3.4.2 perfect competition
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is perfect competition
a market structure in which individual firms have no market power due to the amount of competition and are unable to influence the price
examle of perfect competition
For example, in India farming accounts for nearly 55% of all jobs with estimates at around 120 million people in the farming sector. This satisfies the
requirement for ‘many buyers and sellers’. We can also see there are ‘low barriers to entry’, as farming requires very few start-up costs with most farmers in India already in
possession of land they have inherited. Finally, goods produced by farmers are ‘homogenous’ as the overall temperature and humidity levels are the same across India, meaning farmers grow the same types of crops and all harvest in the same seasons. According to traditional economic theory, perfectly competitive firms would set the price of their goods at point P, in order to profit -maximise where MC=MR, and achieve both productive and allocative efficiency.
characteristics of perfect competition
lots of buyers and sellers
no barriers to entry and exit
perfect information
goods are homogenous
what are sellers in perfect competition market
price takers as lots of market participants
price takers
firms that have no market power and are unable to influence price so have to sell at current market price
barriers to entry
conditions that make it difficult or expensive for a firm to enter a market to compete with the existing suppliers
homogenous
products sold by competing firms are identical and indistinguishable from eachother
why is it bad products are homogenous in perfect competition
this means firms are unable to build brand loyalty as perfect substitutes exist and any price changes will result in losing all customers.
demand in perfect competition
perfectly price elastic
what industries have perfect competition
no market is perfectly competitive but agriculture may be
objective of perfect competition
to profit maximise so produce up to level of output where MC=MR
what is firms selling price
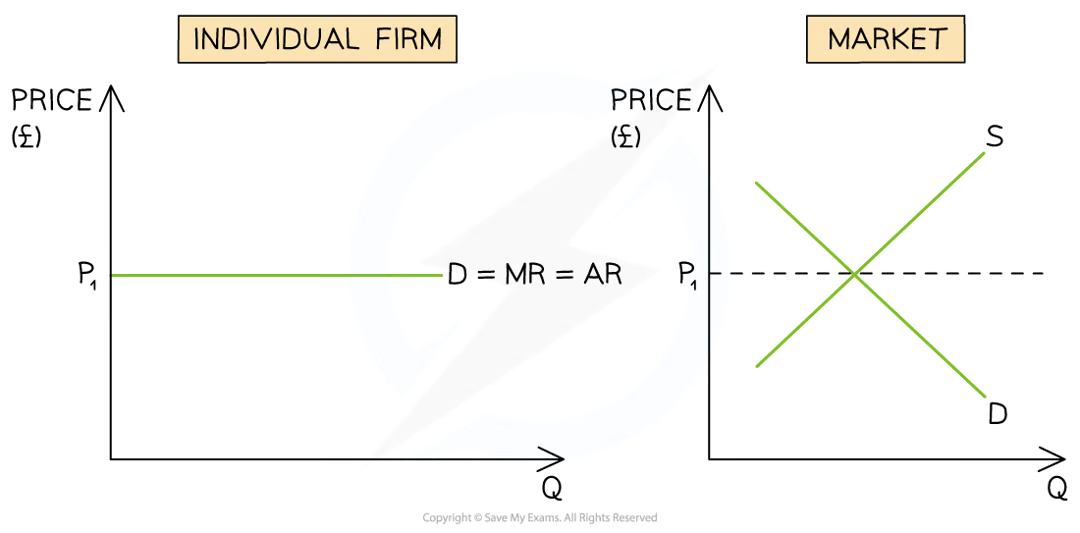
same as market price p1 = MR =AR =Demand
diagram showing how firm in perfect compertion has to accept market price
short run of perfect competition
firms can make supernormal profit or losses
lonf run of perfect competition
always return to long run equilibirium where they make normal profit
why dont any firms make supernormal profit in long run of perfect competition
because any short term supernormal profits attract new firms to the market since no barriers of entry so supernormal profits are competed away in the long term
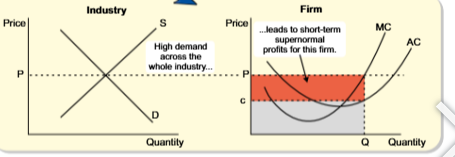
perfect competition diagram in short run
firms total revenue is TR = Q x P (the total area of red and grey triangles)
firms total costs are TC = Q x C (the are of the gret rectangle since c is firms average cost at this level of output)
subtract tc from tr to find firms profit
here tr > TC so firm is currently making supernormal profit (area of red rectangle)
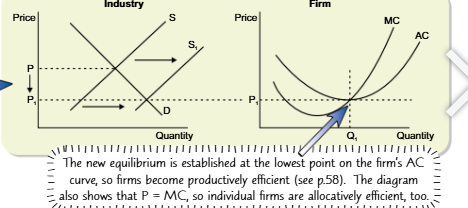
perfect competition diagram in long run
in perfectly competitive market those supernormal profits mean other firms will have icnentive to enter market
results in shift of industry supply curve to the right
meaning market price falls until all excess profits have been competed away and a new long run equilibrium is reachd at price p1
what happens if in long run firms dont make profit
if market price (AR) falla below firms AC firm is making less than normal profit
no barriers to exit in perfectly competitibe market so in long run firm will just leave market
what happens in short run if firm doesnt make profit
if selling price(AR) is still above the firms average variable costs then the firm may continue to trade temporarily
if the selling price(AR) falls below the level of the firms average variable costs the it will leave market immediately
efficiency of perfect competition
productively efficient
allocatve efficient
static efficient
not dynamic efficient
why does perfect competition lead to allocative efficiency
in perfect competition markets demand curve = marginal utility because consumers’ demand reflects what that good is worth to them and that decreases as quantity increases due to law of diminshing marginal utility
markets supply curve = marginal costs because producers marginal costs increase as quantity increase due to law of diminishing returns
allocative efficiency occurs when a goods price is equal to what consumers want to pay and this happens as price mechanism ensure producers supply exaclty what consumers demand
when can perfect competition not be allocative efficient
achieve it assuming no externalities
strictly speaking it occurs when P =MSC
it results in long run equilibrium where P=MPC
but if thre are negatuve externalities MPC<MSC so P<MSC so allocative inefficient as leads to overproduction and overconsumption
why does perfect competition lead to productive efficiency
it comes about as direct result of firms trying to maximise profits
at long run equilibrium firm will produce quantity of goods such that MR=MC
output above this level (MC>MR)reduces profits so firms wouldnt produce
output below this level (MR>MC) would mean firms would earn more revenue form extra output than would spend in costs so expand output
in long run output level is at bottom of AC curve
when can perfect competition only be productive efficieny
if assume no economies of scale in industry
there are infinite number of firms so each firms is very small so cant take advantage of eos
if there are eos then an industry made up of an infinite number of very small firms may be less productively efficient than if there was one very big firm
why doesnt perfect competition lead to dynamic efficieny
no single firm will have enough for research and devlopment and small firms struggle to receive finance,the existence of perfect information also means one firms invention willl be adopted by another firms and so investment will give firm no competitive benefit
why is perfect competition static eficeinty
as allocaive and productive efficiency are achieved nu cant last forveer as techinology and consumer tastes change