Everything >0<
1/1214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1215 Terms
psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
behavior
any action we can observe and record (ex: smile)
mental processes
sensations, thoughts, perceptions, dreams, beliefs, feelings
midbrain
A portion of the brain located just above the medulla. Controls pons and contains basic vision and hearing functions.
in lower animals, it is the center for visual and auditory functions
a brief history of psych
ancient civilizations pondered early psychology; Greek philosophers viewed the mind separate from the body; people would use phrenology and trephining to help understand mental illness
phrenology
the practice of mapping the brain by the bumps of the head
trephining
drill a hole in the head to get out the bad blood
Psychology is based on Empiricism meaning
knowledge is found based on experiments; Science should be observing and experiments
what was the first psych experiment
William Wundt ( pronounced Villham Vunt) creates the “duration of apperception”; tests the lag of subjects when they hear a ball bounce and press a button
RESULTS show: Everyone hears at a different time and speed
what did Wundt’s experiment prove
mental process is different for everyone
what are the two schools of thought
structuralism and functionalism
structuralism
by Edward B. Titchener
Had subjects self reflect and explains their thoughts and emotions (INTROSPECTION)
BUT not everyone was self-aware/articulate thoughts; People also make errors/untrustworthy
Functionalism
by William James (father of psychology/author of first psych textbook)
Focused on the input of mental and behavior functioned; How function? How it’s applied?
Took ideas of Darwinism; those who are mentally fit do better in life
Mary Whiton Calkins
American Psychological Association (APA) first female president
Margaret Floy Washburn
first female psych PHD
what are the 3 big issues in psychology?
stability vs change - ex: do we maintain our traits or do we change
rationality v. irrationality - think or feel
nature v. nurture - genetics or environment
what are the 8 psych perspectives
neuroscience, evolutionary, behavior genetics, psychodynamic, behavioral, cognitive, social-cultural, humanistic
neuroscience
how brain and body work in sensation, emotions, and memory (biological)
you smile because the serotonin makes you feel happy
Perspective on Behavior: neuroscience
evolutionary
how natural selection of traits promote the survival of the genes (Charles Darwin)
you smile because it will attract a mate and thus you can have children
Perspective on Behavior: evolutionary
behavior genetics
this is the newest perspective and is about nature v. nurture; how genes and environment influence our individual differences
you may smile because your family has a gene that makes you prone to smiling or you are surrounded by a positive environment
Perspective on Behavior: behavior genetics
psychodynamic
aka psychoanalytic; how our behavior comes from the unconscious drives/conflicts
you smile because of how unaware you are.
Perspective on Behavior: psychoanalytic
behavioral perspective
how we learn observable responses - learning
you smile because you were taught/told to smile
Perspective on Behavior: behavioral
cognitive/memory
how we encode, process, store and retrieve information - these are about your thoughts
you smile because you thought of your crush
Perspective on Behavior: cognitive
social-cultural
behavior will change across different situations and cultures; involves other people
you smile because I am a women and so culturally and socially I am brought up to be someone that smiles
Perspective on Behavior: social-cultural
humanistic
personal growth fulfillment and education; a perspective that is not official but is often used in therapy; OVERALL TRYING TO BE A GOOD PERSON
smile because you feel good about yourself or life
Perspective on Behavior: humanistic
basic research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base (what is it? - structuralism)
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems (how/why? - functionalism)
sources of intuition overestimation
hindsight bias
overconfidence
tendency to perceive patterns in random events
Hindsight Bias
Tendency to believe after learning an outcome
“I knew it all along” phenomenon
Overconfidence
tend to think we know more than we do
confirmation bias
tendency to confirm our own preconceptions
Monty Hall Problem
When we go by our gut instead of logic
Game show door (you should switch, but it feels better to stay)
Theory
explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts the behaviors or events
Hypothesis
Testable prediction often implied by theory
“if…, then…”
operational definition
carefully worded statements of the exact procedure (operations) used in a research study
Replication
Repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations
Research strategies
description, correlation, causation (experiments)
descriptive research
systematic, objective observations of people
goal: provide clear, accurate picture of people’s behaviors, thoughts, and attributes
case study
examines one person or group in depth
BUT doesn’t provide generalized conclusions
ONLY fruitful ideas on the topic at hand
Naturalistic observation
observing a person’s behavior in a natural setting. Only describes the behavior; do not explain
hawthorne effect
behave differently when you know you are being observed (ruins observation)
survey and interview
examines multiple cases in less depth but allows for more generalizations
wording effect
phrasing of questions could bias answers
random sampling
Taking a random group from a population that represents that population.
correlation is NOT … ?
causation (NOT)
correlation defined
research determining if a relationship between two or more factors exists
positive correlation
(0 to +1.00) Indicates a direct relationship where two things increase or decrease together
Negative correlation
(0 to -1.00) Indicates inverse relationship; as one increases, the other decreases
Correlation coefficient
[r] Provides statistical measure of how closely two things vary together and how one predicts the other
example of correlation coefficient
r = -.37
negative weak correlation
variable
anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure
directionality problem
situation where one knows two factors are related but does not know what is the cause and which is the effect
3rd variable possibility
when two correlated variables can actually be explained by a third unaccounted variable
illusory correlation
perception that a relationship between two variables exists when there is little to no relationship
regression toward the mean
tendency for an extreme or unusual score or event but will later fall back to towards the average
experimentation
when researchers focus on possible causes and effects between factors in several ways. Can manipulate the factors of interest to determine the effect
experimental group
participants who are exposed to independent variable
control group
participants who are NOT exposed to independent variable
double-blind procedure
Procedure to eliminate bias in a study. Neither the participants or those collecting data know which group will receive treatment; only the head researcher will know.
placebo
sugar pill
Placebo effect
When people have an expectation that something will bring a certain effect or response
Example of placebo effect
giving someone advil, a well known medicine that helps relieve pain. Patient will immediately exclaim how they feel much better but advil doesn’t work until 20 minutes after consumption. They had the expectation that the drug would make them feel better.
independent variable
factor that is manipulated and being studied
dependant variable
The item is being measured. This changes when the independent variable is manipulated.
confounding variable
factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect
example of confounding variable
When studying the ability to improve grades with study guides, a confounding variable may be the intelligence of a person and that they do not need study guides to have good grades
random assignment
in order to lessen the effects of a confounding variable in the participants (example: age, gender, beliefs, etc.), researchers can take the participants and mix them up and put each participant into a control or experimental group.
Ethics code of the American Psychological Association (APA) and British Psychological Society (BPS)
obtain potential participants informed consent
Protect participants from harm/discomfort
Keep participant’s information confidential
Fully debrief people (explain)
informed consent
giving a potential participant enough information about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
debriefing
Post experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and descriptions and deception to participants
mode
most frequently occuring scores in a distribution
mean
arithmetic average of a distribution obtained by adding scores and then dividing by number of scores
median
middle scores in a distribution
range
difference between the highest and lowest scores
positive skewed distribution
when the outlier of data is on the right
negative skewed distribution
when the outlier of data is on the left
standard deviation
computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean
example of standard deviation
If the IQ of a group’s standard deviation is 10 units, then most of the group will have an IQ about 10 units from the mean
small Standard Deviation
scores a concentrated and less scattered
variants
average of the squared difference from the mean
rad(variants) = Standard deviation
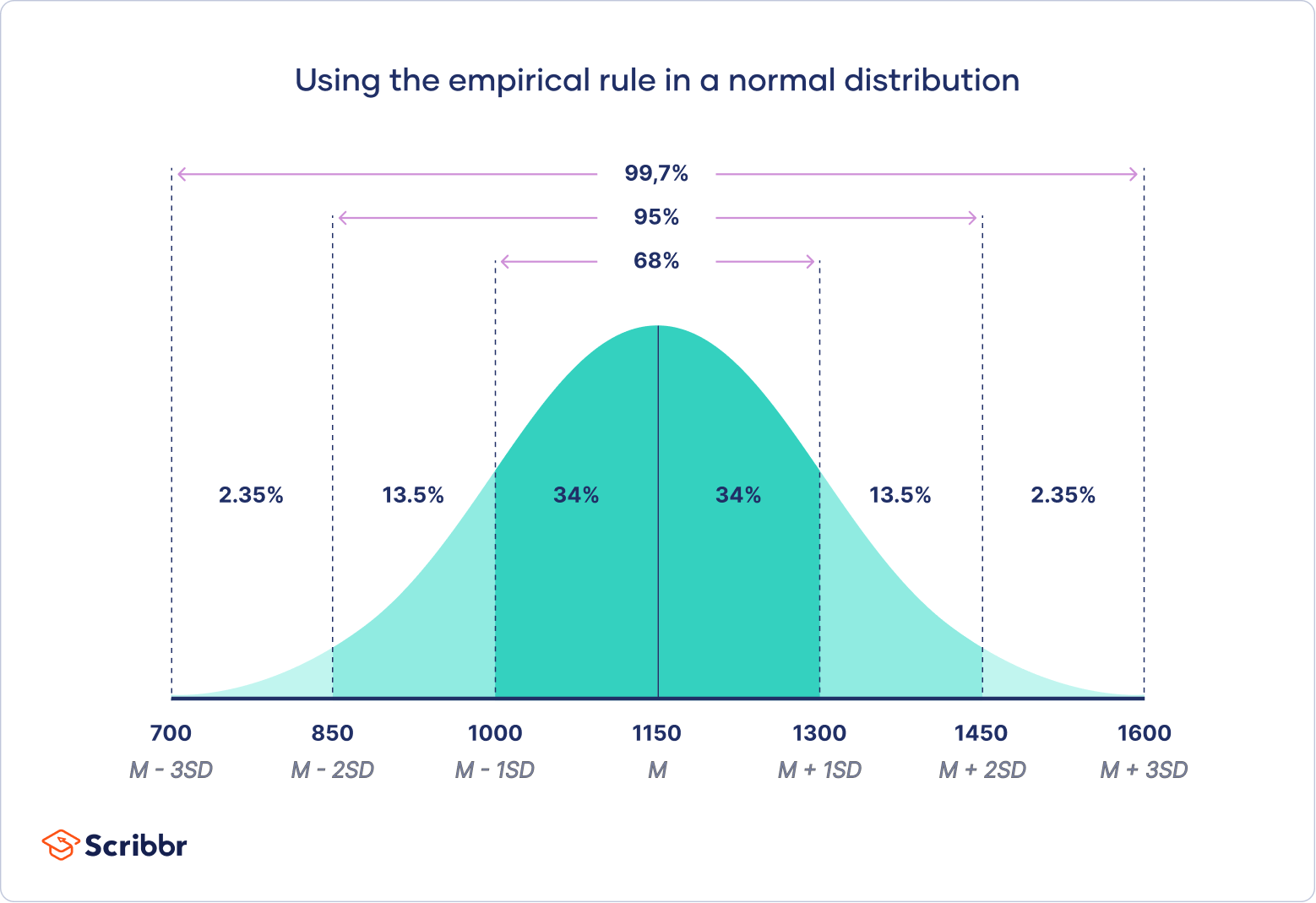
normal curve distribution
symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that described the distribution of data; most scores are near the mean with very few extremes
(68% fall within one standard deviation)
Normal distribution curve example: exam scores
mean = 80
standard deviation = 90-80 = 10
z scores
the number of standard deviations a value is from the mean of a given distribution.
normal distribution percentages
68%, 95%, 99.7%
When is an observed difference reliable?
people are proper representatives
small standard deviation (concentrated)
More cases can allow for generalization
Generalizations based on a few unrepresentative cases are ___________
unreliable
When is an observed difference significant?
when the sample averages are reliable and difference between them is relatively large
(experimental and control results contrast a lot)
statistical significance
likelihood that results happen by chance;
statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained results occurred by chance
research beyond a reasonable doubt means that the odds of an outcome’s occurrence by chance are less than ________
5% or .05
Example of statistical significance
When testing a new speech therapy to an established technique (control), the p-value was 0.032. This statistical statement shows how likely results occurred by chance.
practical significance
statistical significance does not equal
what is practical significance
the likelihood of something to occur in real life.