MTE2201 Module 10 - Mechanical properties of polymers
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Behaviour of thermoplastic polymers and how they can be modelled
They are viscoelastic. So they have:
Elastic behaviour - instantaneous response to stress/strain
Viscous behaviour - Time dependent response to stress/strain
Mechanical behaviour of viscoelastic polymers can be modelled by connecting springs and dashpots in different ways
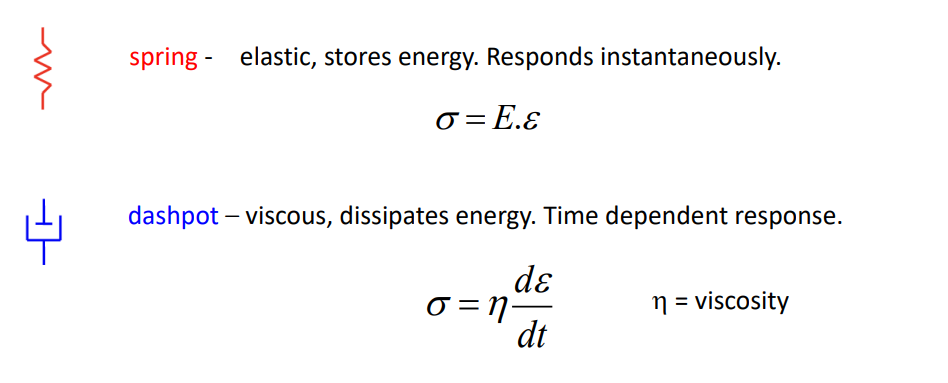
Characteristic behaviour of viscoelastic polymers:
-Stress relaxation (decay of stress with time after fixed deformation)
-Creep (increase in strain with time after application of a constant load)
Both are curved
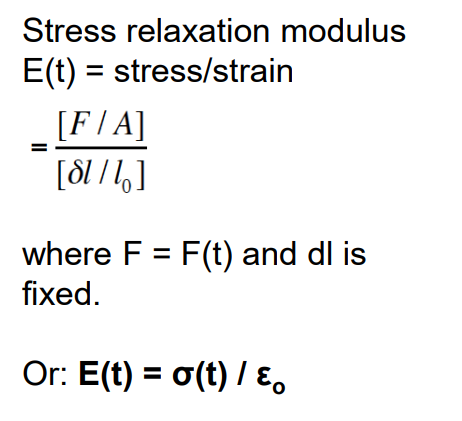
Stress relaxation
Creep compliance

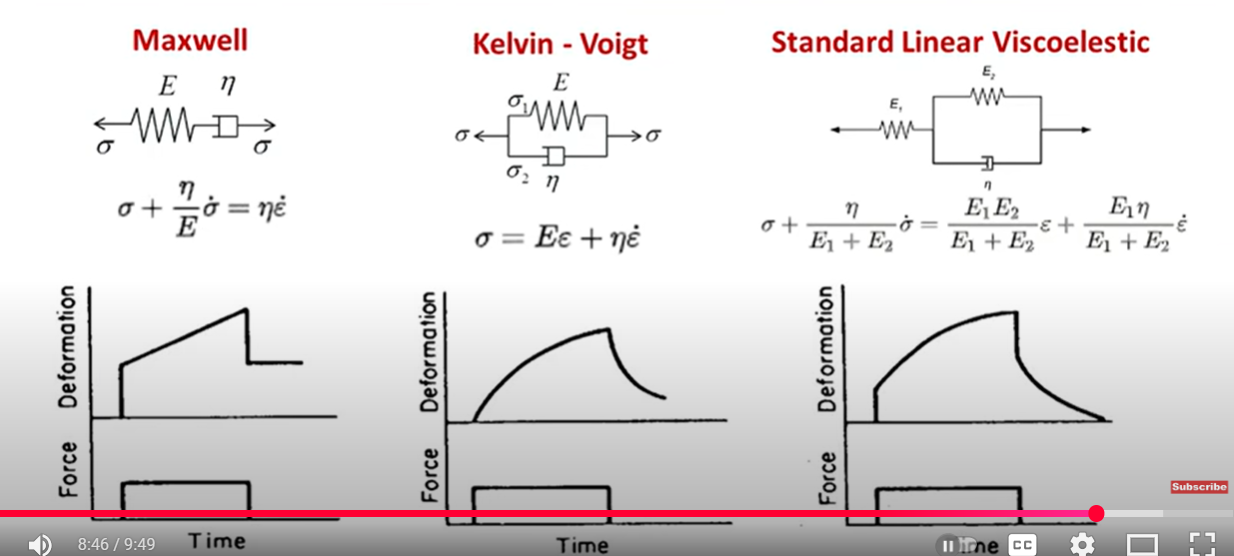
Maxwell model
Connecting a spring and dashpot in series. Can model stress relaxation, but predicts creep to be linear when it is really nonlinear.

Kevin Voigt Model
Spring n dashpot in parallel. Can model creep and creep recovery. Predicts hookean spring behaviour, so not good for modelling stress relaxation.

Standard linear viscoelastic model
Can model both creep and viscoelastic behaviour
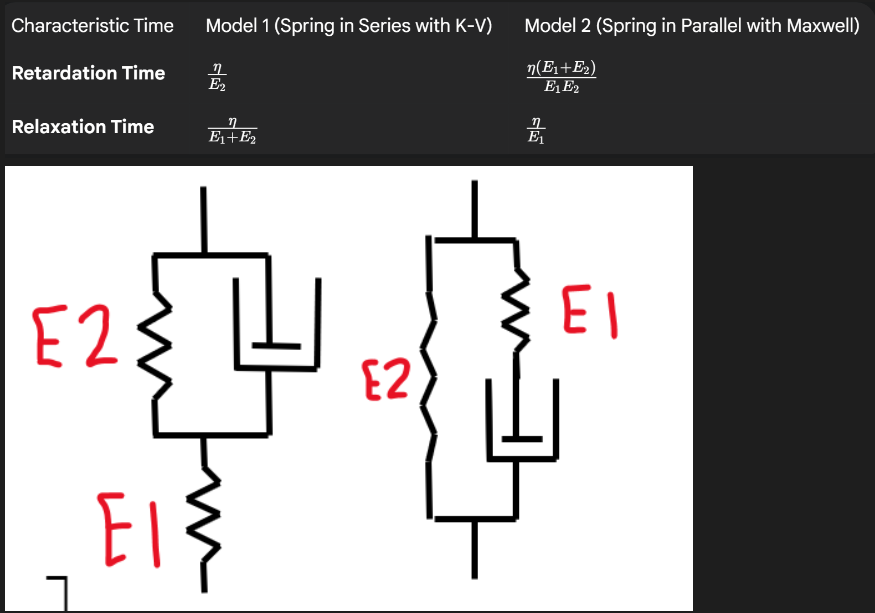
Retardation and relaxation time equations for standard linear model
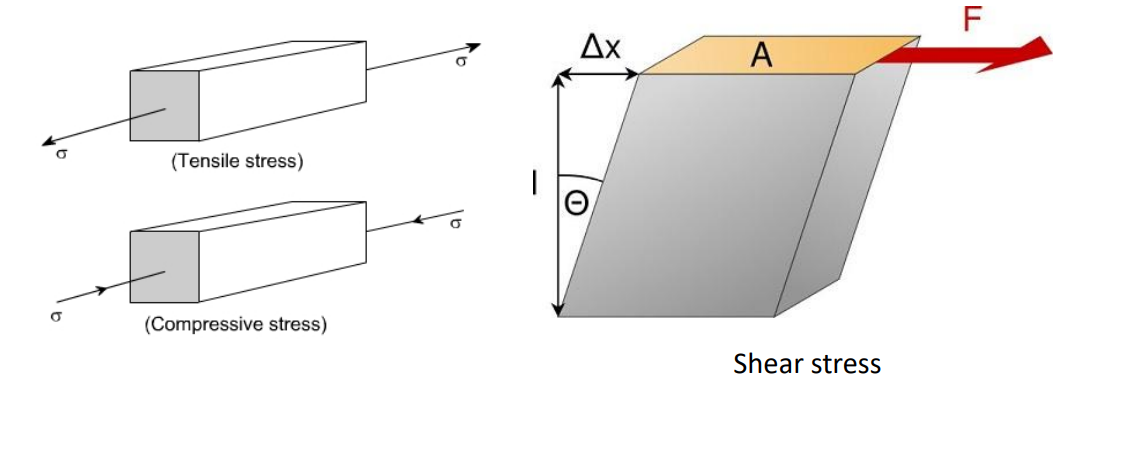
The 3 main modes of deformation
Tensile, compression, shear
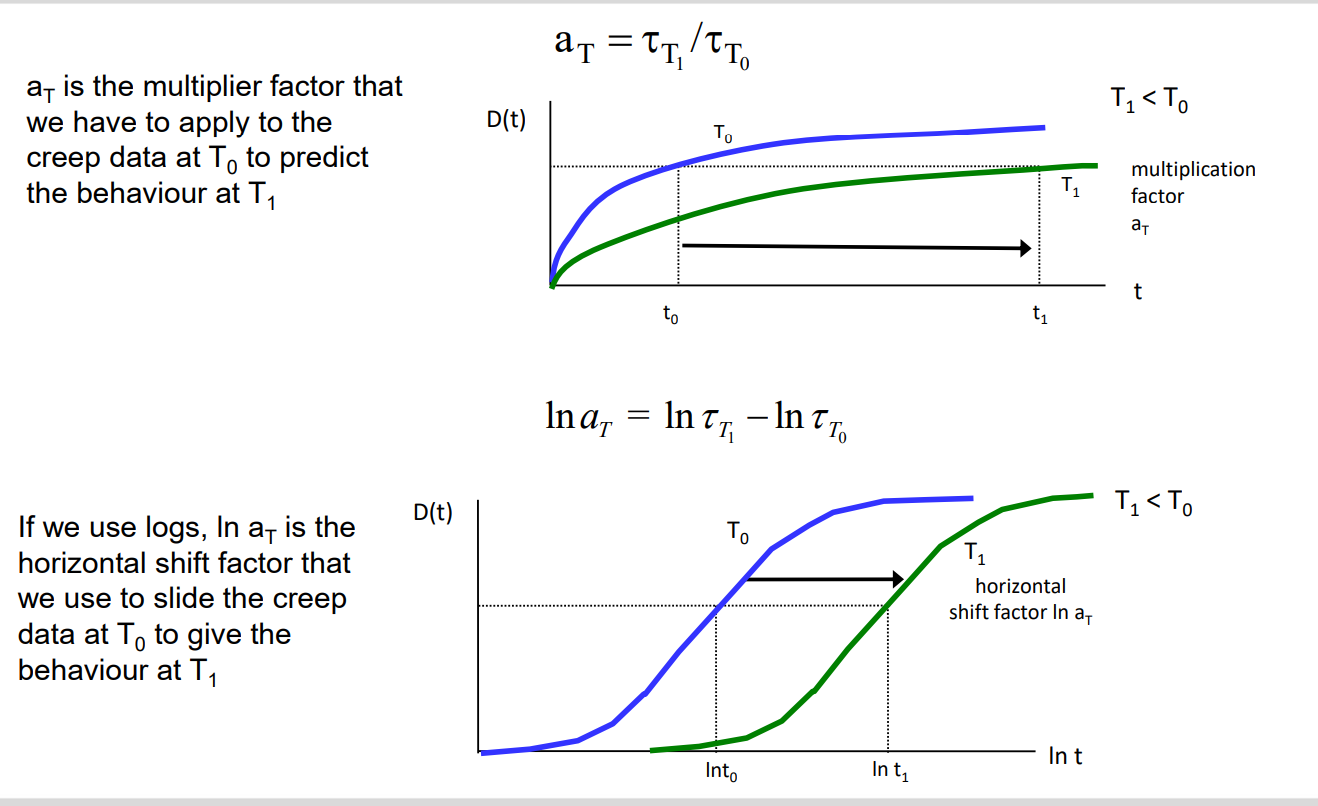
Time temperature superposition with time and log time
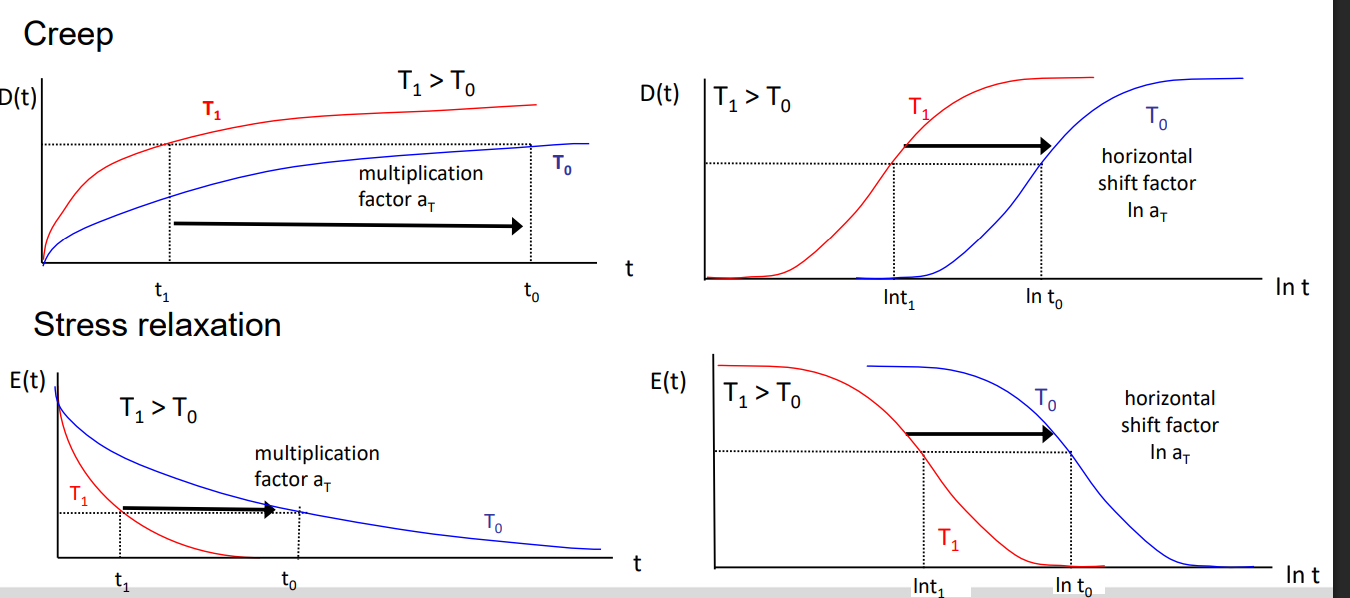
Time temp superposition of creep and stress relaxation
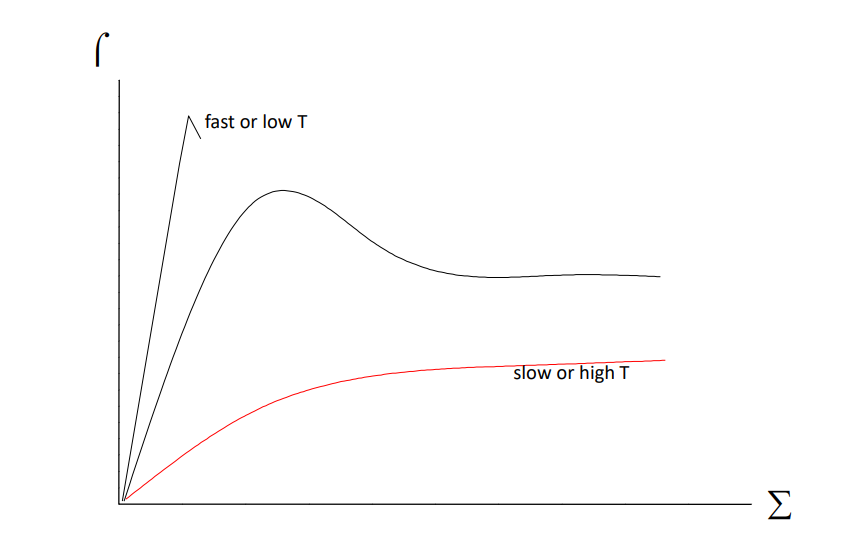
Stress relaxation rate vs temperature
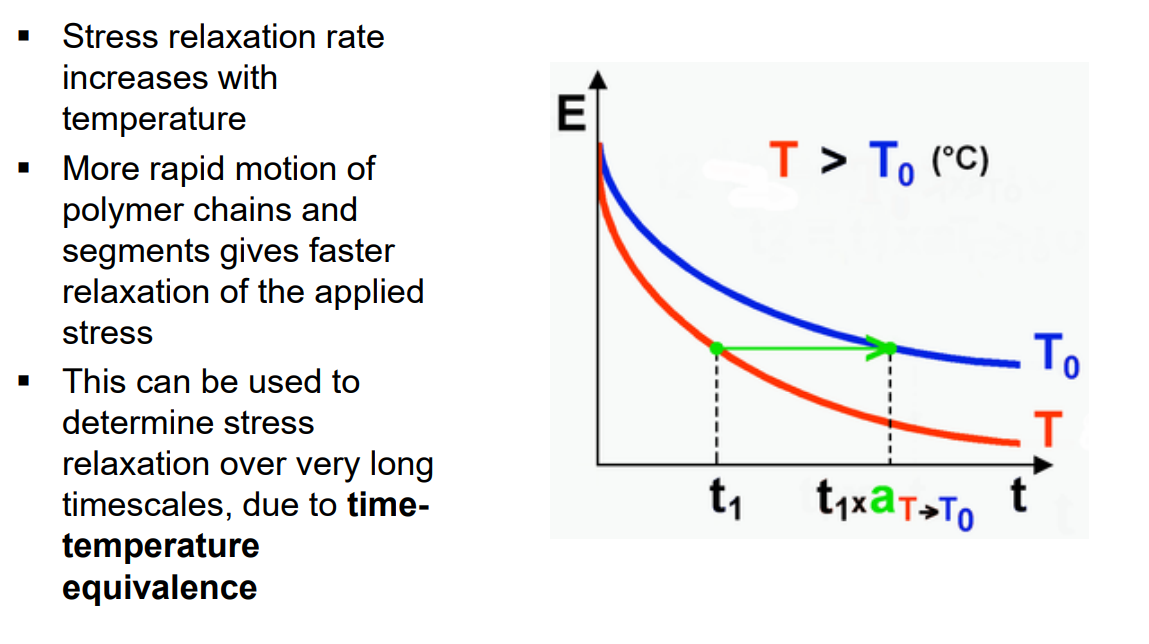
slow rate/ high temp effect on applied stress
At slow rates or high temperatures, the molecular segments have time to rearrange and so reduce the applied stress.
Drawing of an amorphous thermoplastic polymer beyond the yield point causes:
Uncoiling and orientation of polymer chains, causing increased strength and stiffness as intermolecular forces can act more effectively along parallel chains.
Time temp principle
For viscoelastic materials, time and temperature have an equivalent effect on the movement of polymer chains.

Retardation and relaxation time
3 flaws of 2 element models
1.Each model cannot describe all viscoelastic properties, like either creep or SR but not both
2. Neither one alone can describe all materials types
3. The models involve only a single relaxation time with a width of 1.2 decades of time. Polymers relax over much longer timescales eg 10 decades of time!
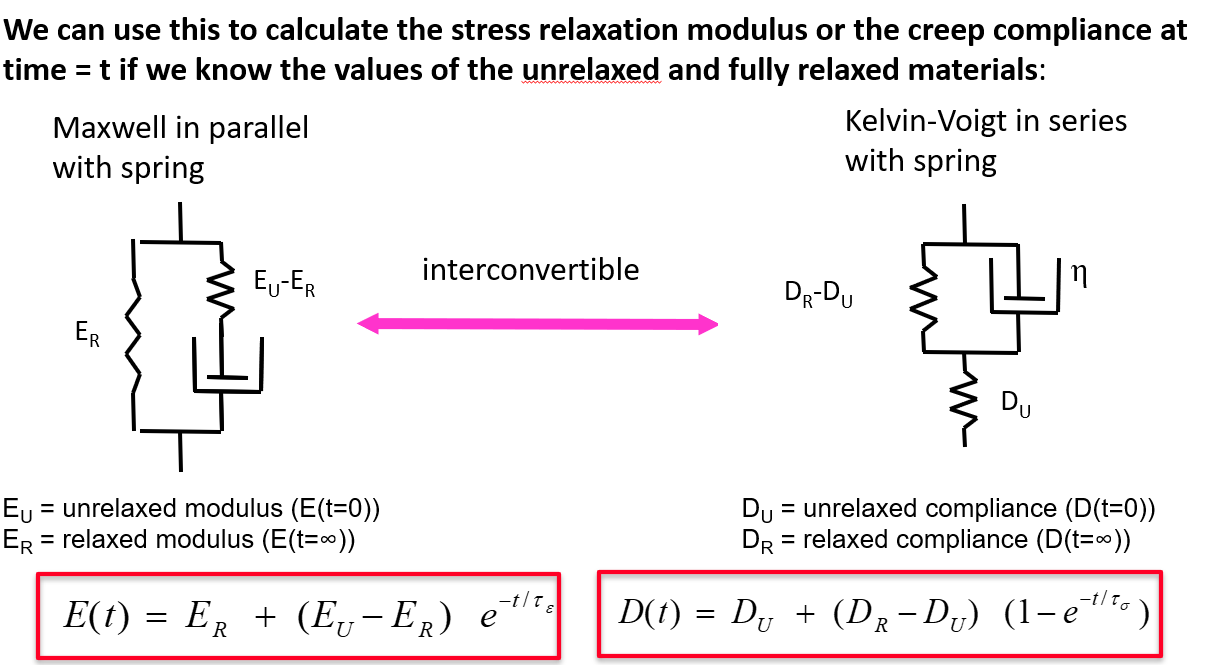
Stress relaxation modulus and creep compliance in 3 element model
compliance is not strain. Compliance is strain / stress.
Same with stress relaxation. stress relaxation modulus is stress/strain.
Stress relaxation modulus and creep compliance in 2 element model
