neuroscience part 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:29 PM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
Autonomic nervous system
subdivision of the PNS
regulates body activities that are not under conscious control
visceral motor innervates non-skeletal muscles
regulates body activities that are not under conscious control
visceral motor innervates non-skeletal muscles
2
New cards
ANS is composed of special group of neurons serving
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle
internal organs and skin
smooth muscle
internal organs and skin
3
New cards
ANS motor neurons
preganglionic (in brain or spinal cord) then to ganglionic (cell body in ganglion outside CNS)
4
New cards
difference between SNS and ANS
somatic neuron goes straight to skeletal muscle
autonomic has preganglionic and post ganglionic fibres going to to smooth muscle glands and cardiac muscle
autonomic has preganglionic and post ganglionic fibres going to to smooth muscle glands and cardiac muscle
5
New cards
divisions of ANS
parasympathetic and sympathetic
6
New cards
parasympathetic
routine maintenance rest and digest
craniosacral
only innervate internal organs
cholinergic (acetylcholine)
craniosacral
only innervate internal organs
cholinergic (acetylcholine)
7
New cards
sympathetic
mobilization and increased metabolism
thoracolumbar
lead to every part of the body
adrenergic post ganglion (noradrenaline)
(acetylcholine in preganglionic)
thoracolumbar
lead to every part of the body
adrenergic post ganglion (noradrenaline)
(acetylcholine in preganglionic)
8
New cards
Central control of ANS
Amygdala
hypothalamus
reticular formation
hypothalamus
reticular formation
9
New cards
Amygdala ANS
main limbic region for emotions
stimulates sympathetic activity
stimulates sympathetic activity
10
New cards
hypothalamus ANS
main integration centre
11
New cards
Reticular formation ANS
most direct influence over autonomic function
12
New cards
ANS diseases
horner’s syndrome
Raynauds disease
Raynauds disease
13
New cards
Horners syndrome
pupillary constriction
ptosis
loss of sweating
vasodilation
enophthalmos
ptosis
loss of sweating
vasodilation
enophthalmos
14
New cards
Raynaud’s disease
hyperactivation of the sympathetic NS causing extreme vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels leading to hypoxia
15
New cards
corticospinal tract
carries movement information form motor cortex to spinal cord
upper motor neurons to lower motor neurons to muscle
\
upper motor neurons to lower motor neurons to muscle
\
16
New cards
corticospinal tract structure
motor cortex to midbrain(cerebral peduncles) to pons and medulla (pyramids) cross to other side of brainstem (pyramidal decussation)
17
New cards
major vertebral regions
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
18
New cards
sensory dermatomes
area of skin supplied by sensory neurons that arise from spinal nerve ganglion
19
New cards
sensory input
comes though dorsal horn
20
New cards
motor output
comes through ventral horn
21
New cards
types of skeletal muscle fibres
slow oxidative (slow fatigue resistant)
fast oxidative (fast fatigue resistant)
fast glycolytic (fast fatiguing)
fast oxidative (fast fatigue resistant)
fast glycolytic (fast fatiguing)
22
New cards
differences in maximal shortening velocities are due to…
myosin enzymes with high or low ATPase activities
23
New cards
Slow oxidative motor units
first during weak contractions
24
New cards
fast-glycolytic motor units
strong contractions
larger average diameter = greater tension but faster fatigue
large number of fibres per motor unit
larger average diameter = greater tension but faster fatigue
large number of fibres per motor unit
25
New cards
Type 1 fibres
red
thin with large amounts of myoglobin and mitochondria
isoform of myosin with low ATPase activity
contraction slower an lower intensity
sustained production of force
thin with large amounts of myoglobin and mitochondria
isoform of myosin with low ATPase activity
contraction slower an lower intensity
sustained production of force
26
New cards
type 2 fibres
white
thick and contain less myoglobin
isoform myosin with high ATPase activity
contraction fast
few mitochondria
short-lasting maximal contraction
rely on anaerobic glycolysis
thick and contain less myoglobin
isoform myosin with high ATPase activity
contraction fast
few mitochondria
short-lasting maximal contraction
rely on anaerobic glycolysis
27
New cards
muscle spindle
in fleshy part of muscle
detects rate of change at which the muscles fibres are stretched
changes in length of muscle fibres
aids in coordination and efficiency of muscle contraction
detects rate of change at which the muscles fibres are stretched
changes in length of muscle fibres
aids in coordination and efficiency of muscle contraction
28
New cards
patellar reflex
patellar ligament is stretched pulling on patella which in turn stretches patellar tendon stretching quads causing muscle spindles to stretch
active muscles spindles excite associated neurons
active muscles spindles excite associated neurons
29
New cards
olfaction
smell
olfactory receptor neurons on olfactory epithelium
olfactory receptor cells synapse with tufted cells and mitral cells becoming the lateral olfactory tract
olfactory receptor neurons on olfactory epithelium
olfactory receptor cells synapse with tufted cells and mitral cells becoming the lateral olfactory tract
30
New cards
gustation
taste
\
\
31
New cards
G olf
G-protein coupled to the receptor cell for olfaction
32
New cards
olfaction pathway
2 pathways
1 to olfactory blub then to thalamus then to cortex
2 to uncus then lateral hypothalamus to cortex
1 to olfactory blub then to thalamus then to cortex
2 to uncus then lateral hypothalamus to cortex
33
New cards
tongue
supplied by cranial nerve
papillae 3 types of undulations on the tongue
papillae 3 types of undulations on the tongue
34
New cards
Papillae
3 types of undulations on the tongue
circumvallate
foliate
fungiform
circumvallate
foliate
fungiform
35
New cards
circumvallate
taste buds on sides
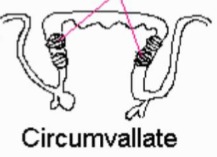
36
New cards
foliate
taste buds in middle
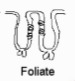
37
New cards
fungiform
taste buds on top
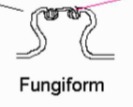
38
New cards
gustatory cell
specialized non neuronal cell
has cilia at the top
has cilia at the top
39
New cards
saliva
dissolves compounds to be brought onto the taste buds
cannot taste without it
cannot taste without it
40
New cards
salt taste receptor cell
enters through sodium channel and depolarizes cell - calcium influx - transmitter release - increased firing in afferent nerve(cannot be manipulated or adapted)
41
New cards
sour taste receptor cell
acidic, hydrogen ions (protons) enter and depolarizes cell - calcium influx - transmitter release - increase firing in afferent nerve
42
New cards
sweet taste receptor cell
binds to a receptor with g-protein activating cAMP depolarizing cell - calcium influx - transmitter released - increased firing of afferent nerve
43
New cards
umami taste receptor cell
g-protein coupled receptor
44
New cards
bitter taste receptor cell
g-protein coupled receptor
increasing IP3 causing calcium release and transmitter release and increasing afferent nerve firing
increasing IP3 causing calcium release and transmitter release and increasing afferent nerve firing
45
New cards
transmission of taste information
from taste buds to cerebral cortex via synapses in the brain stem and thalamus
46
New cards
middle ear bones
malleus
incus
stapes
incus
stapes
47
New cards
cochlea structure
cochlear nerve
scala vestibuli
scala tympani
cochlear duct
==**organ of corti**==
scala vestibuli
scala tympani
cochlear duct
==**organ of corti**==
48
New cards
organ of corti structure
hair cells
stereocilia
tectorial membrane
nerve fibres
blood vessels
basilar membrane
stereocilia
tectorial membrane
nerve fibres
blood vessels
basilar membrane
49
New cards
organ of corti mechanism
basilar membrane vibrates hair cells causing stereocilia to be pushed against tectorial membrane mechanically gated ion channels open up
50
New cards
endolymph
high potassium
potassium enters
depolarizes hair cell
potassium enters
depolarizes hair cell
51
New cards
perilymph
high sodium
52
New cards
basilar membrane responds to high frequency at…
base near oval window
53
New cards
basilar membrane responds to low frequency at…
apex further from oval window
54
New cards
auditory pathway
in through cochleo-vestibular nerve to brainstem, crosses over to superior olive to inferior colliculus to auditory cortex and thalamus
55
New cards
loudness
imp/s along the cochlear nerve
56
New cards
pitch
position along basilar membrane
57
New cards
sound location
interaural timing and intensity differences
58
New cards
vestibular system components
cochlea
saccule
ampulla utricle
3 semicircular canals and ducts
saccule
ampulla utricle
3 semicircular canals and ducts
59
New cards
otolith organs
utricle and saccule (in gelatinous substance)
60
New cards
semicircular ducts function
detects angular acceleration during rotation of the head
61
New cards
otoliths function
move in response to changes in linear acceleration and the position of the head relative to gravity
62
New cards
vestibular hair cells
type 1 kinocilium
type 2 stereocilia
type 2 stereocilia
63
New cards
hair cells move to right
ion channels open
stimulation
depolarization
stimulation
depolarization
64
New cards
cells hairs move to the left
ion channels close
inhibition
hyperpolarization
inhibition
hyperpolarization
65
New cards
connections of vestibular system
into spine through vestibular nerve goes to spinal cord to thalamus to cerebral cortex to eyes
66
New cards
vestibulo-ocular reflex
helps maintain fixation of eyes on an object with movement of the head
67
New cards
vestibulospinal reflex
allows for input from vestibular organs to be used for posture and stability in gravity environment
68
New cards
utricle responds to
linear acceleration in all directions
69
New cards
eye layers
fibrous outer
middle choroidal
inner neural
middle choroidal
inner neural
70
New cards
fibrous outer layer
cornea and sclera
continuous with dura mater
continuous with dura mater
71
New cards
middle choroidal layer
vascular posteriorly
forms iris and ciliary body anteriorly
continuous with arachnoid and pia
forms iris and ciliary body anteriorly
continuous with arachnoid and pia
72
New cards
inner neural layer
retina
continuous with CNS tissue
continuous with CNS tissue
73
New cards
optic disc
where optic nerve exits retina
pale circular region
no photoreceptors (blind spot)
pale circular region
no photoreceptors (blind spot)
74
New cards
macula
circular region adjacent the optic disc
central vision
centre is a depression called the fovea
central vision
centre is a depression called the fovea
75
New cards
anterior chamber
space between cornea and iris
76
New cards
posterior chamber
space behind the iris containing the lens
77
New cards
vitreous chamber
space behind the lens
78
New cards
aqueous humour
substance in the anterior and posterior chamber
oxygenated directly from the atmosphere
oxygenated directly from the atmosphere
79
New cards
the lens and cornea are…
avascular
80
New cards
refractive index
measure of how much the speed of light is reduced traveling through a given medium relative to a vacuum
81
New cards
Rf of lens of the eye
1\.45
82
New cards
refraction
takes place at both cornea and the lens
more refraction at cornea since it has air on one side
more refraction at cornea since it has air on one side
83
New cards
myopia
image falls short of retina
needs corrective concave lens
needs corrective concave lens
84
New cards
hyperopia
image overshoots retina
needs corrective convex lens
needs corrective convex lens
85
New cards
light through the eye
enters the cornea and projected on to back of eye and converted into electrical signals by photoreceptors in the retina
86
New cards
photoreceptors
sensory receptors responsible for vision
87
New cards
sensory receptors
neurons or epithelial cells that can transduce energy from stimulus into electrical signals called receptor potentials
88
New cards
receptor potentials
graded potentials that can either be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing
89
New cards
retinal neurons
2 classes of photoreceptors
3 classes of interneurons
3 classes of interneurons
90
New cards
types of photoreceptors
rods and cones
91
New cards
interneurons
connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells
bipolar, horizontal and amacrine
bipolar, horizontal and amacrine
92
New cards
cones
day vision
loss of function = legally blind
high visual acuity, temporal resolution and mediate colour vision
loss of function = legally blind
high visual acuity, temporal resolution and mediate colour vision
93
New cards
rods
mediate night vision
loss of rods = night blindness
extremely sensitive to light
achromatic
loss of rods = night blindness
extremely sensitive to light
achromatic
94
New cards
photoreceptors structure
inner and outer segment connected by cilium
inner - nucleus
outer - light transducing, stacked membranous discs
synaptic terminal makes contact with photoreceptors target cell
inner - nucleus
outer - light transducing, stacked membranous discs
synaptic terminal makes contact with photoreceptors target cell
95
New cards
types of cones
each contain a visual pigment that is sensitive to different light on the spectrum
96
New cards
fovea composition
higher ratio of cones to rods
ganglion cells have smaller receptive fields
photoreceptors to ganglion cells 1:1
ganglion cells have smaller receptive fields
photoreceptors to ganglion cells 1:1
97
New cards
peripheral retina
higher ratio of rods to cones
photoreceptors to ganglion cells >100:1
more sensitive to light
photoreceptors to ganglion cells >100:1
more sensitive to light
98
New cards
Rhodopsin
visual pigment in rod cells
complex of opsin and retinal
loops across the disc membrane in the outer segment of the rods
complex of opsin and retinal
loops across the disc membrane in the outer segment of the rods
99
New cards
opsin
transmembrane protein
makes rhodopsin
makes rhodopsin
100
New cards
retinal
small light absorbing compound
makes rhodopsin with opsin
derivative of vitamin A
makes rhodopsin with opsin
derivative of vitamin A