Functional Groups and Reactivity
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Level 1, group 7 Halogens
Form Haloalkanes , halogens form only one bond so is very simple to have a bond to just a single halogen
Level 1, group 6 Oxygen and Sulphur
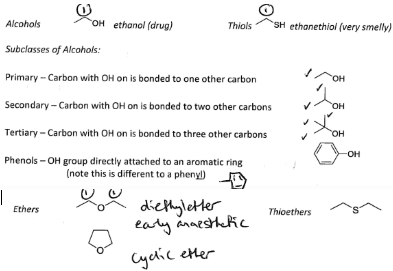
Form Alcohols and Thiols, Both these form two bonds one to a carbon the other a hydrogen.
If the second bond is to another carbon not a hydrogen it forms an Ether or a Thioether.
If the extra bond is used to bond to a different carbon atom we form ethers and thioethers
Level 1, group 5 Nitrogen
Nitrogen forms three other bonds than to carbon. Amines when these bond to Hydrogen or to more carbons in the chain
Can form a nitro group by bonding to two oxygen molecules

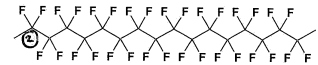
Level 2, group 7 Halogens
Halogens only form single bond so only way to do so is by bonding two halogens to a carbon. Giving a multiple haloalkane
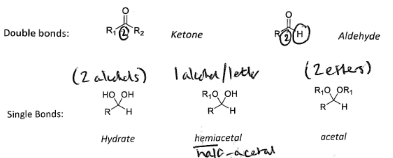
Level 2, group 6 Oxygen
Oxygen can form two bonds, This means that for functional group level 2, it can either form a double bond to the carbon atom, or two oxygen atoms can each be singly bonded.
Level 2, Group 5 Nitrogen
Are similar to oxygen except they can form three bonds instead of two due to extra valency available.

Level 3, Group 7 Halogens
The only option for halogens is to form three single bonds to halogen substituents giving a multiple haloalkane
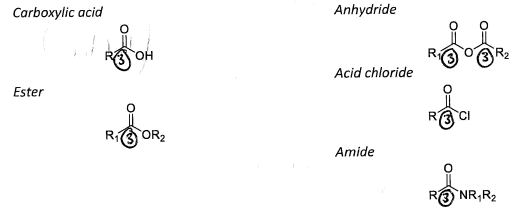
Level 3, Group 6 Oxygen
There are a number of different ways of involving oxygen in forming three bonds to a carbon.
Typically, one forms a double bond and the third bond will come from a single bond to either O,N, or X. These are important and common functional groups
Level 3, Group 5 Nitrogen
Nitrogen can form all three bonds to carbon giving a unique functional group
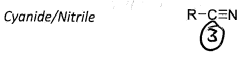
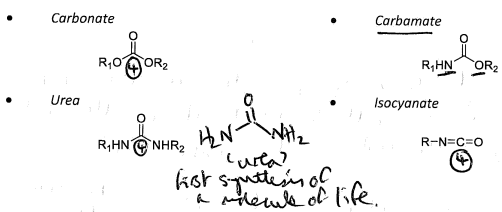
Level 4 functional groups
-Level four functional groups are unusual, they have all four bonds to heteroatoms. Typically, to achieve functional group level 4, there will be a double bond to an oxygen, and then two more bonds to other heteroatoms.
Relationship between functional group levels and oxidation/reduction
The largest functional group levels are the most highly oxidised.
The lowest functional group levels are the most reduced.
When dictating oxidation/reduction what’s the most important factor
-The functional group level change is most important
-Oxidation, gain of oxygen and loss of hydrogen where the functional group level increases
-Reduction, gain of hydrogen and loss of oxygen where the functional group level decreases