Population growth
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
J-shaped (exponential)
dn/dt=rN, but some factors becomes limiting and effects density. Intrinsic rate of increase (R), but conditions in nature are rarely ideal for long. Cause growth to depart from exponential
S-shaped (logistic)
dn/dt= rN [(K-N)/K]. exponential early but checked by natural factors. describes changes in intrinsic growth rate. Exponential phase, plateau phase, decline phase. The highest rate of increase is the inflection point : n1/2K. Environmental resistance K= carrying capacity.
limits growth
Stochastic processes especially important in small populations (genetic drift, inbreeding, allee effect.)
Density independent factors
'factors that do not tend to increase population size when they are small and decrease it when they are large, have “same” effect on population regardless of its size. (ex: variation in weather, abiotic factors)
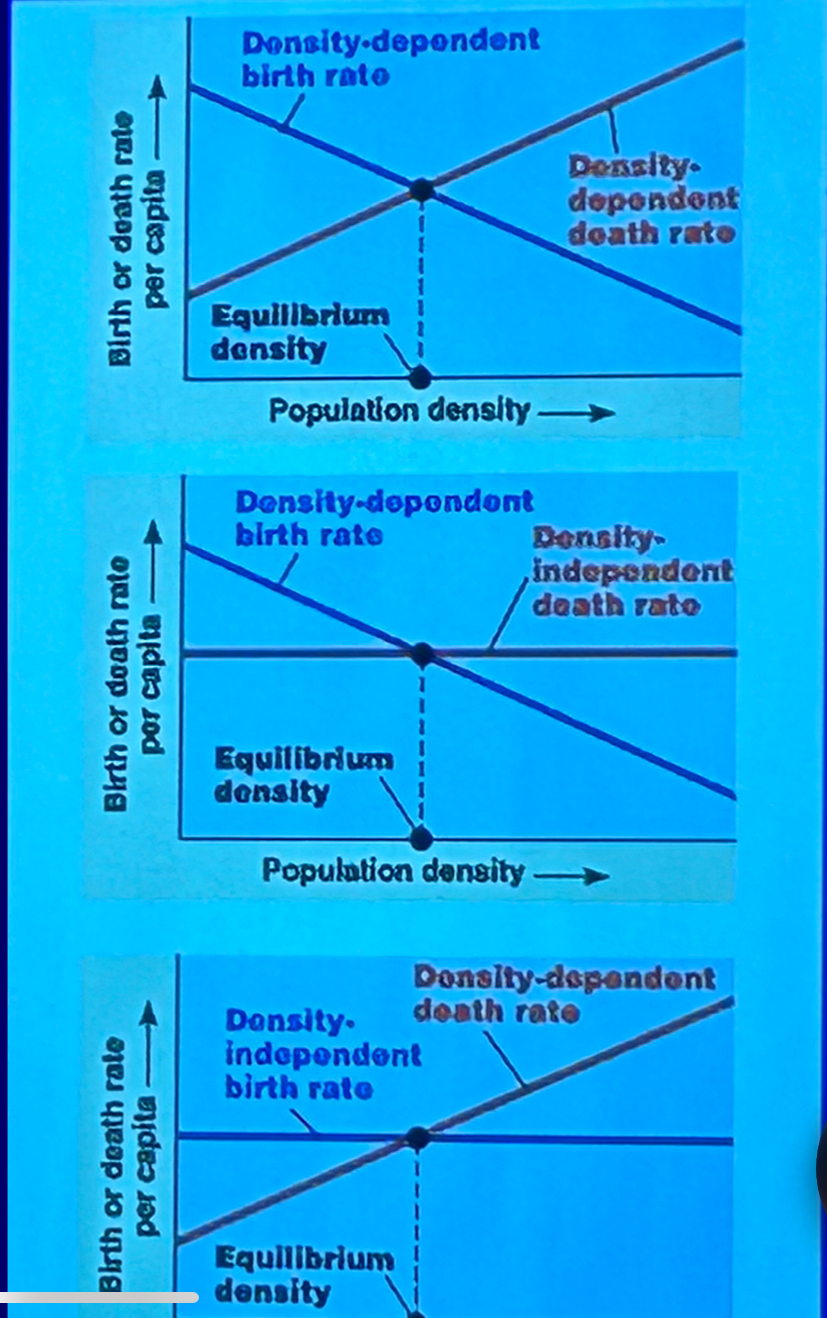
Density dependent
have greater effect when the population is large and lesser effect when it is small. Tend to be biotic factors. Result in population regulation.
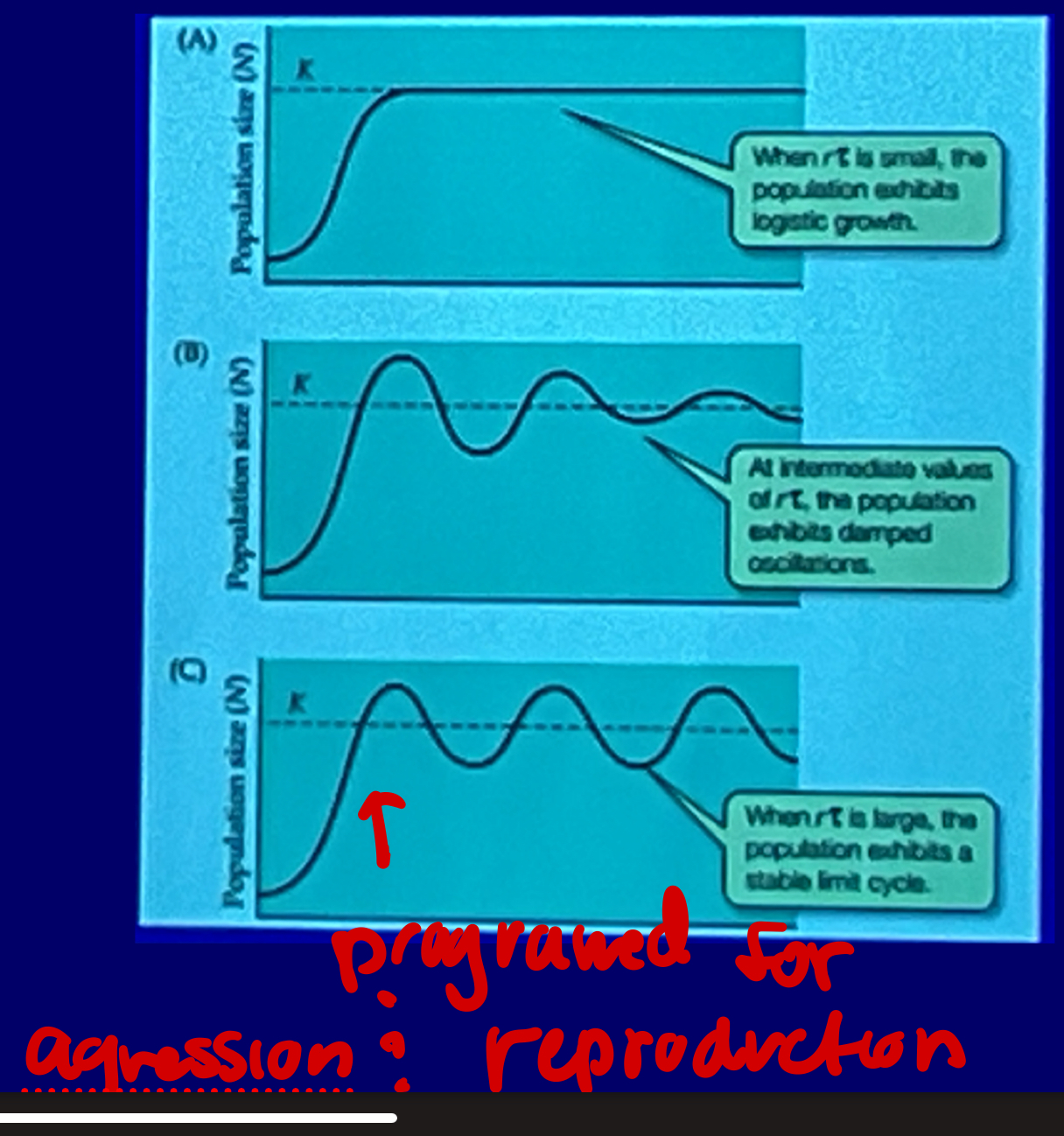
Population cycles
delayed density dependence, predator-prey dynamics, reproductive time lag, genetic factors.
r-selected
short lived, small body size, rapid development, high r at low densities, type 3 survivorship, no parental care, unstable habitats (semel parous), good colonizers/poor competitors, generalists, usually density independent adult mortality.
K selected
long lived, larger body size, slow development, low r at high densities, type 1 survivorship, extensive parental care, stable habitats (iteroparous), poor colonizers/good competitors, specialists, often density dependent adult mortality mortality. S-shape growth.
populations exist in a patchy habitat
there may be local breeding populations, each of which has a risk of extinction, but recolonization may occur following extinction, the dynamics of the local populations are not synchronized.
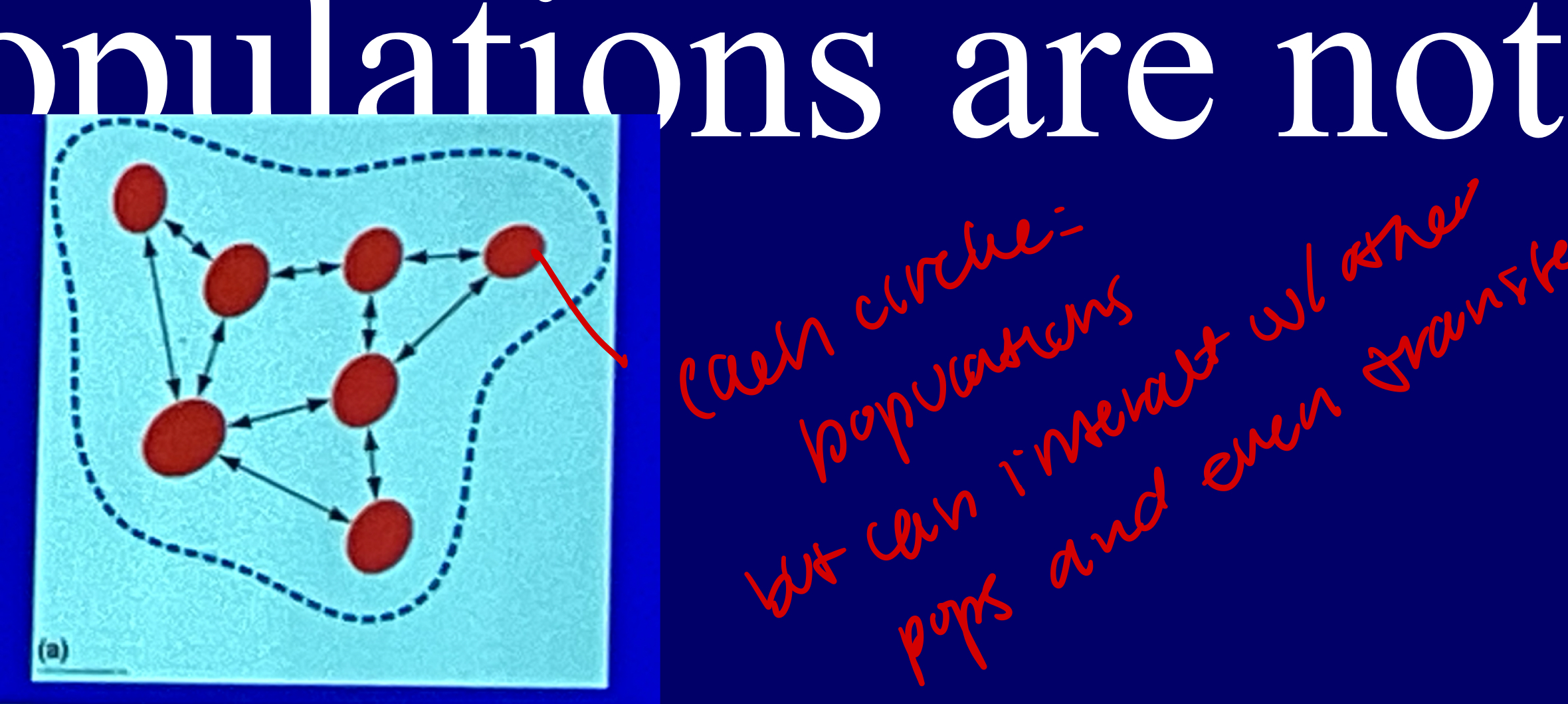
Metapopulations
populations are linked by dispersal, may be caused by fragmentation, extinction and colonization rates vary among patches, source (great) and sinks (drains) dynamics. Rescue effect ( help small populations)