Threats to Biodiversity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Human activities
alter trophic structure, population dynamics, habitat, energy flow, nutrient cycling, & climate; Recent decades have experienced drastic acceleration of modification
Habitat Loss & Degradation
Humans have altered >50% of Earth’s terrestrial surface: deforestation & fragmentation, argiculture, urbanization
implicated in 73% of threatened species decline
Habitat conversion most severely impacts
large-bodied, wide-ranging, specialist, migratory species, endemics

Fragmentation & Deforestation
Global forest area has been cut in 1/2 over last 300 years
130,000 km^2 of tropical forest are cleared each year
50+ nations have lost 90-100% of their forest cover
alters hydrology, nutrients, microclimate
Deforestation degrades habitats
• Agriculture removes soil nutrients → reduction in primary productivity
• Nutrient addition → eutrophication (next week)
• Fire often used to clear land → CO2 release (carbon sink → source)
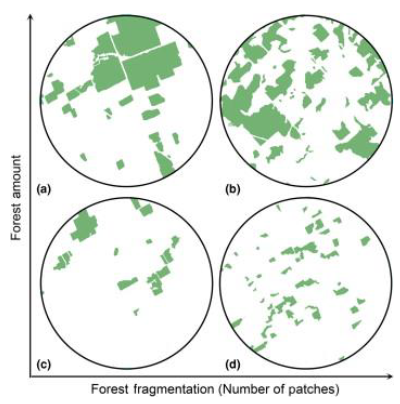
habitat fragmentation
Smaller habitat fragments = Higher extinction probability
Creates edge habitat that favors generalist species; Species specialized in forest interior decline (often large predators)
urbanization
More than ½ of the world population lives in urban areas
By 2030, 5 billion people will live in cities
leads to loss of species across all taxa & trophic levels and global biotic homogenization of ecological communities
aquatic habitat loss
70% of coral reefs have been damaged by human activities
40-50% of reefs (home to 1/3 of marine fish) will disappear in next 30-40 years
Freshwater threatened by dams, reservoirs, & wetland filling
Overexploitation
Occurs when harvesting (removal) of wild organisms at rates exceeding the ability of their populations to persist; Not just food: many species poached for economic value
Overexploitation most severely impacts
Species with restricted habitats (endemics, island species); Large organisms with low reproductive rates
Species Hunted to Extinction
Dodo
Steller’s Sea Cow
Passenger Pigeon
Great Auk
Ivory Billed Woodpecker
Carolina Parakeet
Falklands Island Wolf
Caribbean Monk Seal
Tasmanian Tiger (Thylacine)
ALMOST Northern Elephant Seals
ALMOST Cheetahs
Fishing down the food web
As fish stocks of top trophic levels (predatory fish) decline, fisheries are now fishing lower trophic levels
poaching
illegal hunting
African elephants declining in most of Africa for last 50 years, largely because of ivory; International ban on sale of ivory had opposite of intended effect
Biological Invasions
introduced species when they have a negative ecological impact on native species; contributed to 40% of extinctions since 1750; cost billions in damage & control
Outcompete native species for resources or habitat
Often cause economic harm
May consume native species
Can introduce pathogens to naïve populations
Introduced species
moved (intentionally or accidentally) from native range to a new region by humans
Invasive species have more severe impacts on
ground-nesting birds & small mammals, poor competitors, specialists & endemics
Human-wildlife Interactions
Anthropogenic changes force species into regions where they have closer contact with humans leading to conflict & disease; threats to crops, property, livestock, & human safety → lead to persecution & decline
zoonotic diseases
¾ of emerging human diseases are transmitted to humans from other animals; Transmitted by direct or indirect contact, or an intermediate species (vector); pose risks to both health & economic stability
ex. Rabies, plague, Chagas’, salmonella, sleeping sickness, Malaria, Lyme, Nipah, ebola, zika, monkeypox, avian flu, intestinal worms
Humans (unintentionally) spread wildlife disease
Organisms become more susceptible to disease in degraded ecosystems
Habitat loss & fragmentation alters abundance and dispersal of pathogens and their host