Joints Study Guide
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is Arthrology and Kinesiology?
Arthrology: The study of the anatomy, function, dysfunction, treatment of joints
Kinesiology: Study of musculoskeletal movements
Define Fibrous joints
Bone matrix collagen fibers join bones across gap
Examples: Skull sutures, radius-ulna, tibia-fibula
Sutures: serrate, lap, plane
Gomphoses
Syndesmoses: ligaments joining bones
Define Cartilaginous joints
Synchondroses
Hyaline cartilage
EX: between epiphysis and diaphysis of growing bone; also joint between rib and sternum (costal cartilage)
Symphyses
Fibrocartilage
EX: pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs, intervertebral articulations
Define bony joints
Synostoses: formed by fusion of bones in certain fibrous and cartilaginous joints as they age
EX: mandibular bone, frontal bone; shafts and head of long bones; 1st rib and sternum
Define Synovial joints
Bones separated by space that contains lubricating fluids
EX: jaw, elbow, hip, knee
Freely movable
What are the 6 types of synovial joints (give examples; are they monaxial, biaxial or multiaxial)
Ball-and socket
Multiaxial
Hinge joint
Move only in one direction, monoaxial
Condyloid joint
Biaxial
Saddle joint
Trapeziometacarpal joint (base of thumb) and sternoclavicular
more movable than fingers, allow opposition/reposition movement
Pivot joint
Bone projection of one bone joining ringlike ligaments of another bone
Atlantoaxial and radioulnar joint (elbow)
Gliding joint
Almost flat bone surfaces which glide past each other
Amphiathrosis (little movement at joint)
EX: carpals, between tarsals, articular process of vertebrae, strenoclavicular joint
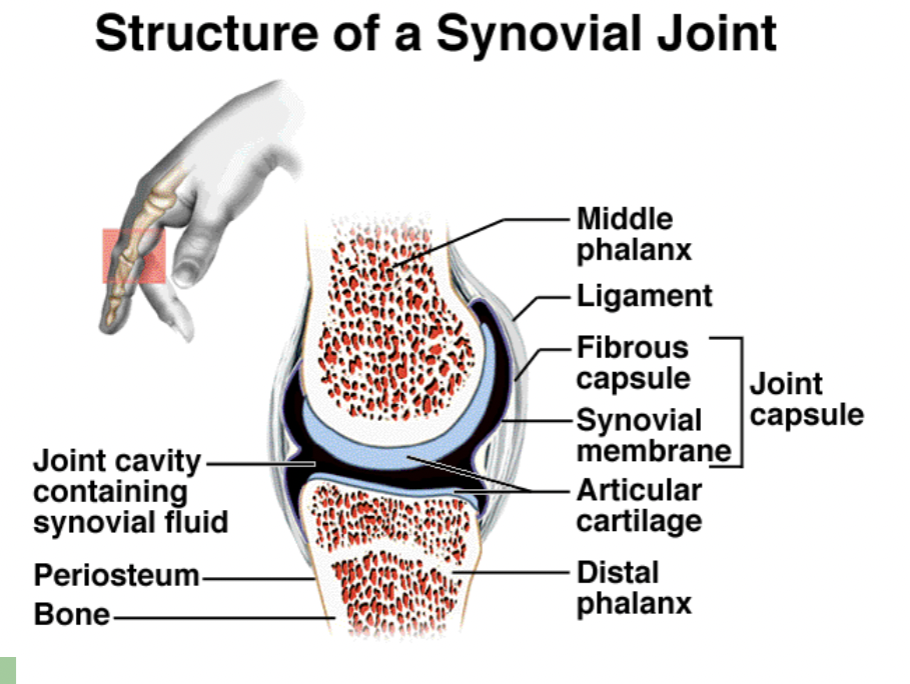
What is the structure of a synovial joint?
Joint cavity: between bones
Synovial fluid: lubricant
Albumin and hyaluronic acid (a GAG)
Phagocytes
Adjoining surfaces covered with hyaline cartilage (articular cartilage)
Joint capsule: encloses cavity
Fibrous capsule continuous w/ periosteum (dense irreg)
Synovial membrane of areolar tissue which secretes fluid
Some joints have meniscus
Cartilage grows inward to form cushion
Tendons: Muscle to bone
Ligaments: Bone and bone
Bursa
Sac between muscles or where tendon passes over bone; fibrous fluid filled; cushions muscles
Tendon sheath:
Numerous in the hand and foot
Elongated cylindrical bursa wrapped around a tendon
What structure makes synovial fluid?
Areolar tissue, hyaluronic acid and lubricin, proteinase, and collagenases.
Flexion and extension
Flexion: decreases angle of joint (sagittal plane)
EX: Bending elbow
Extension: increases angle of joint (sagittal plane)
EX: Straightening elbow
Hyperextension
Extension beyond anatomical position
Looking up at the ceiling
Abduction and adduction
Abduction: movement away from midsagittal line
EX: raising arms to side
Adduction: Movement toward midsagittal line
EX: Lowering arms to body
Elevation and depression
Elevation: Raises bone vertically
EX: Closing mouth by raising mandible
Depression: Lowering bone vertically
EX: Opening mouth, as in surprise
Protraction and retraction
Protraction: Movement of bone anteriorly
EX: Moving shoulders forward
Retraction: Movement of bone posteriorly
EX: Pulling shoulders back
Circumduction
Arm, head, or leg movement describing a cone
EX: A windup for an underhand pitch
Medial and lateral rotation
Arm or leg rotation, spinning in place
EX: Toes pointing out, toes pointing in
Supination and Pronation
Supination: Outward rotation of forearm or foot, faces upward
Pronation: Inward rotation, causing the palm or sole to face downward
Lateral flexion + right rotation + left rotation (of trunk)
Lateral flexion: Tilting head or trunk to the right or left of the midline
Lateral and medial excursion of the mandible
Side to side movement
EX: Mandible movement while chewing gum
Ulnar and radial flexion + opposition and reposition of hand
Ulnar flexion: Tilt hand toward little finger
Radial flexion: Tilt hand toward thumb
Opposition: thumb approaching fingertips
Reposition: Thumb back to anatomical position
Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
Dorsiflexion: Toes are raised, heel on ground
Plantar flexion: Toes down, heel raised
Inversion and eversion (of foot)
Inversion: Soles turn medially
Causes bowleg
Eversion: Soles turn laterally
Causes knock-knee
What are factors affecting range of motion at a joint (Read Axes of rotation pg 281-283)
Muscle tone: Prevents over-stretch or over-contraction
Structure of articulating bones
Muscle bulk
Tightness of ligaments, tendons, joint capsule
Fusion of bones (arthritis, syntosis)
What is the glenoid labrum (shoulder joint)
Ring of fibrocartilage
What is the 4 bursae in a shoulder joint
Subacromion
Subcoracoid
Subscapular
Subdeltoid
What is the 4 rotator cuff tendons in a shoulder joint
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. Their tendonds form the rotator cuff
Is fused to the joint capsule on all sides except the inferior
What is the biceps brachii tendon (shoulder joint)
Two headed muscle located on the front of the upper arm, between shoulder and elbow. Functions is bending elbow joint, rotating forarm, shoulder flexion, shoulder stabilization
What are the 5 ligaments (shoulder joint)
Glenohumeral ligaments (3): Relatively weak and sometimes absent
Coracohumeral (2): Extends from the coracoid process of scapula to greater tubercle of the humerus
Transverse humeral ligament: Extends from the greater to the lesser tubercle of humerus, forms a tunnel housing the tendon from the long head of the biceps.
What is the patellar ligament (Knee joint)
Articulates with the femur to form a gliding patellofemoral joint
What is intrascapular ligaments (Knee joint)
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Posterior Cruciate ligament (PCL)
Named based off of location of tibia (not femur). PCL precents femur from sliding off the front of the tibia and prevents tibia from being displaces backwards. ACL is pulled tight and prevents hyperextension when knee is extended.
What are extrascapular ligaments (Knee joint)
Supports knee in the popliteal region
What are the 2 joints in the knee
Tibifemoral: Largest and most complex diarthrosis of the body
Primarily hige joint
Patellofemoral: Patella and patellar ligament also articulate with femur to form the patellofermoral joint.
Gliding joint
What is a sprain
Torn ligament or tendon, sometimes with damage to a meniscus or other cartilage
What is strain
Painful overstretching of a tendon or muscle without serious tissue damage. Often result from inadequate warm-up before exercise.
What is rheumatism
Broad term for any pain the supportive and locomotory organs of the body, including bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles
What is arthritis
Broad term for pain/inflammation at joint
Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear, associated with degeneration of articular cartilage, exposure of bone and development of boney spurs
Rheumatoid arthritis: Immune system
Attacks synovial membranes
Ankylosis (bone fusion) occurs
What is tendonitis
Form of bursitis in which a tendon sheath is inflamed
What is bursitis
Inflammation of bursa, usually due to overuse of joint
What is gout
Hereditary disease, most common in men, uric acid crystals accumulate in joints and irritate other articular cartilage and synovial membrane.
Causes swelling, pain, tissue degeneration, sometimes fusion of joint, gouty arthritis. Most commonly affects great toe.