Integumentary
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
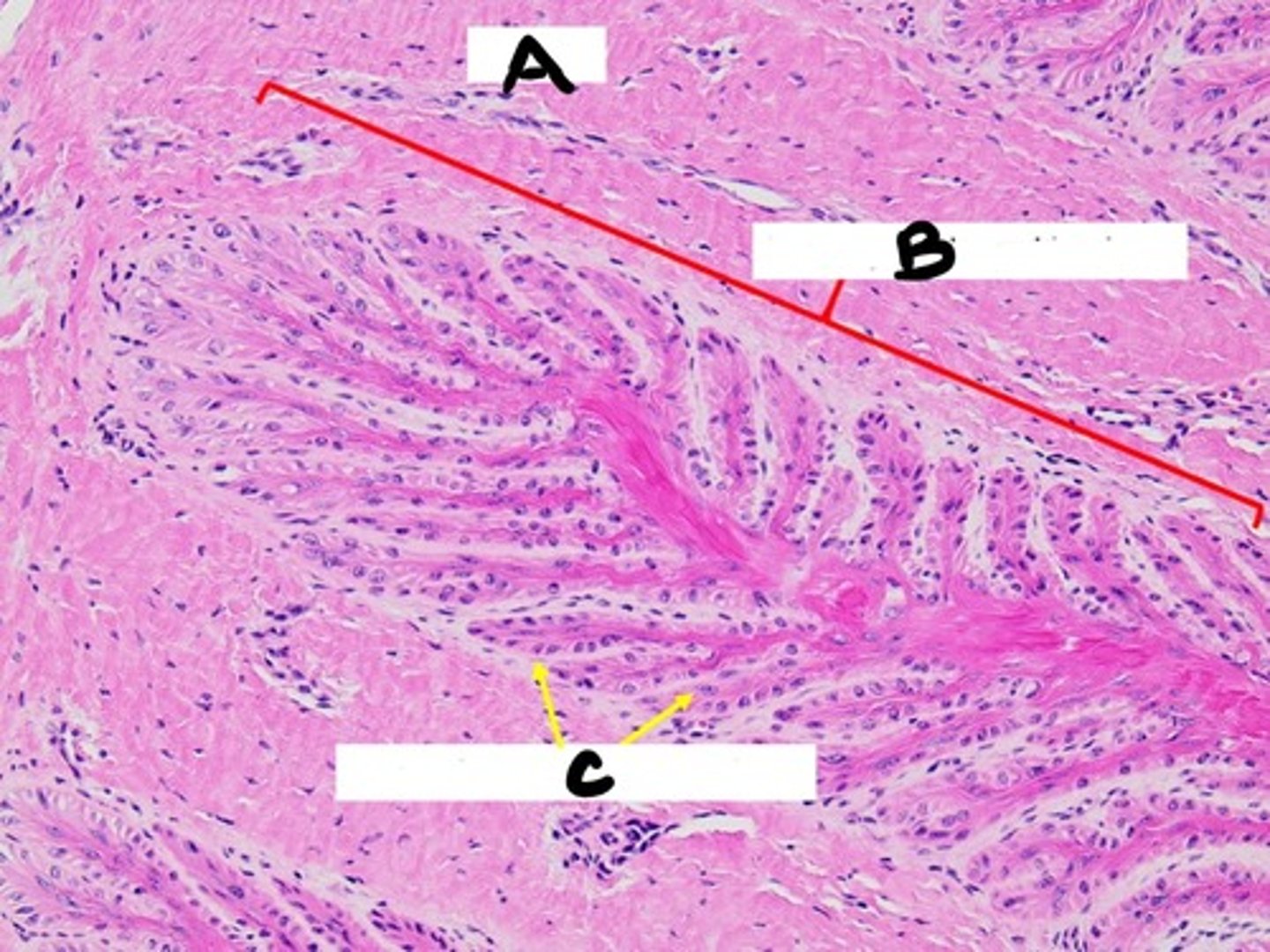
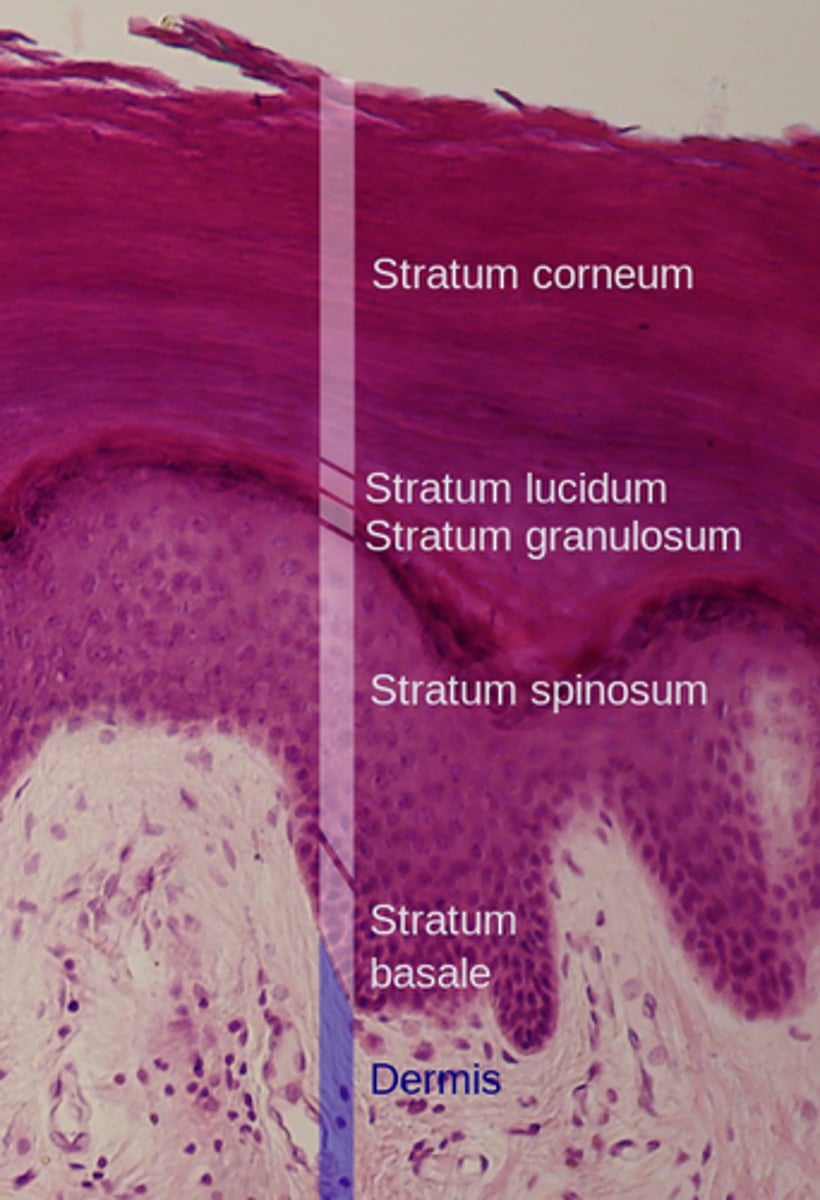
layers of epidermis
Stratum Corneum (Top)
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
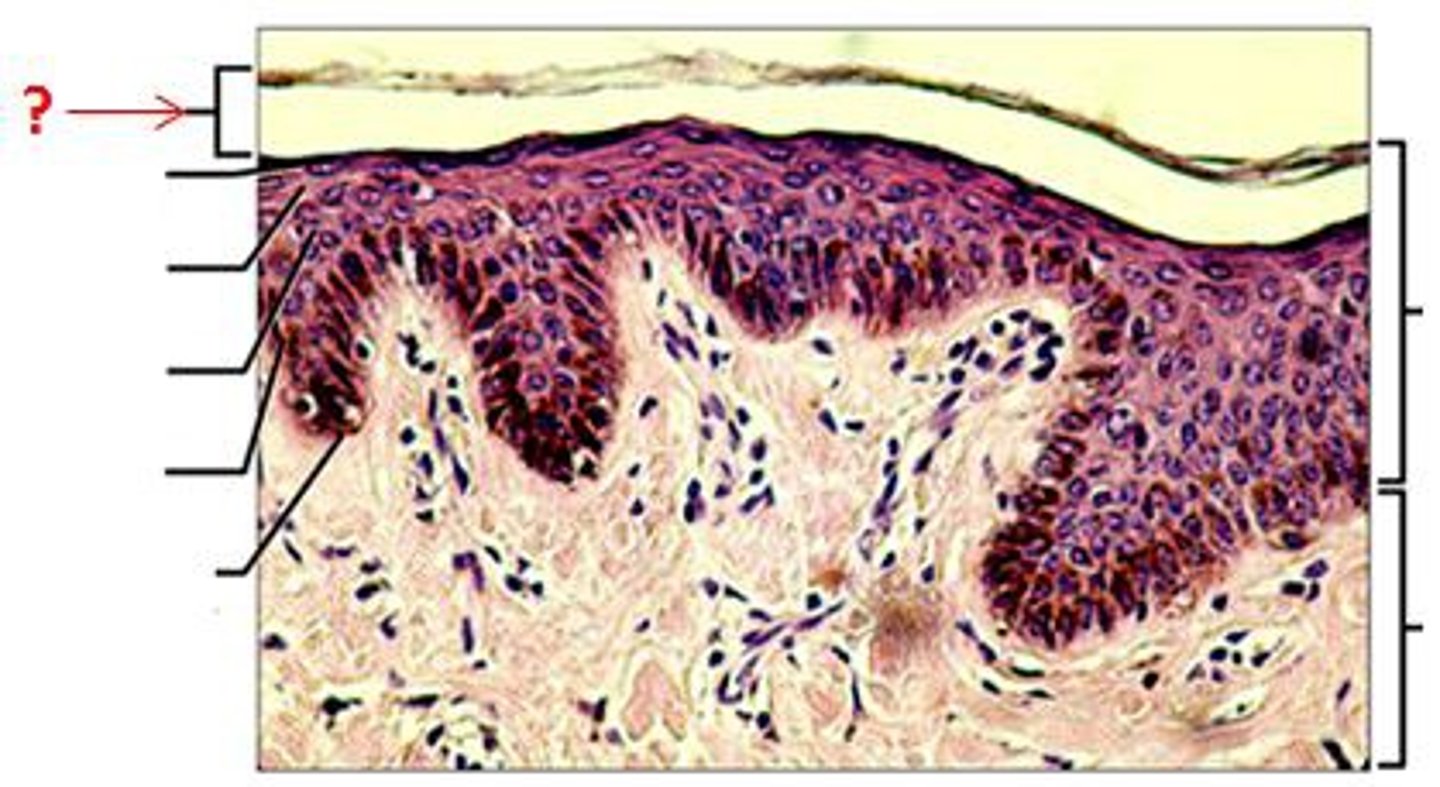
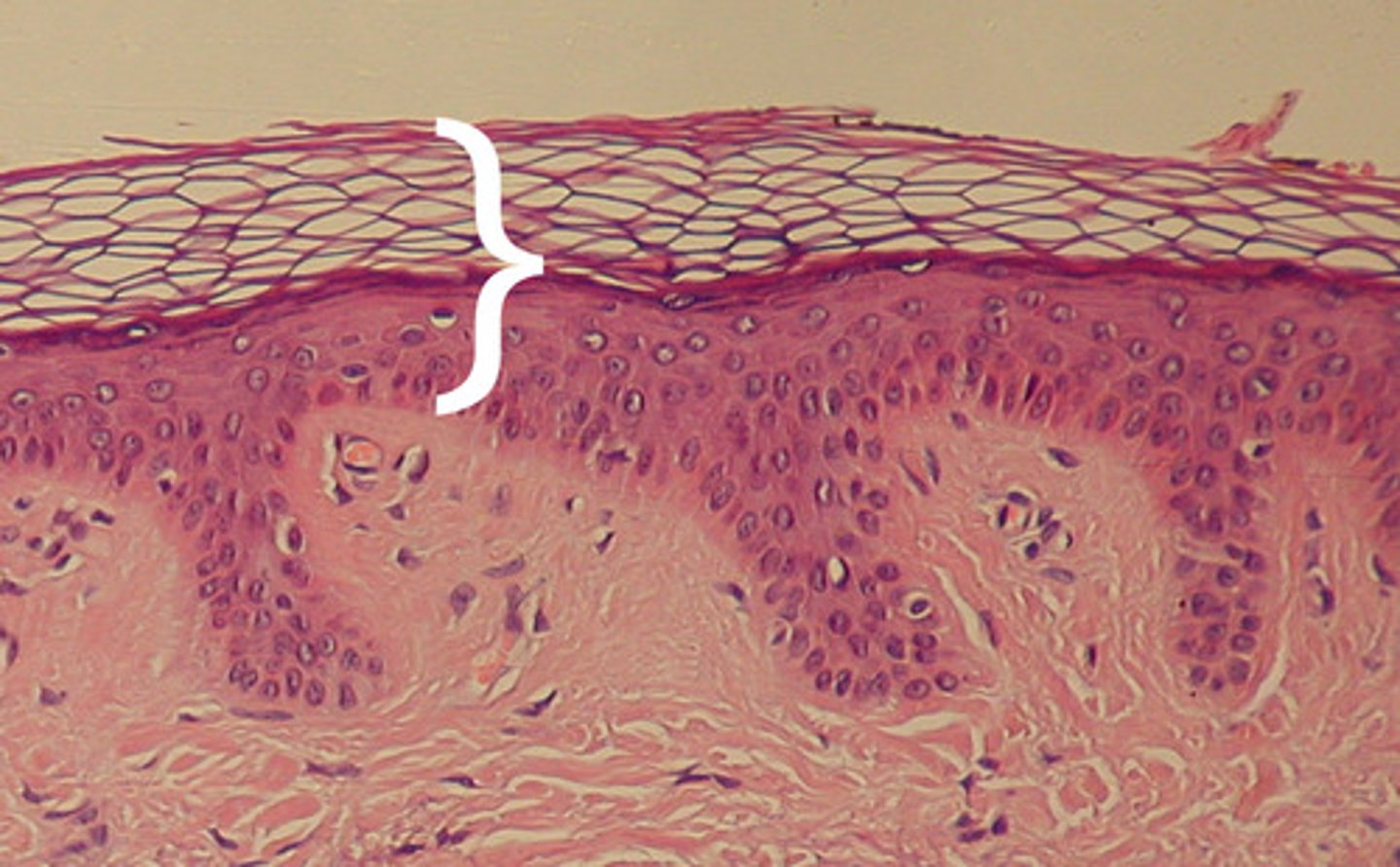
Stratum Corneum
the most superficial layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells (flattened keratinocytes with no nuclei)
function: protection for epidermic, physical insults/water loss
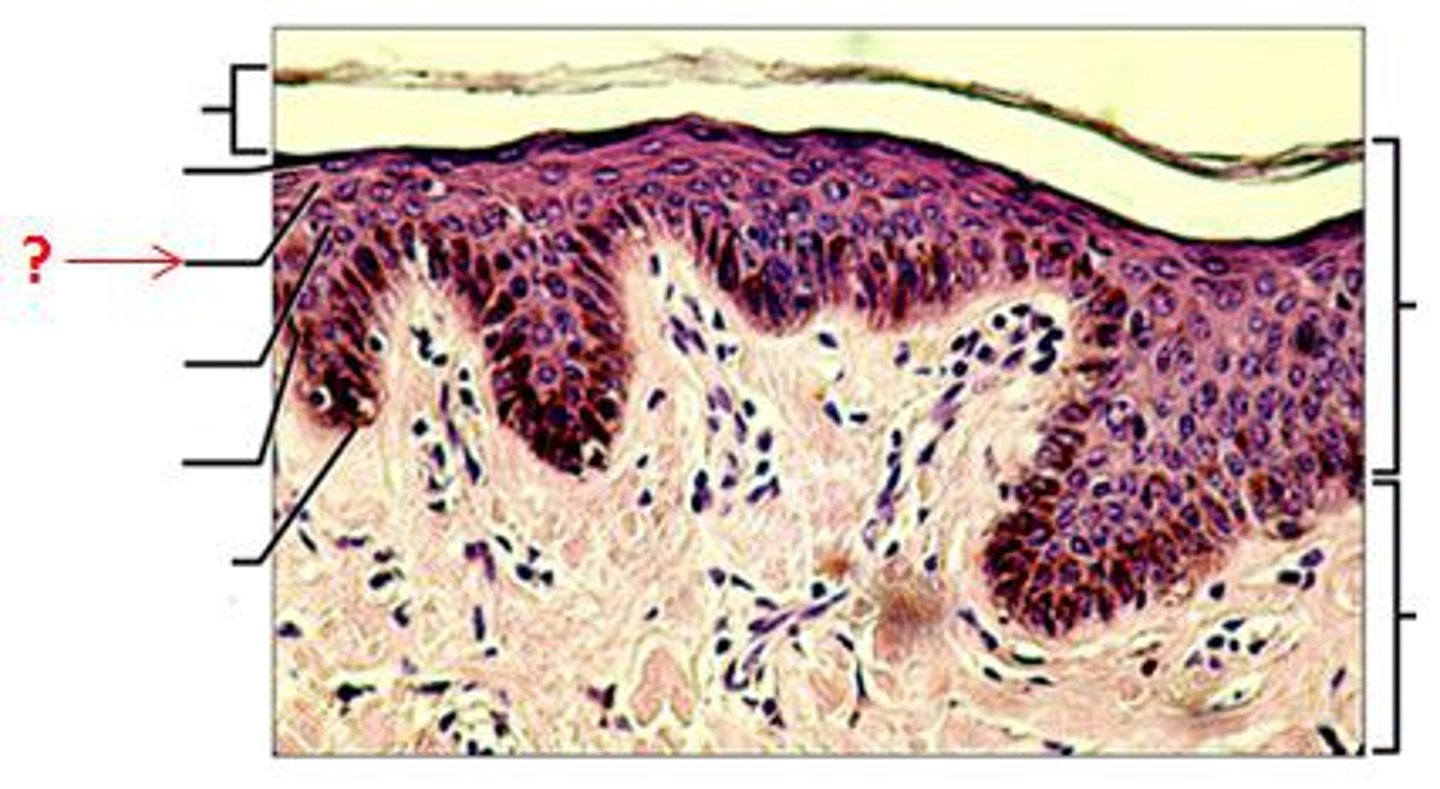
stratum granulosum
granular layer
think layer of keratinocytes
basophilic (blue/purple)
function: keratinization
stratum spinosum
a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
"prickly" appearance from cell-cell junctions of desmosomes
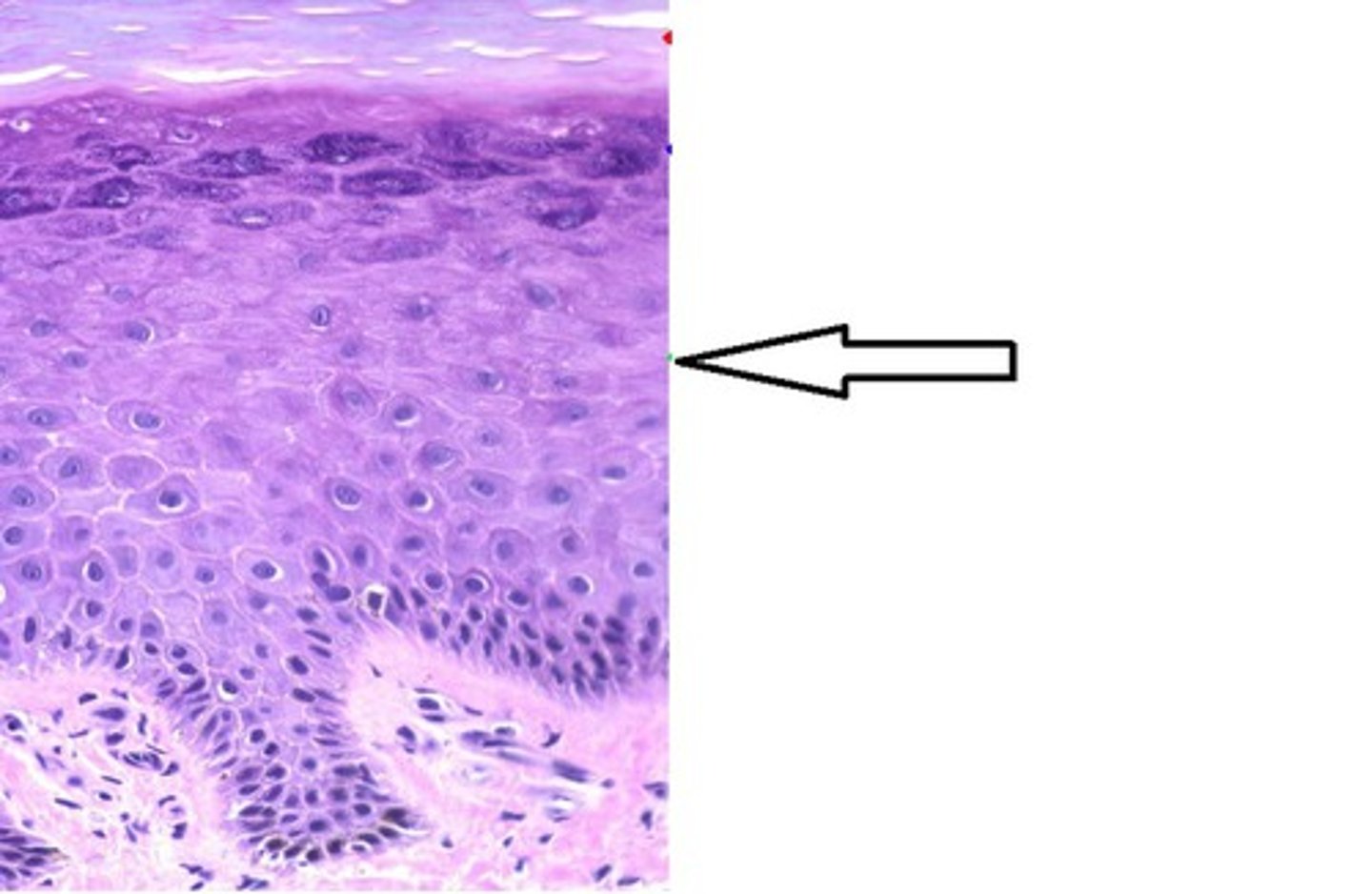
stratum basale
the deepest layer of the epidermis consisting of stem cells capable of undergoing cell division to form new cells (becomes Stratum spinosum)
cuboidal keratinocytes
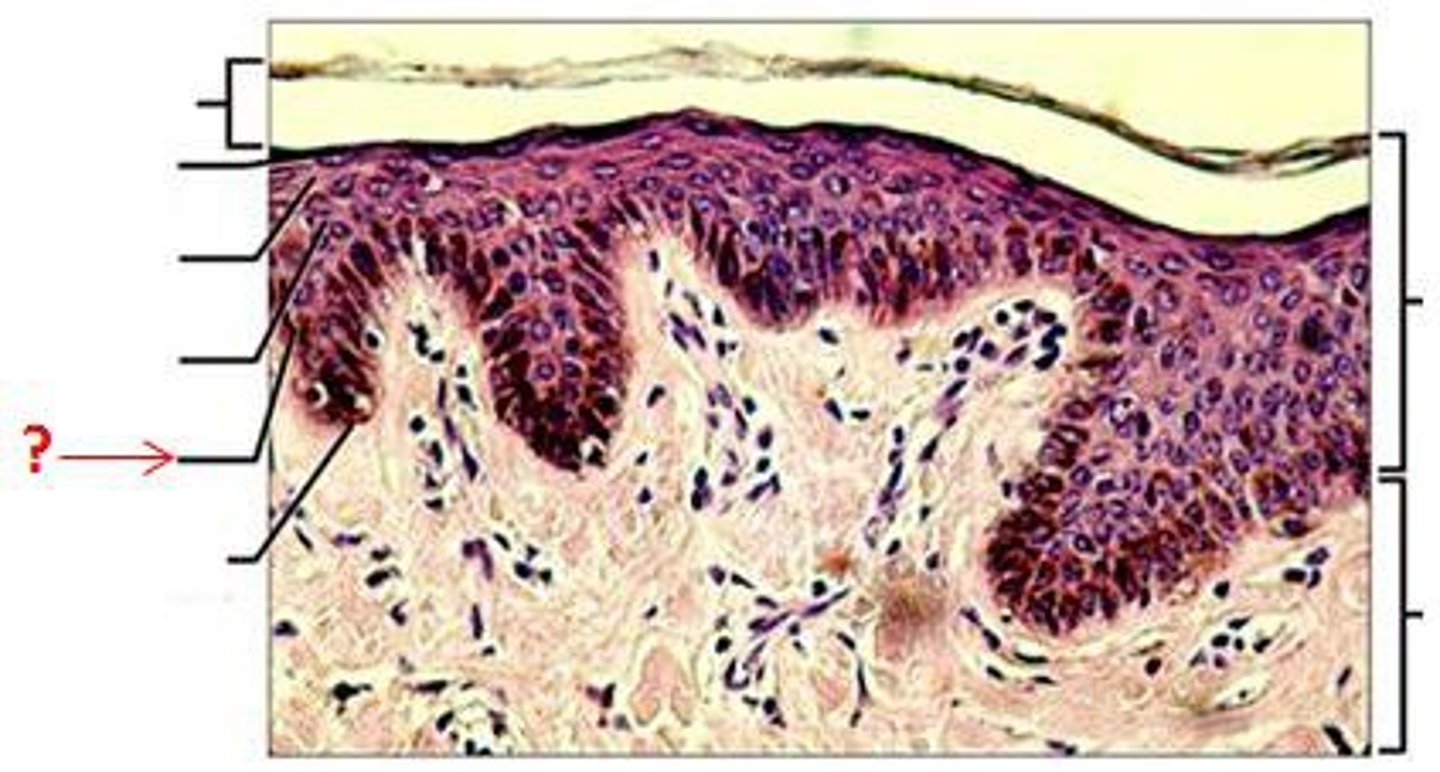
basement membrane
- dense protein layer
- hemidesmosomes connect s. basal to BM
- function: physical barrier, connects epidermis -> dermis
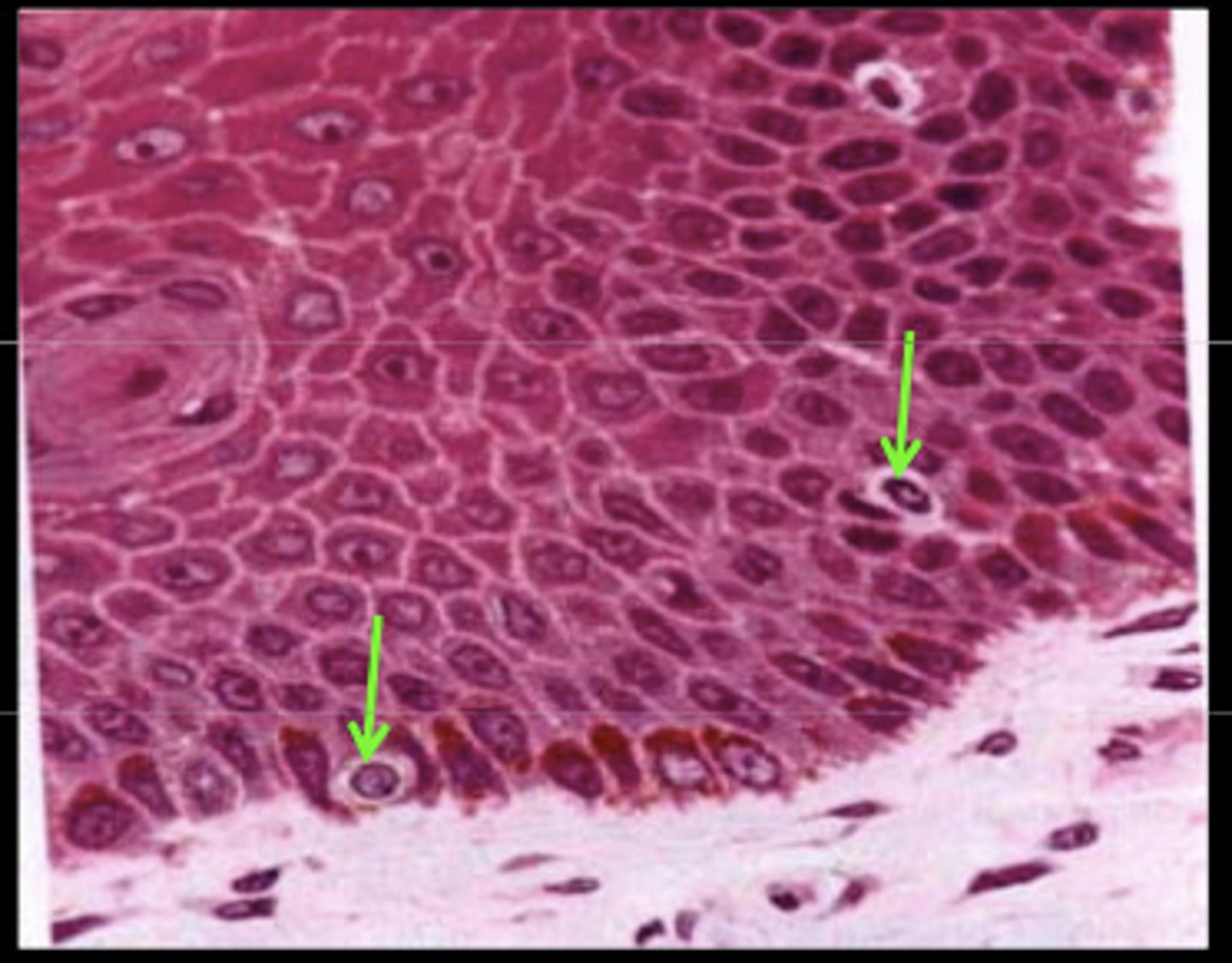
melanocytes
Synthesize melanin
- with melanosomes + tyrosine a.a.
clear cells
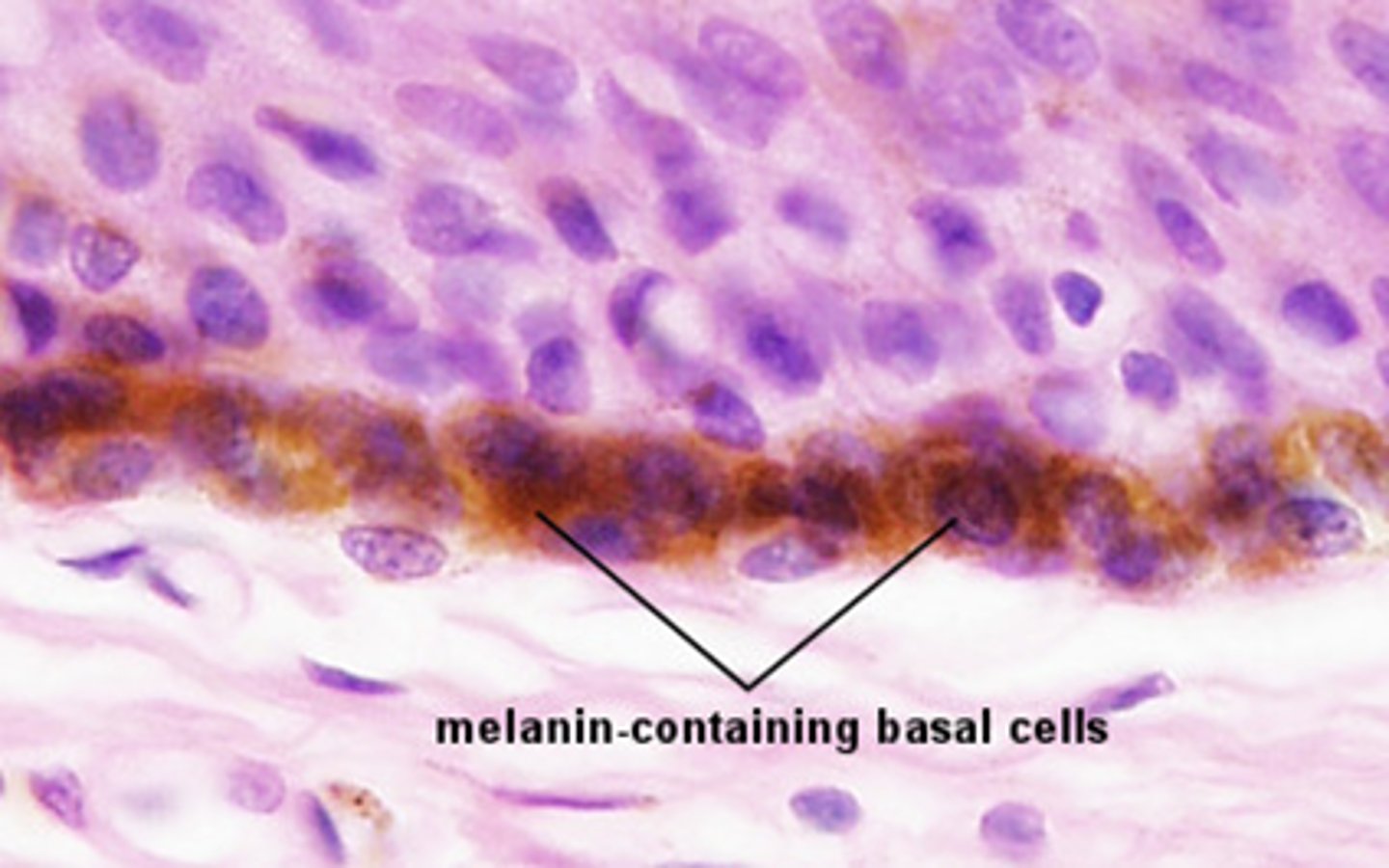
melanin
A pigment that gives the skin its color
decrease in tyrosine =
loss in hair coat pugmentation
- sheep/cattle
- copper enzyme
dermis
Inner layer of skin
small amount of elastin
collagen main protein
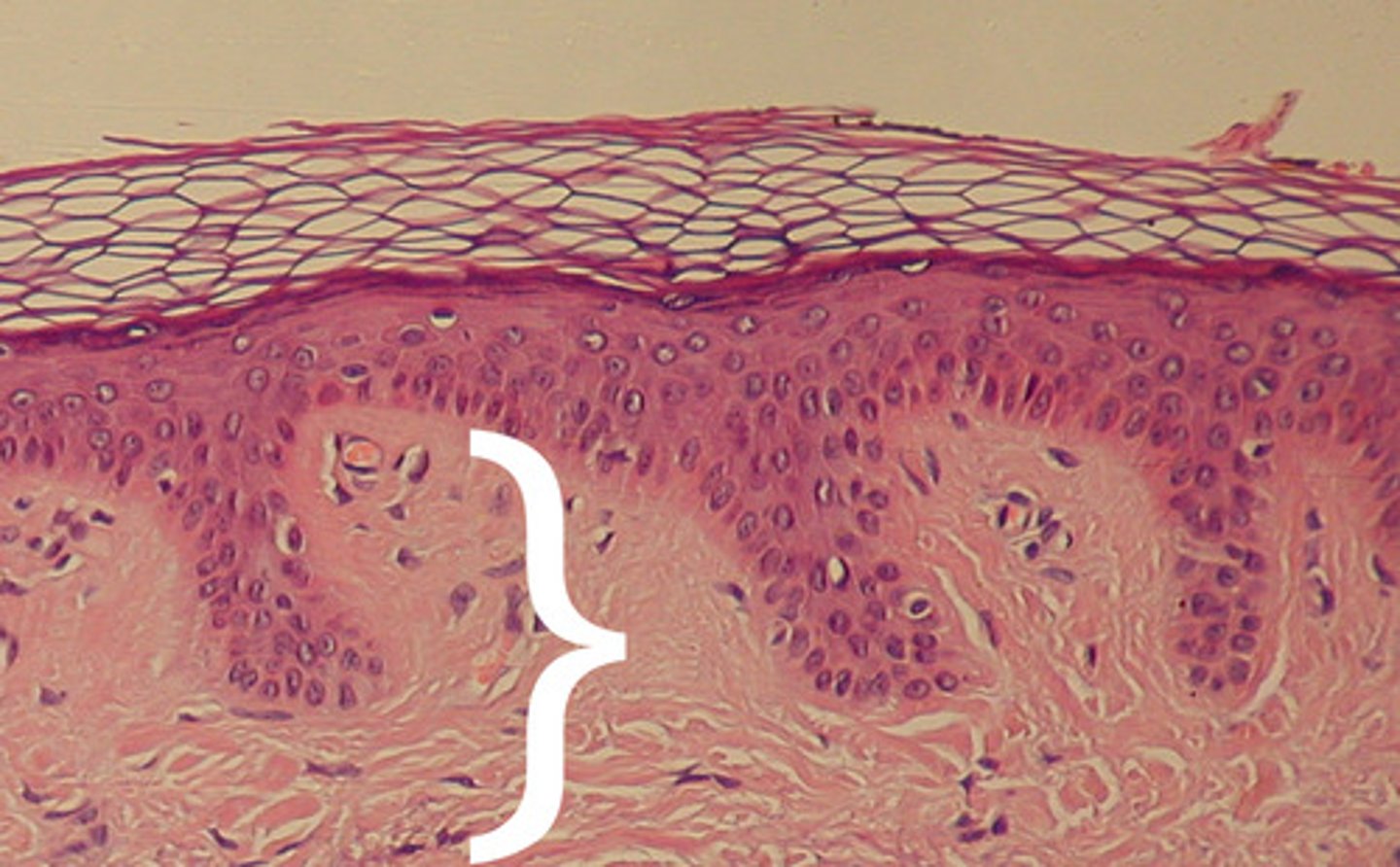
epidermis
dermal Fibroblasts
Collagen to repair a deep skin wound is produced by __________.
dermis functions
- provides blood supply for the epidermis
- anchors epidermis in place
- focus of immune response
- Thermoregulation
dermal adnexa
- hair/feather follicles
- sebaceous gland
- apocrine gland
hair/feather follicle
a small tubular cavity containing the root of a hair
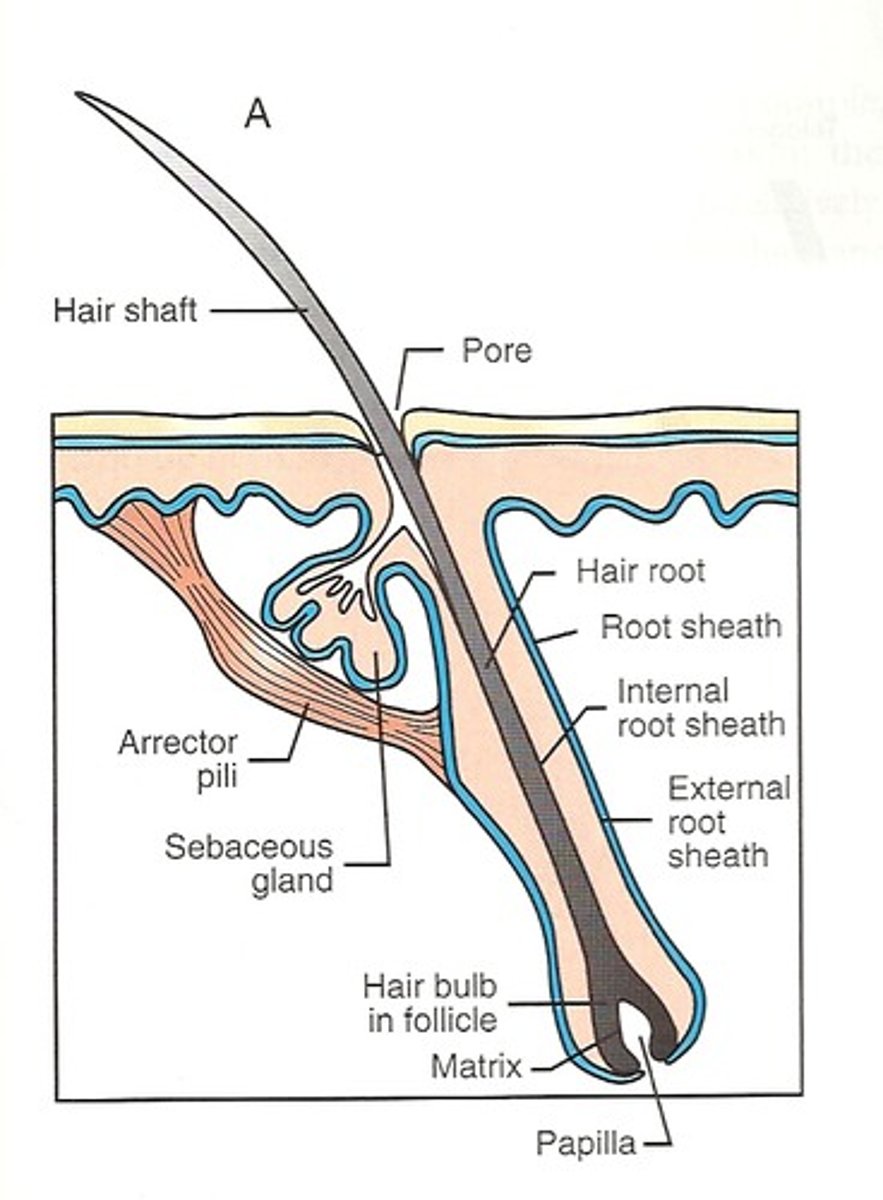
hair/feather functions
protection
sense touch
reduce heat loss
3 parts of the hair follicle
bulb (where growth starts)
root
shaft
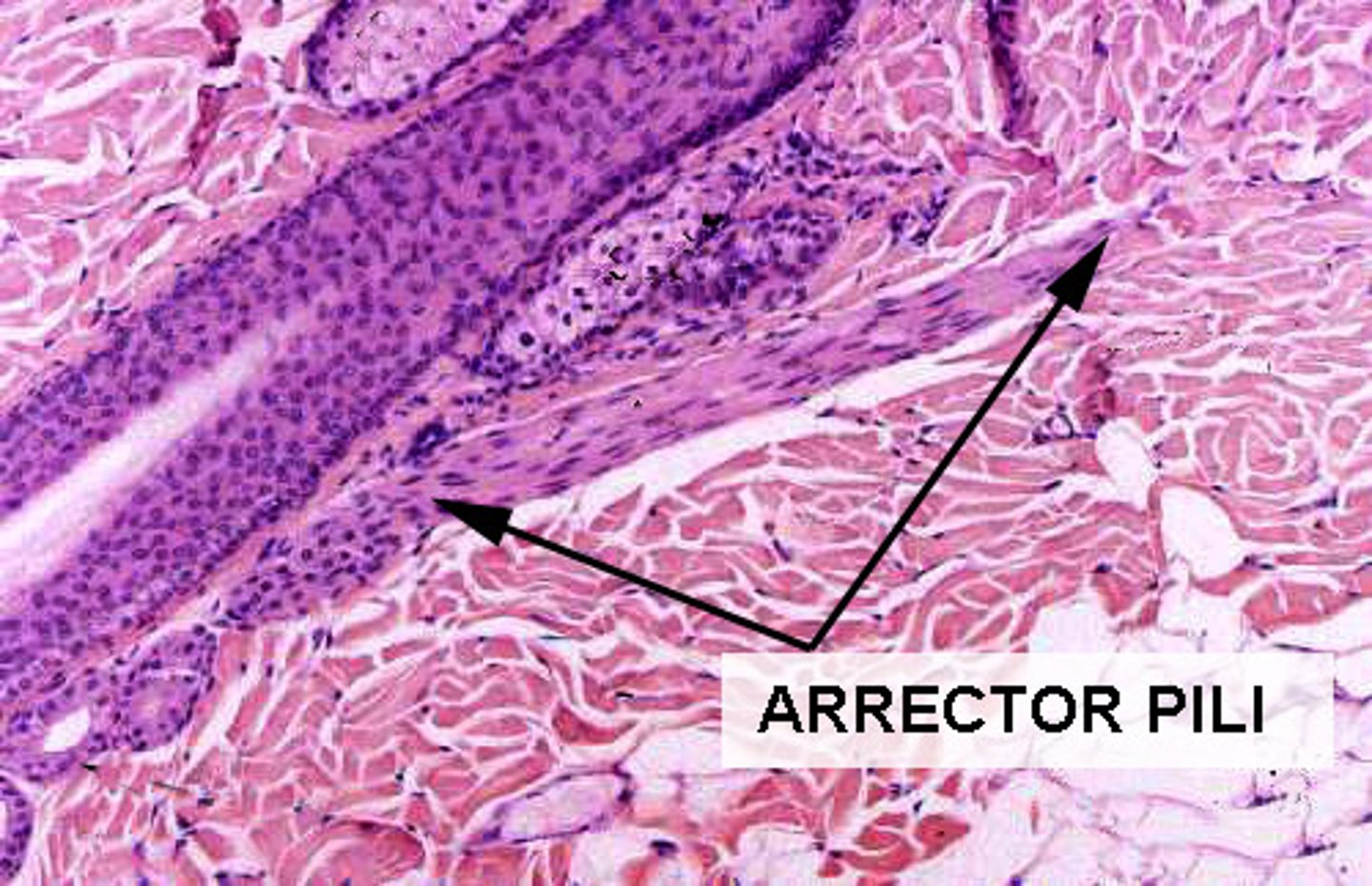
arrector pili
tiny muscle fibers attached to the hair follicles that cause the hair to stand erect
primary hair
guard hair
secondary hair
undercoat
simple hair follicle
- where a single hair emerges from a singular orifice
sebaceous glands
secrete sebum (oil) into the hair follicles where the hair shafts pass through the dermis
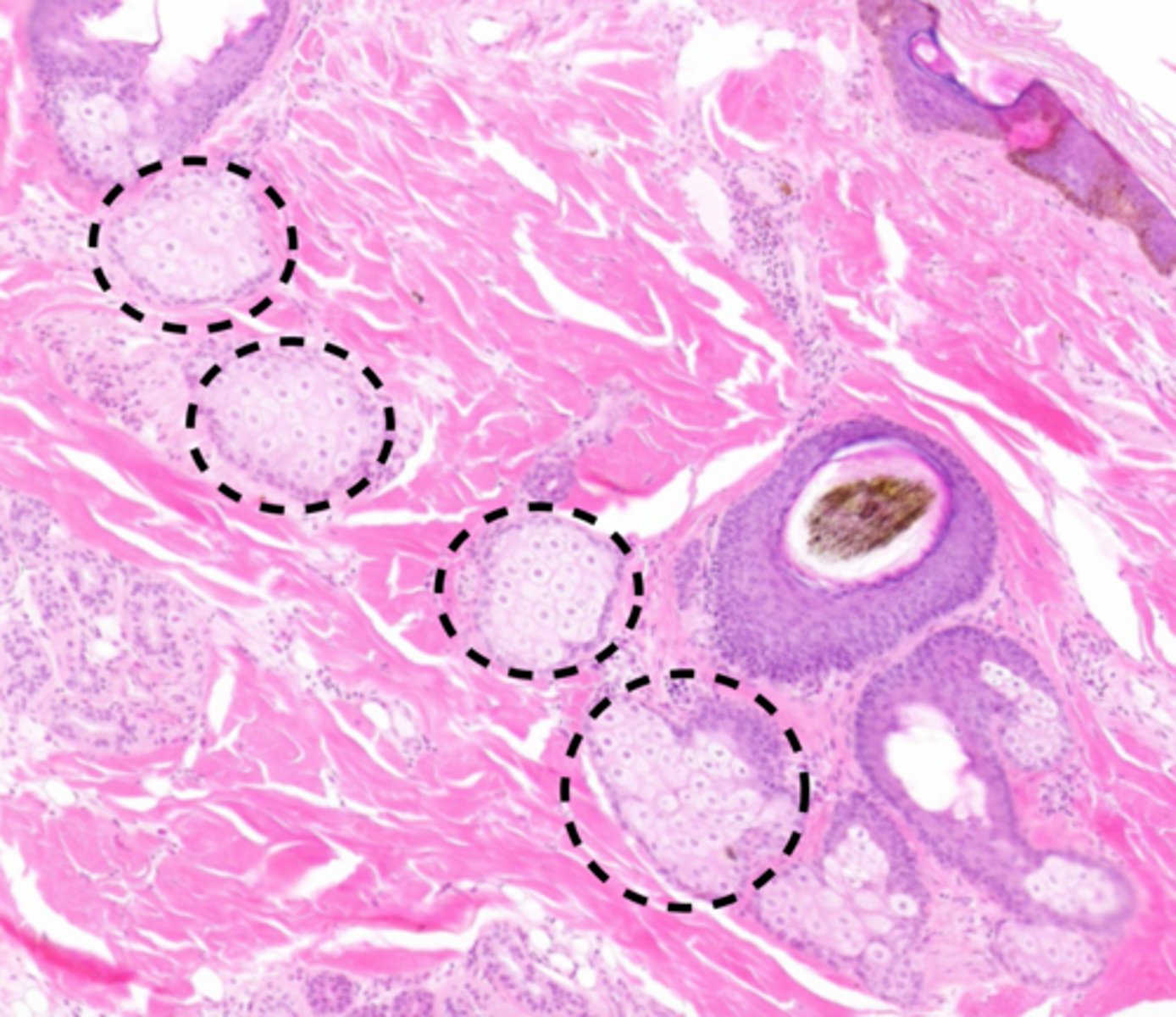
sebocytes
Cells that produce sebum in sebaceous glands.
rupture to release sebum
apocrine glands
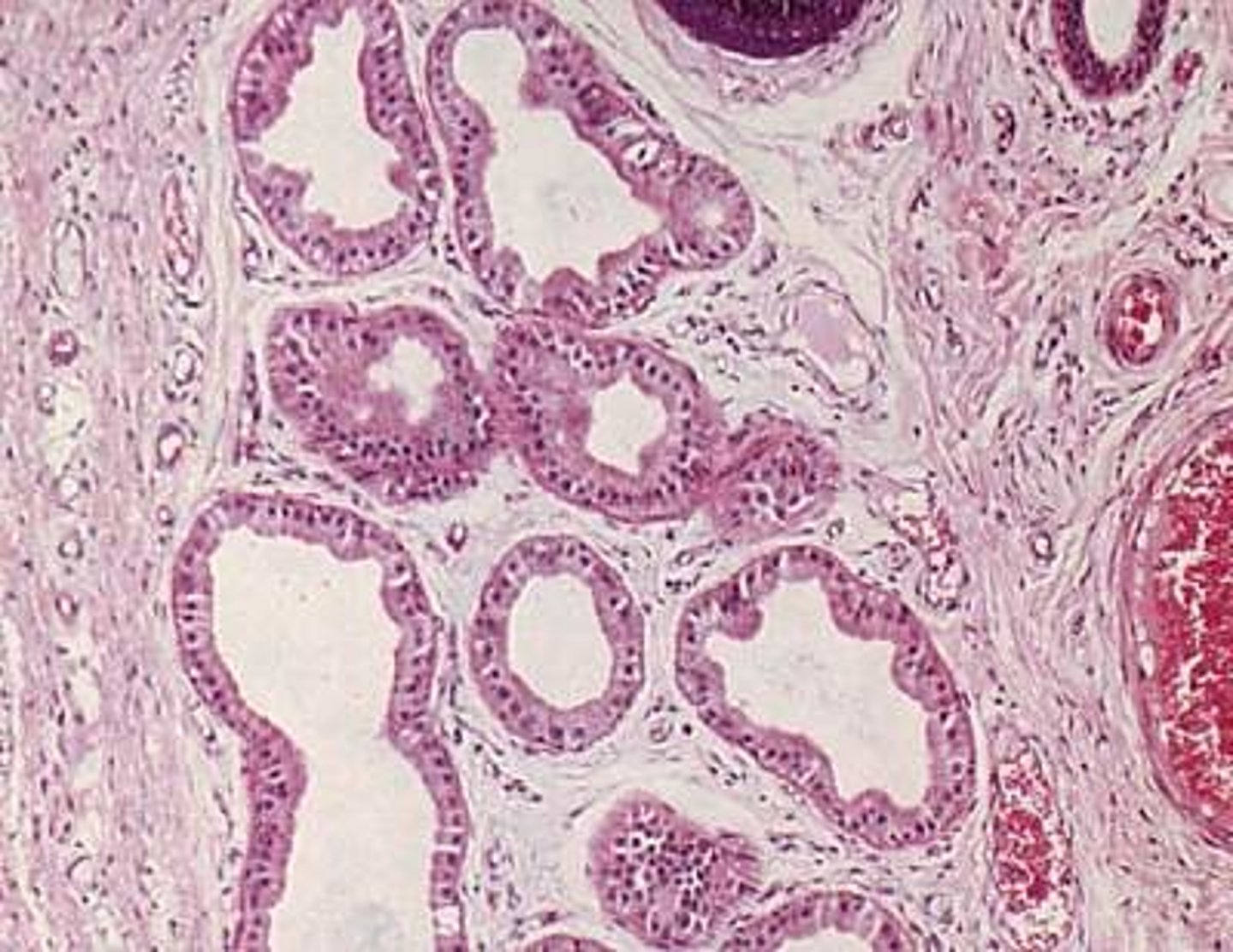
Coiled structures attached to hair follicles found in the underarm and genital areas that secrete sweat.
digital pad
- ventrum of the digit
- toughest/thickest skin of body
- fibroadipose tissue
nail quick
the pink, sensitive part of the nail close to the nail bed that contains nerves and blood supply
vascular
what layer is clipped of the dog nail?
compact stratum corneum
direction of nail growth
epidermis -> nail fold
What anchors the claw to the digit?
dermis fuses with P3's periosteum
Layers of the hoof wall
1) Stratum externum
2) Stratum medium
3) Stratum internum (white line)
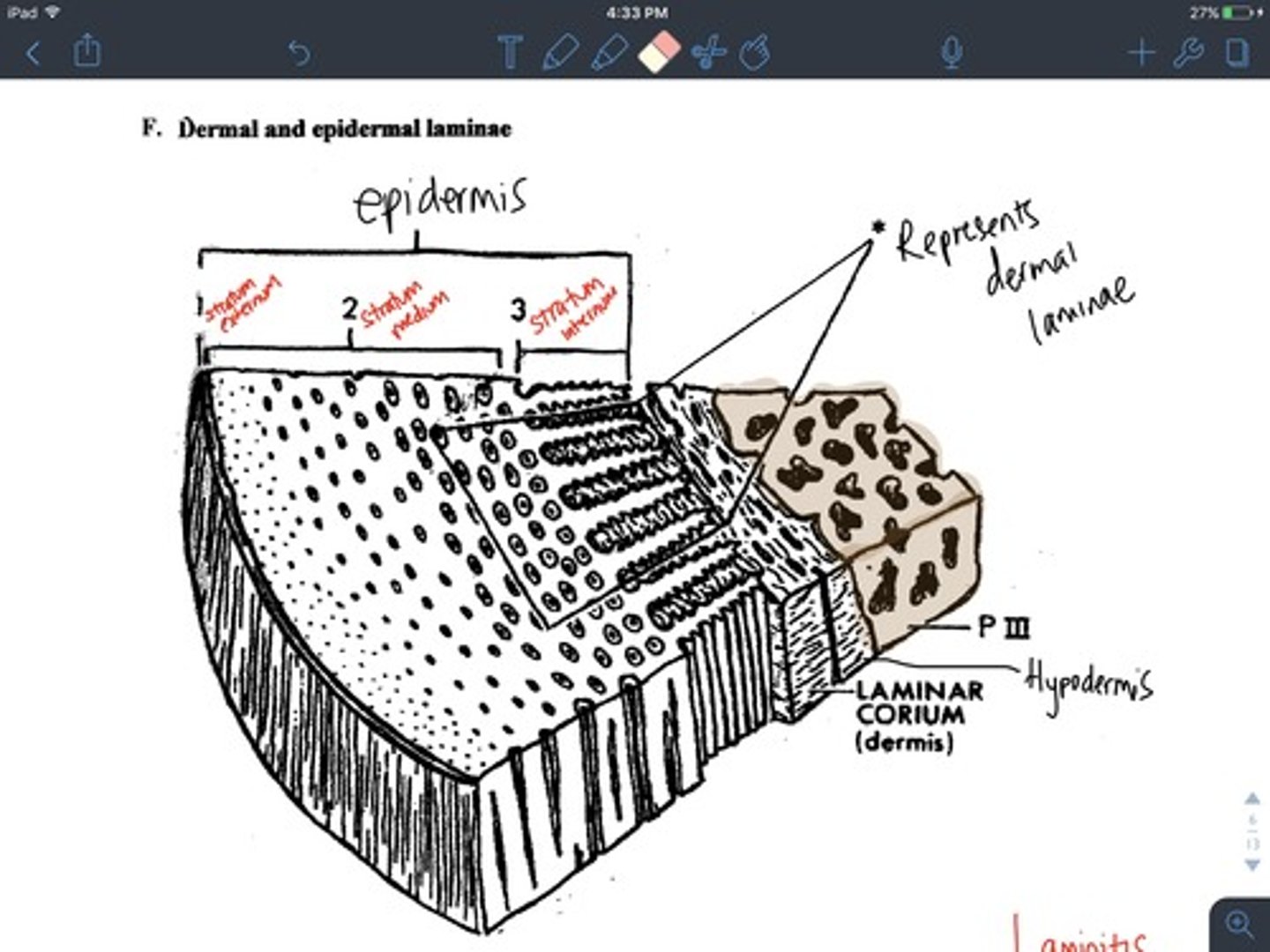
What hoof layer is the thickest and has the most pigment?
stratum medium
laminae in hoof
The finger-like projections of the strong tissue that attach the hoof to the bones underneath.
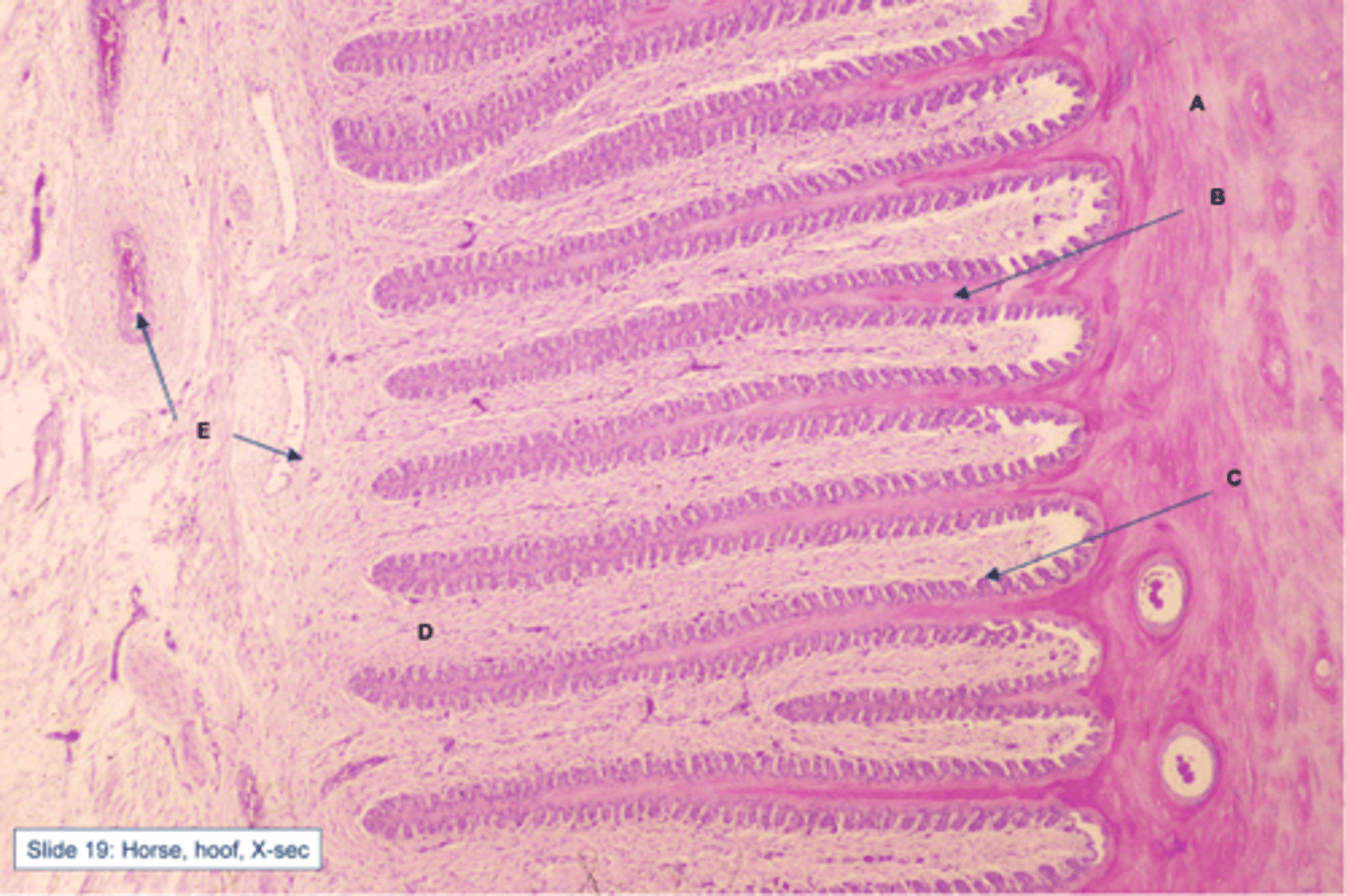
secondary laminae
perpendicular to primary laminae
- increase surface area & resistance to separation