Cell Organelles
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
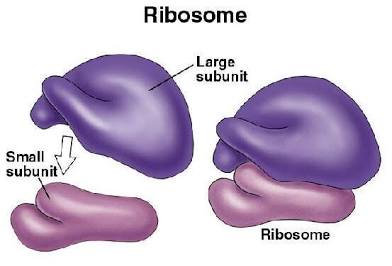
Ribosomes
(membrane or not, function (main), pro or eukar, what it looks like, translation)
non membrane
Function: protein synthesis
Found: prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Made: proteins and rRNA
Both types of cells have a large and small
In translation: ribosomes assemble amino acids into polypeptide chains following the mRNA sequence
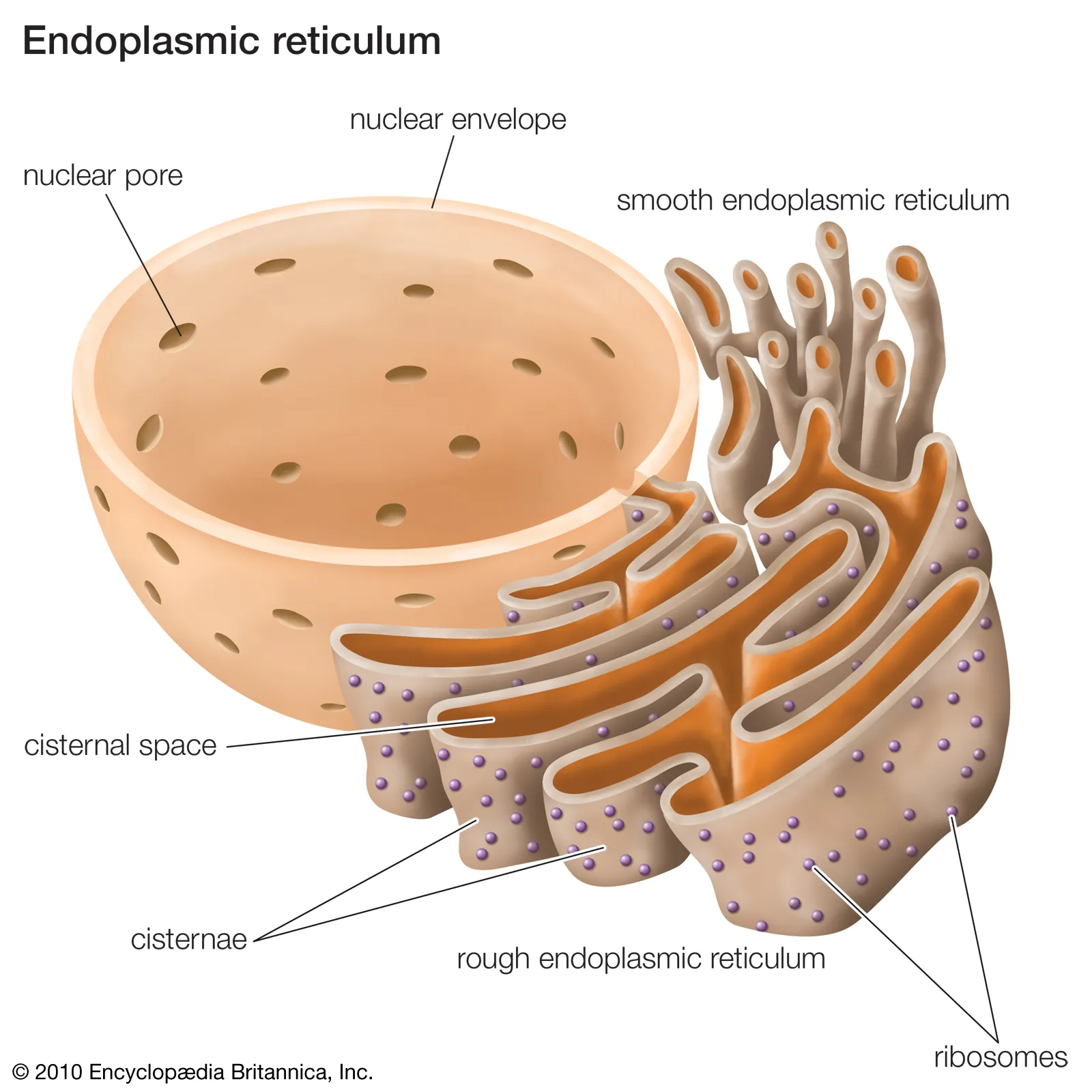
Endoplasmic Reticulum
membrane channeles
Found: eukaryotic cells
TWO PARTS, rouch endoplasmic and smooth endoplasmic
Rough: has ribosomes bound to the membrane
Smooth: no ribosomes attached
Function: synthesis of lipids and detoxifying substances.
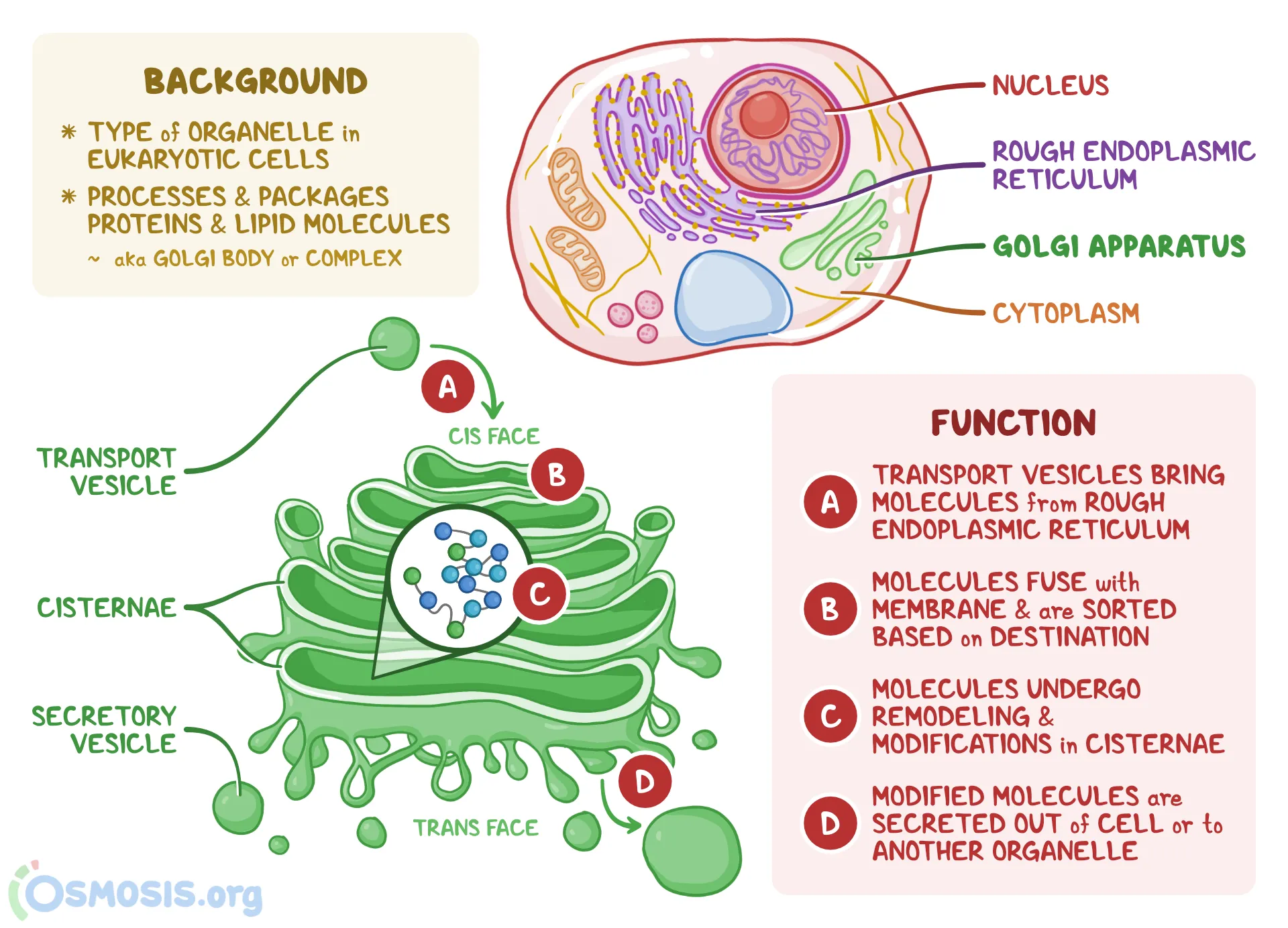
Golgi Complex/Body
Stack of flattened membrane sacs called cisternae
Interior: “lumen”
Conteols modification and packaging of proteins for transport
In eukaroytic cells
Proteins made on the free ribosomes or rough endoplasmic reticulum are sent to the golgi which odifies the proteins into their final formation + packages the finished proteins into VESICLES for transport throughout the cell
Found near the rough endoplasmic reticulum
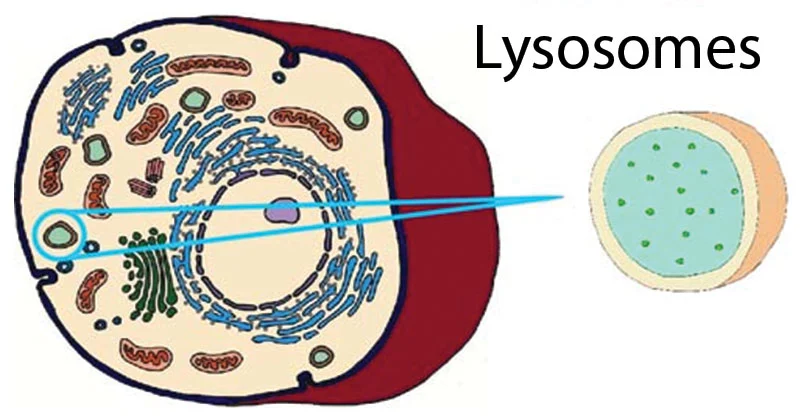
Lysosomes
Eukaryotic cells mostly in animal cells
membrane bound sacs containing hydroloytic enzymes that are used in MANY cell processes
Helps digest macromolecules, breakdown worn out cell parts, function in apoptosis, and destorys bacteria and viruses that have entered the cell
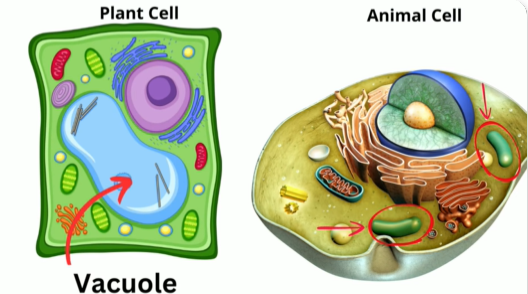
Vacuoles
membrane bound sac found in EUKARYOTIC CELLS
function: food or water storage, water regulation, waste storage
In hydrated plant cells vacuoles occupy most colume by filling up cell space
Provide plant cell with tugor pressure and support
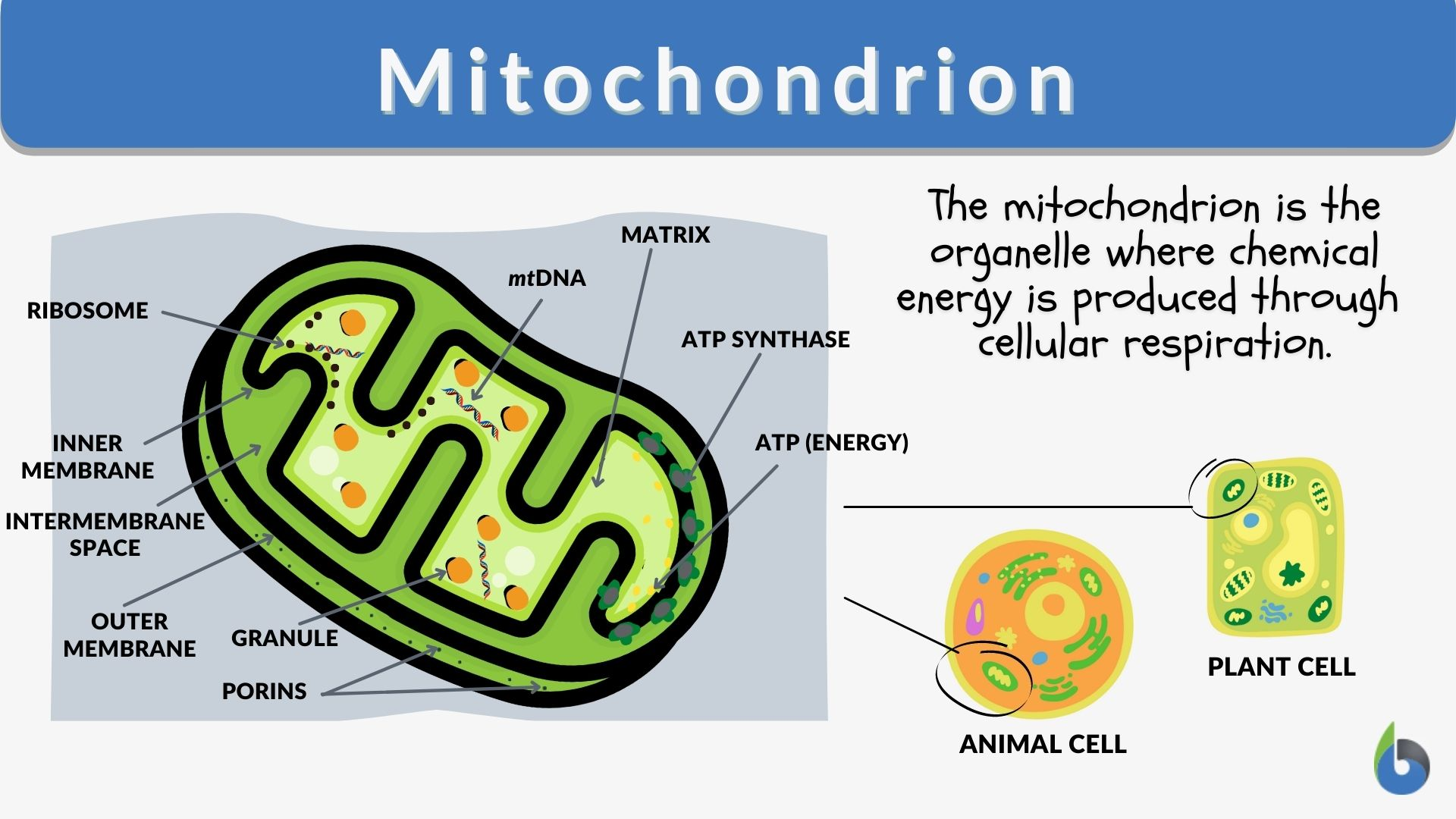
Mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell
produce energy for the cell
double membrane
smooth outer and folded inner membrane to increase surface area
Center = enzyme containing fluid called the matrix
Krebs/citric occur here
Contains mDNA and ribosomes
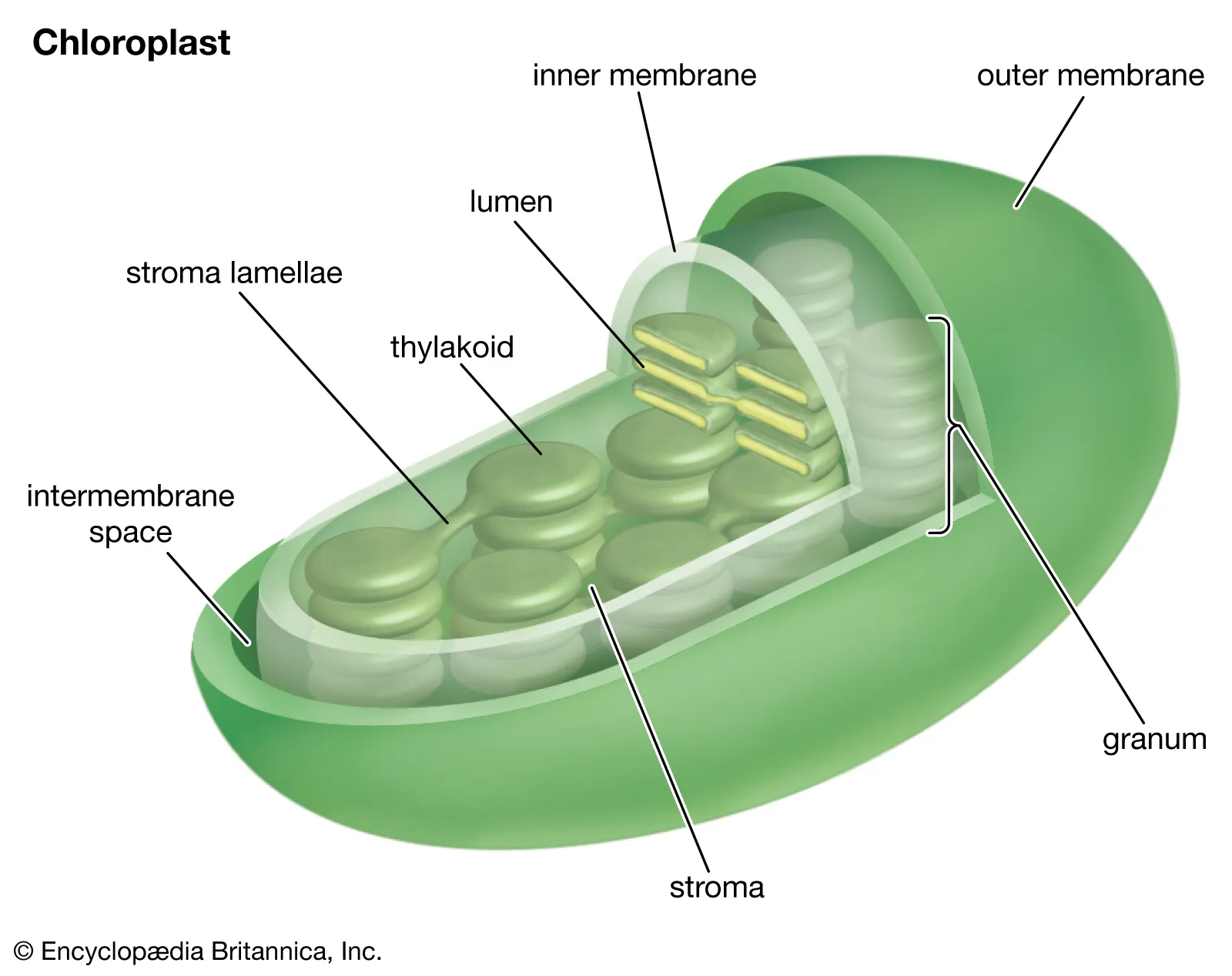
Chloroplasts
in plants and algae
used in photosynthesis (light dependent)
double membrane —> smooth outer and membranous saccs called “thylakoids” —> stacked grana
liquid = stroma (enzymes in the stroma used in photosynthesis)
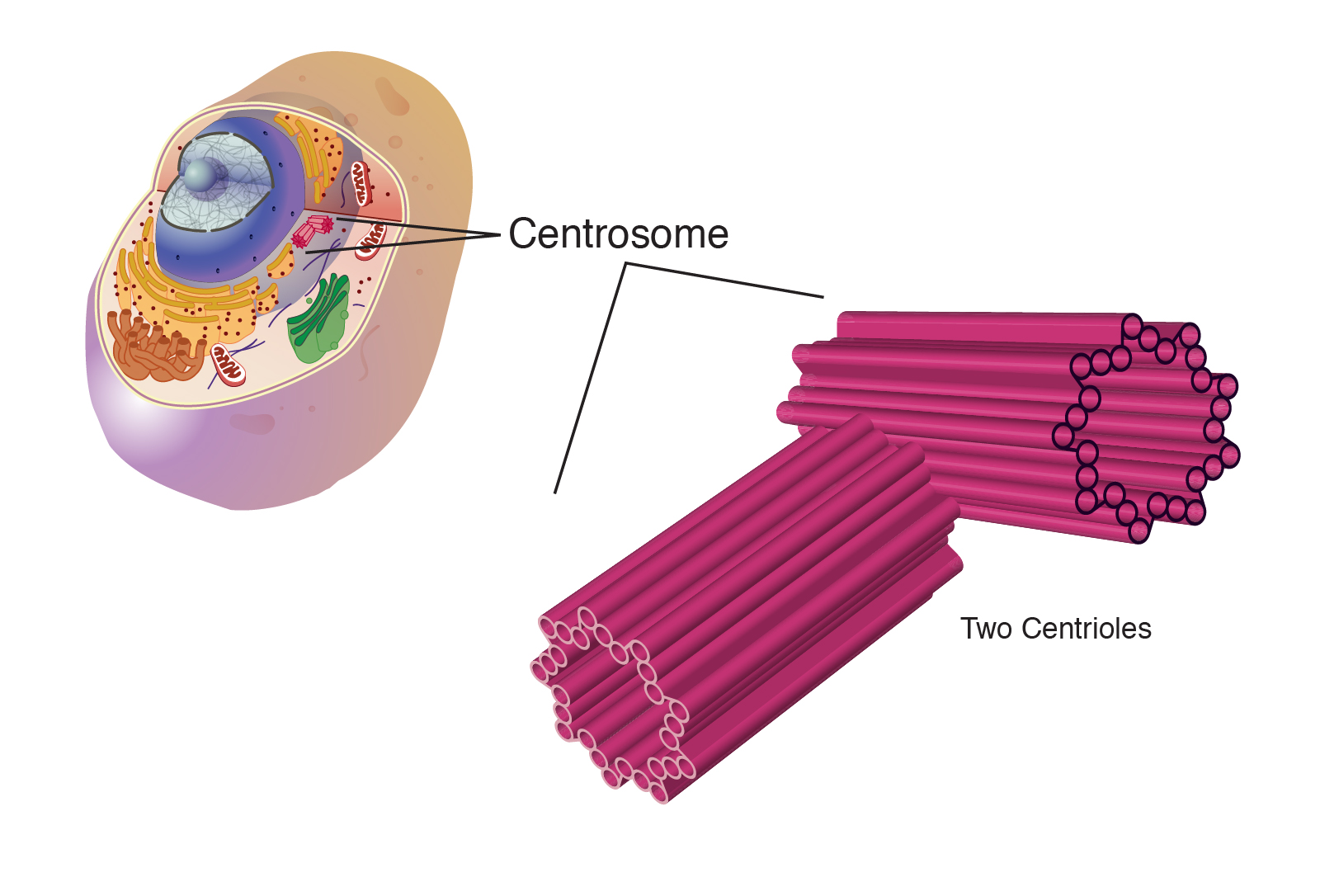
Centrosome
animal cells
helps microtubules assemble into spindle fibers needed for cell divison
defects associated w/ disregulation of cell cycle (leading to cancer)
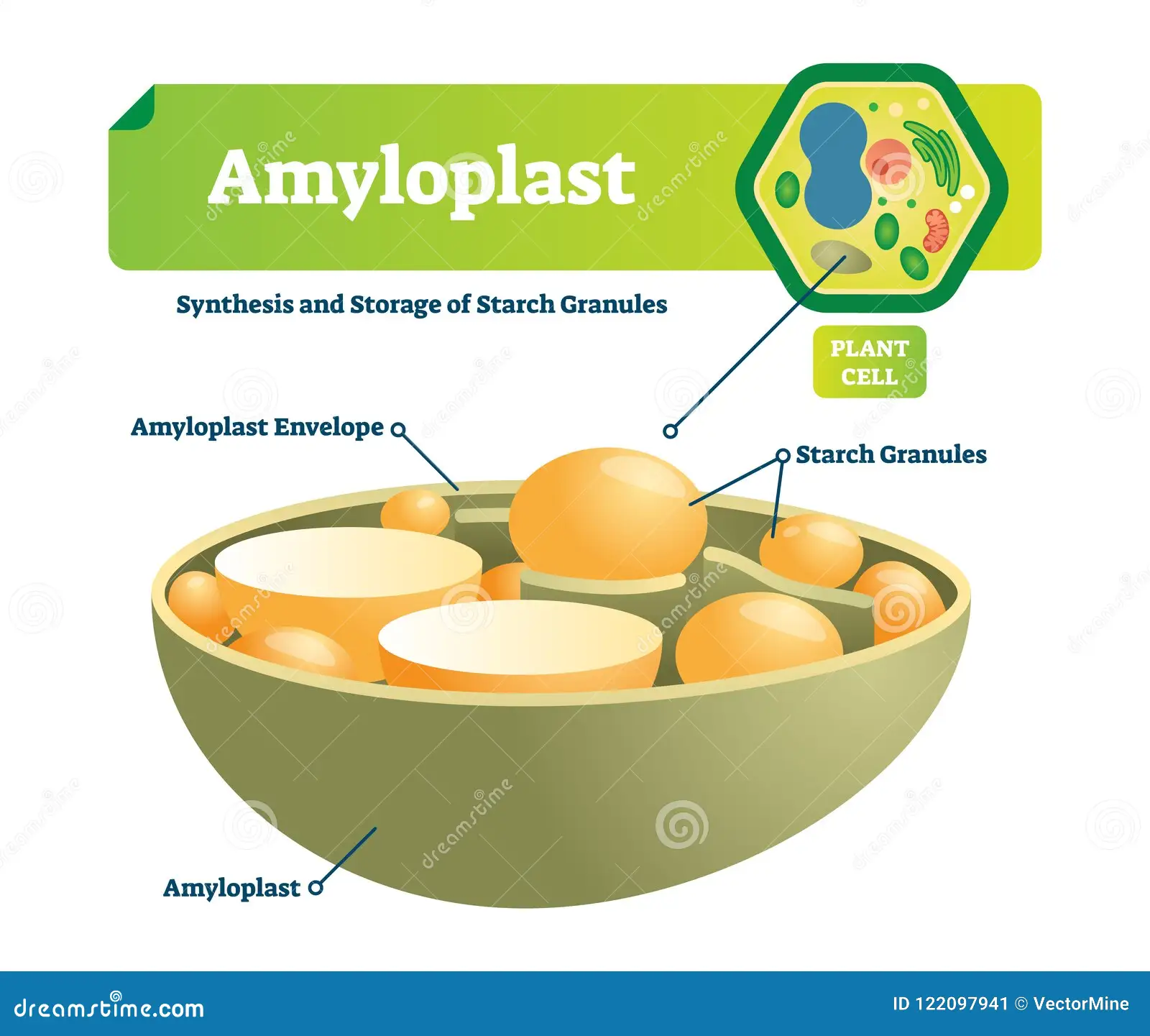
Amyloplast
plant cells
excess glucose is stored as starch molecules
found in the root and rubers of starchy vegatbles
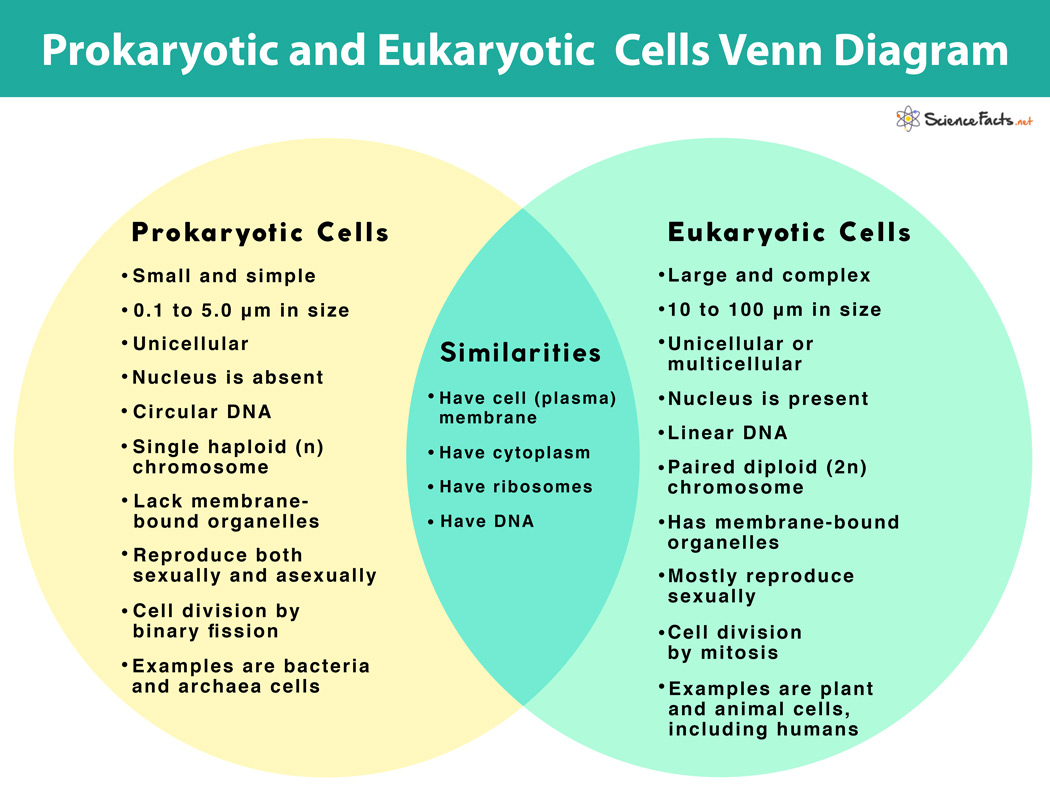
Prokaryotic versus eukaryotic
Prokaryotic = simple
Eukaryotic = more complex
Animal and plant cells are both eukarotic