Models of Macroeconomic Activity and Growth (UNDONE ADD INB NOTES)
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Assessment 5 - covering ch 6,7,8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Macroeconomics
. the study of aggregate economic behaviour or activity in the economy as a whole
Expenditure (E)
. spending on goods and services by households, businesses and the gov
—> households = consumption spending
—> business = investment spending
—> gov = gov spending
—> overseas = net overseas spending (X-M)
Output (O)
. total production of goods and services produced in an economy during a specific period
. measured in dollar terms = GDP
Income (Y)
. total earnings of individuals, businesses, and the gov over a period of time
—> largely generated as result of the production + sale of products
—> comes in form of welfare payments (without g+s being received in return)
Aggregate demand (AD)
. the total amount of domestically produced final products demanded in an economy at a given overall price level and in a given time period
. AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
Aggregate supply
. the total supply of goods and services produced within an economy at a given overall price level in a given time period
GDP
. the total market value of final goods and services produced within an economy over a given time period
CFY model description
. macroeconomic model that describes the flows of resources, goods and services, and income and expenditure
. an economic model that illustrates how money moves from producers to consumers and back again in an endless loop
GDP and total/national income relationship in CFY model
. GDP is equal to total income claims generated by the production of goods and services
. the circular flow of income and products implies that GDP is equal to national income
Draw the simple CFY model
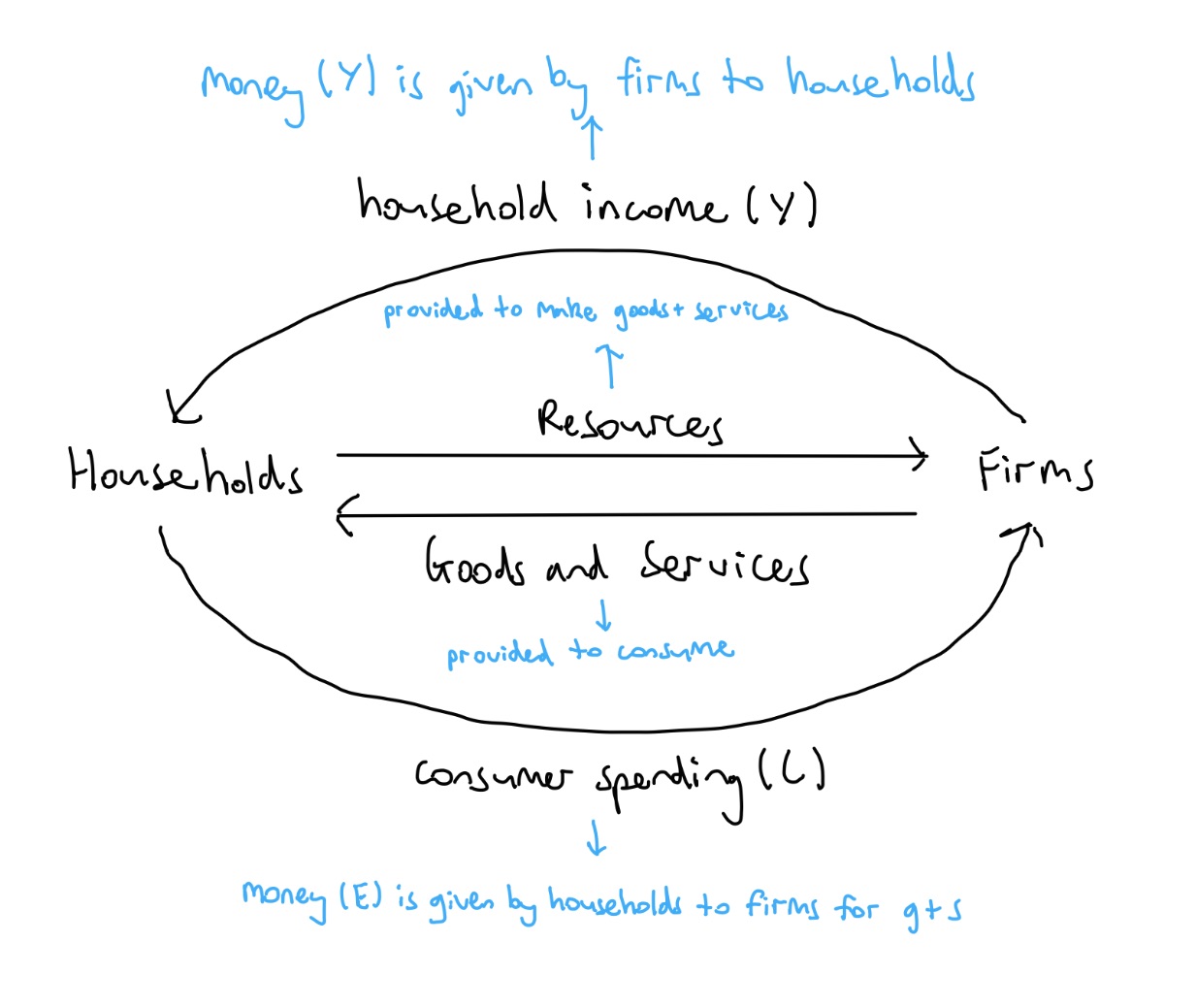
Simple CFY model assumptions
. only 2 sectors in economy (households + firms)
. all output produced by firms is sold to households (no surplus)
. households spend all of their income (no savings)
. no gov sector
. no overseas trade
Where are real and money flows on the CFY model
. inside flows (resources and goods + services) = real flows
. outside flows (income + spending) = money flows
Outline households
. consumers
. consist of 1 or more persons who live in the same housing unit
. owners of productive resources (natural, human and capital)
Outline firms
. producers
. employers of resources which they use to produce products for the economy
Outline the factor market
. consists of resources + income
. firms hire natural, human and capital resources from households
—> in return for which firms provide various types of income:
. wages or salaries: money for working
. rent: money in return for land or property
. dividends: money in return for capital they have invested in companies
. interest: payment on surplus money lent to banks or financial institutions
. profits: money from their managerial + entrepreneurial skills (enterprise)
Outline the product market
. consists of goods + services, and consumer spending
. households exchange their income they have earned for goods and services produced by firms
Simple CFY model and interdependence
. demonstrates that people in modern economies are interdependent (dependent upon one another)
. it’s a much better use of scarce resources, both for individuals + groups to specialise and exchange
Specialisation
. concentrate on and become expert in the production of something
Exchange
. an act of giving one thing and receiving another
Household sector
. made up of individuals in the economy
. provide their time + skills or labour to firms in exchange for income (wages)
. are consumers who buy g + s from firms
. may borrow from or save money with financial sector
. pay taxes to gov
Firms sector
. made up of all businesses in the economy
. produce output (g+s), which they sell to consumers + receive revenue
. may borrow money from or save money with financial sector
. pay taxes to gov
Injections
. the introduction of money into the circular flow of income, increasing the overall level of economic activity
—> investment, gov spending, exports
Leakages
. the withdrawal of money from the circular flow of income and expenditure in an economy
—> uses of income that are not spent on domestically produced goods and services
—> savings, taxes, imports
—> reduce the overall level of economic activity
Outline the financial sector (capital market)
. made up of financial institutions in the economy such as banks, credit unions, and superannuation funds
—> receive savings from households + firms
—> help households + firms invest by lending them money
—> exists to match the needs of households with surplus income + firms that wish to draw on these funds for investment
Savings
. portion of household (disposable) income not spent on g+s for current consumption
Investment
. purchase or production of capital goods that will be used to produce final goods, including assets such as buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles and tools
Describe the leakages in the financial sector (and their effects)
. when money is saved instead of spent by households, this means it leaves circulation
. every dollar saved is 1 less dollar spent by households (every dollar entering a household must exit, being either saved or spent)
. if S increases then C decreases
—> results in reduced output, because less money is flowing into firms
—> slow down an economy as they reduce the amount of total spending that flows into firms
. leakages > injections = contraction
Household savings rate
. the proportion of household income that’s saved
. savings rate = S/Y = the marginal propensity to save (MPS)
Marginal Propensity to consume formula and definition
1-MPS
—> because income has to either be saved or spent)
—> the proportion of an aggregate raise in pay that a consumer spends on the consumption of g+s as opposed to saving it
Formula for household income
Y=S+C
Describe the injections in the financial sector (and their effects)
. when firms borrow money to expand = investment
—> increases the amount of spending flowing into firms, meaning household income also increases, which means households spend more, etc
—> results in increased output as more money is flowing into firms
. injections speed up an economy as they increase the amount of total spending that flows into firms
. injections > leakages = expansion
Describe the relationship between S and I
. independent of each other because different groups are controlling these
—> decision to save (instead of spending) made by households
—> decision to borrow money for investment made by firms
How do S and I affect the economy
. S=I —> economy is in equilibrium (neither growing nor shrinking)
. S>I —> economy is out of balance + will contract until it re-establishes equilibrium
. S<I —> economy is out of balance + will expand until it re-establishes equilibrium
Outline the government sector
. made up of all bodies in national, state and local governments
. includes all levels of government
—> receive taxation revenue from households + firms
—> spend tax money on public g + s (roads, parks, schools, hospitals)
. uses taxation from the income + spending flows to provide community needs
Taxation
. a compulsory payment to the gov (income tax, tax on profits, GST, excise duties)
Government spending
. any expenditure by the gov. into the economy
—> transfer payments: provision of social welfare (eg: age pensions)
—> current expenditure: spending on current g+s (wages, fuel, power)
—> capital expenditure (public or social infrastructure): spending on capital or investment goods (roads, schools, hospitals)
Describe the leakages in the government sector (and their effects)
. when money is collected in the form of taxation it means that households + firms cannot spend it, meaning it leaves circulation
. taxes collected aren’t injected back into economy until the gov. decides to spend the money
—> particularly, this can come in the form of a surplus for the gov: where the taxation money collected exceeds gov expenditure
Describe the injections in the government sector (and their effects)
. when gov chooses to spend money, it’s injected back into economy (returns into circulation)
. with transfer payments, this directly means that consumers have more money to spend on g+s
. other expenditure flows on into firms
—> eg: if a new hospital needs to be built, the gov. is giving money to firms to do so thus these firms are then able to use this money for investment
Describe the relationship between T and G
. are interdependent when it comes to the gov - as there’s 1 group controlling this
—> decision on how to tax + how long taxation is withheld from being injected is decided by gov.
—> decision on how/when to spend tax money is decided by gov
. the collection of taxes directly allows for a government to spend
Describe how T and G affect the economy
. T=G —> economy is in equilibrium (neither growing nor shrinking)
. T>G —> economy is out of balance + will contract until it re-establishes equilibrium (surplus-contractionary fiscal policy) —> in expansion phase of trade cycle
. T<G —> economy is out of balance + will expand until it re-establishes equilibrium (deficit-expansionary fiscal policy) —> in contraction phase of trade cycle
Open economy
. an economy where there’s trade with others
Imports
. a good or service bought in one country that was produced in another
. money flow is from Aus to overseas
Export
. Goods and services that are produced in one country and sold to buyers in another
. money flow is from overseas to Aus
Overseas sector
. relates to a country’s trade with other nations
—> a Aus sells g+s, produced by businesses in Aus, to other countries (exports)
—> Aus buys g+s, produced by businesses in other countries (imports)
. imports provide for needs that the economy itself cannot satisfy, in return for domestically produced g+s that are surplus to the economy (exports)
Describe the leakages in the Overseas sector (and their effects)
. when money is sent overseas for either g or s or investment, it leaves circulation
—> doesn’t mean there’s no benefit of having imports - allows access to more g+s as well as having investment projects overseas that may benefit Aus in the long-run
. however it’s still a flow of money out of economy so it’s a leakage
Describe the injections in the Overseas sector (and their effects)
. when money is used to buy Aus g+s or for investment projects it’s put into circulation
. one of Australia’s biggest sources of income
—> 26.8% of Aus GDP in 2023
Describe the relationship between M and X
. can be dependent on each other but also are independent
—> money flows out of Aus can be sourced from exports but also can come from income received by households, investment or from the gov
—> money flows into Aus come from other economies + thus can come from many sources (they’re all just considered money flows into the country)
Describe how M and X affect the economy
. M = X —> economy is in equilibrium (neither growing nor shrinking)
. M>X —> economy is out of balance + will contract until it re establishes equilibrium
. M<X —> economy is out of balance + will expand until it re-establishes equilibrium
Draw and label the full CFY model
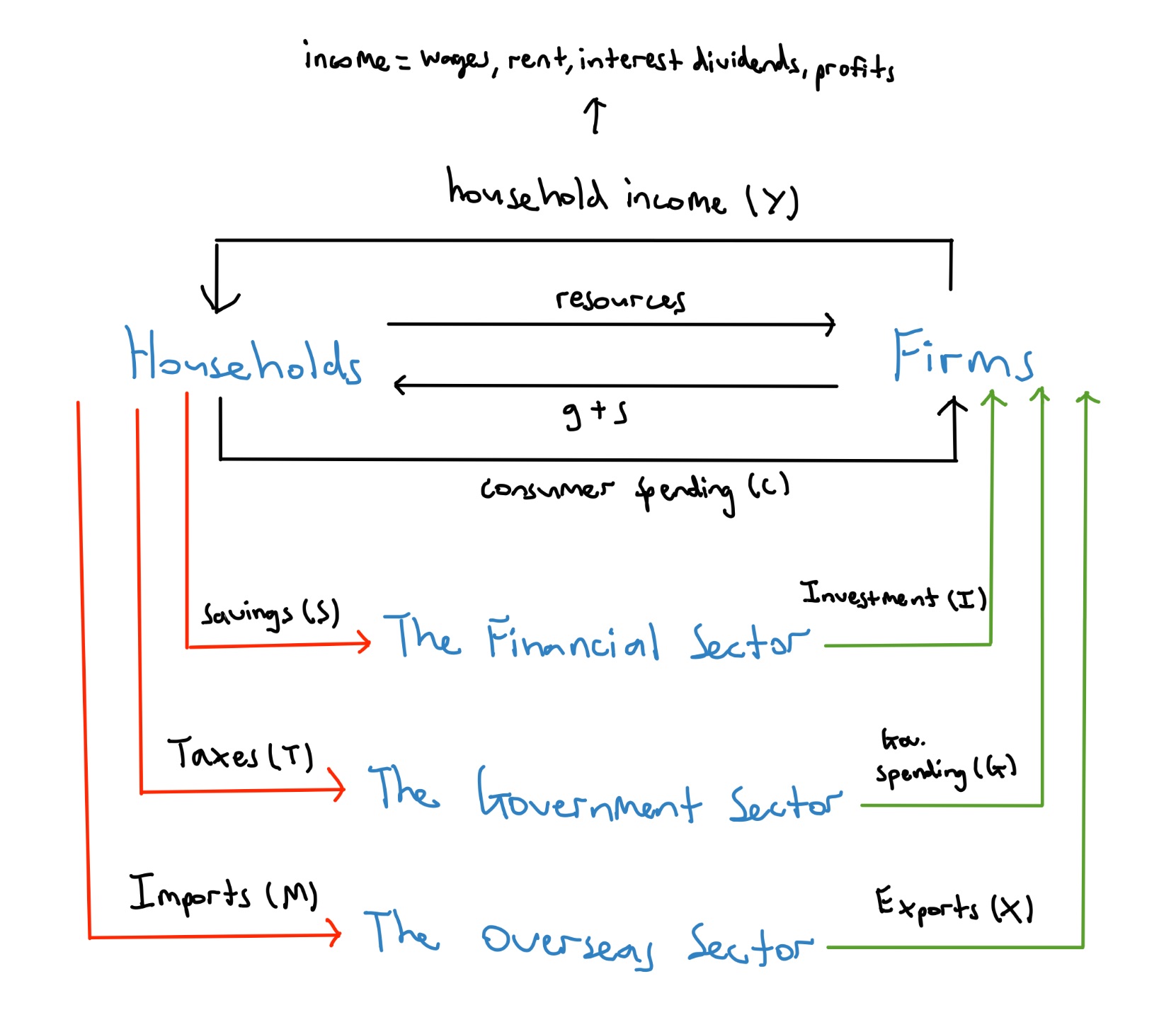
Describe the main concept(s) that the full 5 sector CFY demonstrates
. highlights the interdependence between the major sectors of the economy
—> helps understand the relevance of macroeconomic events to those in economy
—> whenever levels of spending are changing, the size of the real money flows must also change:
. increase in investment = everyone benefits
. increase in taxation = everyone loses (less income to spend + benefits only gained from this increased taxation if and when the gov spends the money which may then be on socially beneficial things - but if gov raises taxes but doesn’t raise gov expenditure, people aren’t better off until expenditure occurs)
—> raise prices
—> lower production
—> less to consume
—> increase welfare payments
What is Macroeconomic equilibrium
. a condition or state in which economic forces are balanced
—> in the flow, the value of the output produced by firms must equal the value of income paid to resource owners, which must in turn equal the value of spending by households to produce the output
—> the state of the economy when the quantity of goods and services supplied in an economy equals the quantity of goods and services demanded in an economy
What is happening to an economy when it’s in equilibrium
. an economy is in equilibrium when it’s neither growing nor shrinking (household income is stable)
Identify the formula for Macroeconomic equilibrium and explain why this is
Describe the equilibrium for the financial sector
Describe the equilibrium for the government sector
Describe the equilibrium for the overseas sector
When is an economy at disequilibrium and how does it escape this?
What generally happens it injections increase
Why will the economy expand if injections increase?
Injections changing affect on investment
Injections changing affect on government spending
Injections changing affect on exports
What generally happens it leakages increase?
Why will the economy shrink/contract if leakages increase?
Leakages changing affect on savings (S)
Leakages changing affect on Taxes (T)
Leakages changing affect on imports (I)
Changes in leakages and injections in relation to the Financial sector (why occur and relationship)
Describe the situation if savings > investment in the financial sector
Describe the situation if savings < investment in the financial sector
Describe the steps in the textbook method
Describe the steps in the precise/simple method
Describe the situation if T>G in the government sector
Describe the situation if T<G in the government sector
Describe the situation if M>X in the overseas sector
Describe the situation if M<X in the overseas sector
Describe the situation if leakages are greater than injections in relation to the general economy
Describe the situation if injections are greater than leakages in relation to the general economy
Outline the Multiplier effect