Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibular
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Vestibular system is…
TRAINABLE
What are the functions of the vestibular system?
coordinate eye movements
maintains equilibrium
maintains head position
gives us a “sense” of head position
What is the key to understanding the vestibular system?
REMEMBER THE HAIR CELL
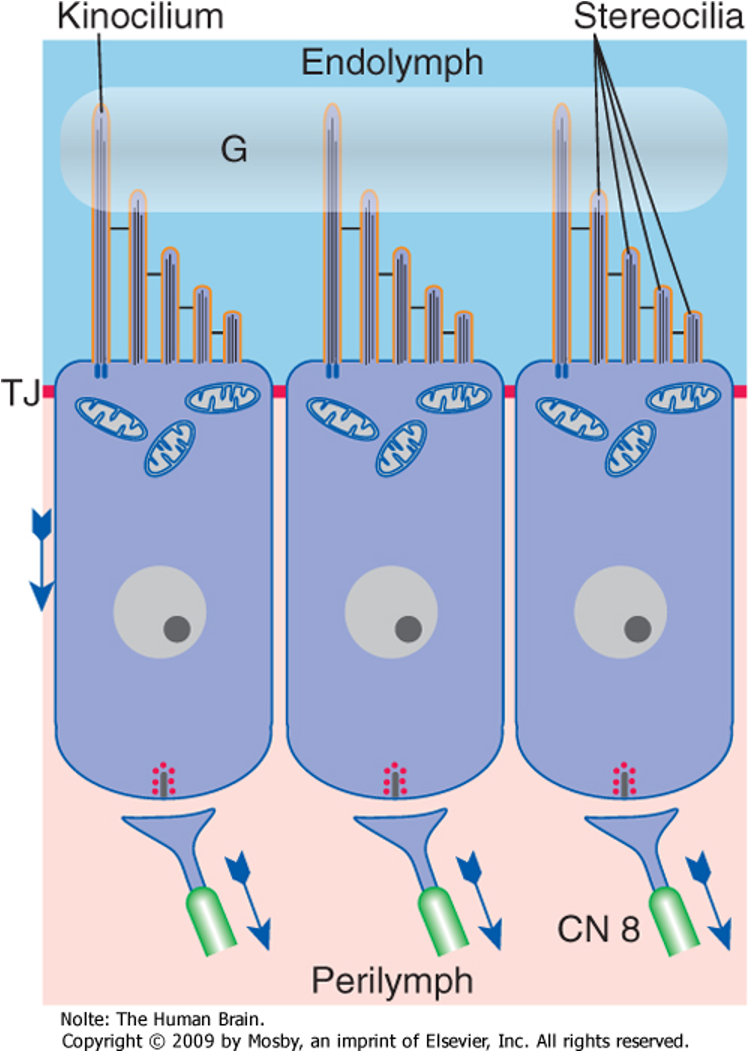
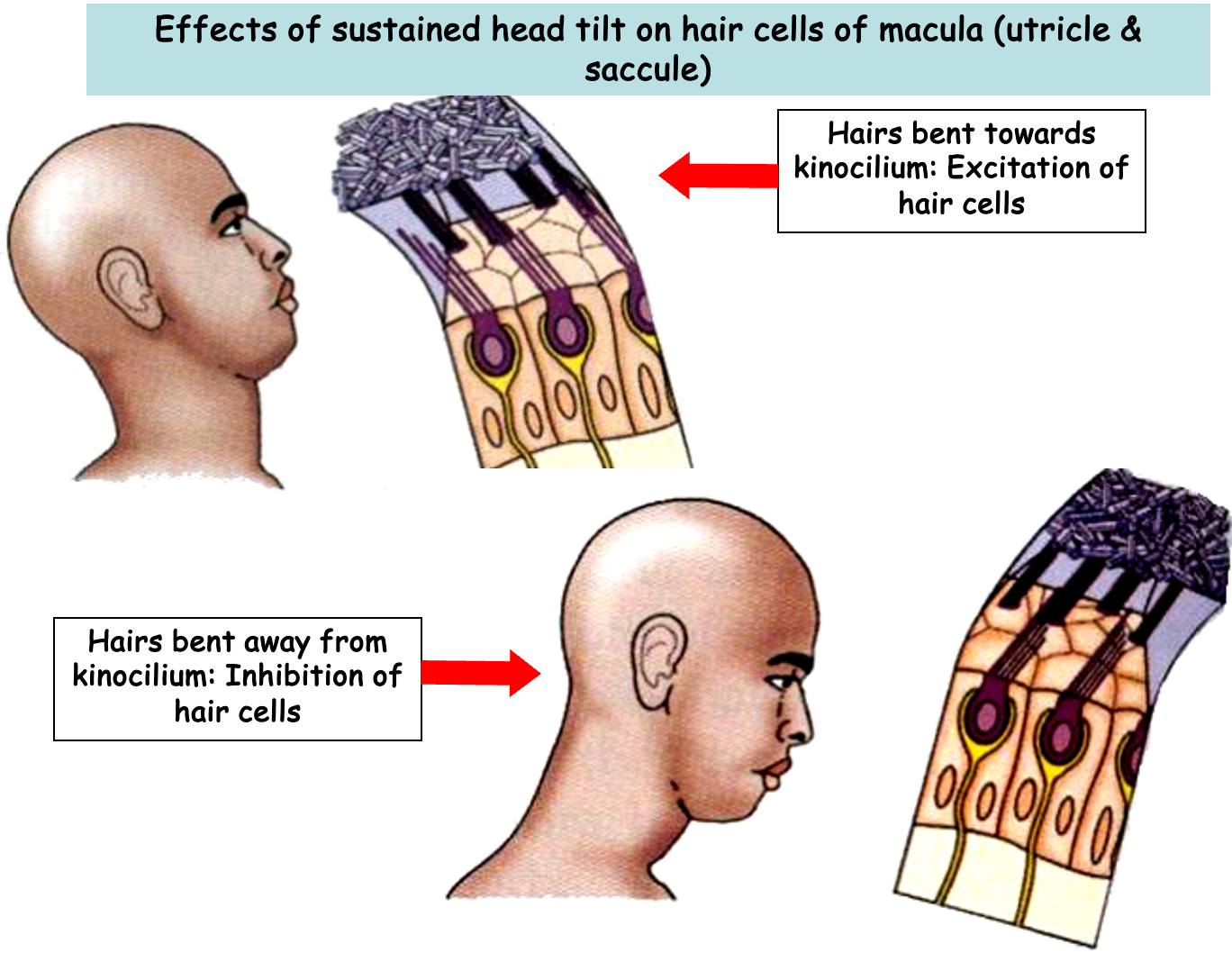
Hair cells are directionally sensitive, meaning…
swaying towards kinocilium tends to fire the nerve and hyper polarize the system
What do tight junctions do?
join hair cells to one another near the microvillar ends
each hair cell is bathed in…
partly endolymph and partly perilymph
Characteristics of endolymph
can accumulate too much because it is a fluid
projection of hair cells into it
drains into VENOUS SINUSES of dura mater
Disruption in normal production or drainage of endolymph results in what?
swelling of cochlear duct and utricle/saccule - MENIERE’S DISEASE
What is Meniere’s Disease?
also known as endolymphatic hydrops
makes hair cells discharge in absence of sensory input - both auditory and vestibular symptoms
What are the primary and secondary complaints of Meniere’s disease?
hearing loss and ringing in the ears
vertigo
What is in the three semicircular canals of the ear?
crista - hair cells
ampulla - swelling at the base of SCC
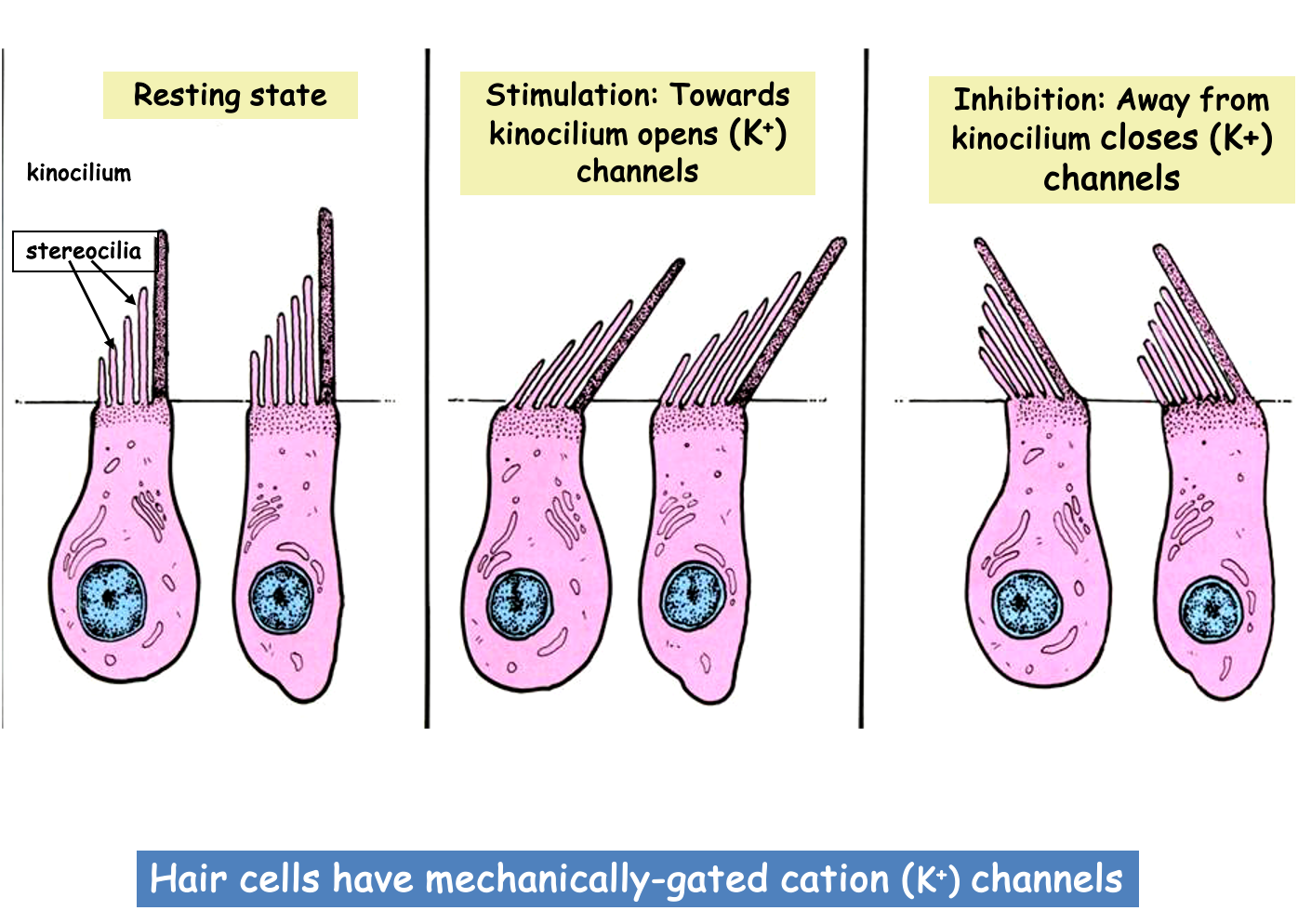
What are the three SCC?
anterior
posterior
horizontal - tipped posteriorly 30 degrees
What is the cupula?
gelatinous mass that swings over hair cells
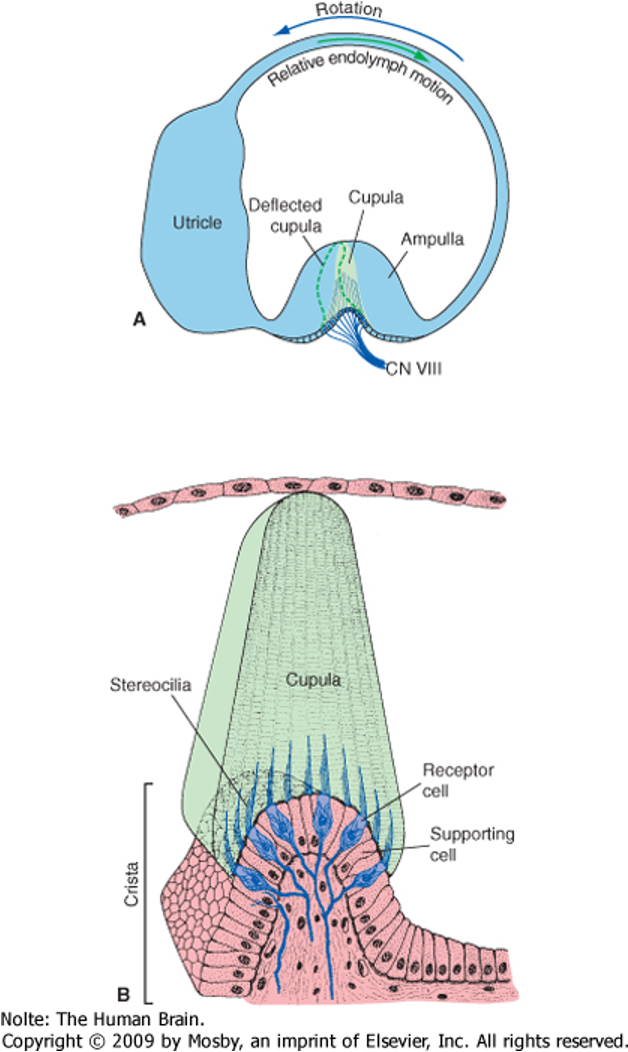
Vestibulo-Ocular Reflex
fluid will swoosh cupola over the hair cells WHEN YOU TURN YOUR HEAD
changes in firing rate transmitted by CN VIII
functional result: ability to keep gaze on a target as you turn your head
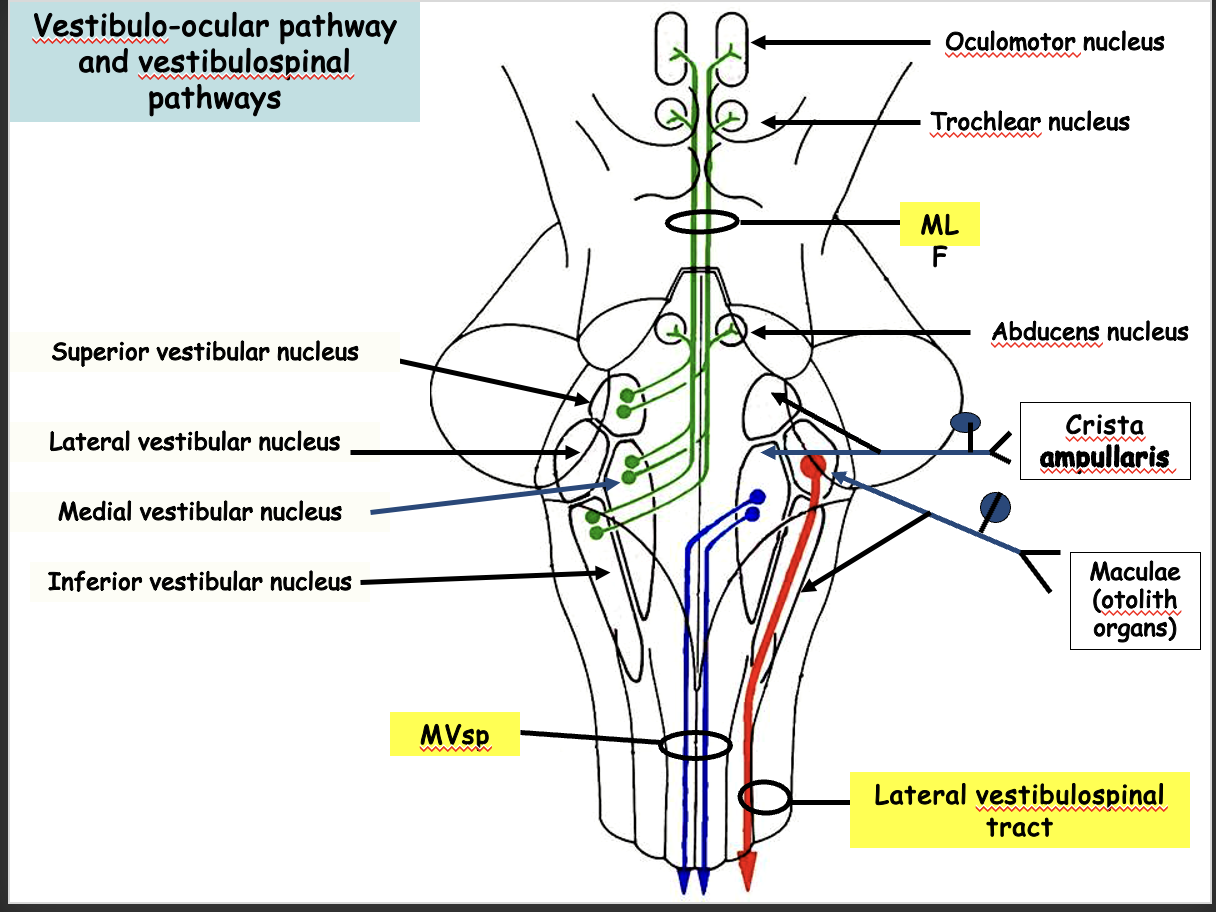
What happens as you turn your head to the left?
Contraction of left medial rectus and right lateral rectus results in drifting of eye to right
What is a nystagmus?
stimulated by rotation of head/body in space
begins with VOR pattern (slow eye movement)
followed by a compensatory rapid eye movement (a saccade)
How do you name a nystagmus?
by the FAST phase… right or left “beating” nystagmus
What is a rotatry nystagmus?
occurs DURING rotation
slow eye movement OPPOSITE direction of rotation
rapid eye movement IN direction of rotation
What is a post-rotary nystagmus?
occurs AFTER rotation has ended
slow eye movement IN the direction of rotation
rapid eye movement OPPOSITE the direction of rotation
What are the three principle sources of input the CNS uses for equilibrium and posture?
visual, vestibular, somato/proprioceptive
Macula characteristics
lives in utricle and saccule
covered with gelatinous substance
contain calcium carbonate crystals called otoconia
hair cells respond to gravitational force exerted by otoliths and otolithic membrane
sensitive to LINEAR ACCELERATION - GRAVITY
What is the gold standard for identifying unilateral vestibular loss?
caloric testing
What is a normal response to caloric testing?
COWS: cold opposite, warm same
cold into R ear = LEFT beating nystagmus
warm into R = RIGHT beating nystagmus
What are the signs and symptoms of vestibular dysfunction?
nystagmus
dizziness
vertigo
ataxia and gait disturbance
What are the treatments for vestibular dysfunction?
medical - pharmacologic and surgery
mechanical - maneuvers in BPPV (repositioning otoconia)
habituation
adaptation
substitution