1. MVHS Marine Biology Ecology review
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
abiotic
nonliving, physical features of the environment, including air, water, sunlight, soil, temperature, and climate

biotic
Pertaining to life; environmental factors created by living organisms
carnivore
organism that obtains energy by eating animals

community
(ecology) a group of interdependent organisms inhabiting the same region and interacting with each other

consumer
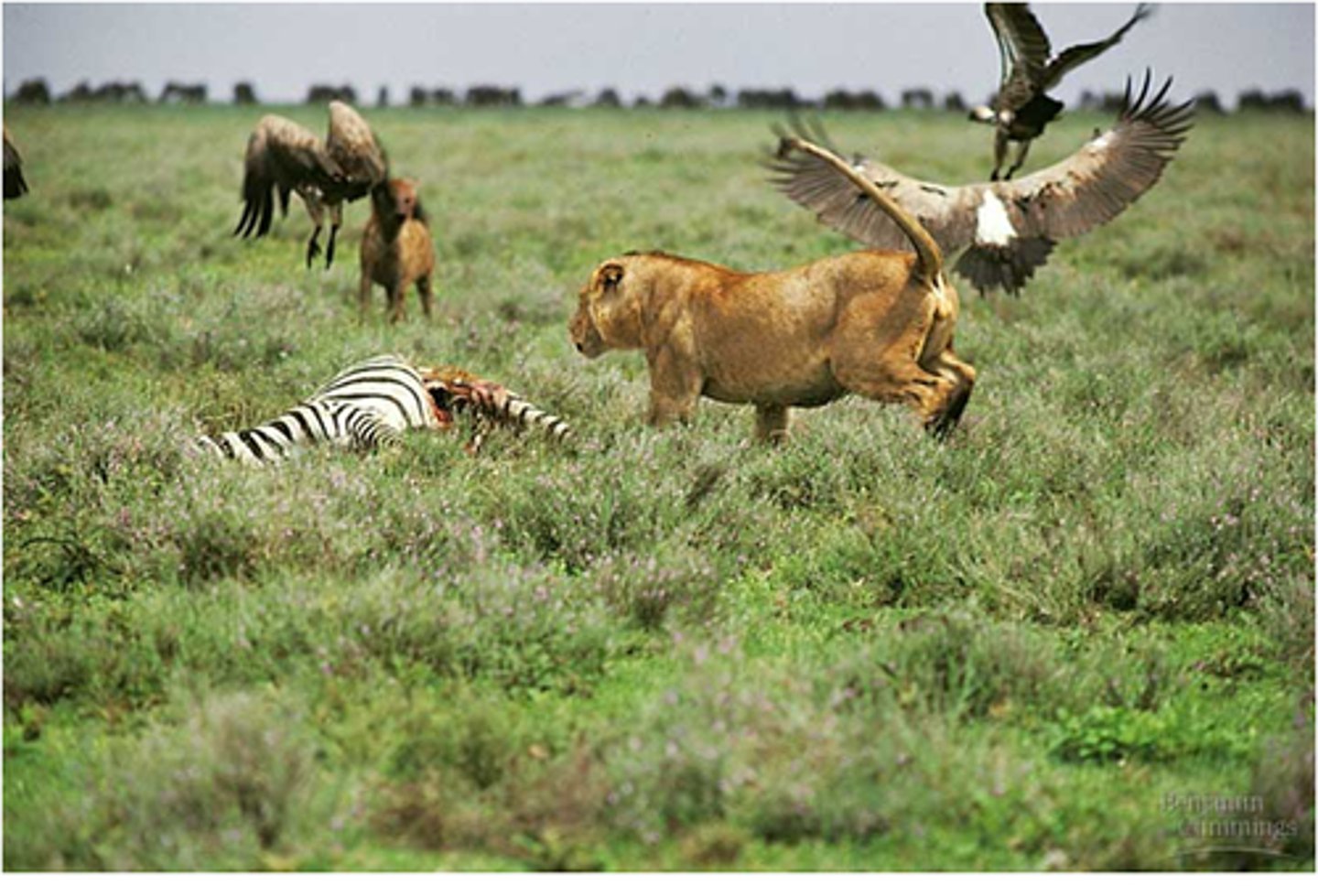
an organism that obtains energy by feeding on other organisms

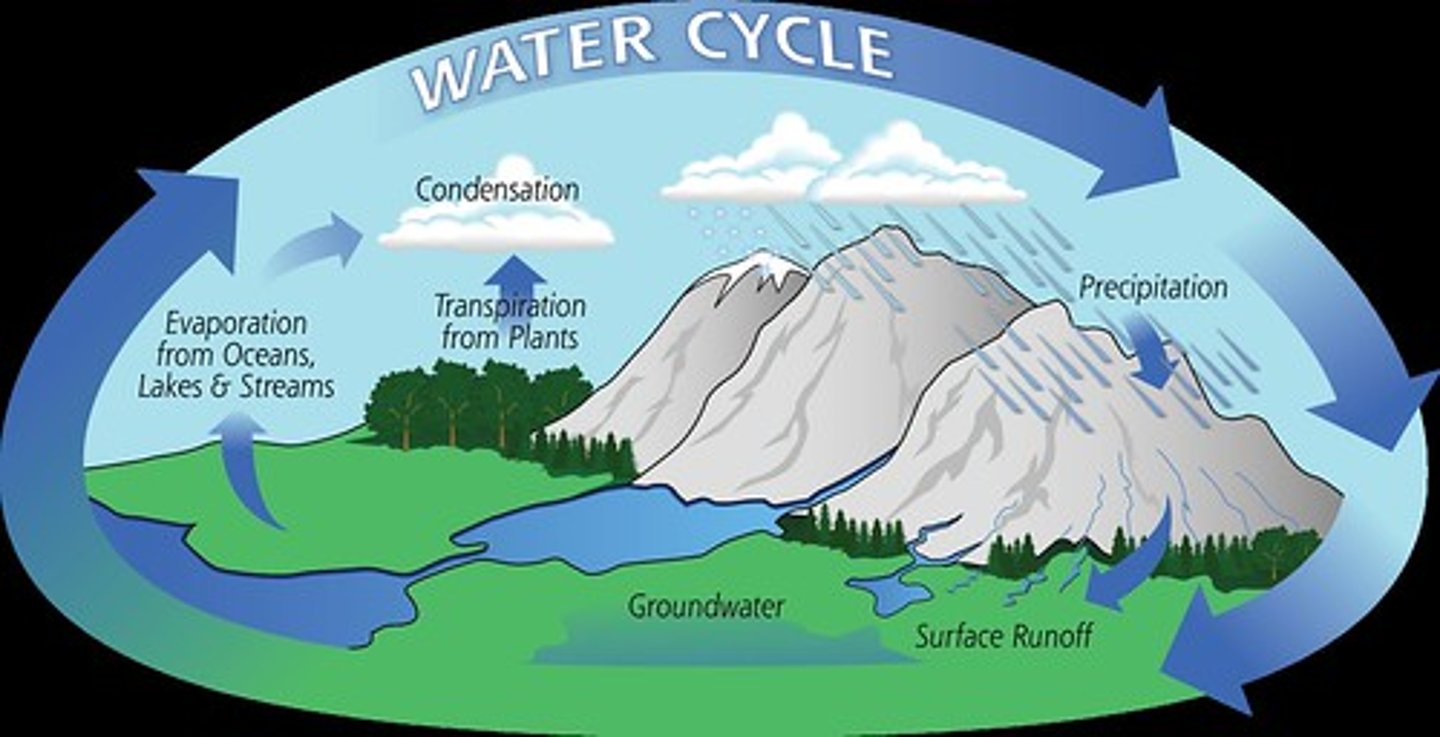
cycle
an interval during which a recurring sequence of events occurs
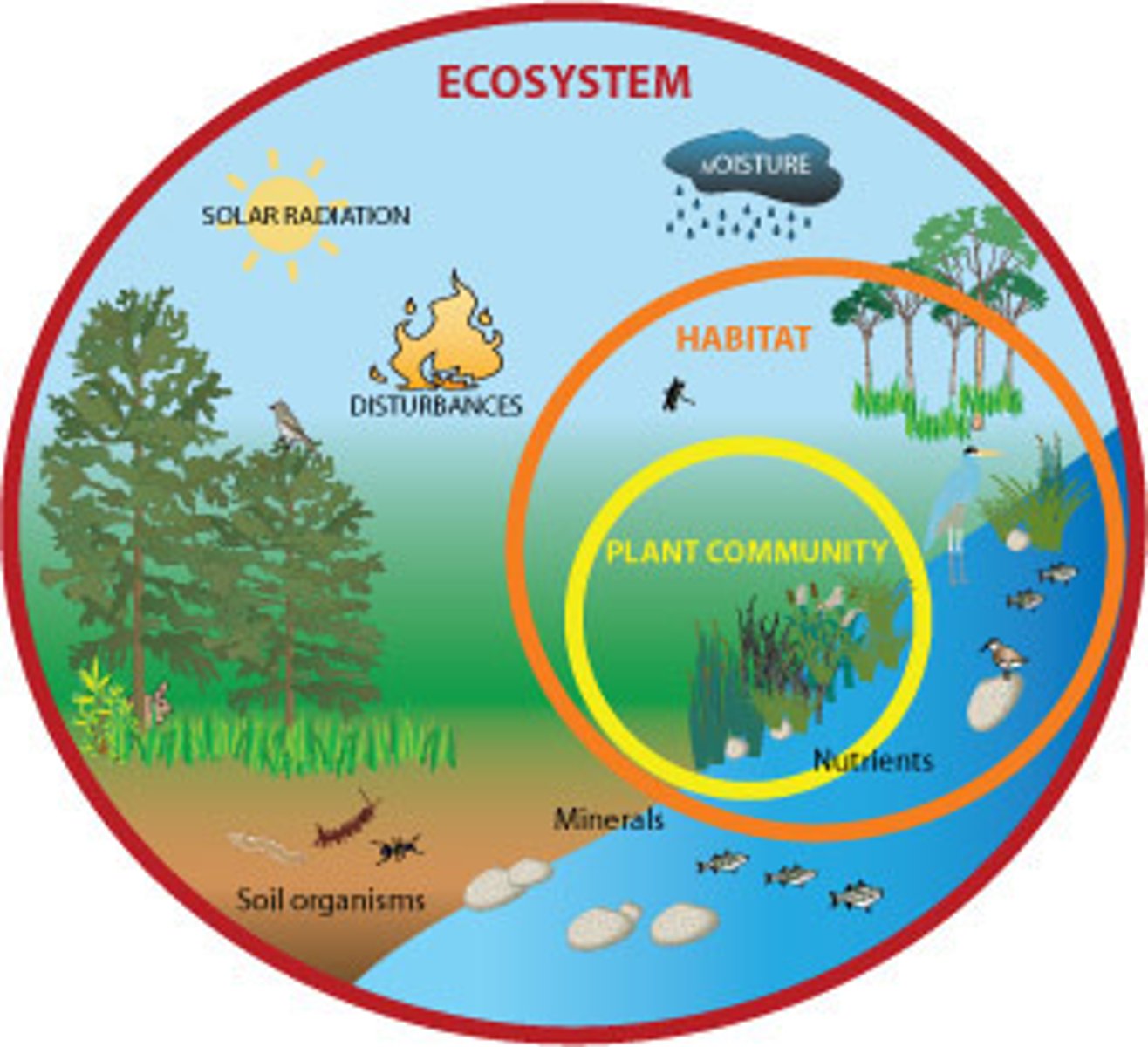
ecosystem
a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
herbivore
any animal that feeds chiefly on grass and other plants

omnivore
organism that obtains energy by eating both plants and animals

population
a group of organisms of the same species populating a given area

predation
when an organism the feeds directly on other organisms in order to survive
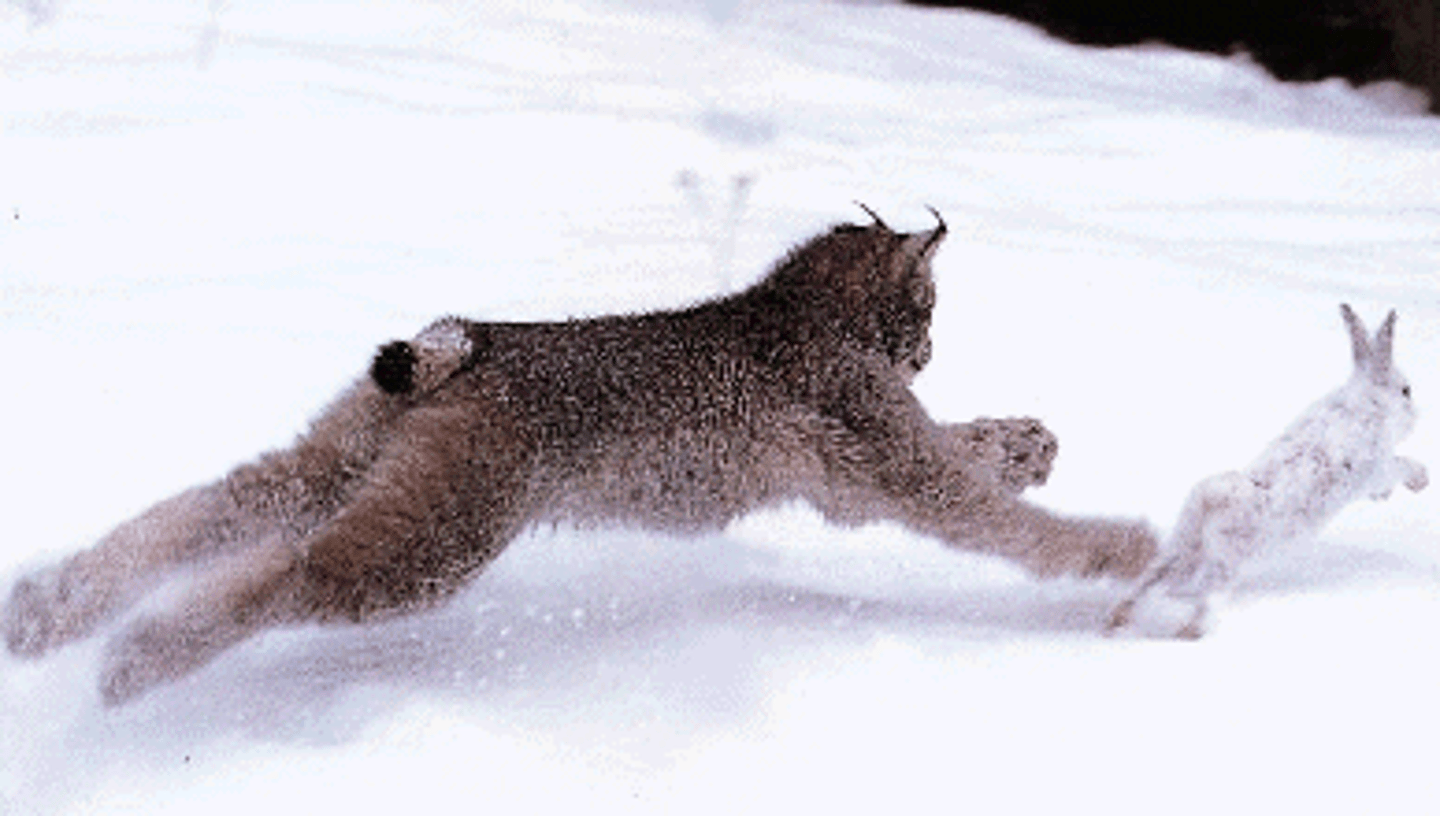

prey
an organism that is killed and eaten by another organism

producer/autotroph
an organism that can make its own food by using energy from its surroundings

species
a group of similar organisms that can mate with each other and produce fertile offspring

Food Web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
Biosphere
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere of the earth (or analogous parts of other planets) occupied by living organisms.
Detritivore
an animal that feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus.
Biome
a large naturally occurring community of flora and fauna occupying a major habitat, e.g., forest or tundra.
Food Chain
a hierarchical series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food.
Decomposer
an organism, especially a soil bacterium, fungus, or invertebrate, that decomposes organic material.
Photosynthesis
the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesize foods from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis in plants generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is what cells do to break up sugars into a form that the cell can use as energy. This happens in all forms of life. Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create ATP, a chemical which the cell uses for energy.
Nitrogen Fixation
the chemical processes by which atmospheric nitrogen is assimilated into organic compounds, especially by certain microorganisms as part of the nitrogen cycle.
Trophic Level
each of several hierarchical levels in an ecosystem, comprising organisms that share the same function in the food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of energy.
Organism
an individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form
Ecology
the study of interactions between organisms and their envirionment
Habitat
area where a species lives
niche
the job or role a species does in the food web to survive
heterotroph
another name for consumer. This animal must find food as it cannot make its own!
Primary producer level
The beginning of the food chain, usually plankton in the ocean world.
primary consumer level
The second level of the food chain, this group eats plants.
detritus
dead and decomposing material in an ecosystem.
Rule of 10
in an ecosystem only 10% of the available energy at a trophic level can be passed onto the next level.
commensalism
when one member of the food chain is benefitted by another member, and the first member is not impacted.
mutualism
two members of a food web both benefit by working together
parasitism
one member of the food web benefits at the expense of another.
symbiosis
type of mutualism where it is nearly impossible for the individuals to survive separately.
scavenger
organism which does not kill, but rather feeds of dead animals
biomass
the amount of living material at a trophic level
Microbeads
tiny plastic beads the size of sand used for a variety of purposes including separation of cellular material and cosmetics
microfiber
Superfine manufactured fiber, Made from polyester, nylon, rayon, and acrylic which shed from your clothes and pollute the air and water.
Nurdles
small plastic pellets used for shipping the beginning of plastic products
photodegrade
(of a substance or object) be decomposed by the action of light, especially sunlight. Breaks plastic into tinier bits
Biomagnification
the concentration of toxins in an organism as a result of its ingesting other plants or animals in which the toxins are more widely disbursed.
600 years
How long plastic lasts in the environment.
reduce
the best of the 5 Rs because it means there will be less plastic pollution
10x
the amount of energy and water needed to fill a bottle of water.