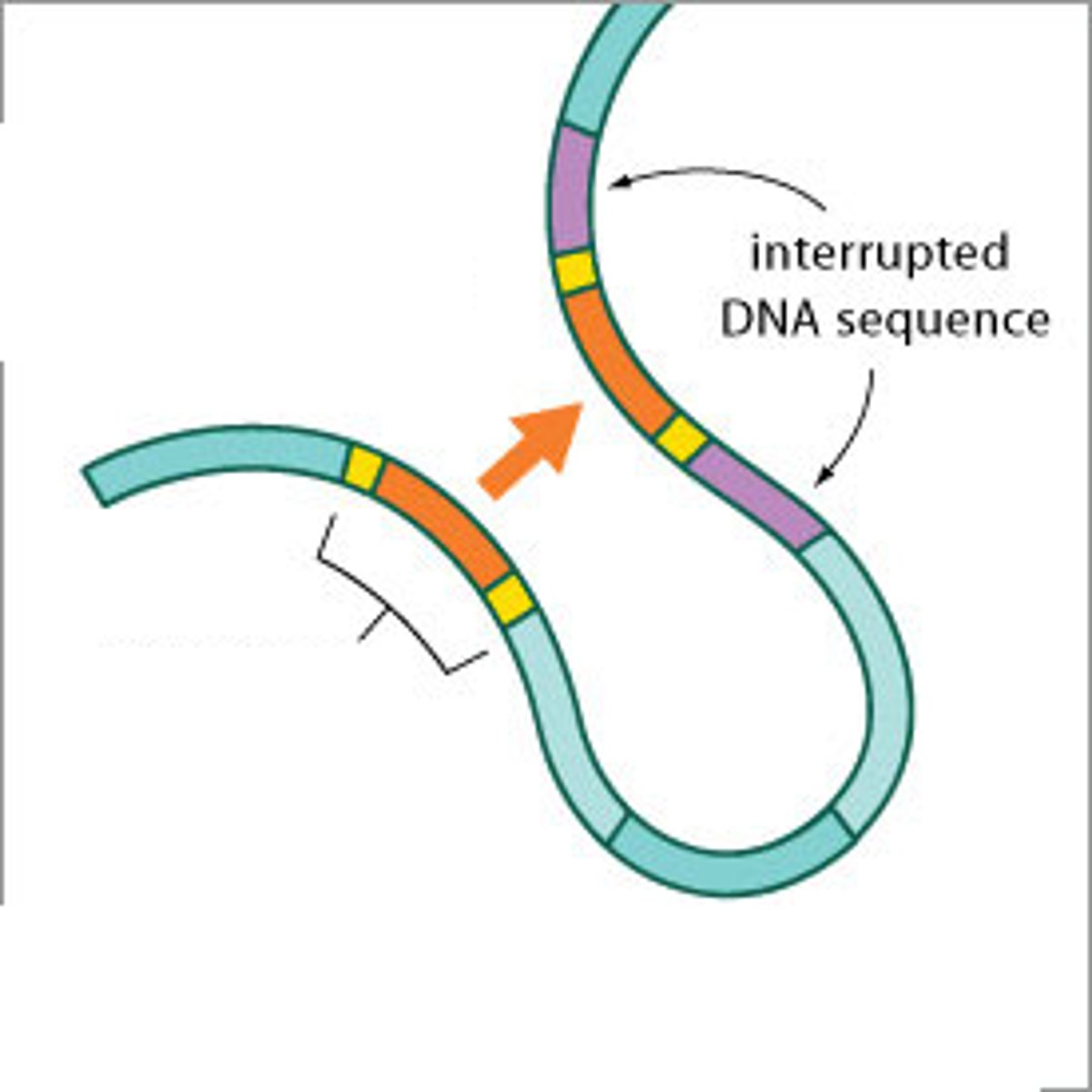
Transposons
Genetic material that is capable of inserting and removing itself from a genome.
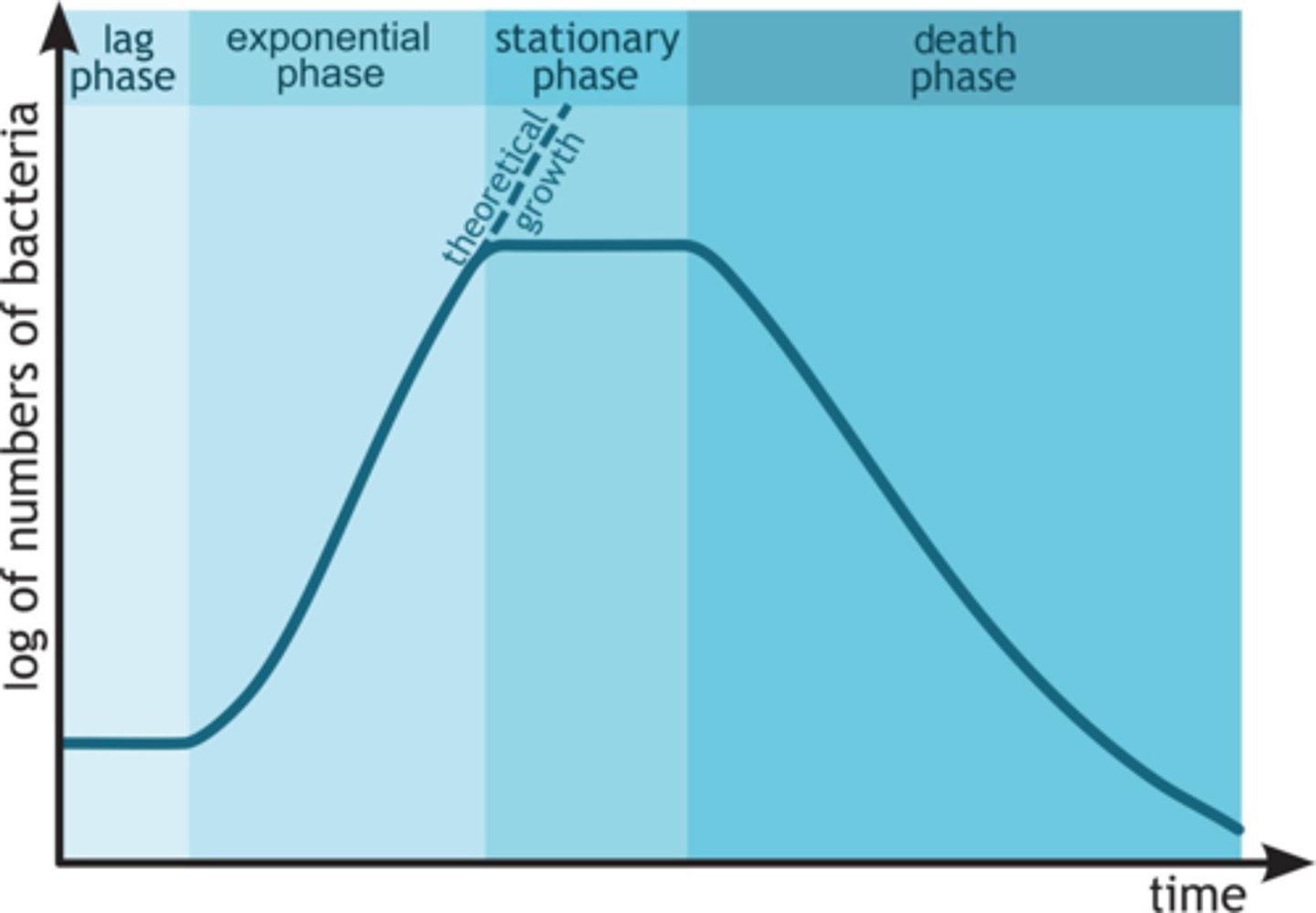
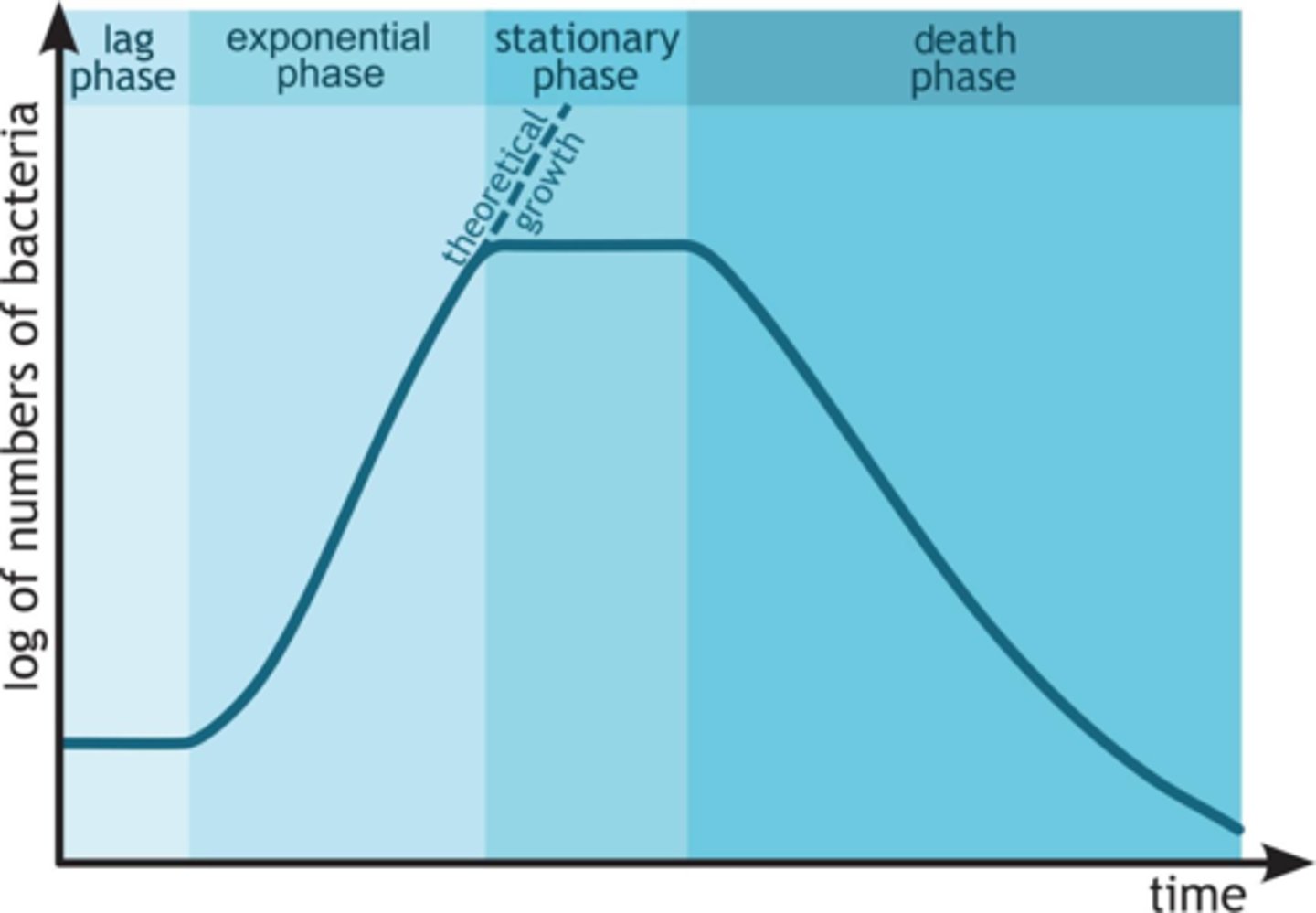
Lag Phase
Bacteria first adapt to local conditions during this time.
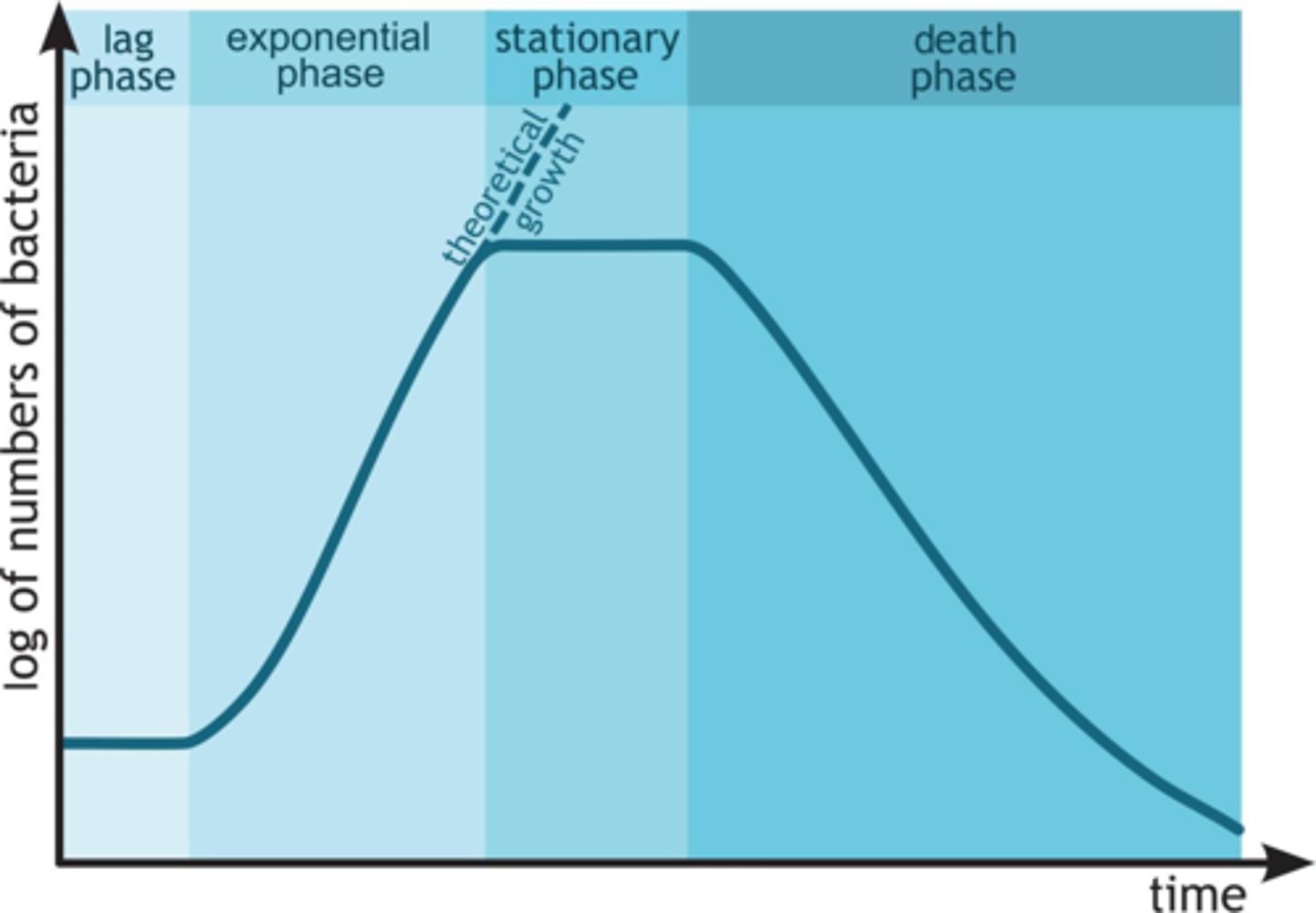
Exponential Phase
As the bacteria adapt, their growth grows exponentially.
Log Phase
Another name for the exponential phase.
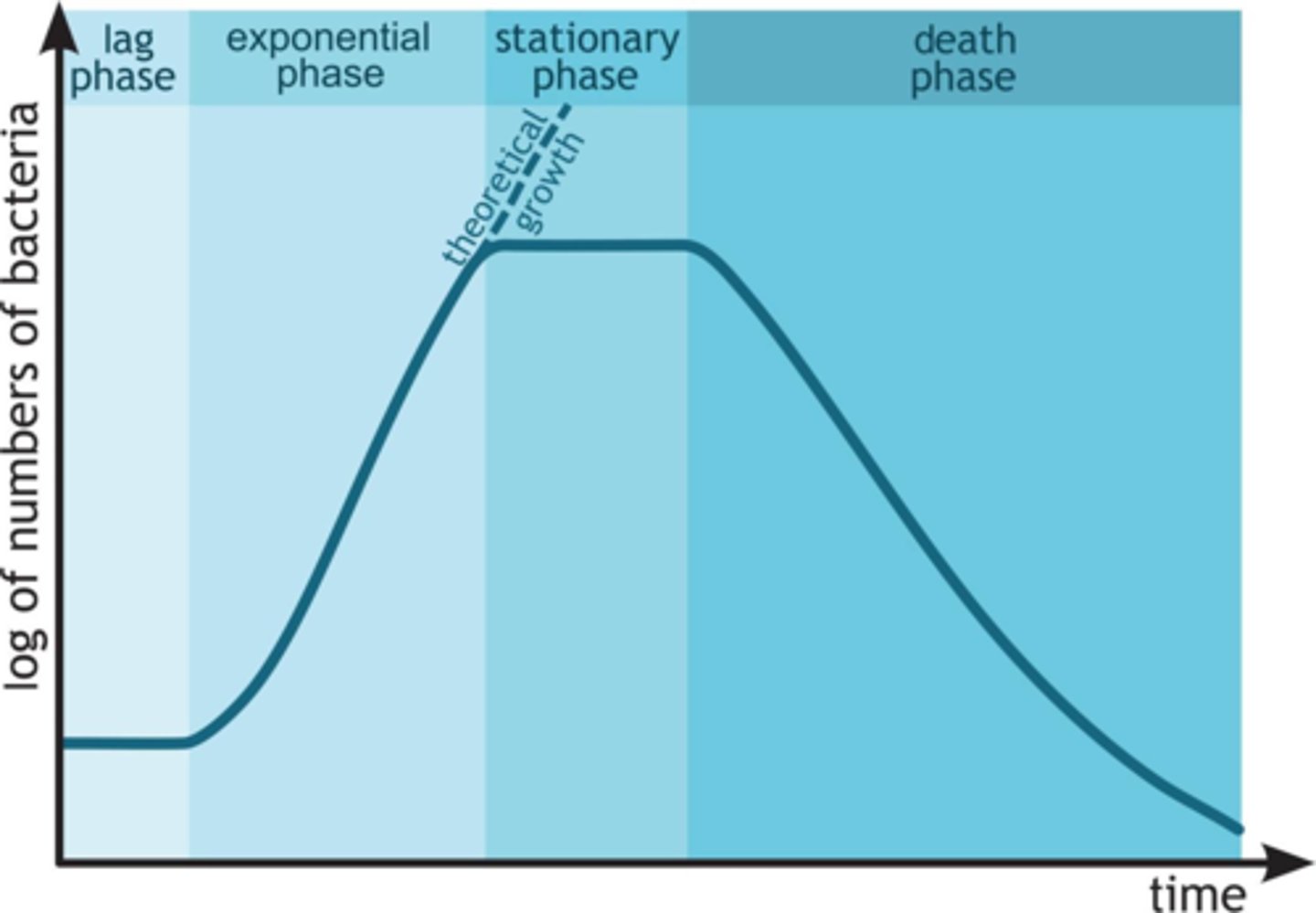
Stationary Phase
As the bacteria grow so rapidly, nutrients and materials become scarce. This scarcity causes the growth to slow down.
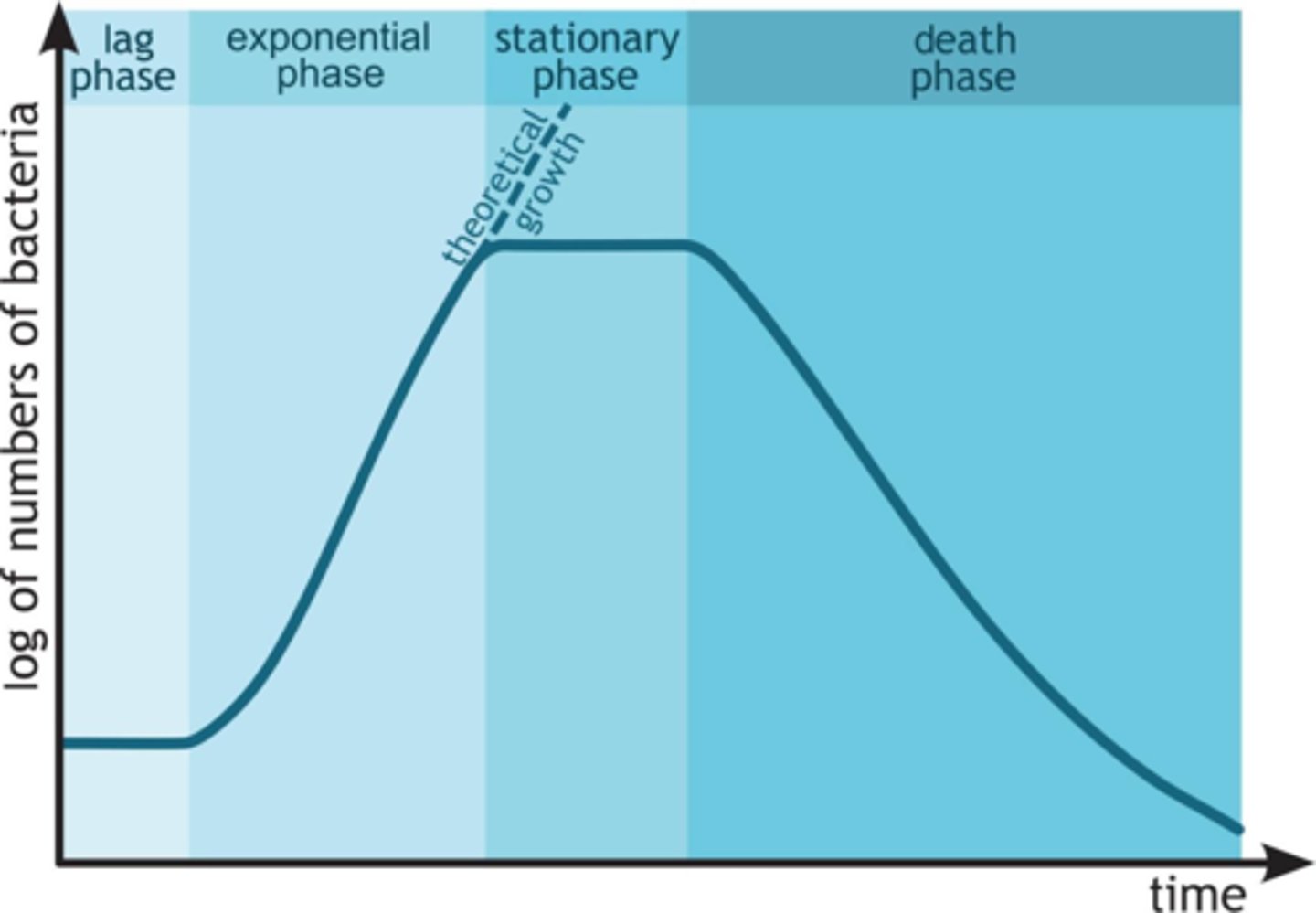
Death Phase
Once the bacteria have exhausted the resources of their environment, they all die.