Atom & nuclear history - concepts and people
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
The Law of Multiple Proportions
the same elements can combine into multiple compounds with the same ratio of elements individually.
John Dalton
3 - "father of atomic theory"
The Law of Multiple Proportions - the ratios of elements in compounds divide to whole number ratios therefore Elements are made of atoms, all elements of the same type are identical, atoms are indivisible, and cannot be created or destroyed and atoms can combine in simple ratios to make compounds.
Cathode Ray Tube (CTR)
tube that has two charged plates (negative and positive with a hole) which creates an electronic force that goes through the hole and creates and electronic beam
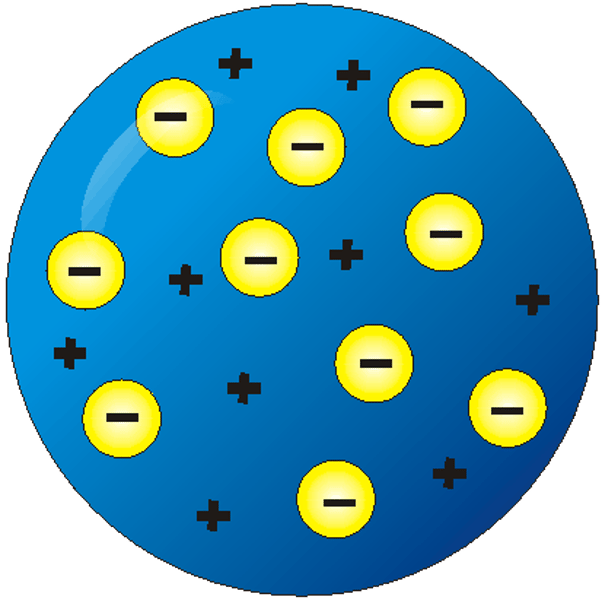
JJ Thompson
4 - discovered electrons: using CTR that there are negatively charged particles smaller than an atom because the mysterious ray created in the CTR deflected more towards the positive plate than H+ ions (the lightest atom) did. = Plum Pudding Model
Oil Drop Experiment
A drop of oil was placed in a cylinder with negative and positive plates, the drops were charged using an x-ray. Different waves of xrays let the drops fall at different rates.
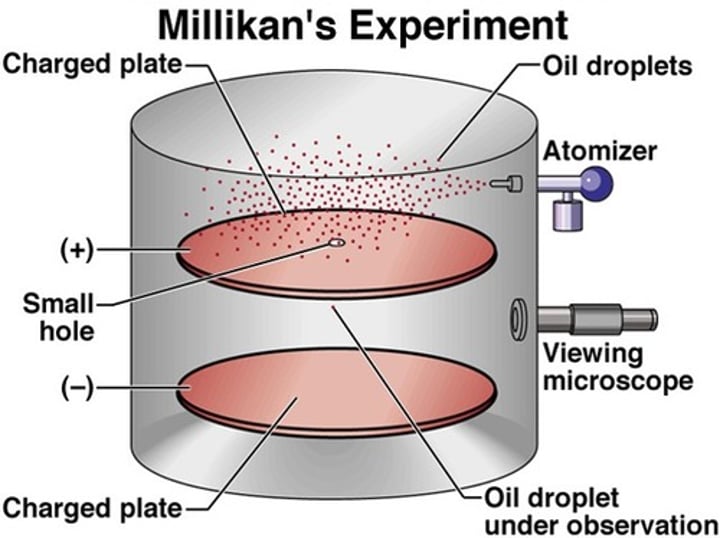
Robert Millikan
5 - discovered electron charge = 1.6E-19 using oil drop experiment: analyzed many drops and each drops charge was a multiple of 1.6E-19 C therefore thats the charge of electronEr
Gold Foil Experiment
Alpha particles that were shot at gold foil were deflected when they hit the positive center of gold atoms.
Ernest Rutherford
6 - discovered the nucleus using gold foil experiment: instead of going straight thru plum pudding model rays were deflected thus the nuclear model of the atom
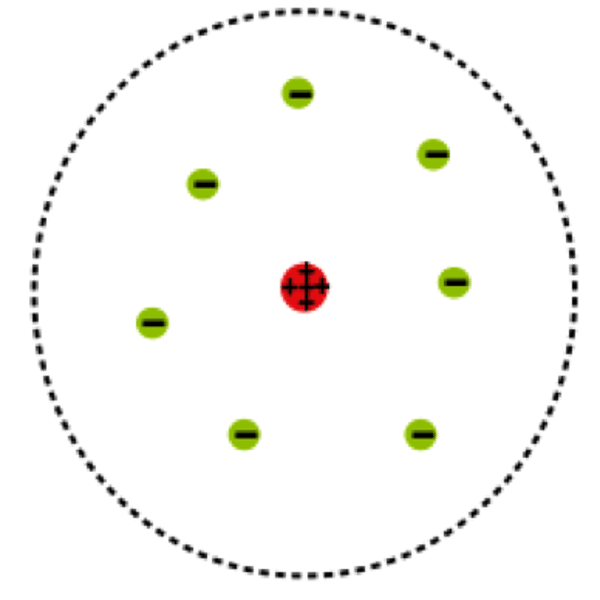
Neils Bohr
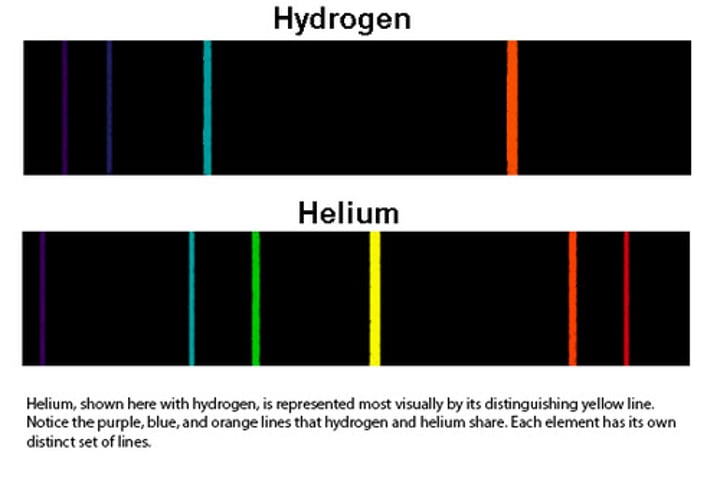
7 - Discovered planetary model: energy electrons can emit is predetermined shown by the emission spectrum of hydrogen
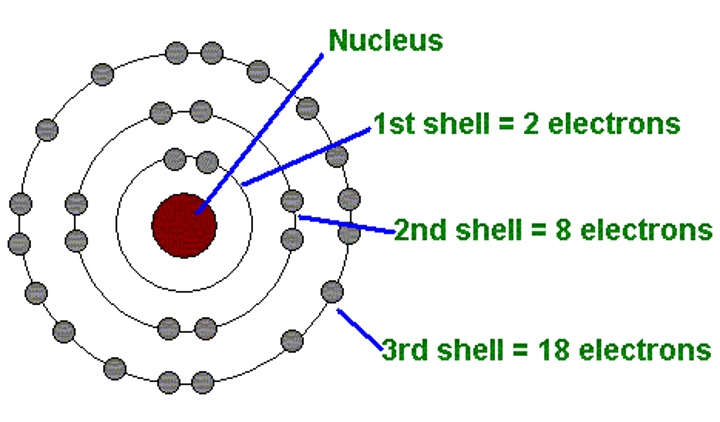
The energy of an electron
- the farther from the nucleus the more energy
- when electrons fall towards the nucleus they release energy in the form of light (an electromagnetic wave)
Types of electromagnetic radiation released by electrons
- larger electrons will release radiation with higher energy (UV, gamma)
- smaller electrons will release radiation with lower energy (radio, IR)
emission spectrum
a spectrum of the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a source - electrons when given energy
Marie Curie (1867-1934)
found evidence of radiation/radioactivity, discovered radium and polonium, therefore won Nobel prize in chemistry and physics:
-Invented something that detected charges in the air and found that uranium and thorium gave off these rays - names rays radiation/radioactivity
- found elements that behaved like barium and bismuth but were radioactive therefore after isolating them --> radium and polonium
Irene Joliet Curie (1934)
discovered nuclear reactions:
- if you slam particles together/bombard stable elements with radiation you can make new radioactive elements
Lise Meitner (1934)
Found evidence of splitting atoms which creates energy, therefore Nobel prize in chemistry, and element named after her:
- worked in Germany but had to leave
- bombarded uranium with neutrons to try to make bigger atoms but atoms got smaller instead and realized that the atom was splitting from einsteins equation E=mc^2
- discovered fission
Continuous Theory of Matter
the concept that matter is continuous, infinite, and comes in every form all around us, and could be divided and subdivided into smaller and smaller pieces without limit.
The Law of Definite Proportions
states that, regardless of the amount, a compound is always composed of the proportions of the elements it uses.