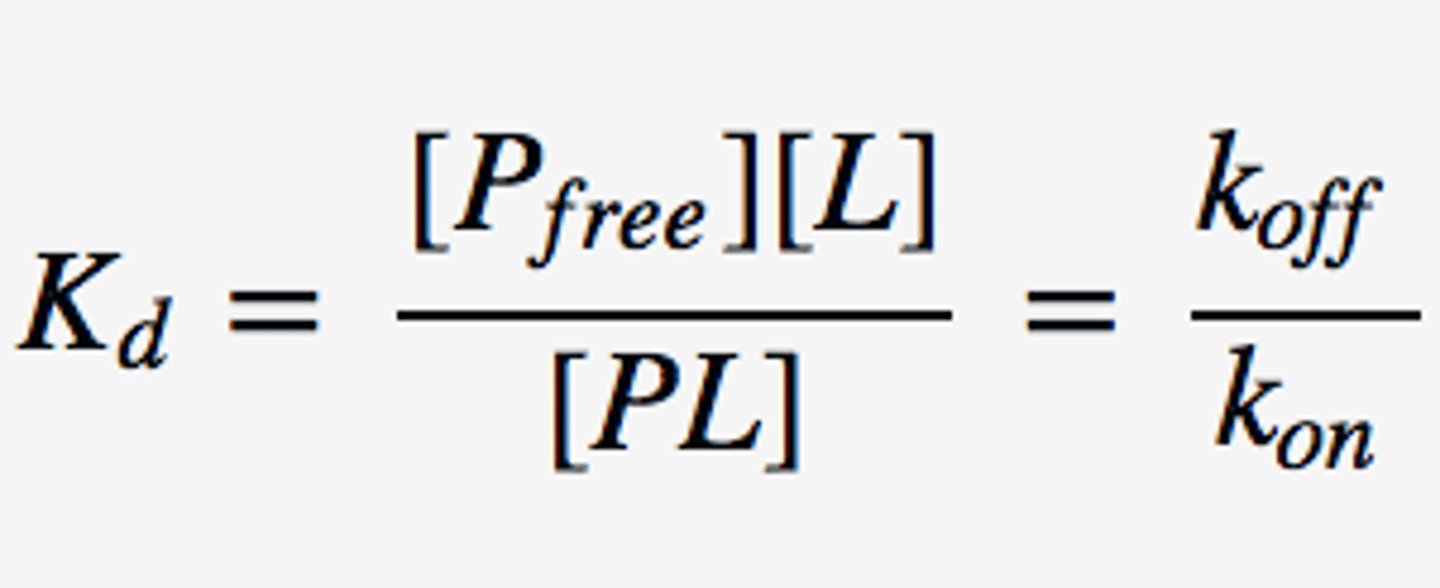MCAT Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
reaction rates
change in concentration over time
rate = (-1/a)(delta [A]/time)
![<p>change in concentration over time</p><p>rate = (-1/a)(delta [A]/time)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c6378a8a-ef17-499f-bd2a-02d098548498.jpg)
factors that affect the rate of a reaction
Temperature, surface area, concentration, catalyst, pressure
rate constant
the probability that a collision will result in a successful reaction. inversely proportional to activation energy, directly proportional to temperature
k = Ae^(activation energy/RT)
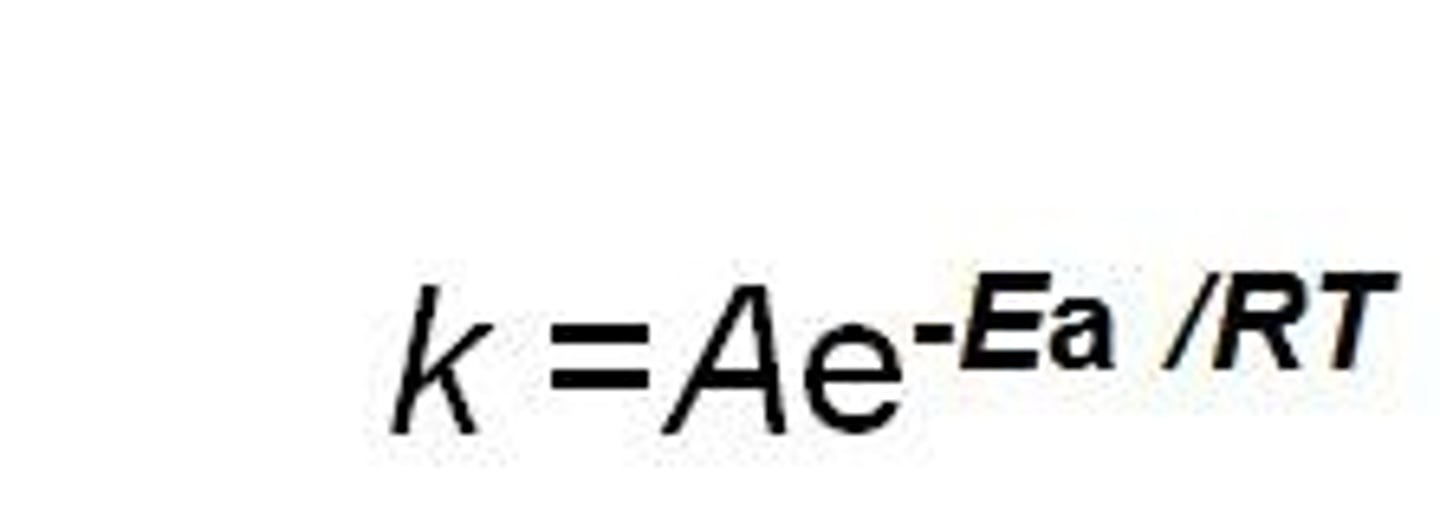
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction; used then regenerated, constant in overall reaction
intermediate
produced than used, detectable (unlike transition states), high-energy
transition state
high-energy, unstable state; not shown in mechanisms, undetectable
rate law
rate in terms of the initial concentrations of reactants and the rate constant only for elementary steps WITHOUT solids/solvents
rate = k [A]^m
![<p>rate in terms of the initial concentrations of reactants and the rate constant only for elementary steps WITHOUT solids/solvents</p><p>rate = k [A]^m</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac47fe09-e43c-4b09-859a-53bc5d7cebad.jpg)
method of initial rates
given rates with changing concentrations of reactants
- write out generalized rate law
- make sure all powers of 10 are the same
- compare rates where only one reactant changes: use this to determine the power in the rate law (0th, 1st, 2nd)
- you are able to find rate constant from concentrations and rate
dynamic equilibrium
when the forward and reverse rates are equal
equilibrium constant
describes the position of the equilibrium, ratio of product to reactant concentrations/partial pressures at equilibrium
Kc=[products]^[coefficients] / [reactants]^[coefficients]
![<p>describes the position of the equilibrium, ratio of product to reactant concentrations/partial pressures at equilibrium</p><p>Kc=[products]^[coefficients] / [reactants]^[coefficients] </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9834c6c3-326d-49fb-a530-fdf8244c829e.png)
reaction quotient
The ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants at any point during the reaction aside from equilibrium,
Qc=[C][D]/[A][B]
![<p></p><p>The ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants at any point during the reaction aside from equilibrium,</p><p>Qc=[C][D]/[A][B]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac6ec1d0-4bdc-489b-bf79-f2251feb782a.jpg)
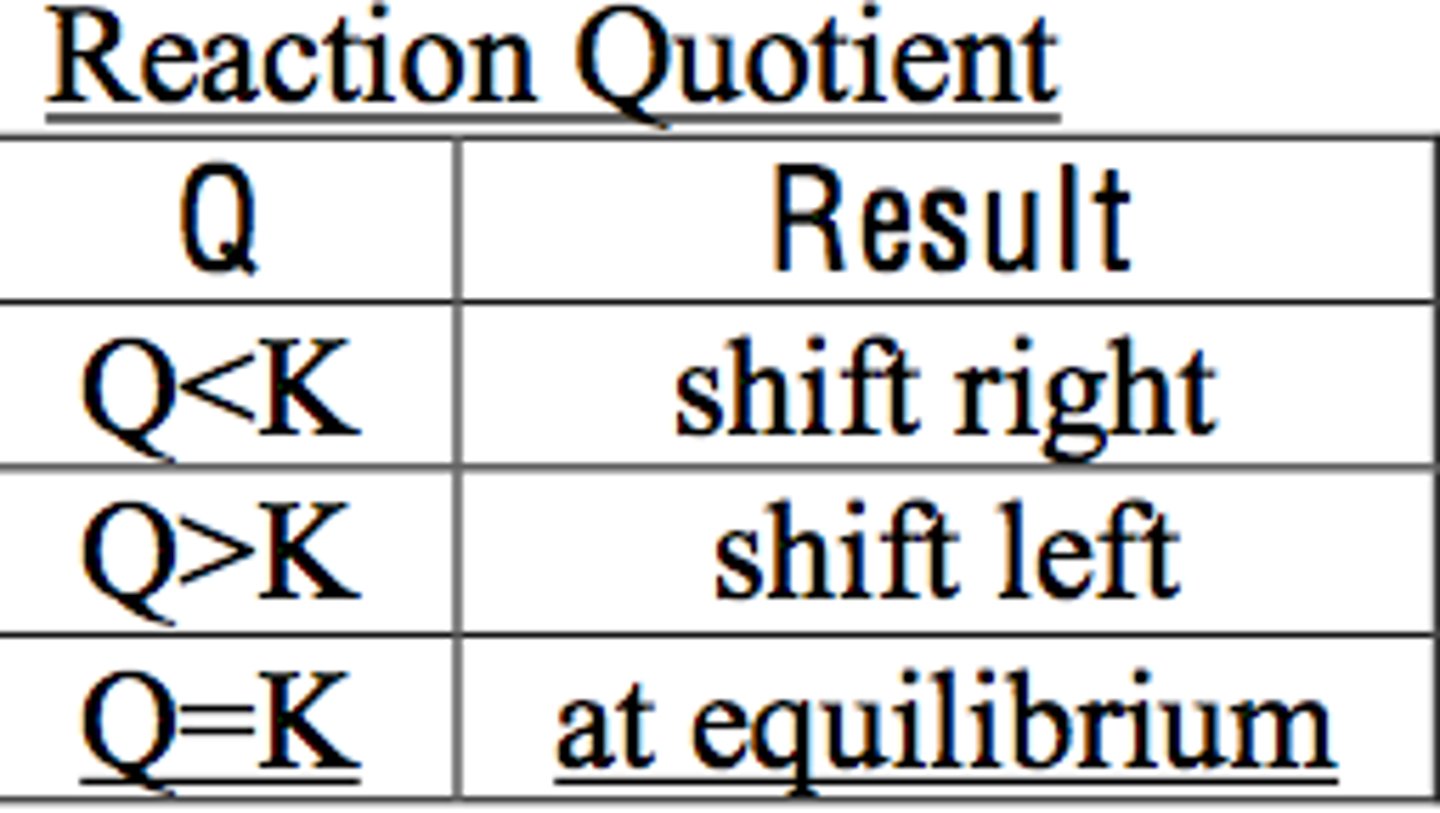
Q vs K
Q<K: shift right
Q=K: at equilibrium
Q>K: shift left
free energy with the reaction quotient
Grxn= Gstandard + RTlnQ
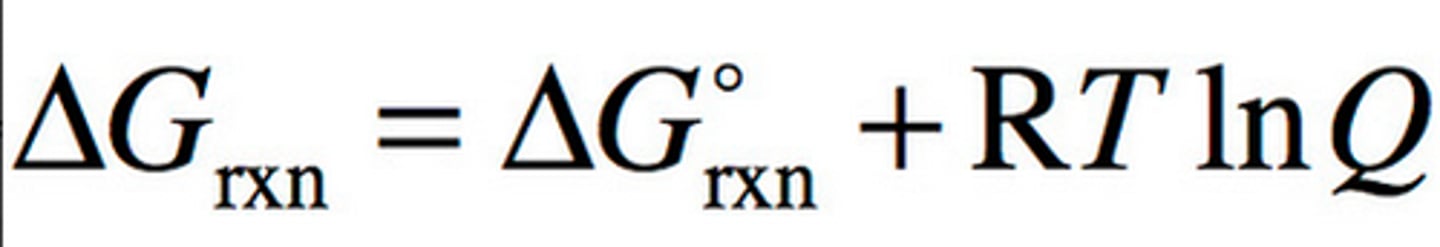
free energy at equilibrium
Gstandard = -RTlnKeq
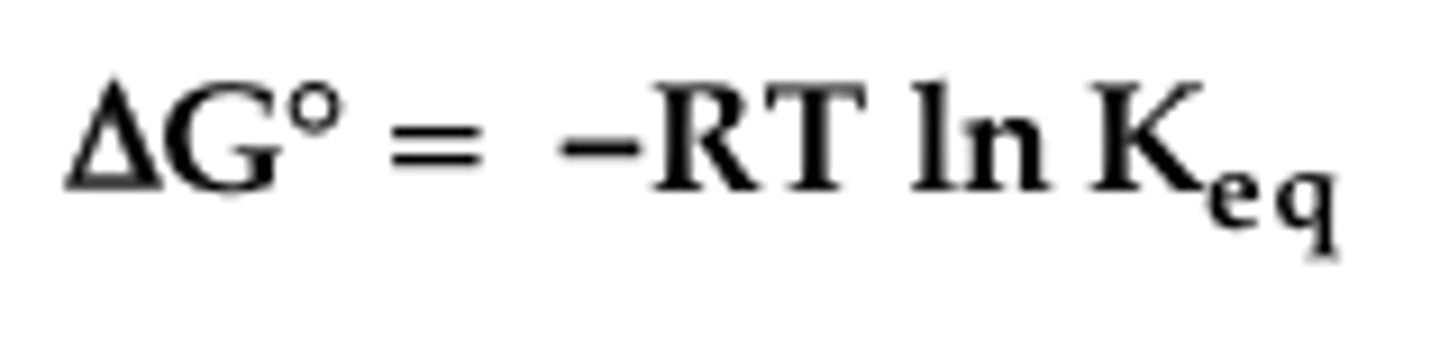
Le Chatelier's Principle
States that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that relieves the stress. stress can include changes in: concentration, volume, pressure and temperature
volume stresses an equilibrium
only if the number of moles of gas changes over the reaction. increasing pressure by decreasing volume shifts towards fewer mols of gas, and vice versa
temperature stress at equilibrium
if the reaction is endothermic: heat is a reactant, if the reaction is exothermic: heat is a product
forward vs reverse rate constants
If the reaction occurs in a single step, at equilibrium, the forward and reverse rates are equal. Keq=kf/kr
equilibrium of a coordination complex
is a formation constant; combining multiple equilibria results in multiplication of the equilibrium constants
solubility product
the constant for the equilibrium expression representing the dissolving of an ionic solid in water. as Ksp increases, solubility increases
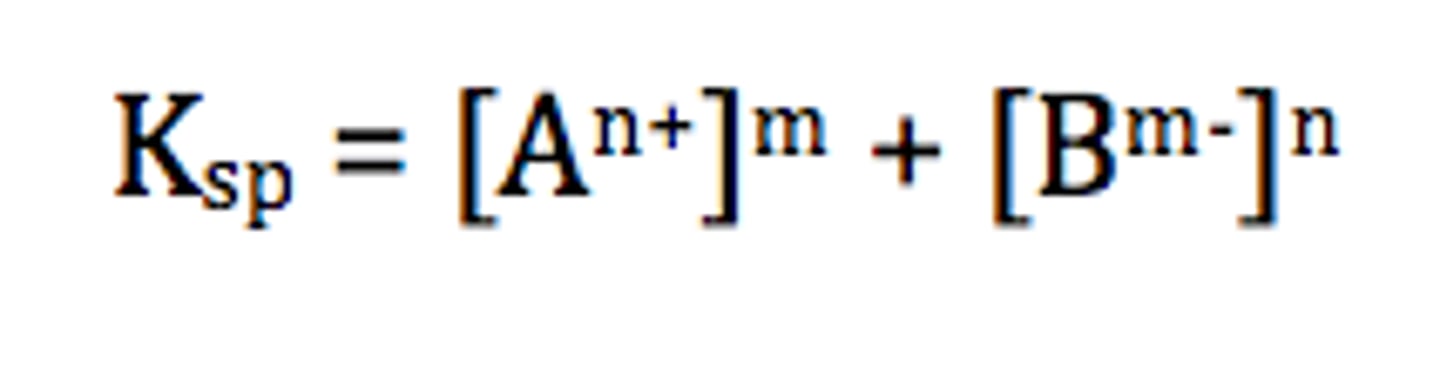
molar solubility
(S) the solubility of a compound in units of moles per liter
comparing Qsp to Ksp
when a precipitate will form:
Qsp > Ksp: percipitates will form
Qsp < ksp: no precipitate will form
Qsp=Ksp: saturated solution

common ion effect
a decrease in the solubility of an ionic compound caused by the addition of a common ion
solubility effects in acid/base
salt's solubility will increase if it is added to a solution containing something that removes a common ion
affinity constant
Reciprocal of the dissociation constant.
Kd= 1/Ka; affinity constant (Ka)