Kingdom Fungi Lab Quiz
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
;-;
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Kingdom Fungi
eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
movement?
cell wall is made of?
autotrophic or heterotrophic?
eukaryotic
non-motile
chitin
heterotrophic
What is saprophytic fungus?
A fungus that feeds on and decomposes dead organic material.
What is parasitic fungus?
A fungus that lives on a living organism and harms it while taking nutrients.
What do fungi release into the environment?
Digestive enzymes
What do fungi’s digestive enzymes do?
Break down nutrients
plant cell walls
insect exoskeletons
How do fungi absorb nutrients?
Hyphae
Yeast
multicellular or unicellular?
2 types?
unicellular
Saccharomyces cerevisiae: baker’s
yeastCandida albicans: causes Thrush
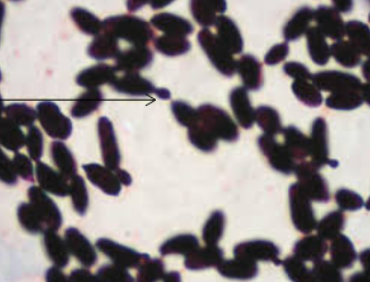
What is this called?
Budding
Mold
multicellular or unicellular?
composed of what?
reproductive structures are called?
multicellular
hypha (pl. hyphae)
fruiting body
How is mold classified?
by the type of fruiting body they form
Types of fungi reproduction
what do they produce
capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction
both produce spores
Types of hyphae and what they are
Mycelium: mass of hyphae
Rhizoid: modified hypha
anchors the mycelium
What is the scientific name for bread mold?
Rhizopus stolonifer
Is Rhizopus stolonifer a saprophyte or parasite?
Saprophyte

What is this?
?
?
?
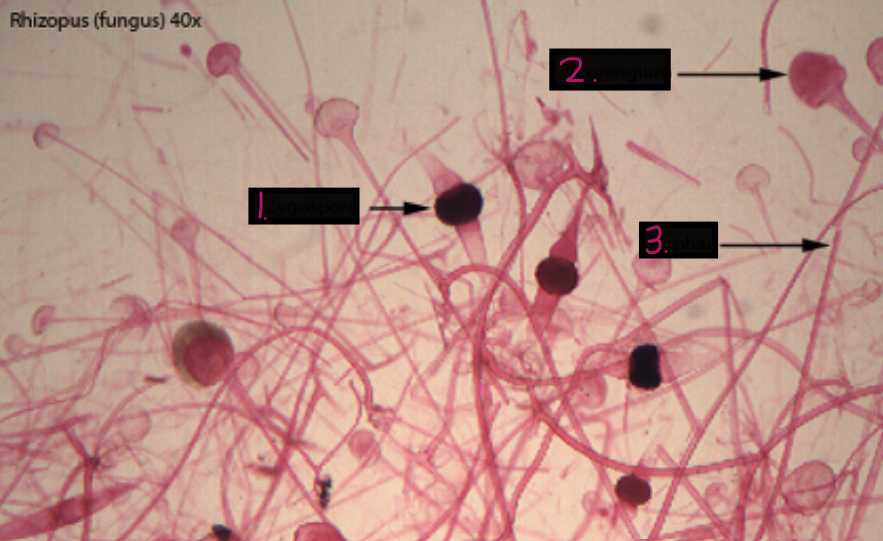
Rhizopus stolonifera (bread mold)
Sporangiophores
stolon
rhizoid
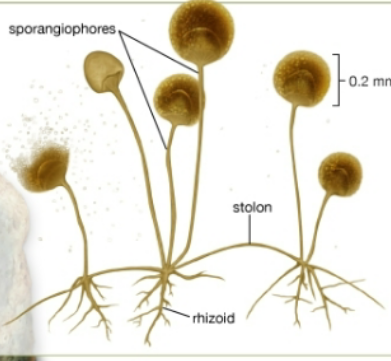
Where does rhizopus stolonifer grow?
bread, cheese, moist food items, and soft fruits and vegetables
What disease can Rhizopus stolonifer cause in humans?
Zygomycosis (also known as mucormycosis)
Rhizopus stolonifer can act as a ______ ____?
causes what infection?
opportunistic pathogen (infects weakened hosts)
Zygomycosis
The role of Rhizopus stolonifer’s sporangium
produces genetically identical spores through asexual reproduction
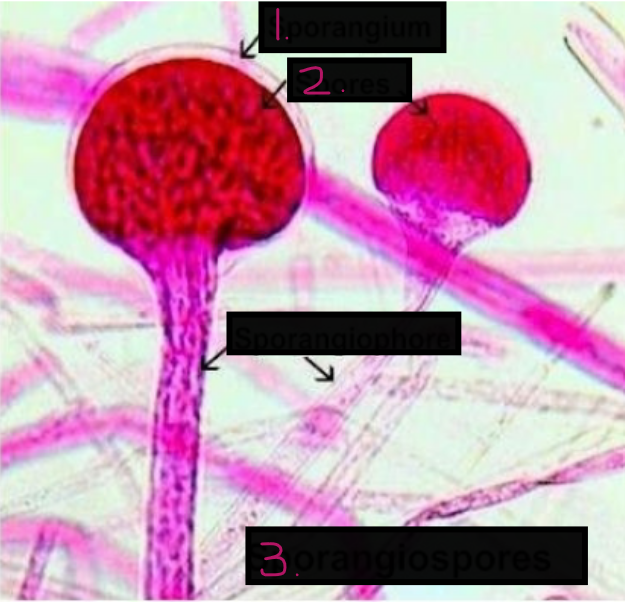
What is this?
?
?
?
Rhizopus stolonifera
Sporangium
Spores
Sporangiospores
What is a zygosporangium?
A structure formed when the hyphae of two different mating types join during sexual reproduction
What type of reproduction forms zygospores?
Sexual reproduction
Zygosporangium produces:
spores that are genetically diverse
What is this?
?
?
?
Rhizopus stolonifera
Zygospore
Sporangium
Hyphae
What mold produces the antibiotic penicillin?
Penicillium notatum
Who discovered Penicillium notatum and how?
Alexander Fleming
noticed that Staphylococcus aureus did not grow near the green mold
isolated the green mold and grew it in a fluid medium
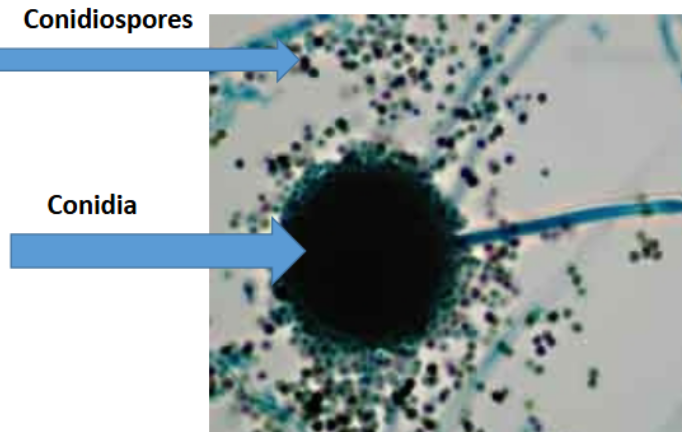
What is this?
?
?
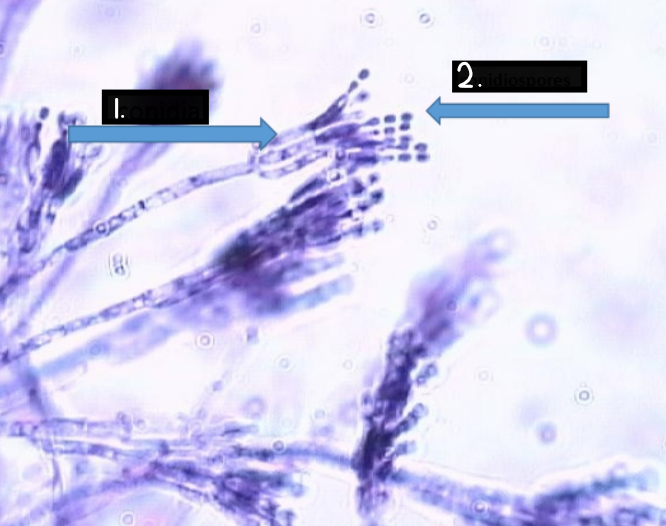
Penicillium notatum
conidia
conidiospore
What is this?
?
?
?
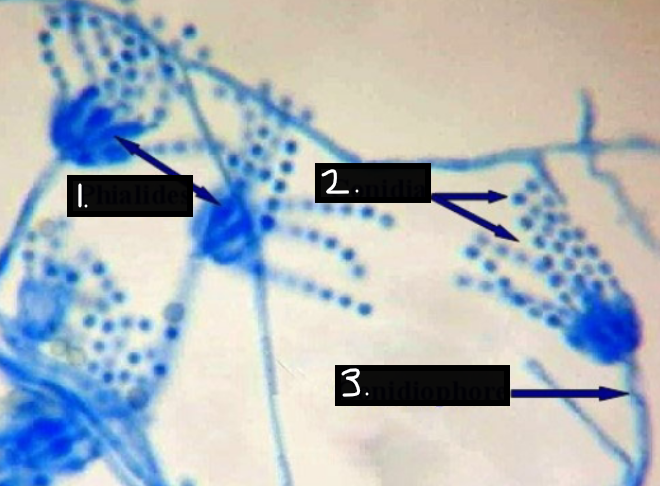
Penicillium notatum
Phialides
Conidia
Conidiophore
What is this?
mode of transportation
infective stage
type of fungus
can lead to?
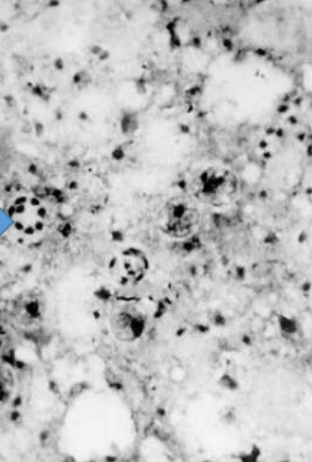
Pneumocystis carinii
Respiratory route
spore
parasitic fungus
fatal case of pneumonia in patients (compromised immune system)
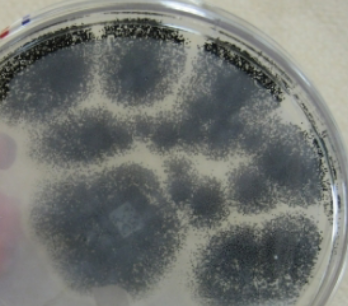
What is this?
where are its spores found?
can cause what?
Aspergillus
in the environment: dirty AC, flood damaged wood and sheet rock
lung infections in people with compromised immune systems
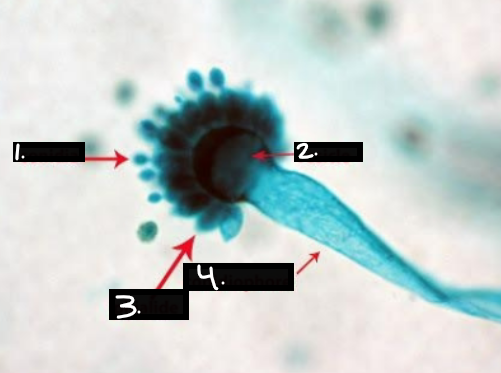
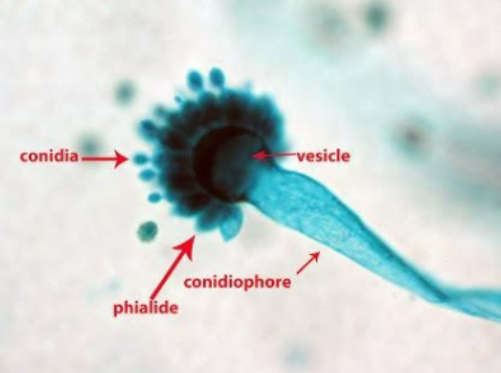
What is this?
?
?
?
?
Aspergillus
Conidia
Vesicle
Phialide
Conidiophore
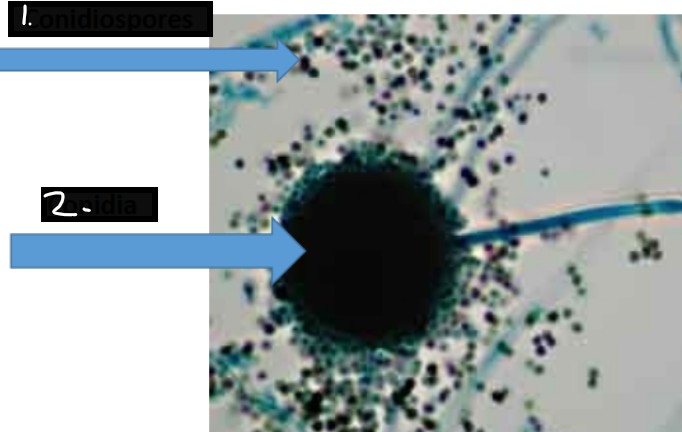
?
?
Conidiospores
Conidia